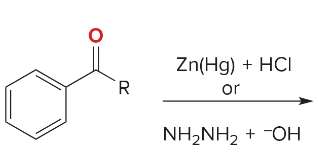
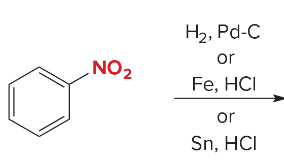
Synthesis Reactions (Orgo I + II) Ch 1-23
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
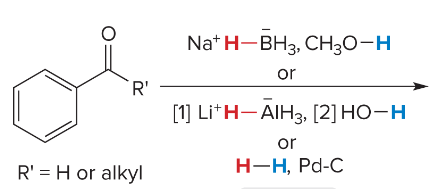
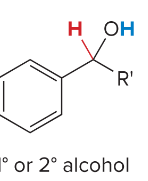
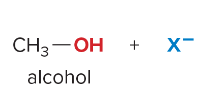
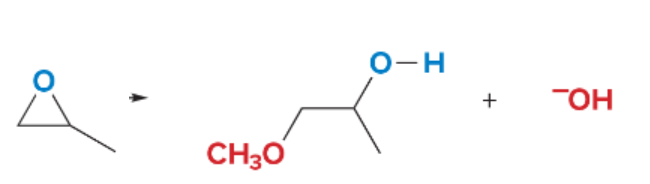
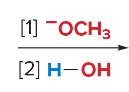
SN2 reactions are ____ step(s). They are faster with ______ steric hindrance. There is a _______ attack by the nucleophile. They are favored by ______ nucleophiles that usually bear a negative charge. They are favored by polar ______ solvents.
1, less, backside, strong, aprotic
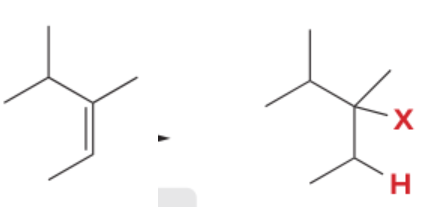
SN1 reactions are _____ step(s). They are faster when the ______ is most stable. They undergo frontside and backside attack, which forms ________. Favored by _______ nucleophiles and polar _____ solvents.
2, carbocation, enantiomers, weak, protic
When weak bases are used, _______ is favored.
substitution
When strong, bulky bases are used, _______ is favored.
E2
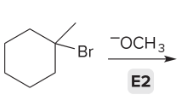
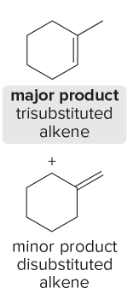
Strong nucleophiles and strong bases favor _____ and _____.
