Biology Final Review: Cell Cycle, Genetics, and Evolution
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
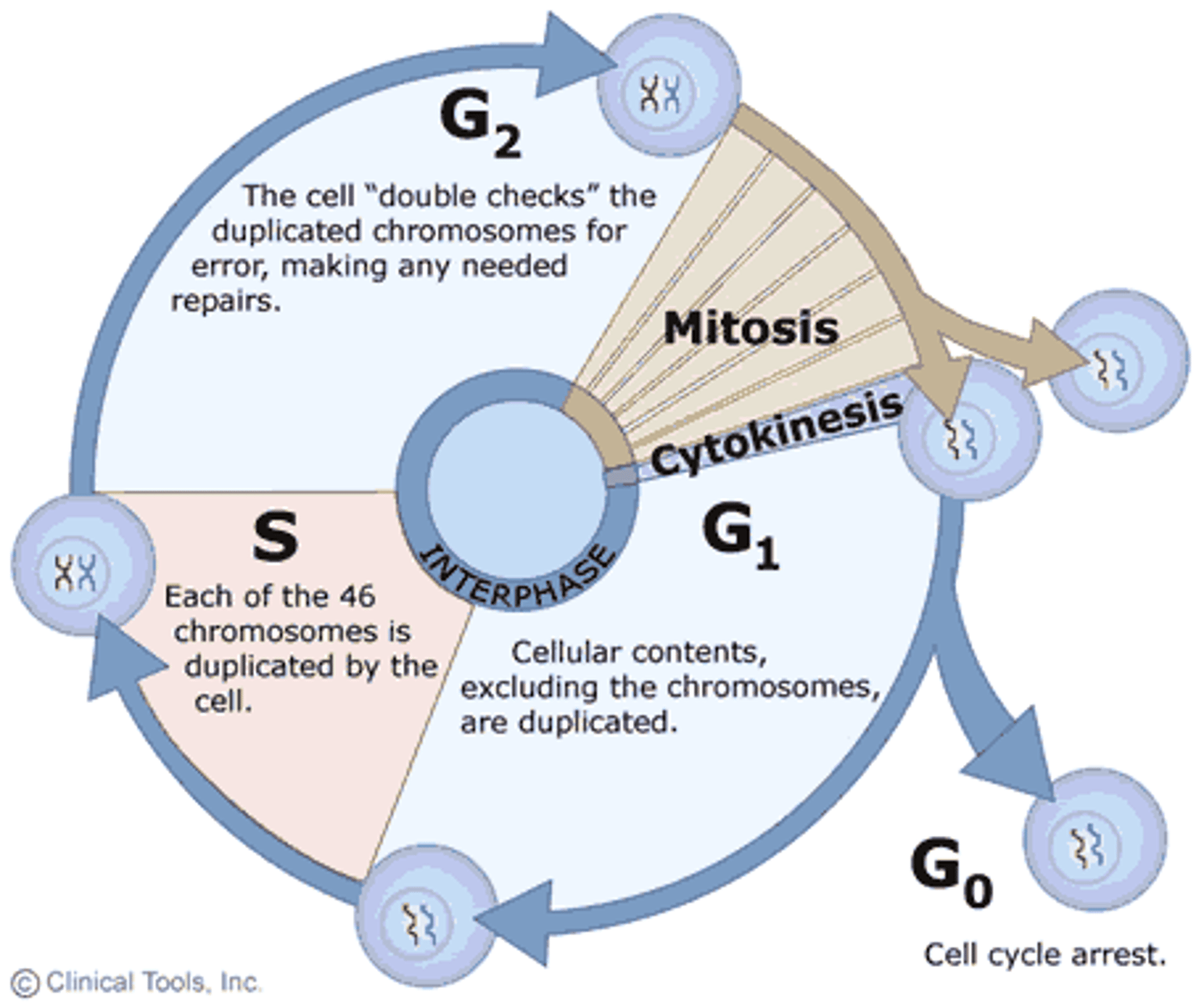
G1 (Gap 1)
Cell grows, performs normal functions, prepares for DNA replication.
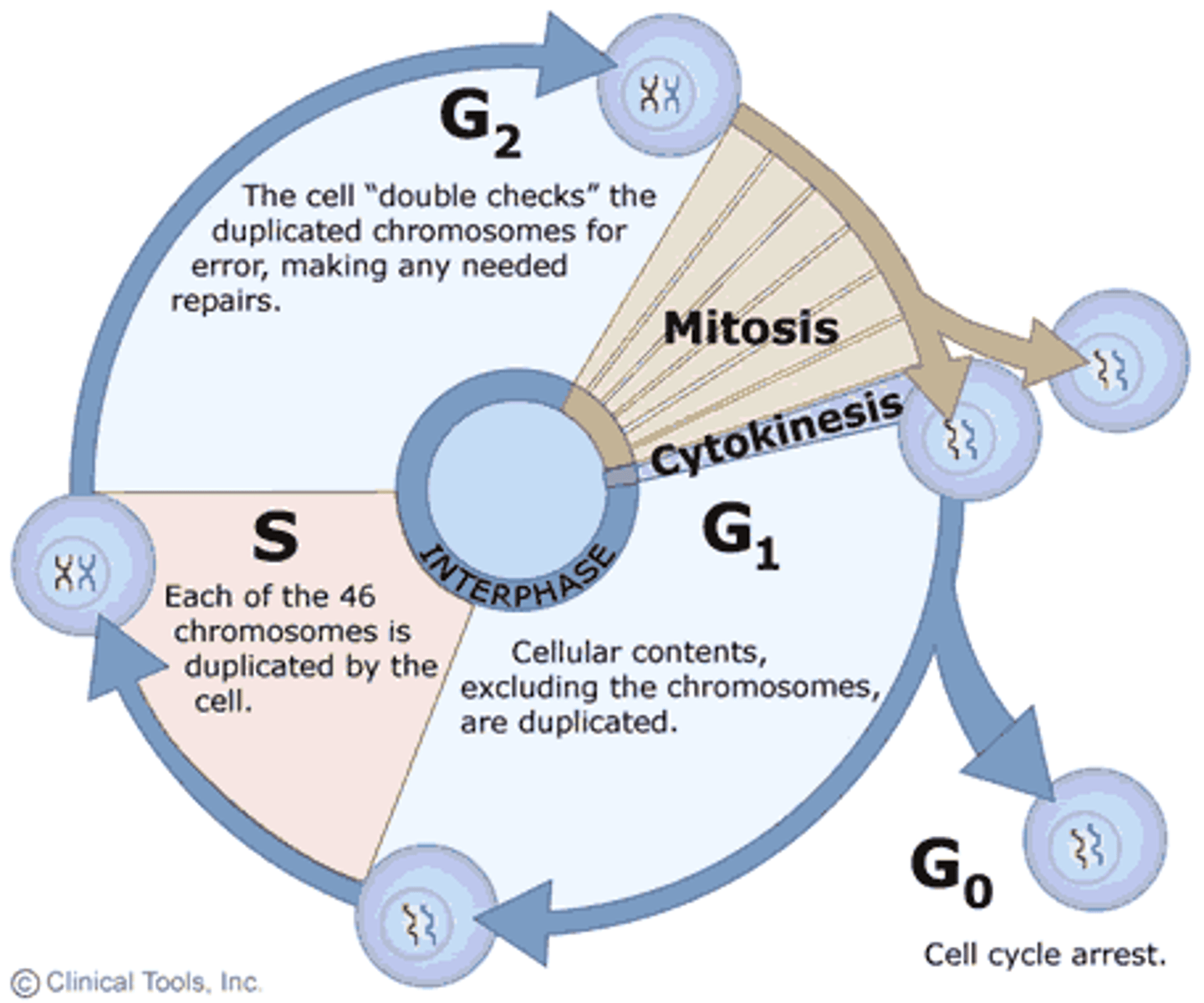
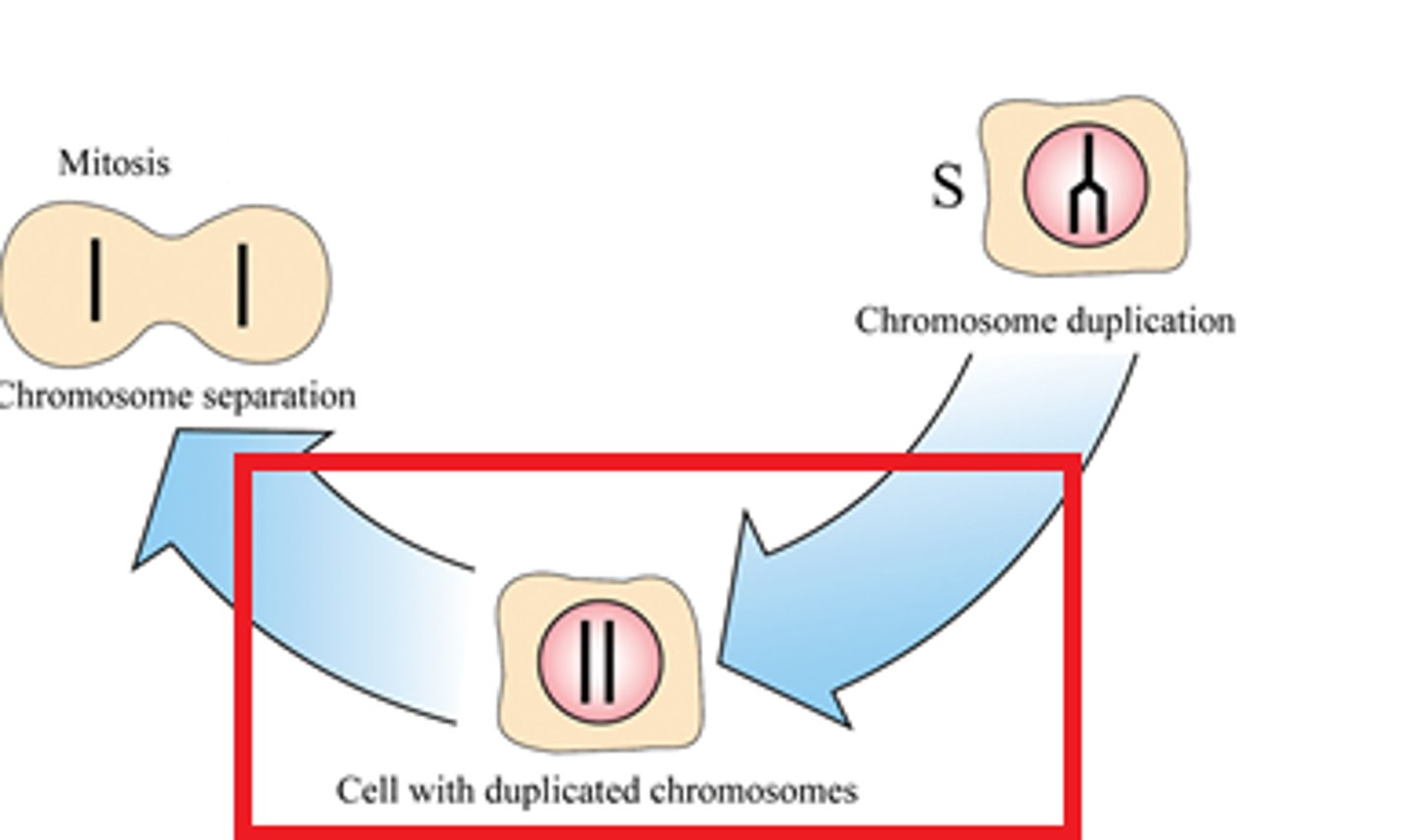
S (Synthesis)
DNA is replicated.
G2 (Gap 2)
Prepares for mitosis (protein and organelle synthesis).
Checkpoints (G1, G2, M)
Control transitions; ensure conditions are right.
Cyclins/CDKs
Proteins that regulate the cycle.

Apoptosis
Programmed cell death if errors are detected.
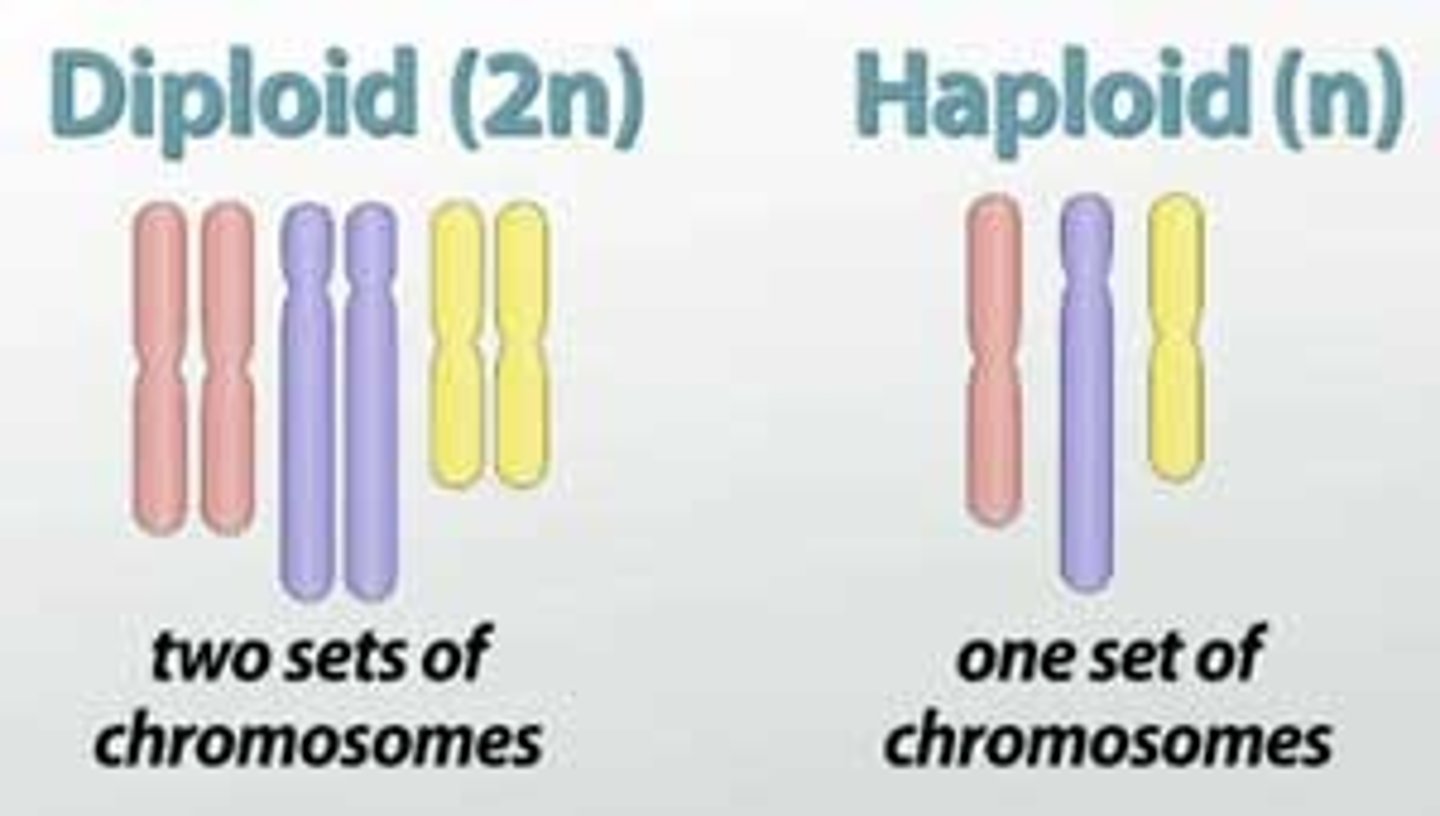
Diploid (2n)
Full set of chromosomes (e.g., somatic cells).
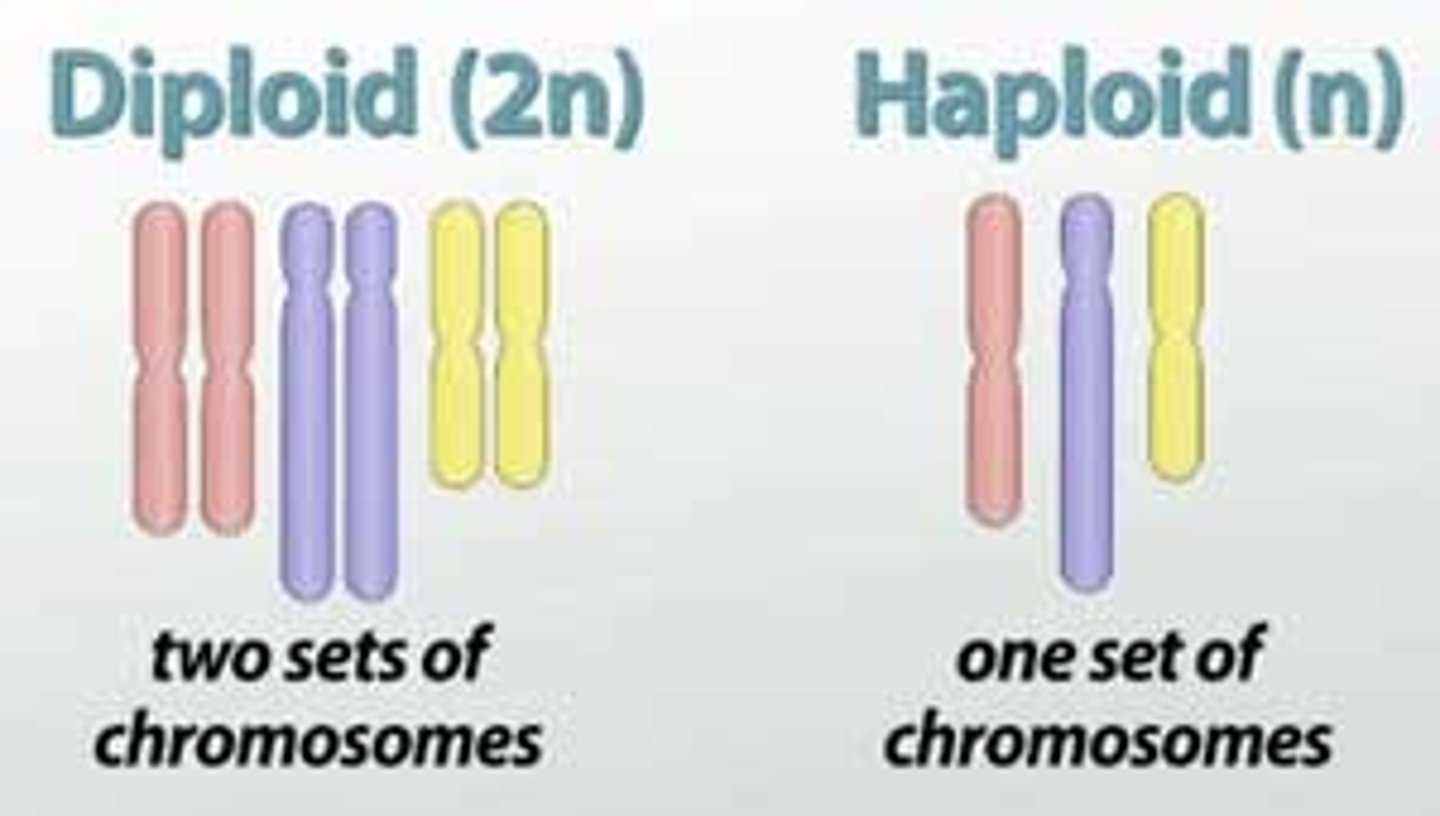
Haploid (n)
Half the number of chromosomes (e.g., gametes).
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm/egg), haploid.
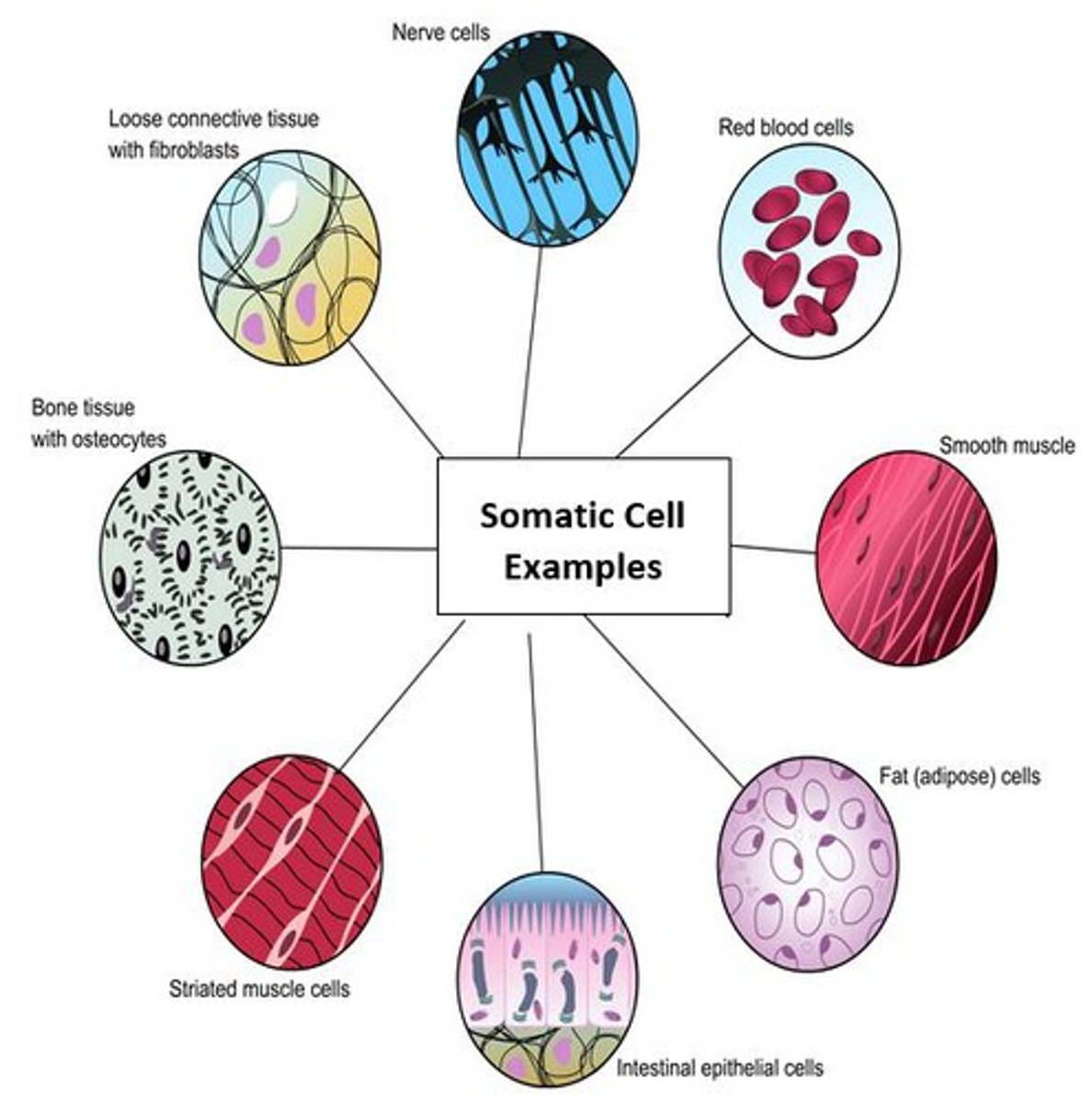
Somatic Cells
All body cells, diploid.
Chromatin
Unwound DNA in interphase.

Chromosomes
Condensed DNA during cell division.
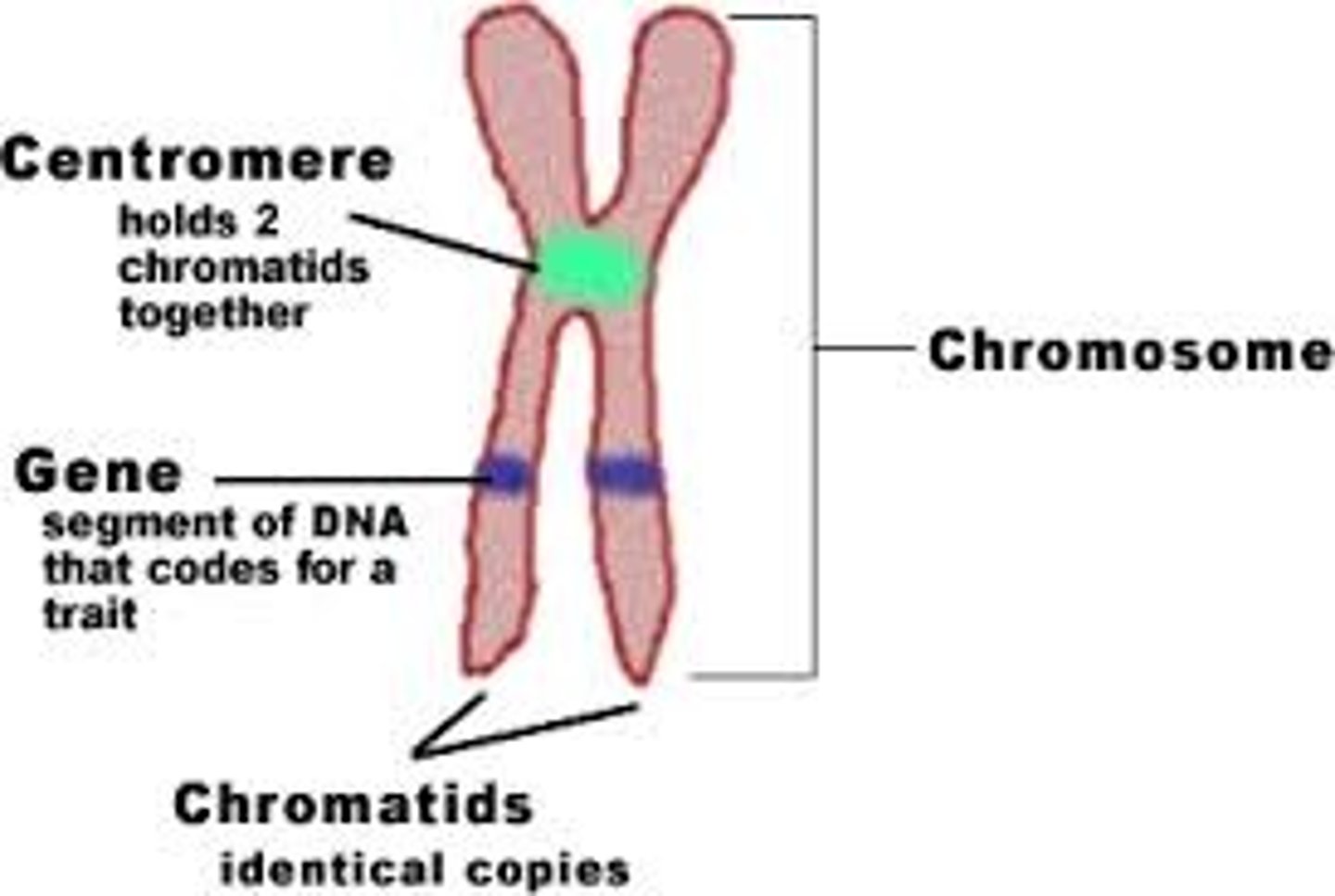
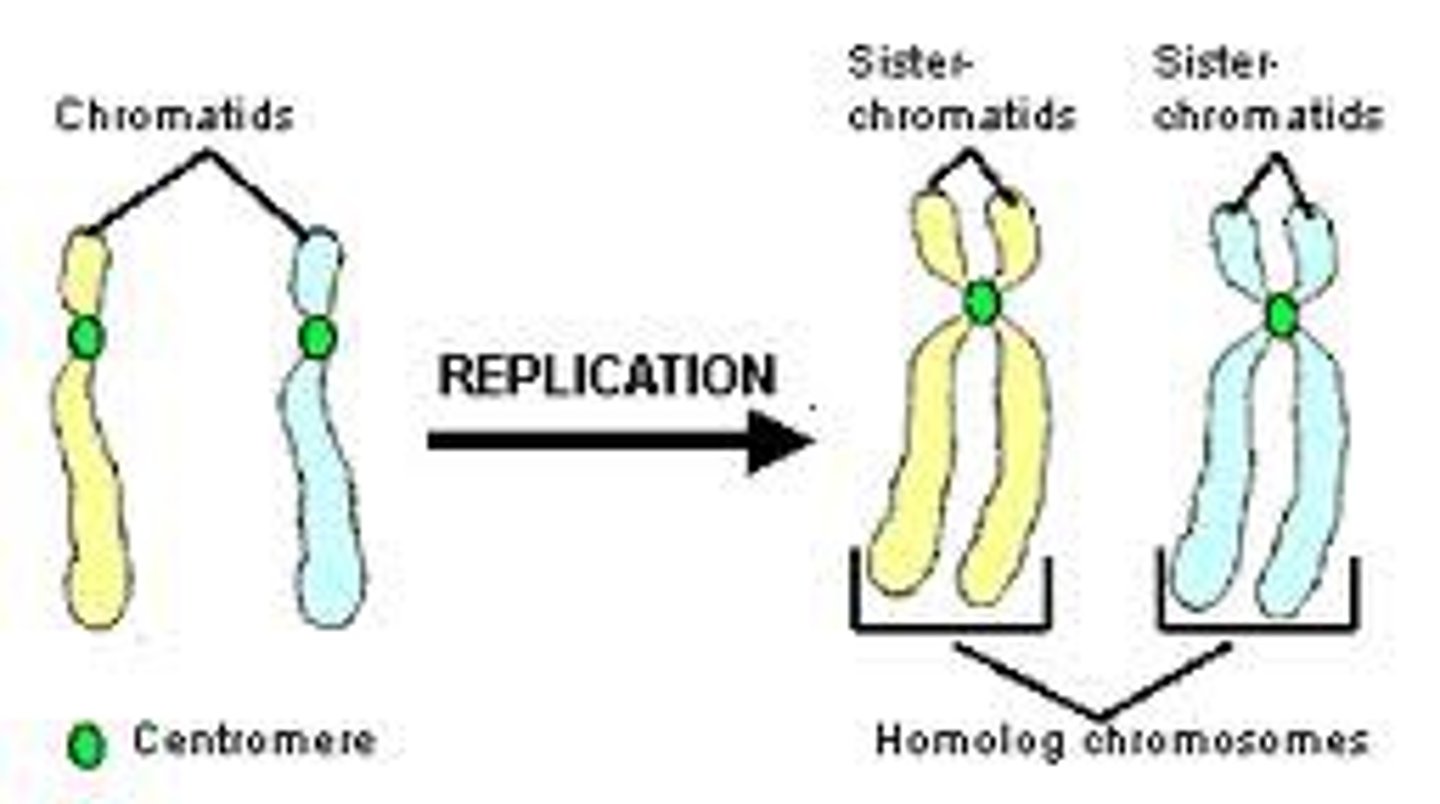
Chromatid
One of two identical DNA strands.