SN2, E2
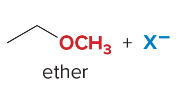
Weak nucleophiles and weak bases favor ______ and ______.
SN1, E1
E1 and E2 reaction speed increases with ______ classification
carbon
E1 favored by polar _____ solvents. Increased R groups increase stability.
aprotic
E2 favored by polar ______ solvents. Increased R groups increase stability.
protic
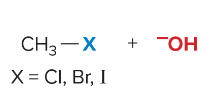
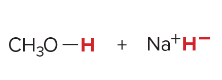
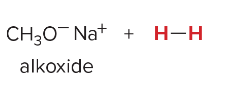
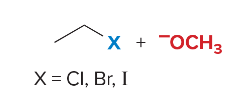
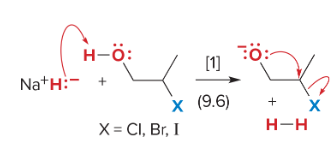
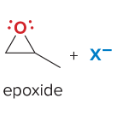
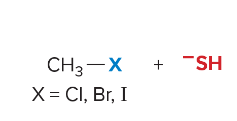
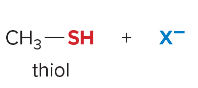
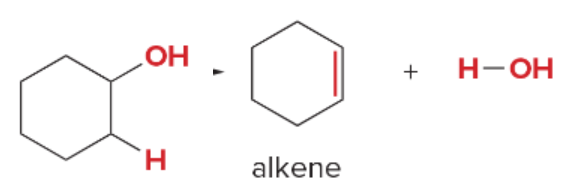
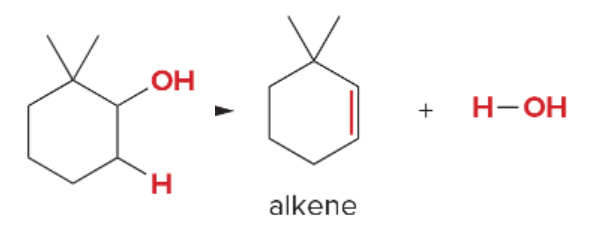
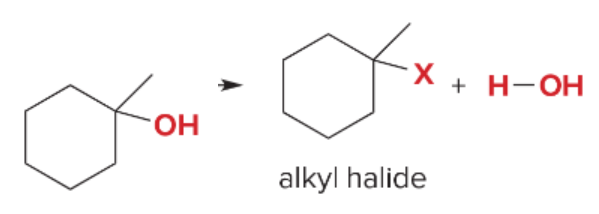
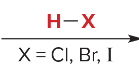
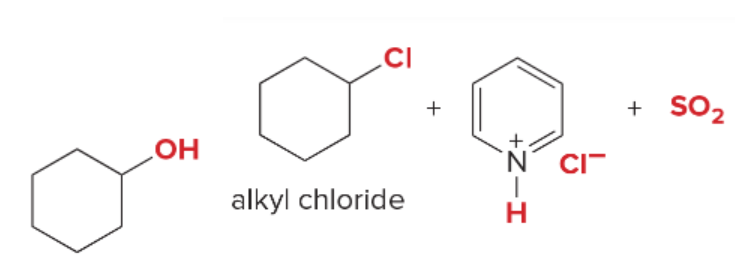

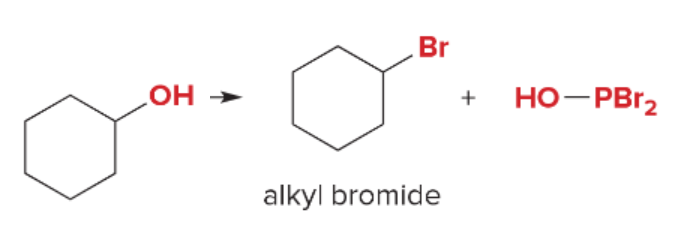

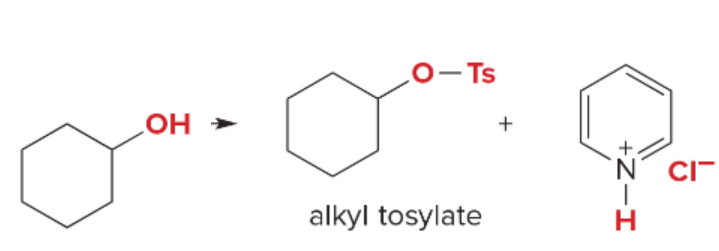
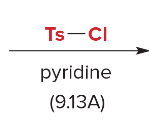
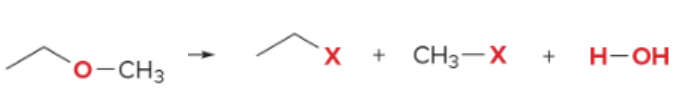
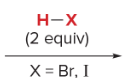
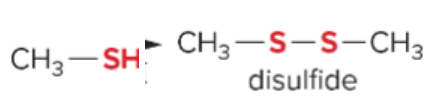
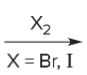