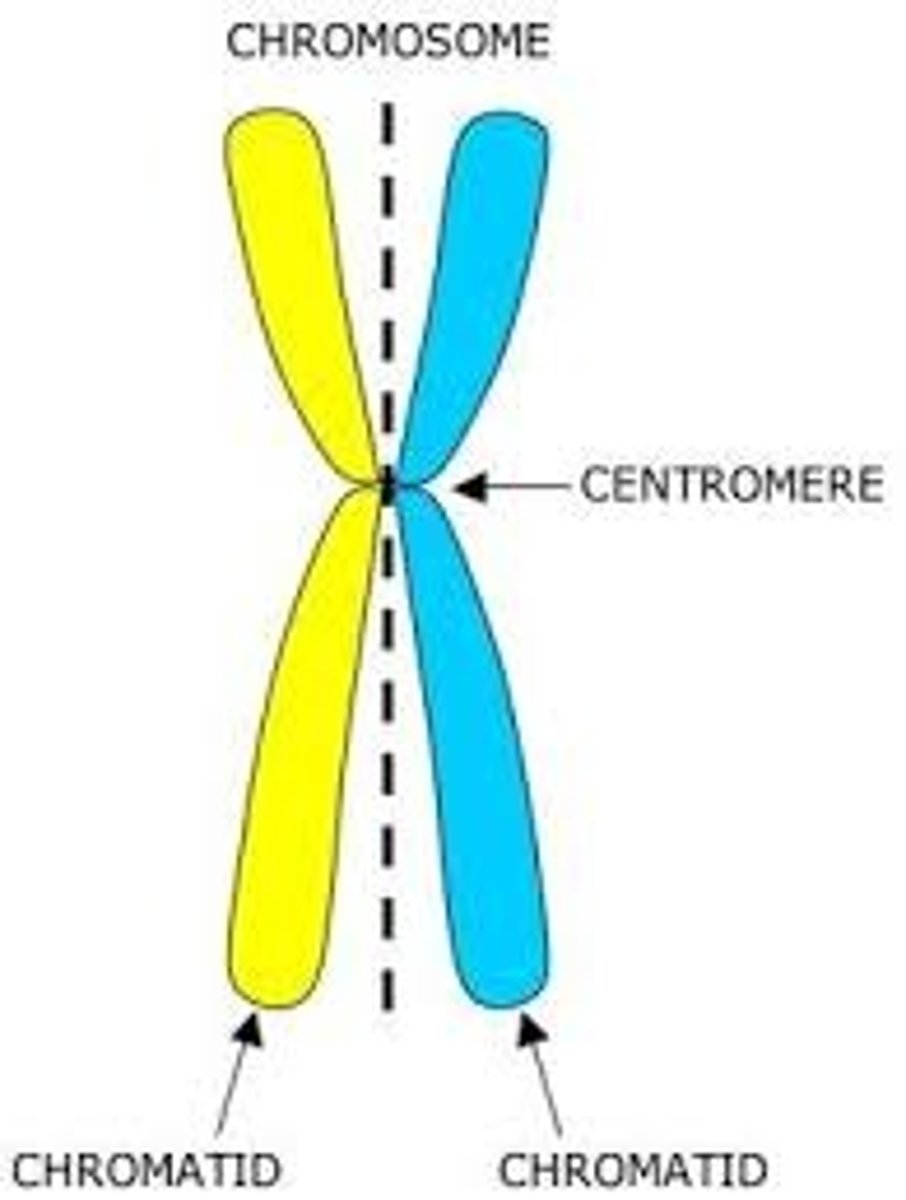
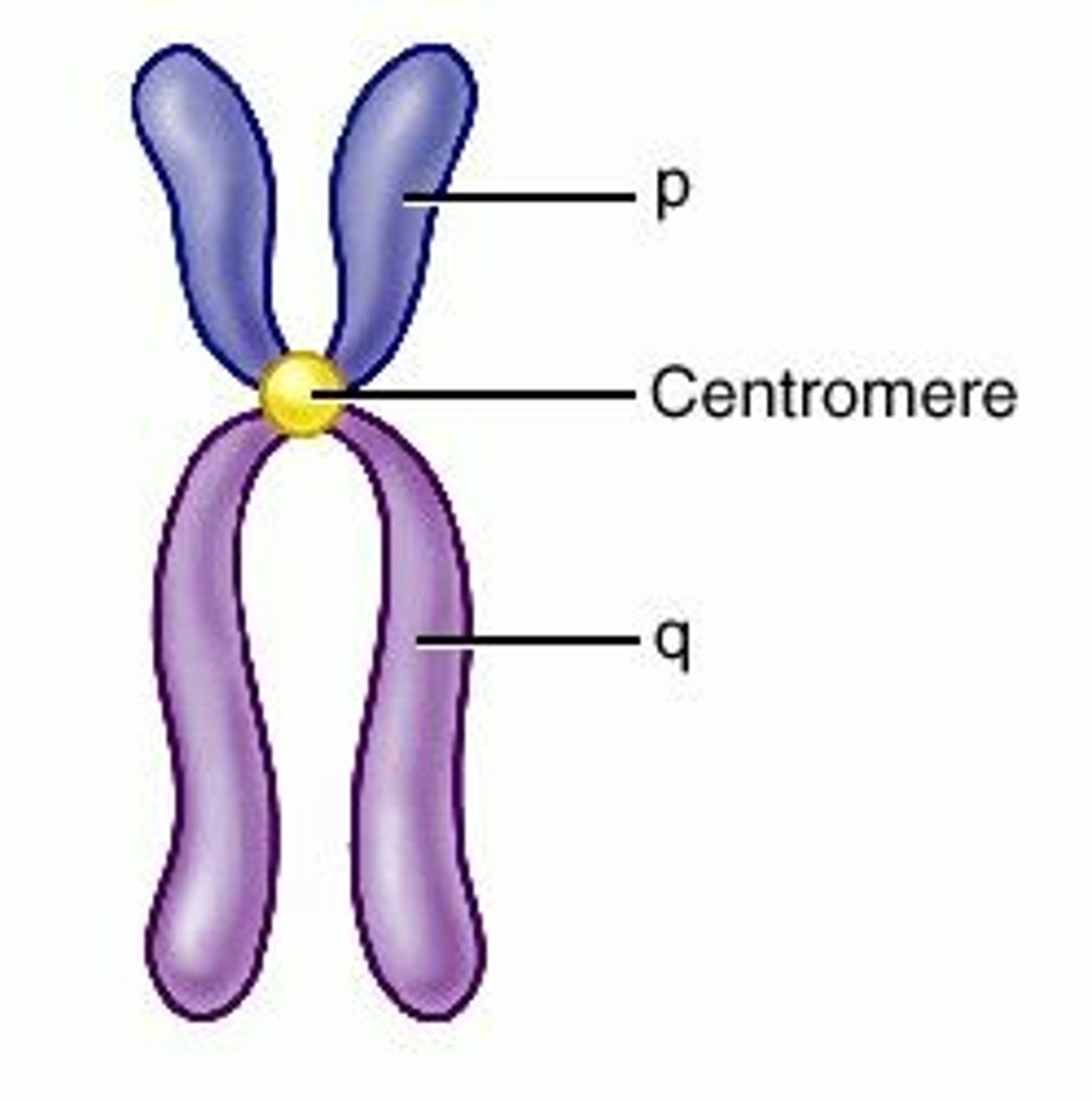
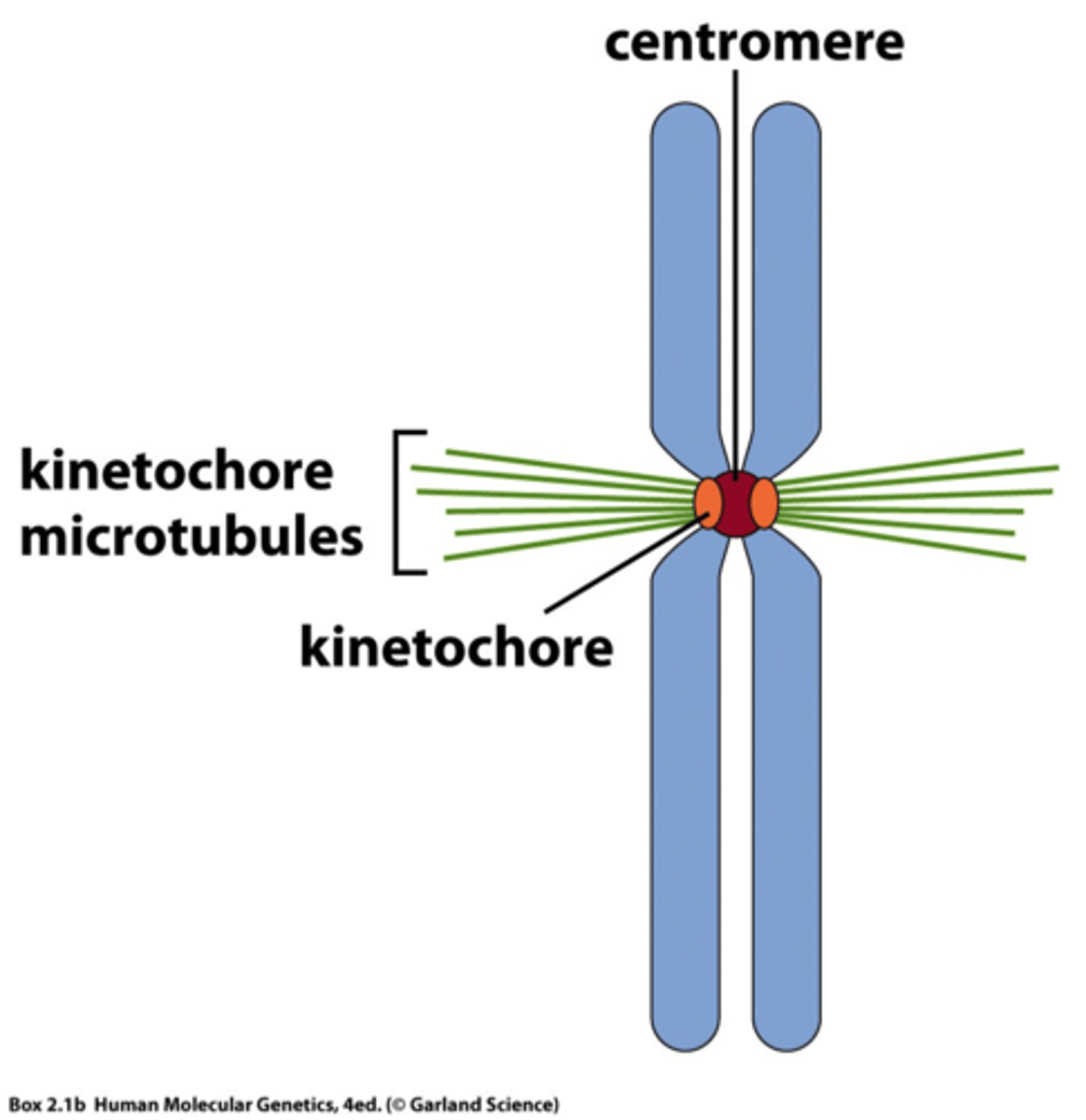
Centromere
Region joining sister chromatids.
Telomere
Protective ends of chromosomes.
Kinetochore
Protein where spindle fibers attach.
Prophase
Chromosomes condense, spindle forms, nuclear envelope breaks down.

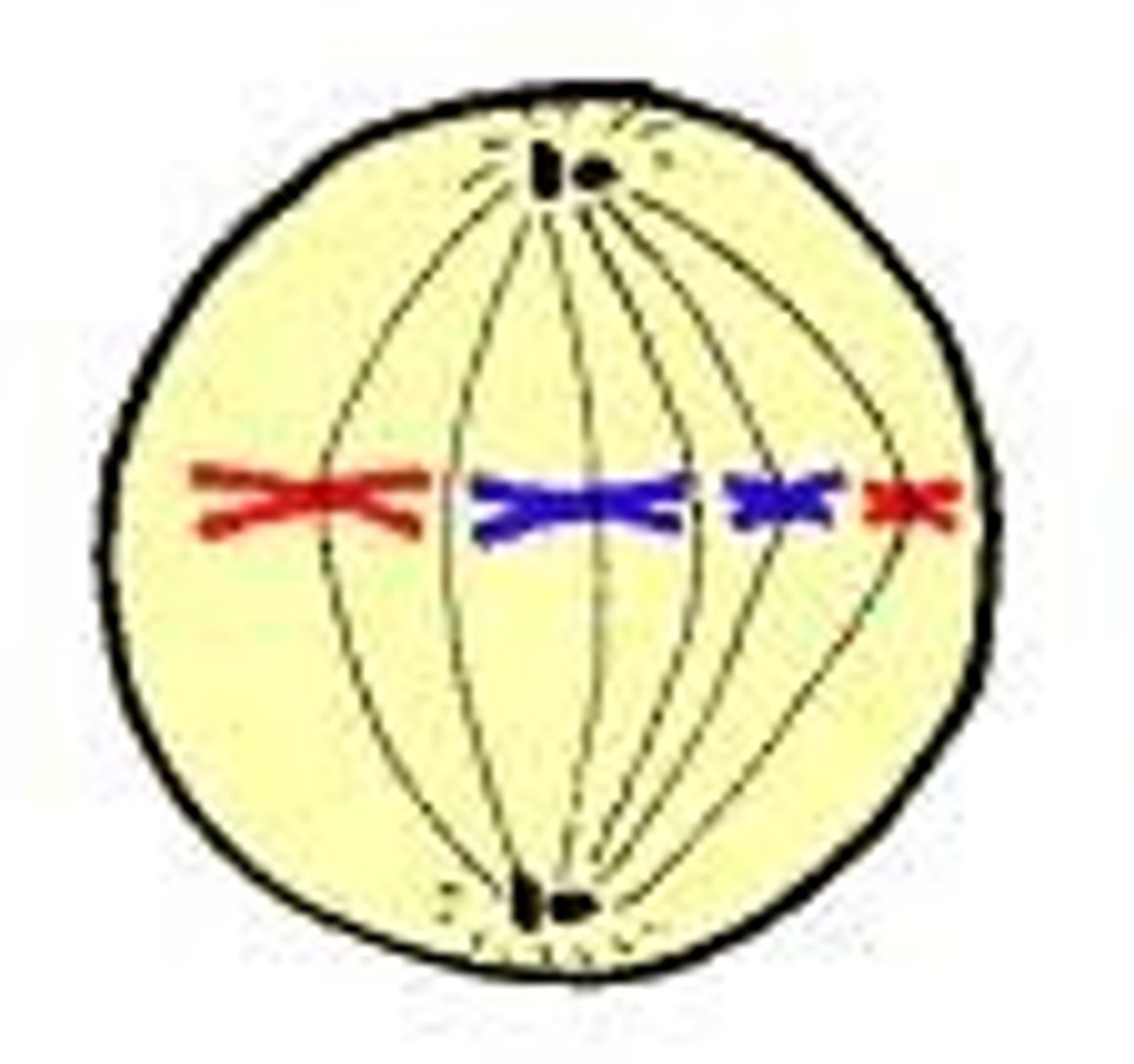
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at cell center.
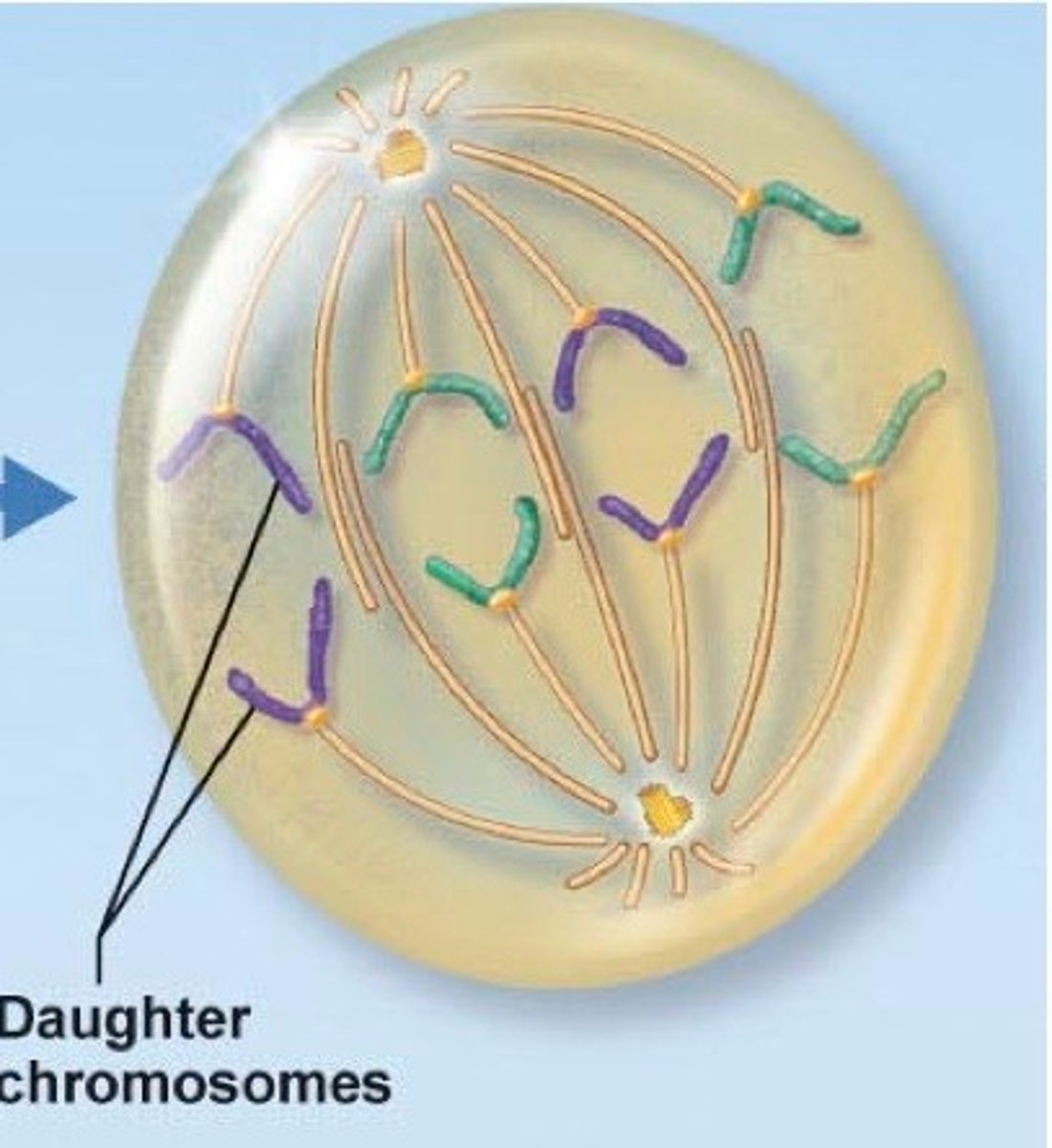
Anaphase
Sister chromatids pulled apart.
Telophase
Nuclear envelopes reform, chromosomes uncoil.
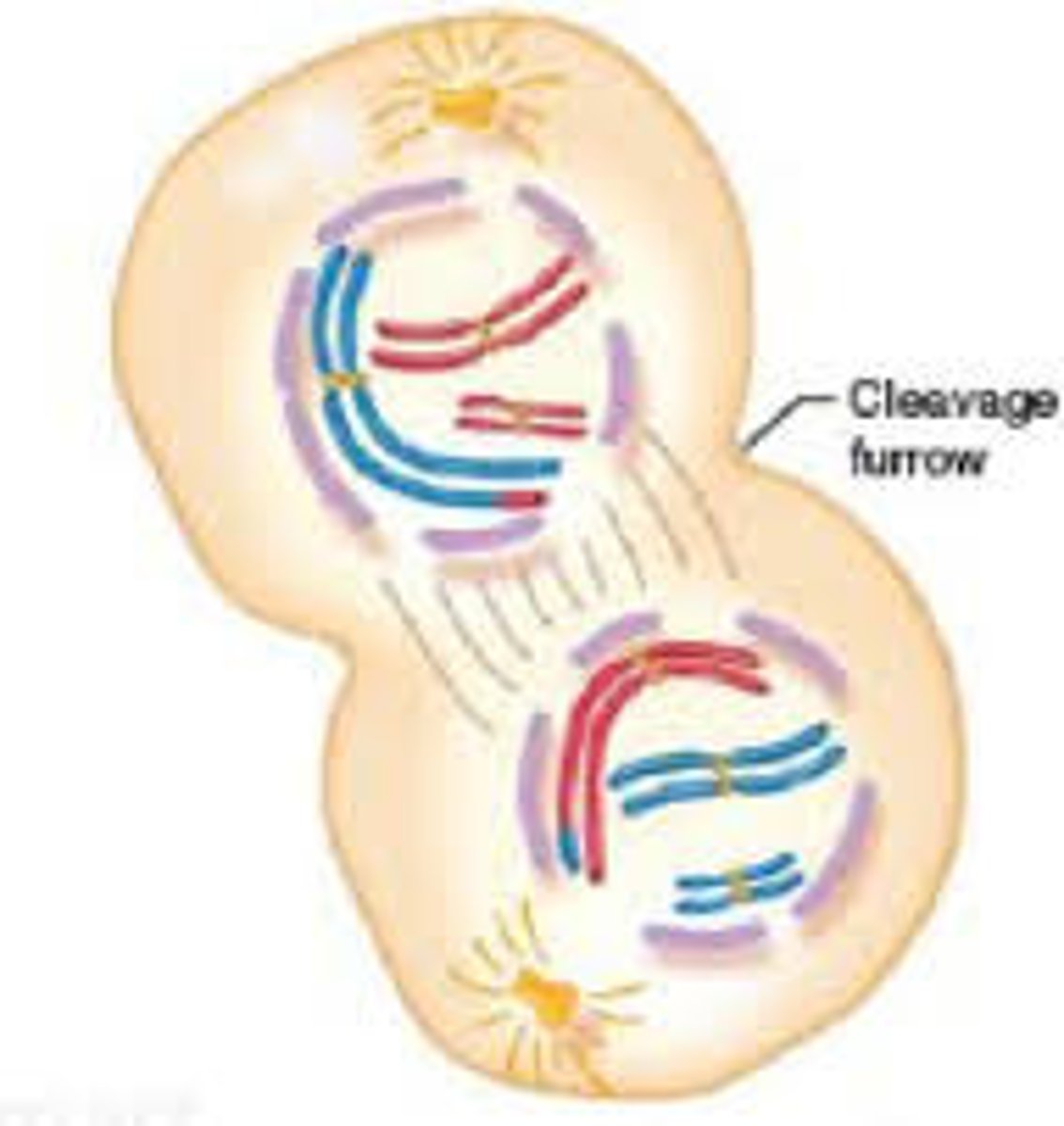
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides (cleavage furrow or cell plate forms).
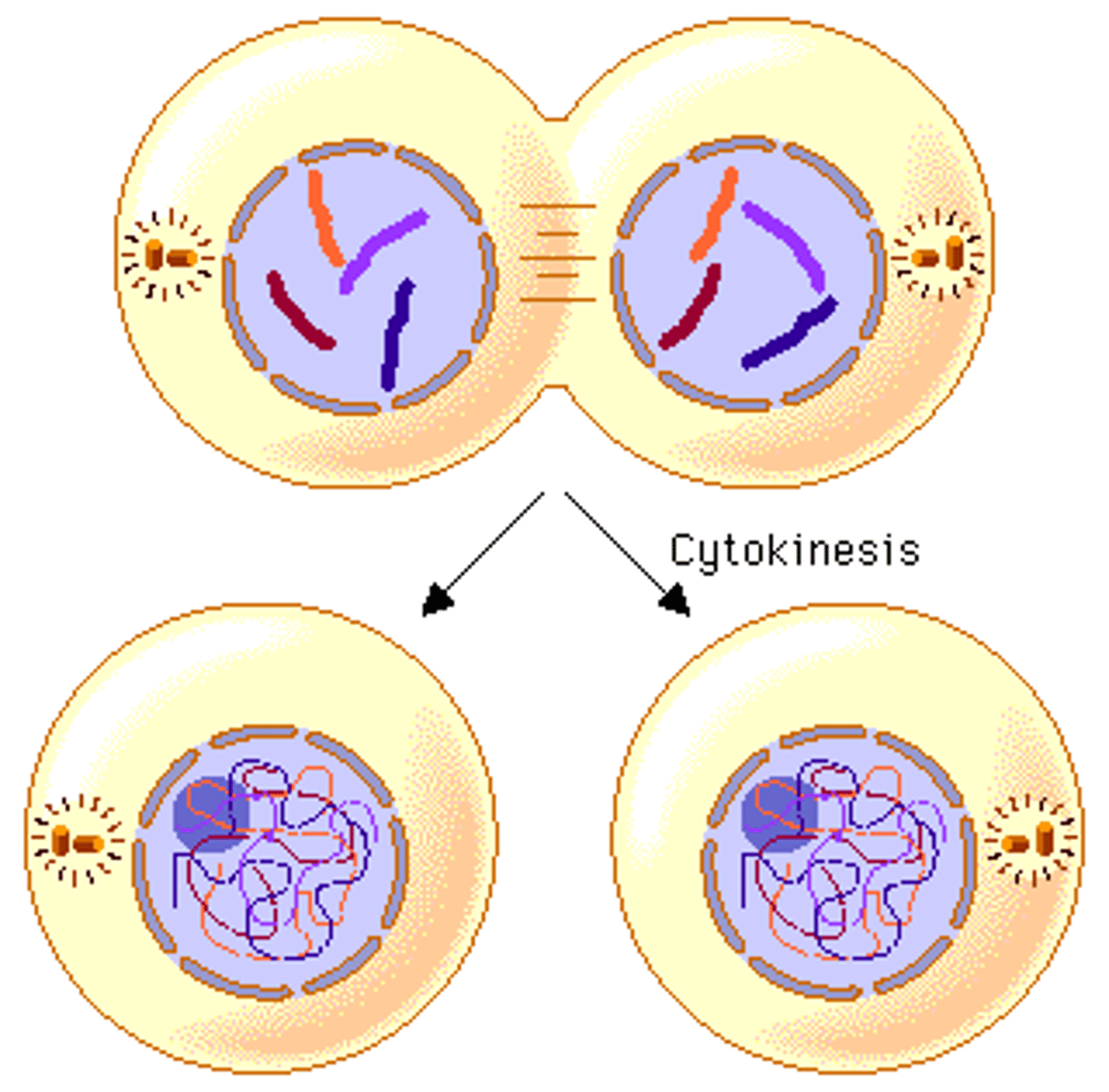
Mitosis
1 division round resulting in 2 identical diploid cells for growth & repair.