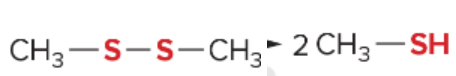

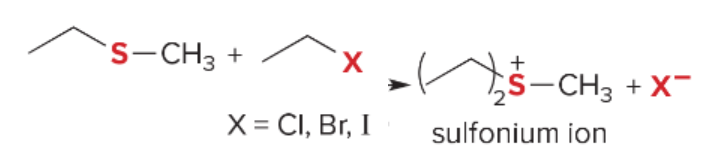
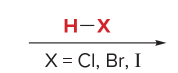
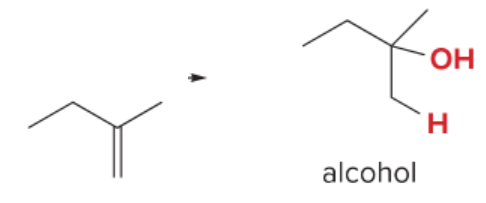
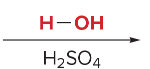
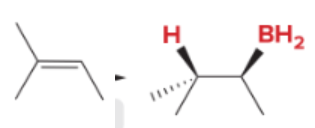

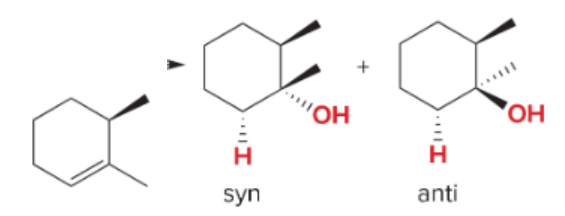
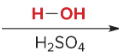
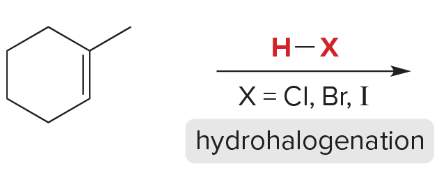
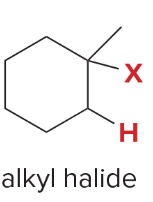
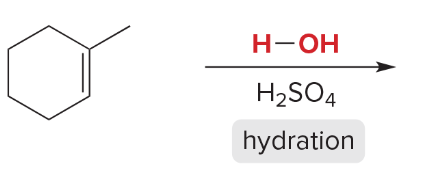

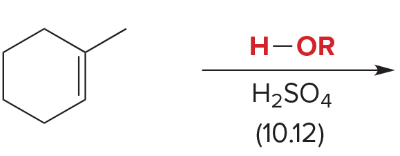
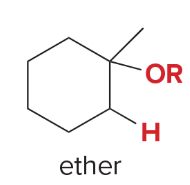
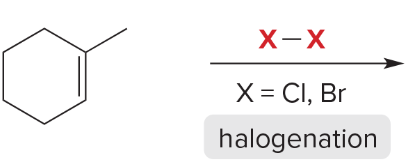
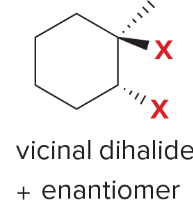
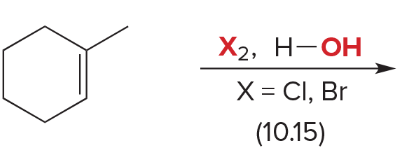
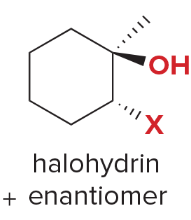
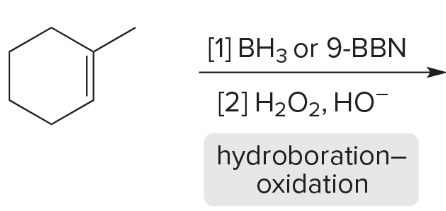
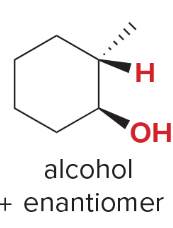
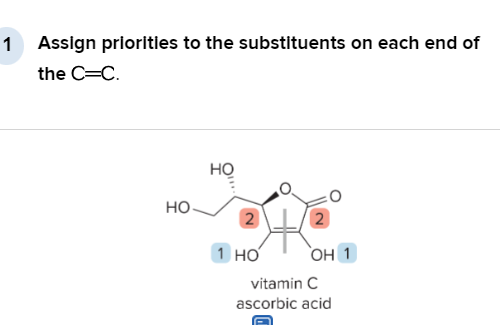

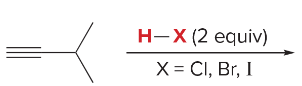
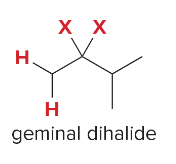
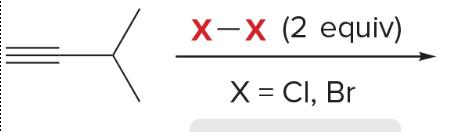
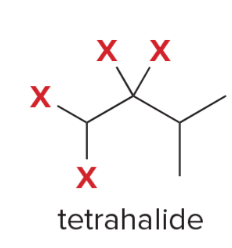
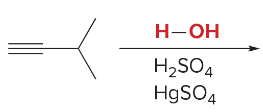
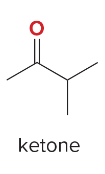
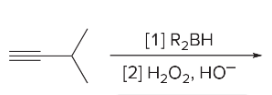
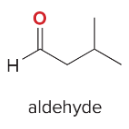