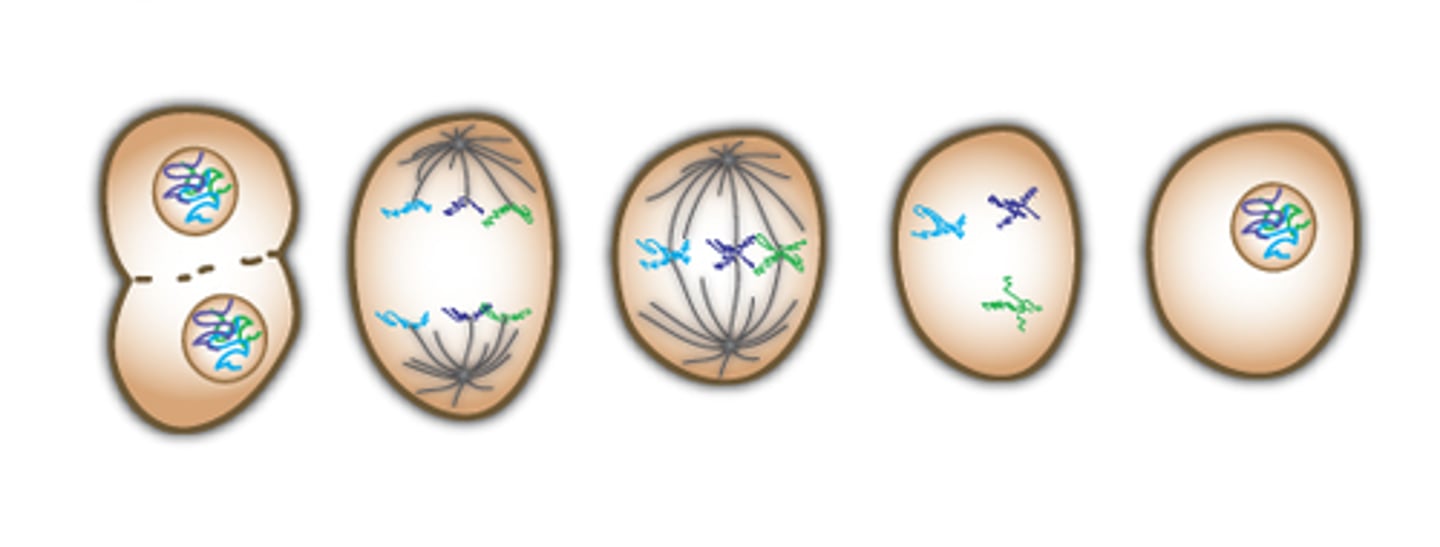
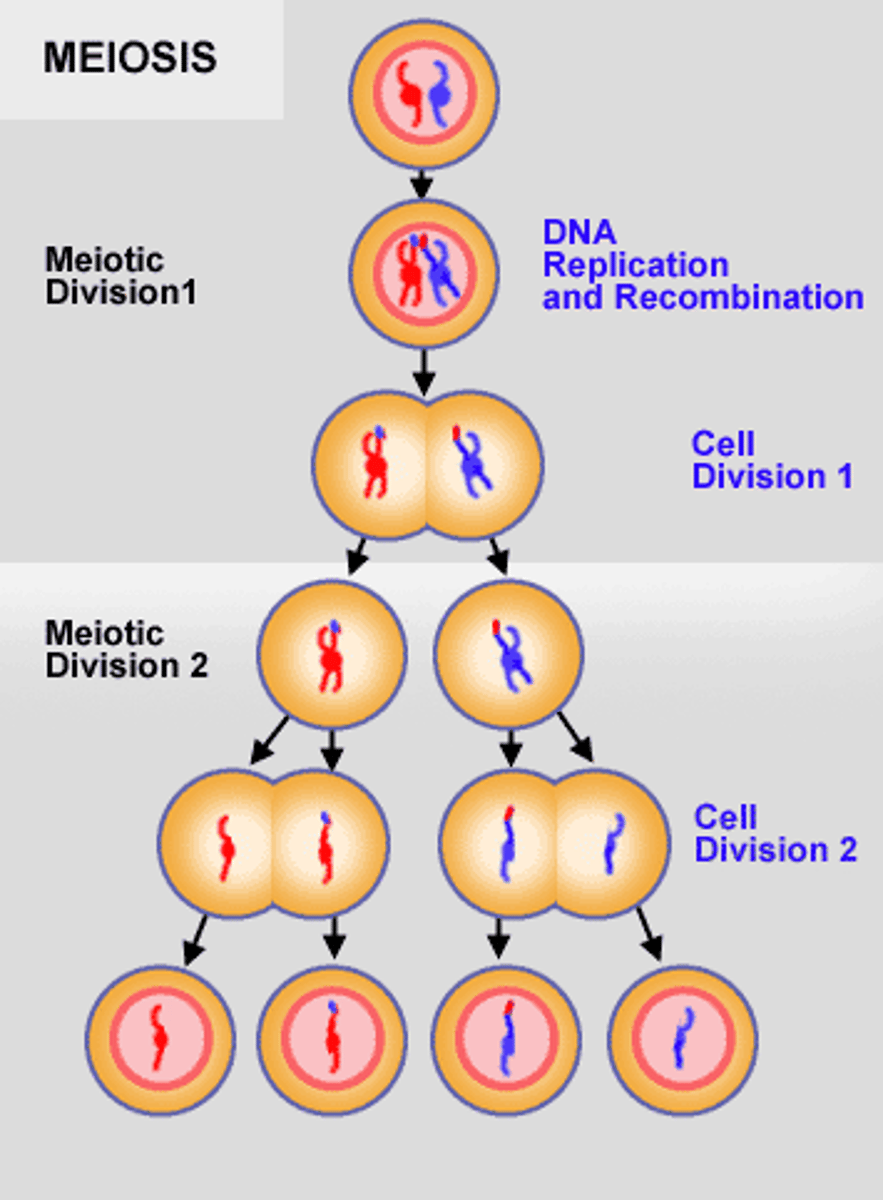
Meiosis
2 division rounds resulting in 4 unique haploid cells for sexual reproduction.
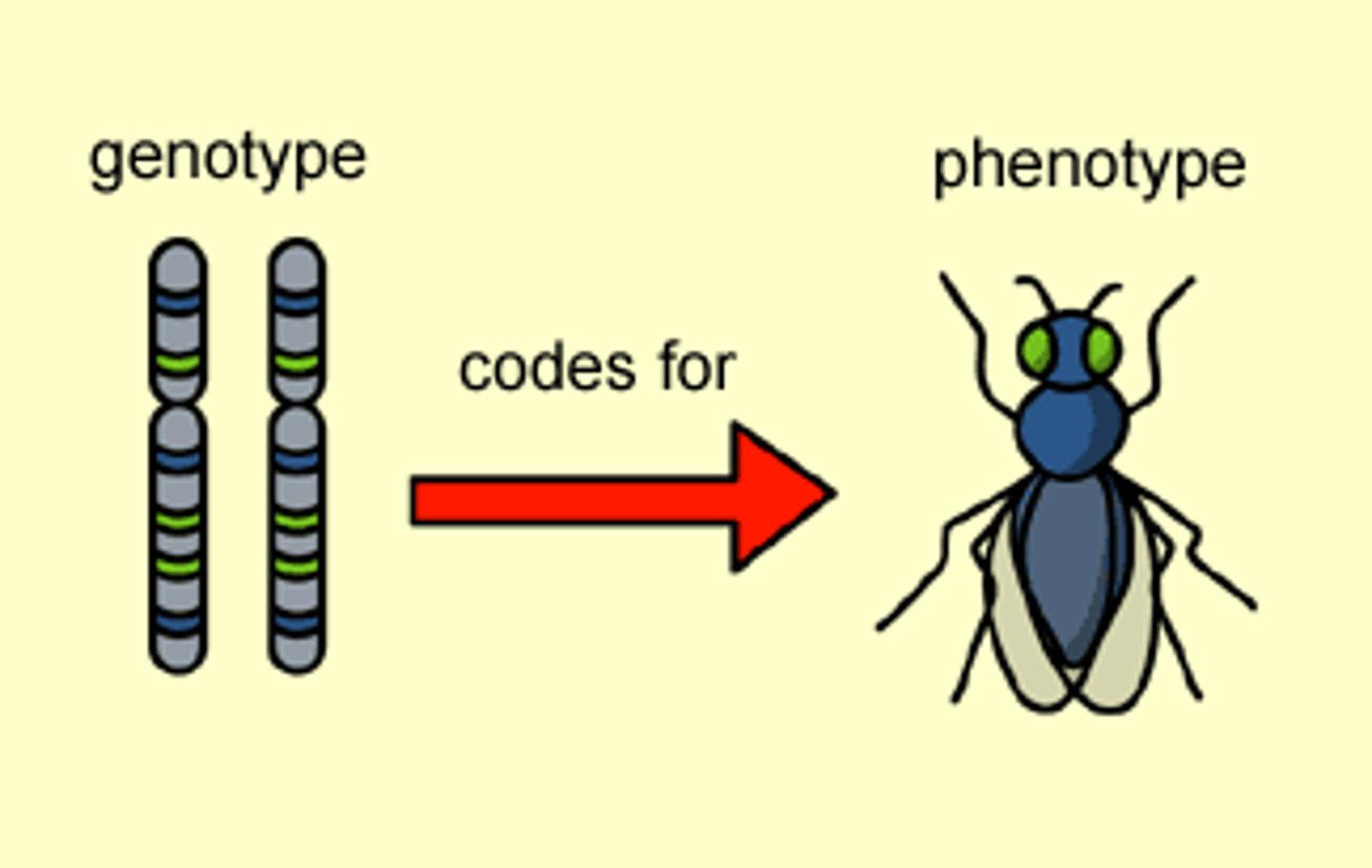
Genotype
Genetic makeup (e.g., Bb).
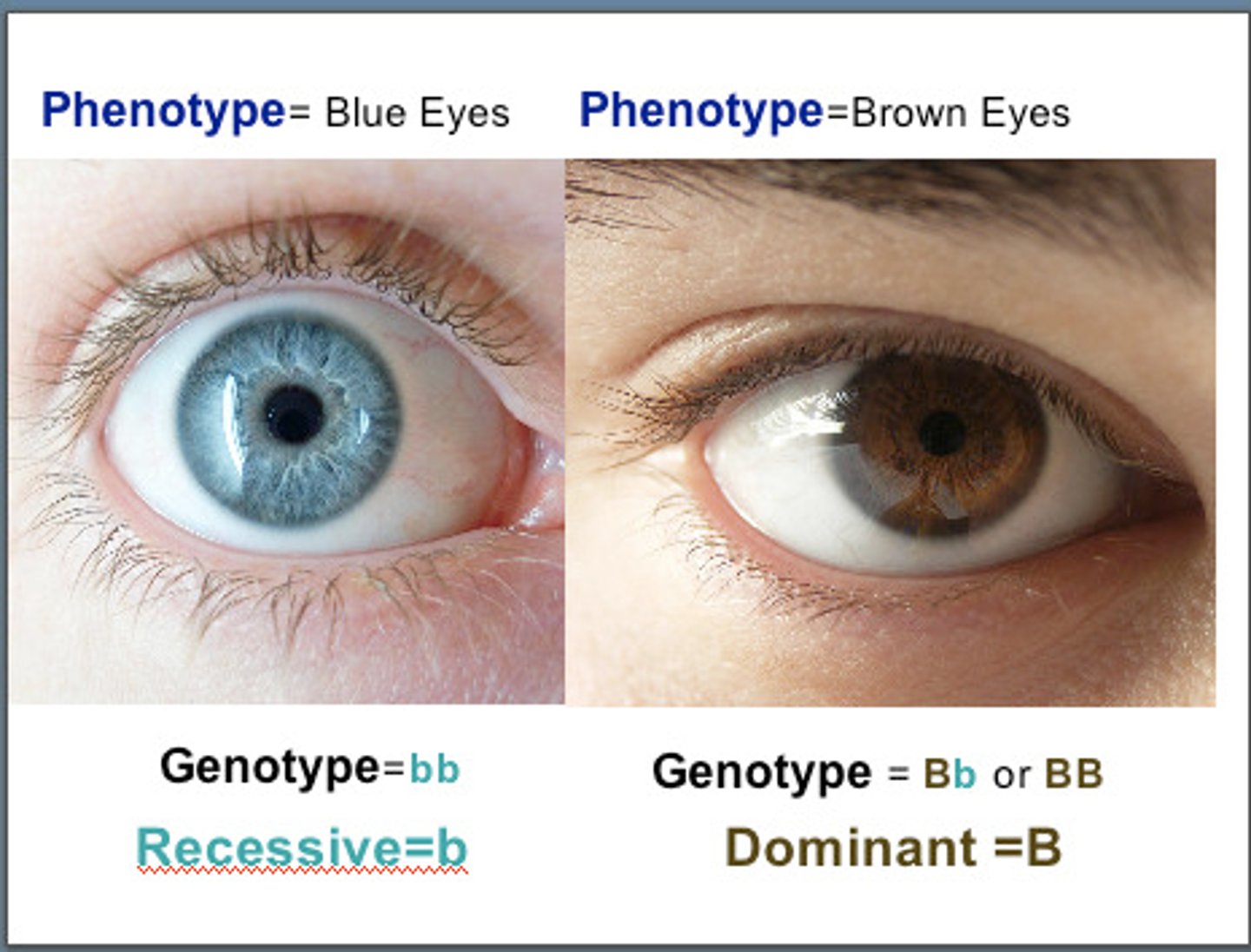
Phenotype
Physical expression (e.g., brown eyes).
Homozygous
Two identical alleles (AA or aa).

Heterozygous
Two different alleles (Aa).

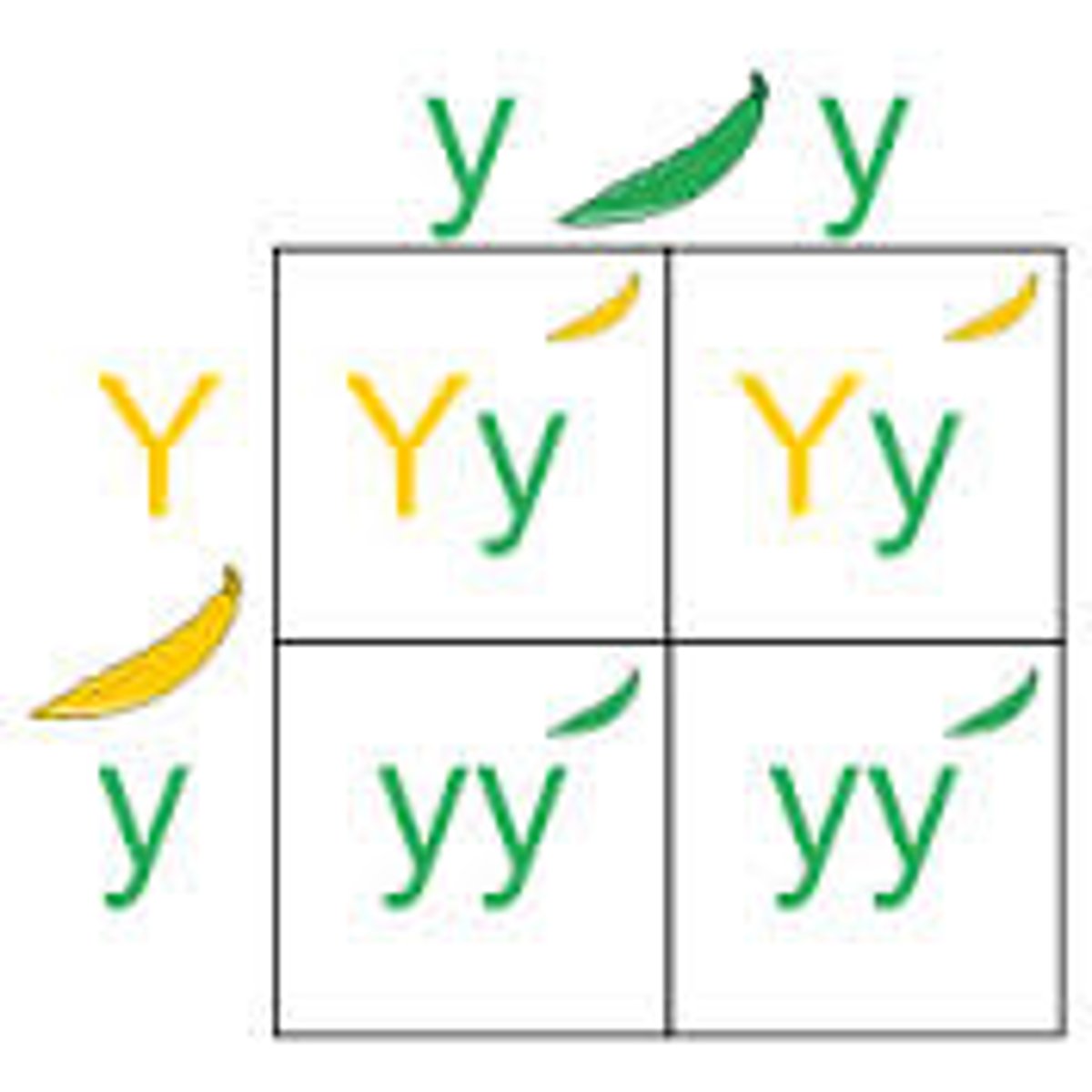
Monohybrid Cross
1 trait (e.g., Aa × Aa).
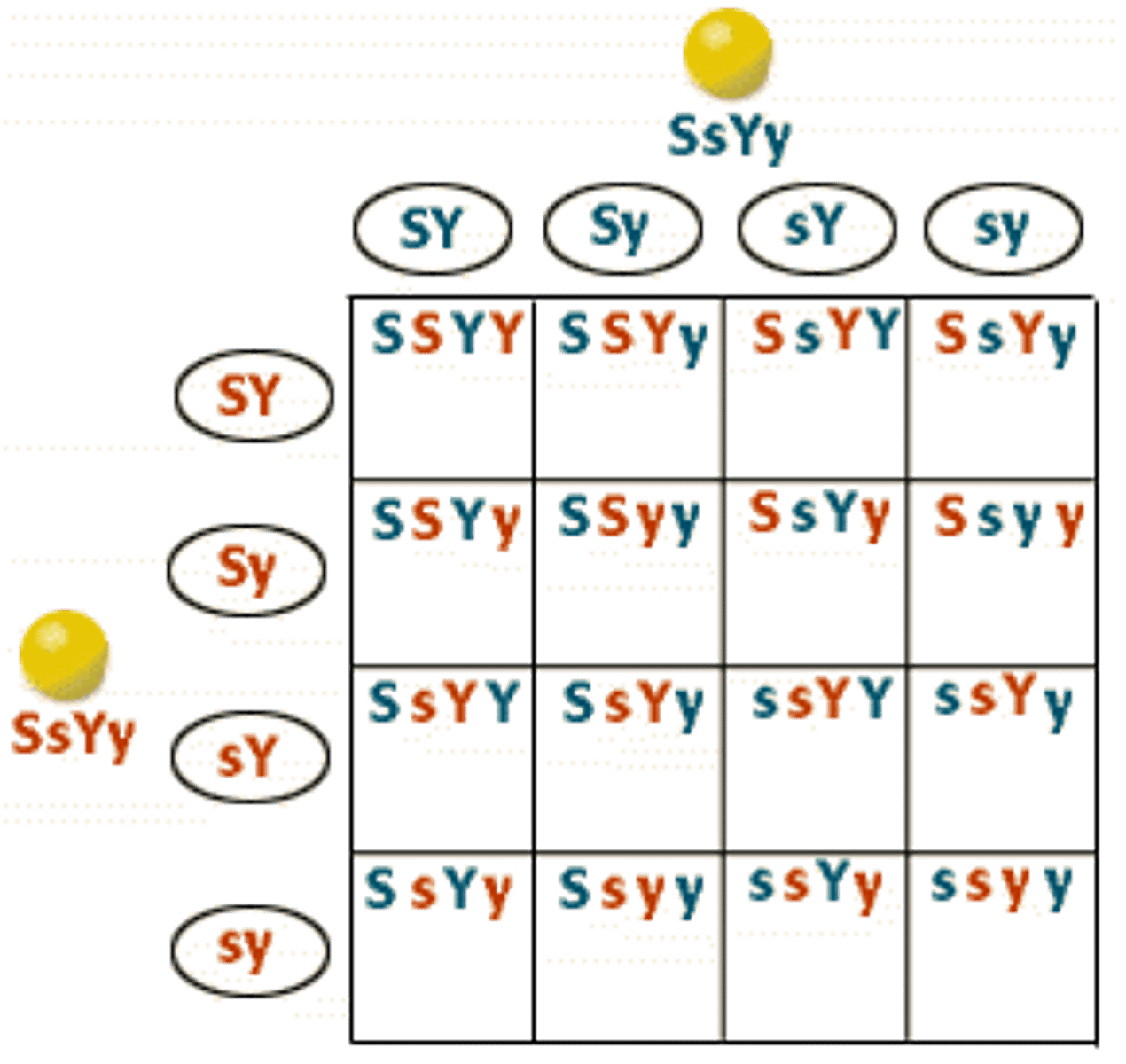
Dihybrid Cross
2 traits (e.g., AaBb × AaBb).
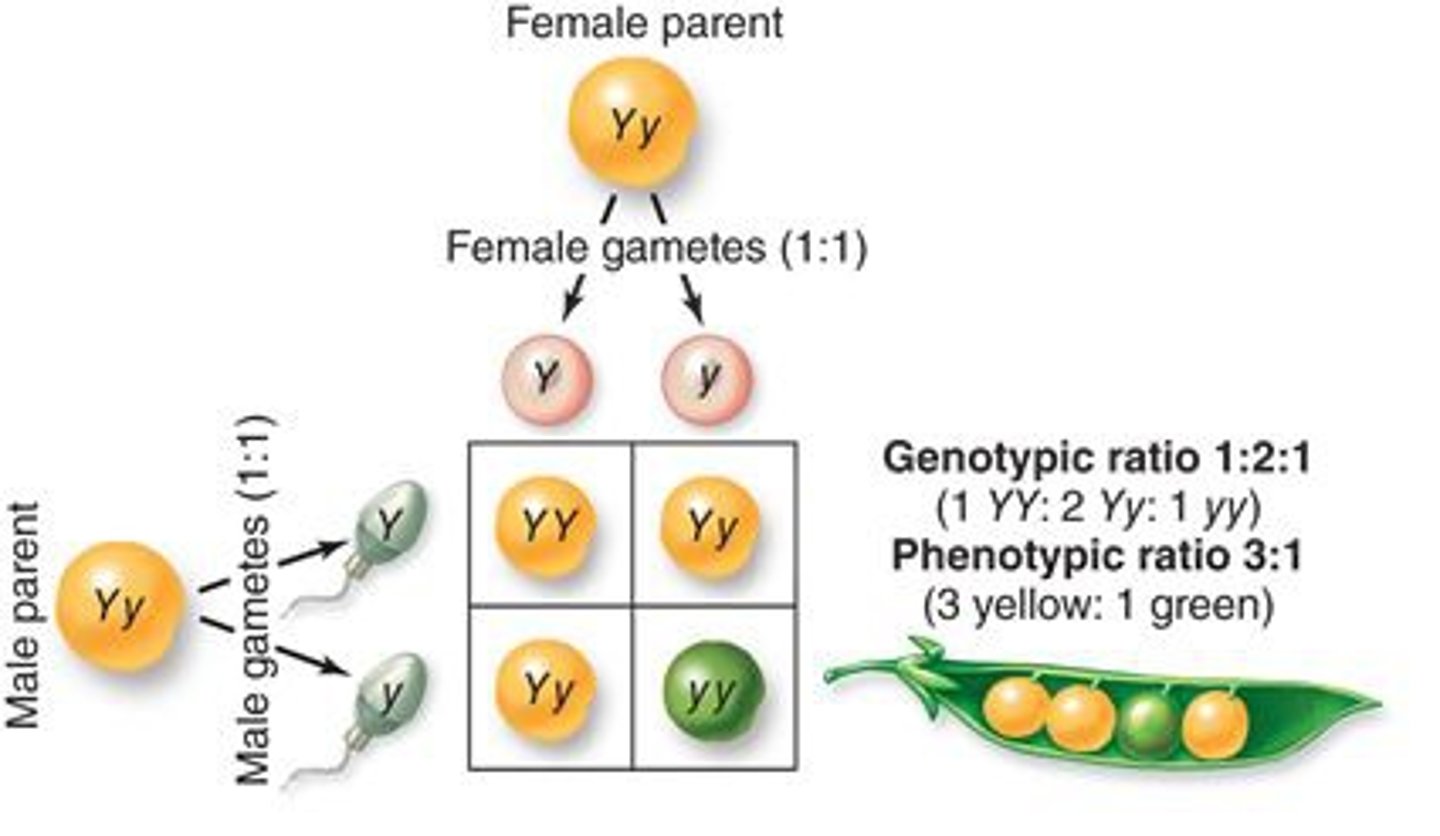
Genotypic ratio
Count each genotype (e.g., 1:2:1).
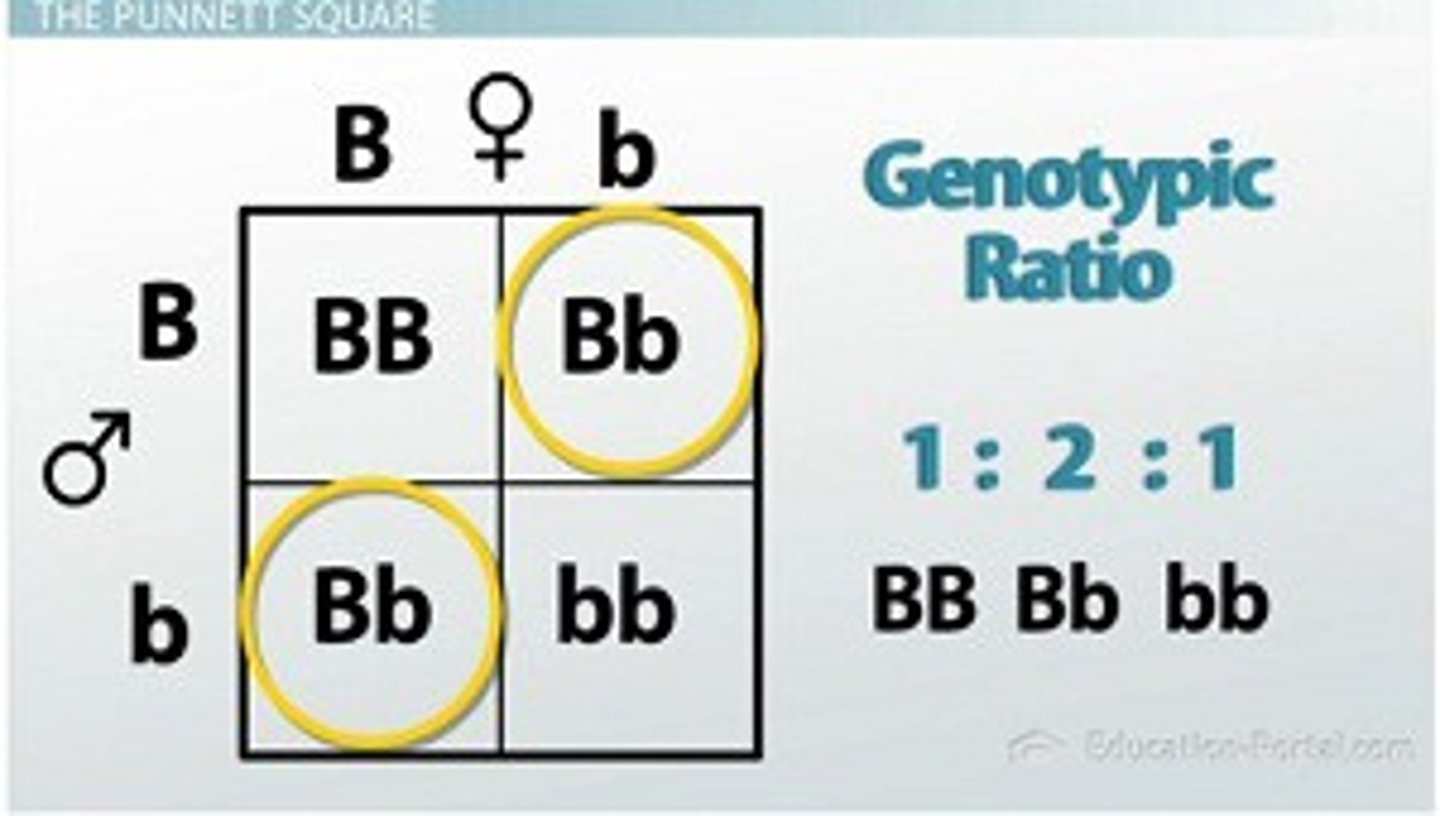
Phenotypic ratio
Count dominant vs recessive traits.
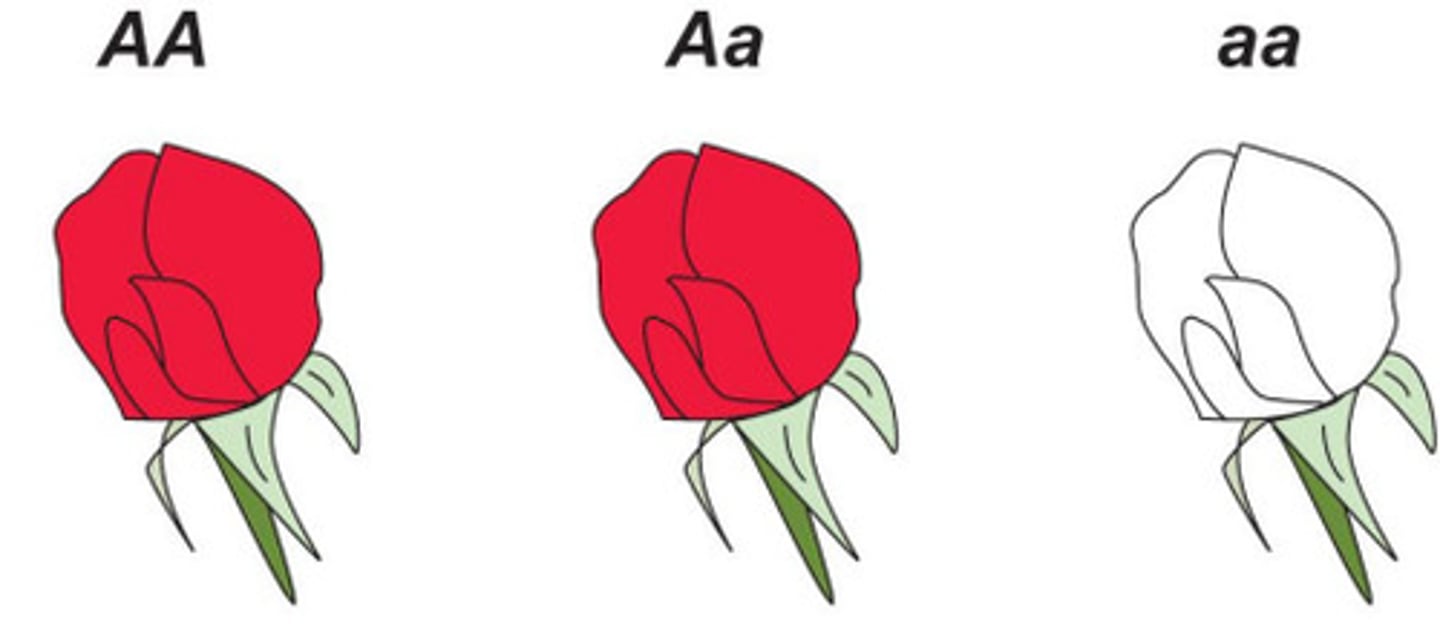
Dominant/Recessive
One allele masks the other.