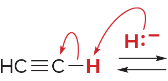
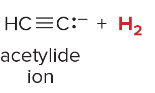
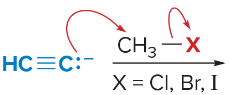
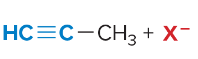
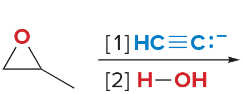
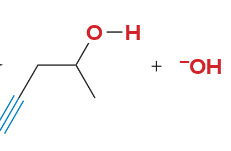

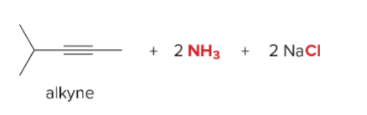
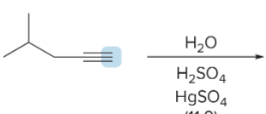
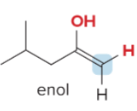
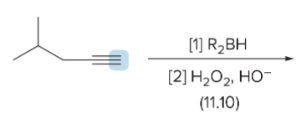
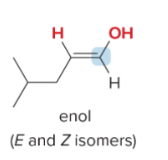
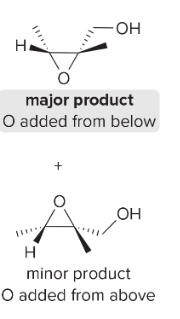
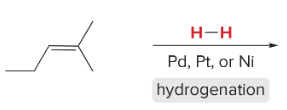
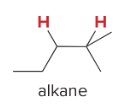
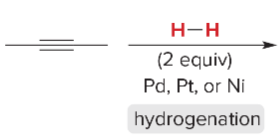
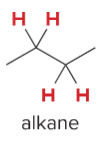
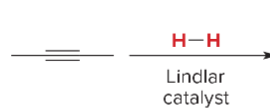
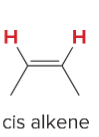
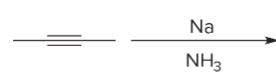
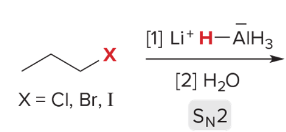
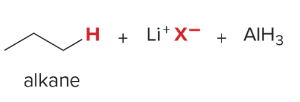
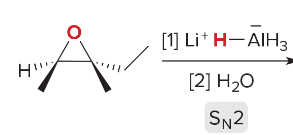
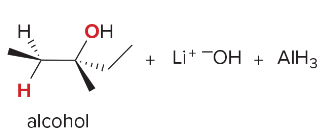
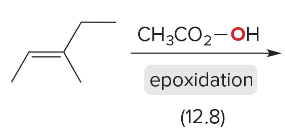
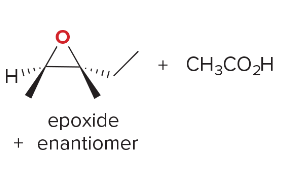
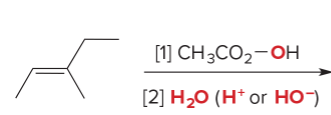
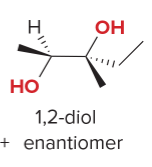
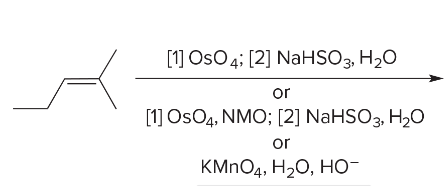
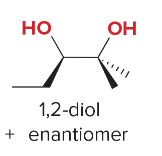