Codominance
Both alleles are expressed (e.g., AB blood).
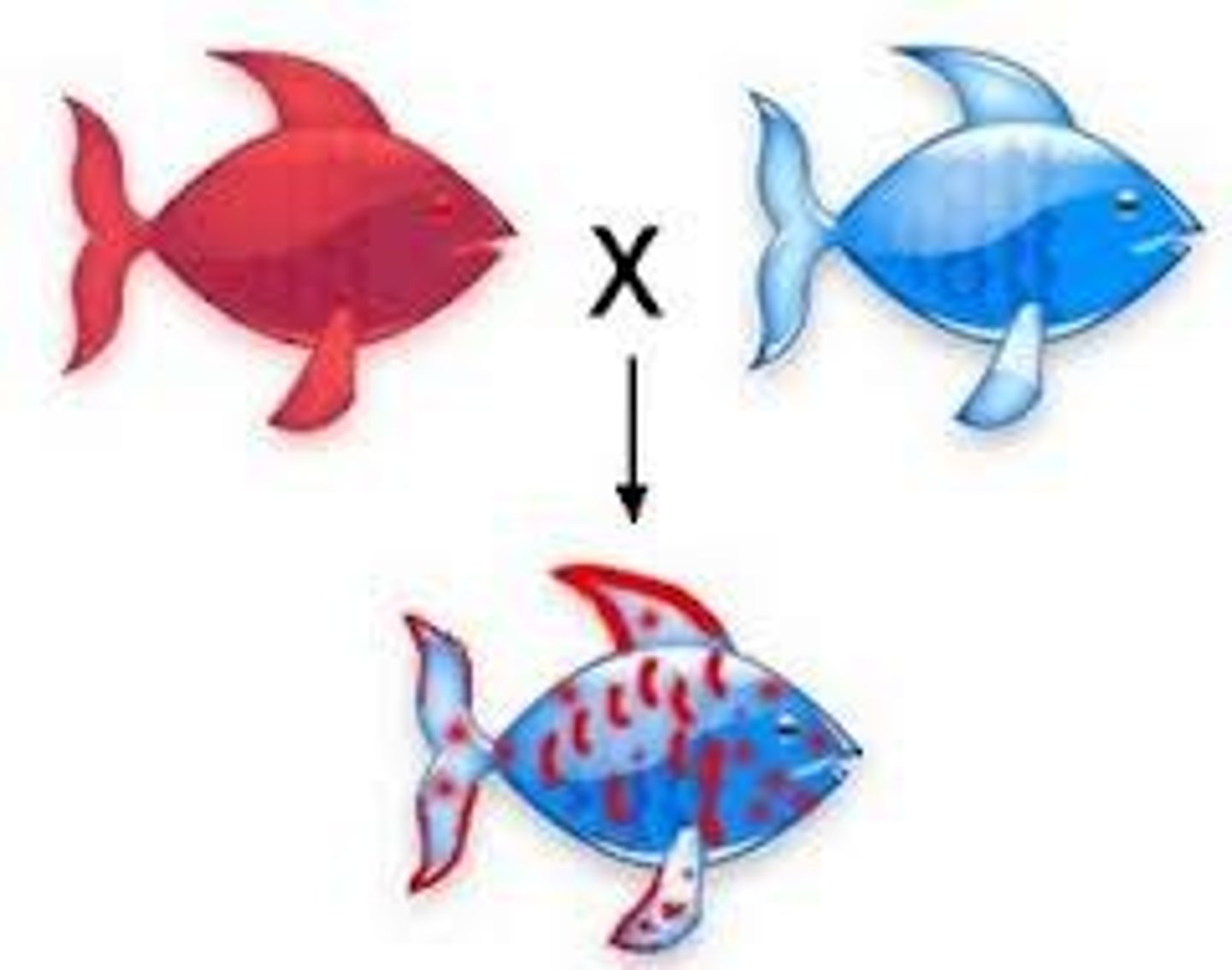
Incomplete dominance
Blended phenotype (e.g., red + white = pink).

sex-linked traits
On X or Y chromosome (e.g., color blindness).

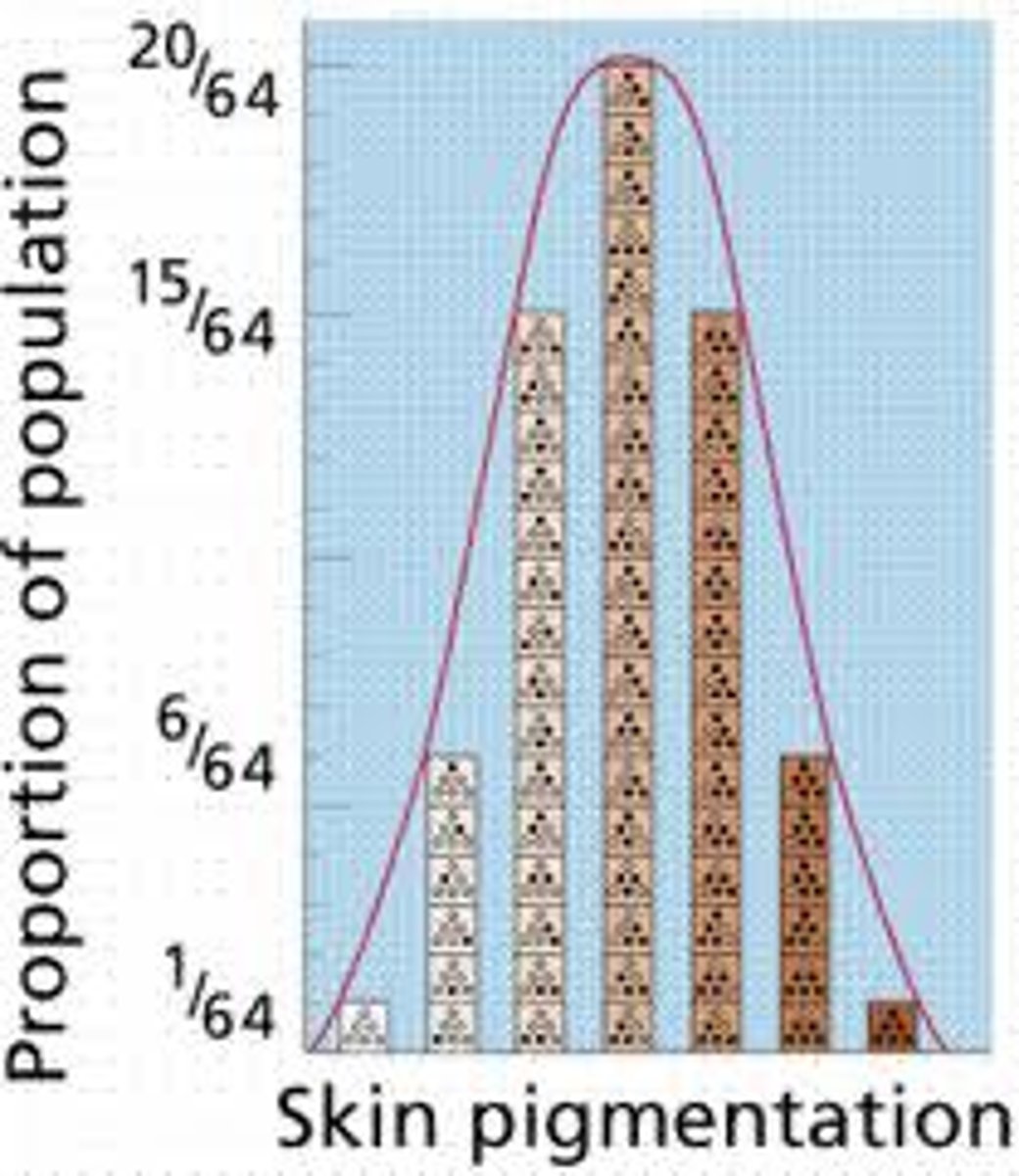
Polygenic Traits
Multiple genes (e.g., height, skin color).
Acquired Traits
Traits gained after birth; not inherited (e.g., scars, dyed hair).

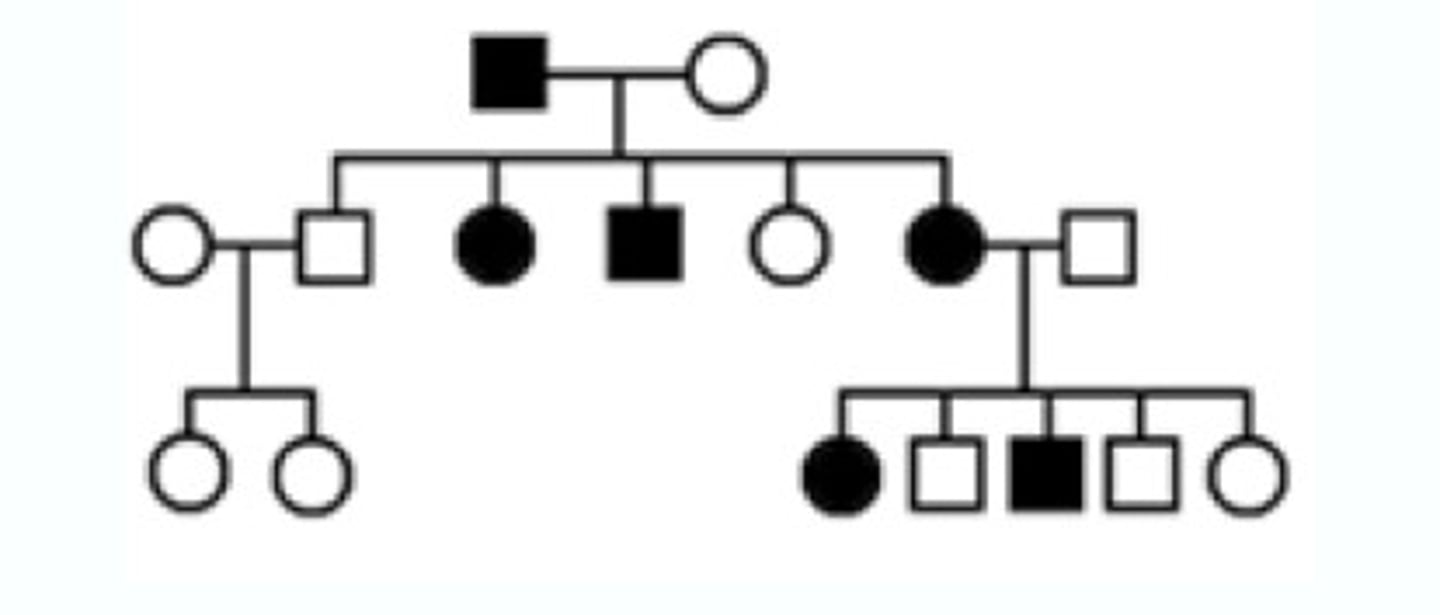
Pedigrees
Circles = females, squares = males; shaded = expresses trait.
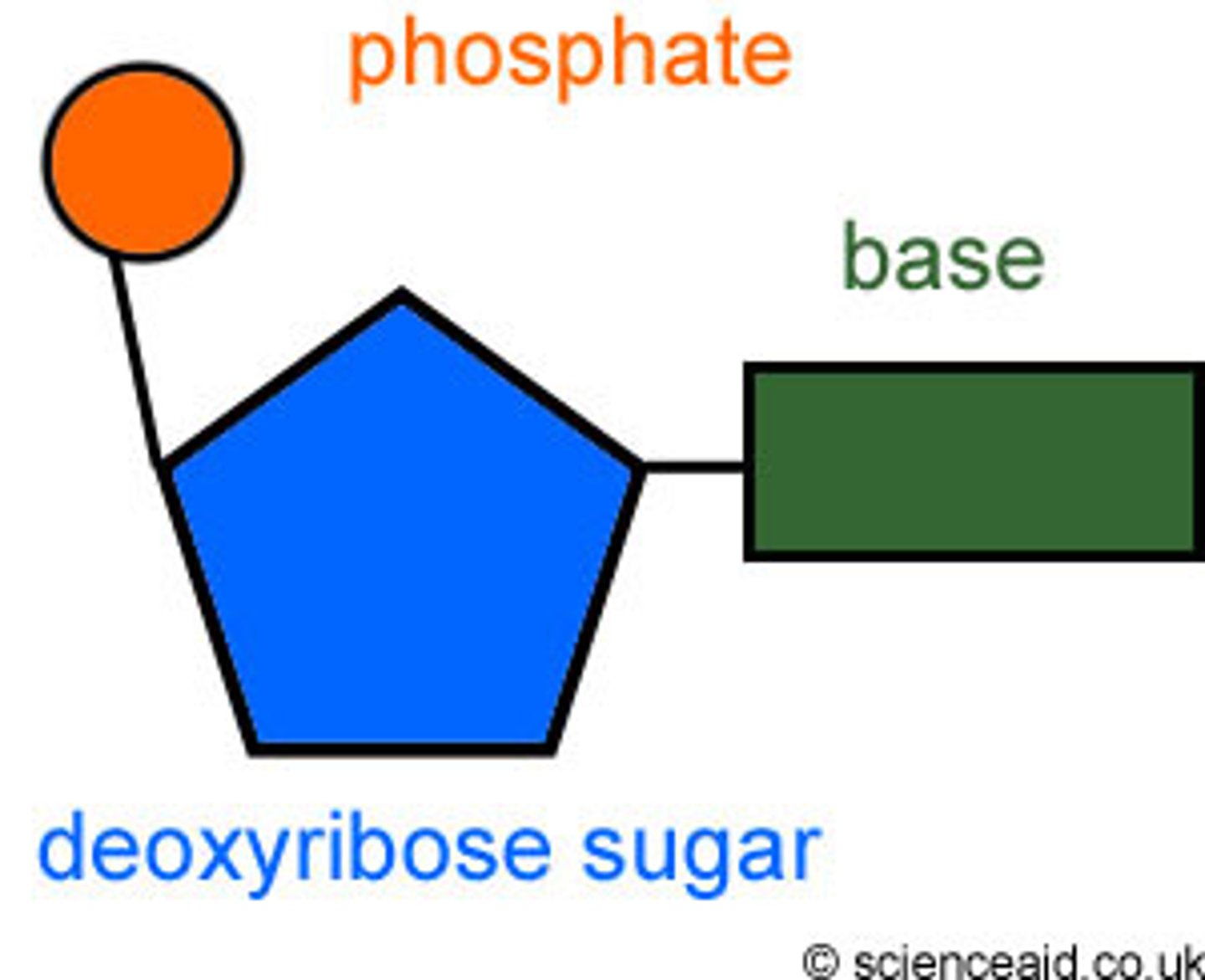
DNA Nucleotide
Deoxyribose + phosphate + A/T/C/G.