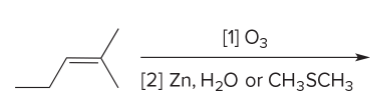
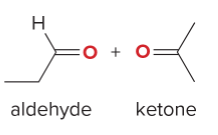
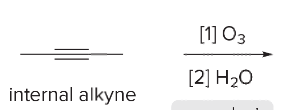
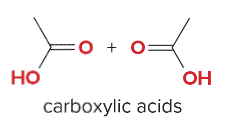
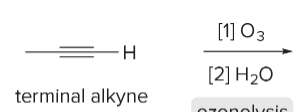
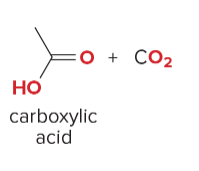
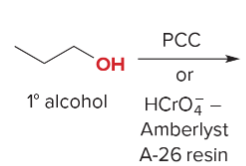
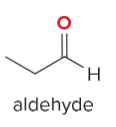
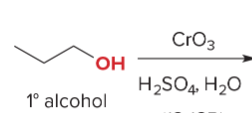
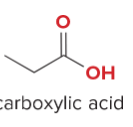
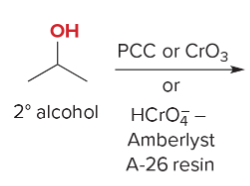
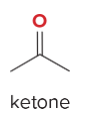
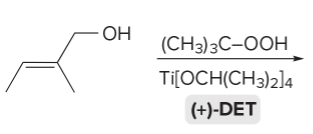
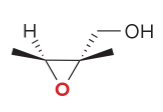
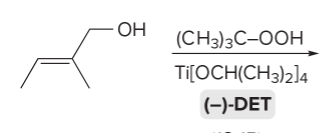
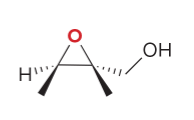
T/F: Degree of unsaturation is calculated by (diff. of Hs between actual H & max. H)/2
T
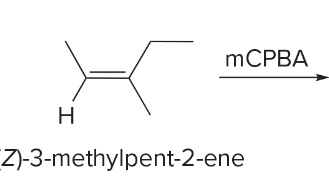

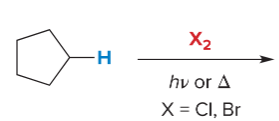
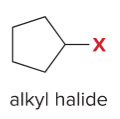
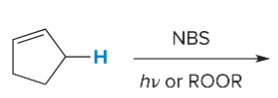
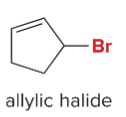
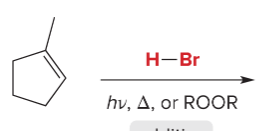
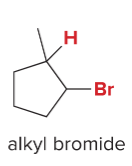

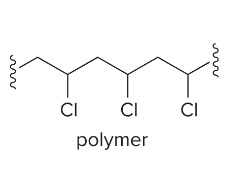
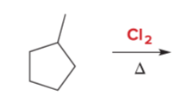
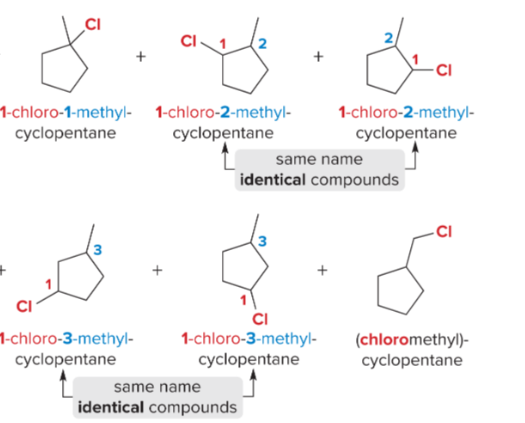
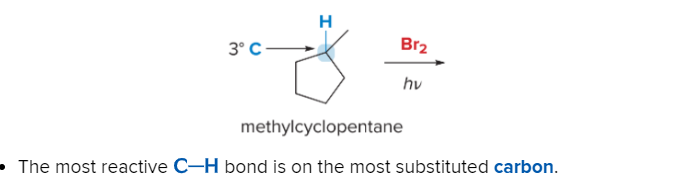
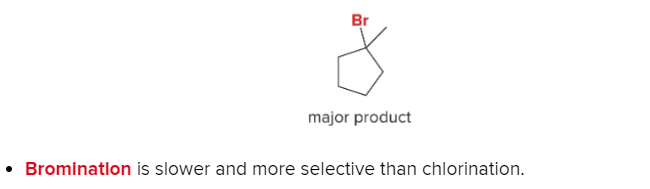
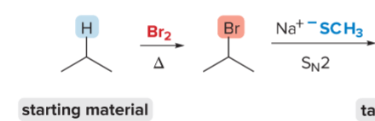
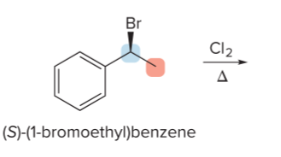
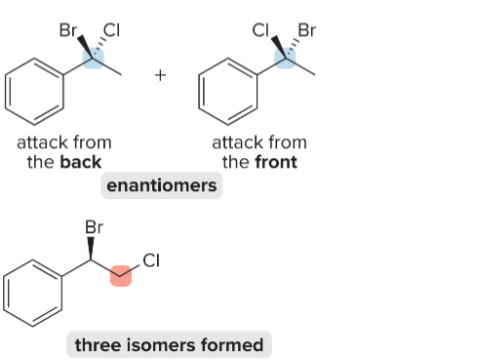
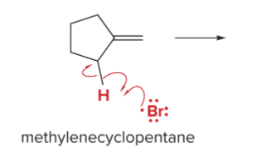
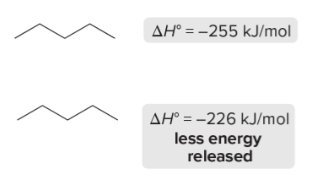
T/F: Increased conjugation of double bonds increased the max wavelength
T
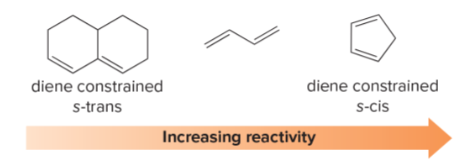
T/F: Diene reactivity
T
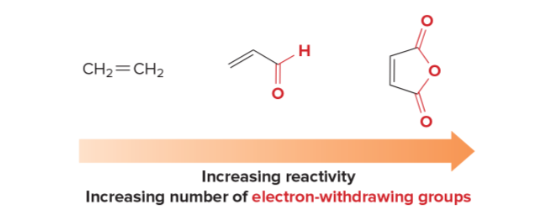
T/F: Dienophile reactivity
T
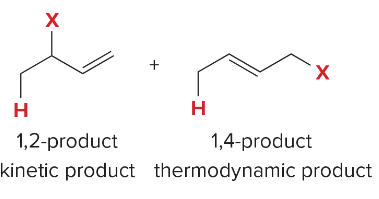
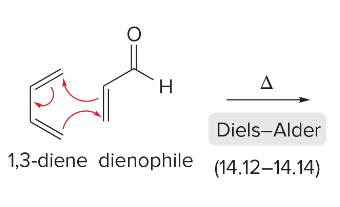
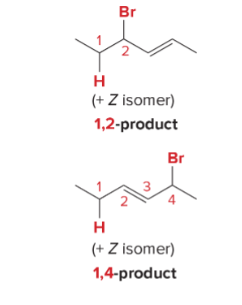
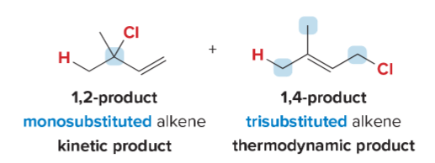
T/F: Aromatic compounds need to be completely conjugated, cyclic, and planar (all Cs are sp2 hybridized)
T
T/F: Antiaromatic compounds have 4n pi electrons.
T
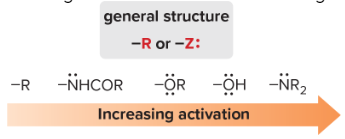
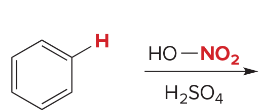
All ortho/para directors activate the benzene ring, except halogens.
T
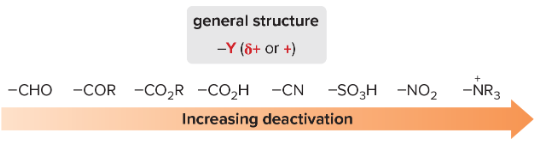
T/F: All meta directors deactivate the benzene ring
T
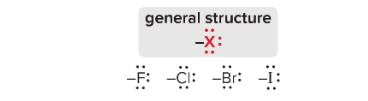
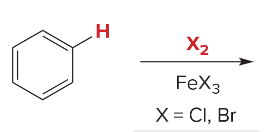
T/F: Halogens direct ortho/para and deactivate the benzene ring
T