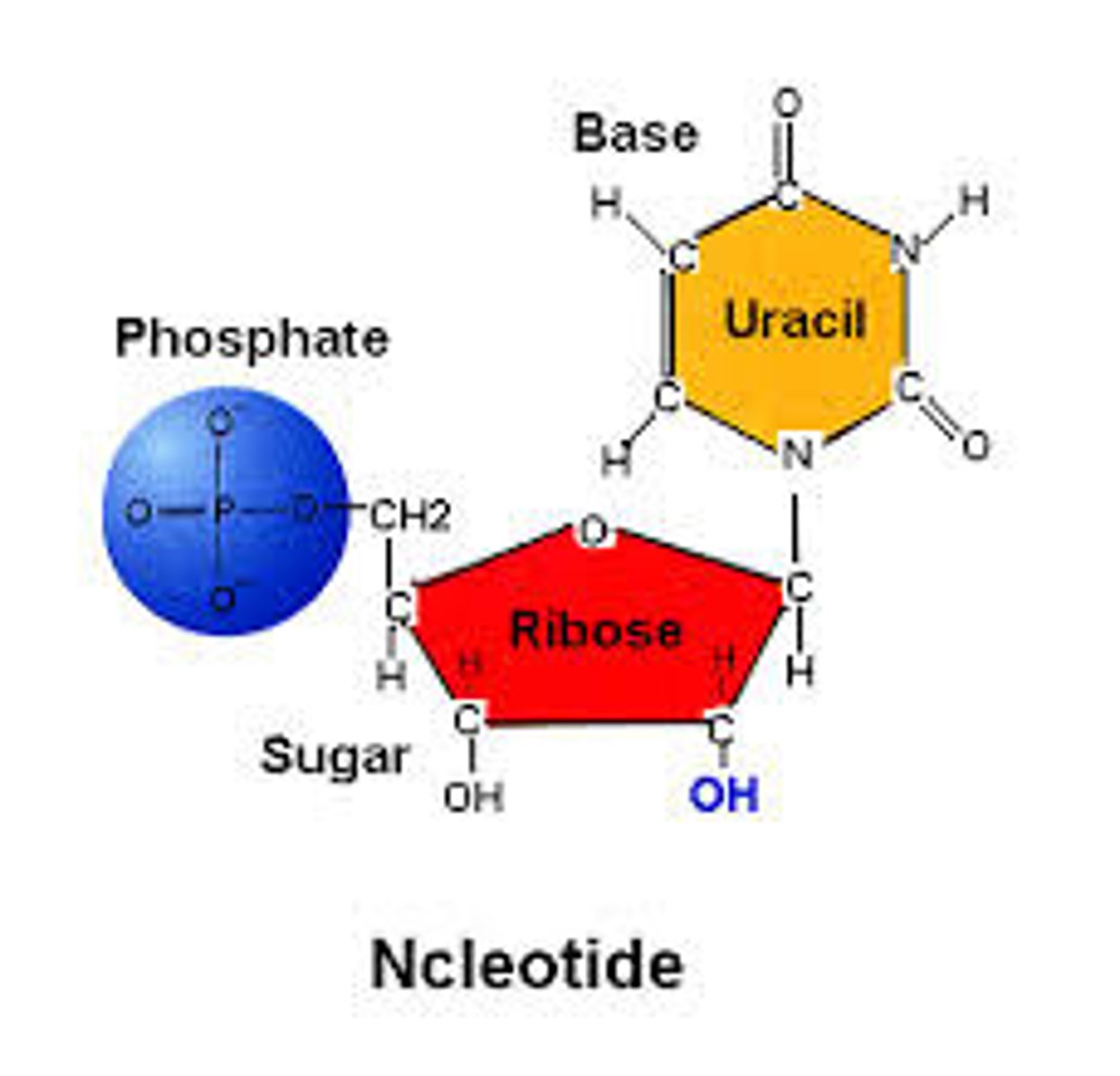
RNA Nucleotide
Ribose + phosphate + A/U/C/G.
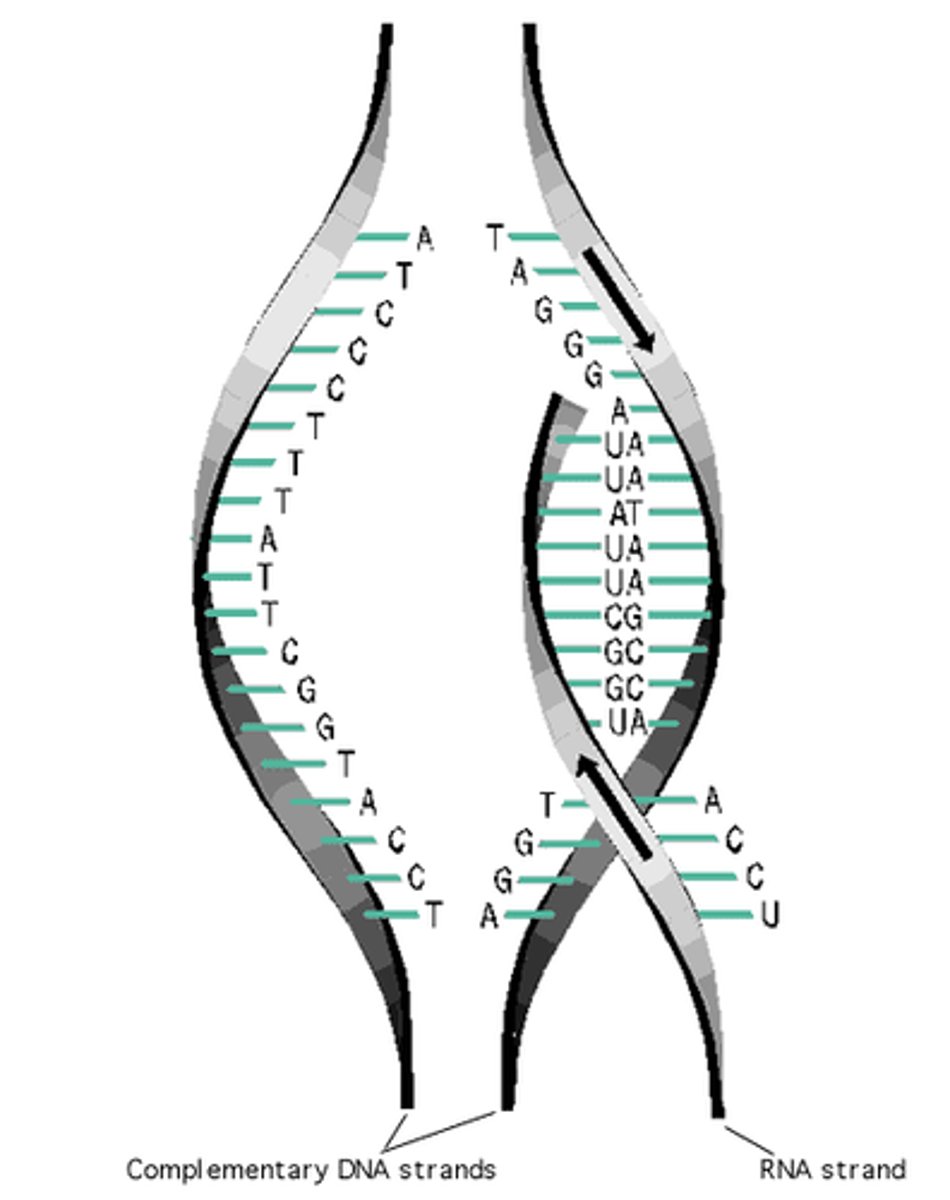
Helicase
Unzips DNA.
DNA polymerase
Builds new strands.
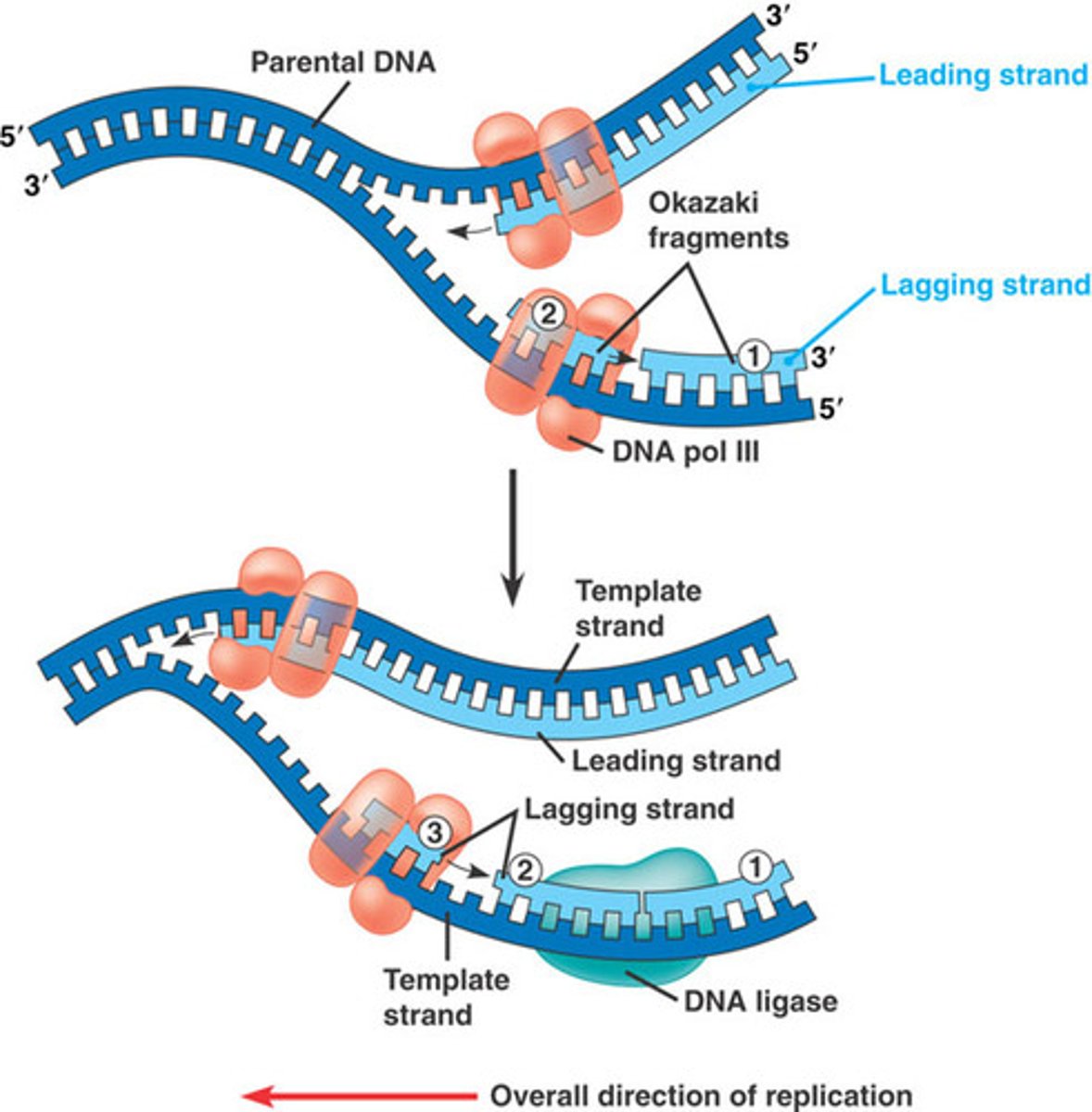
Ligase
Seals fragments.

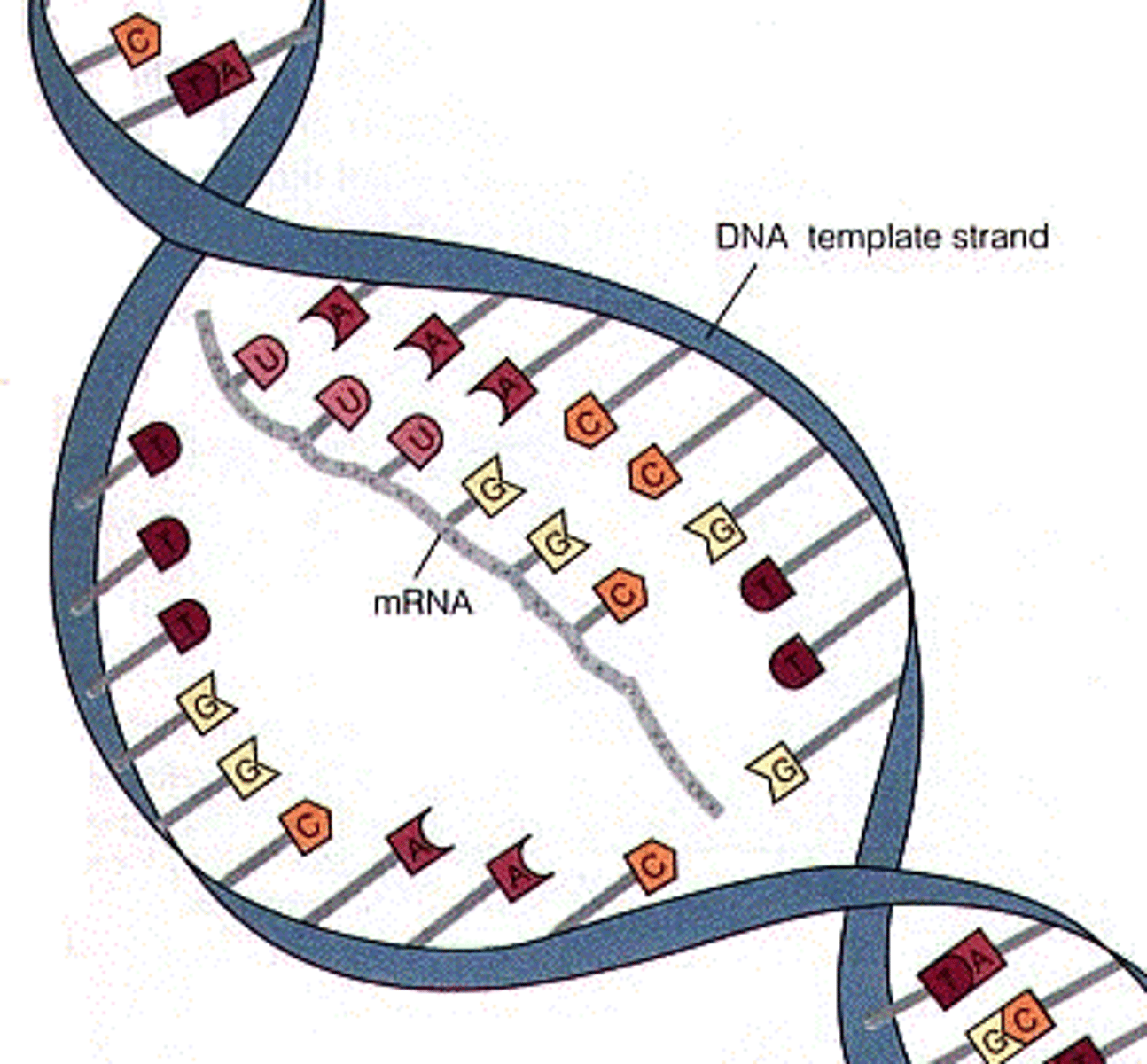
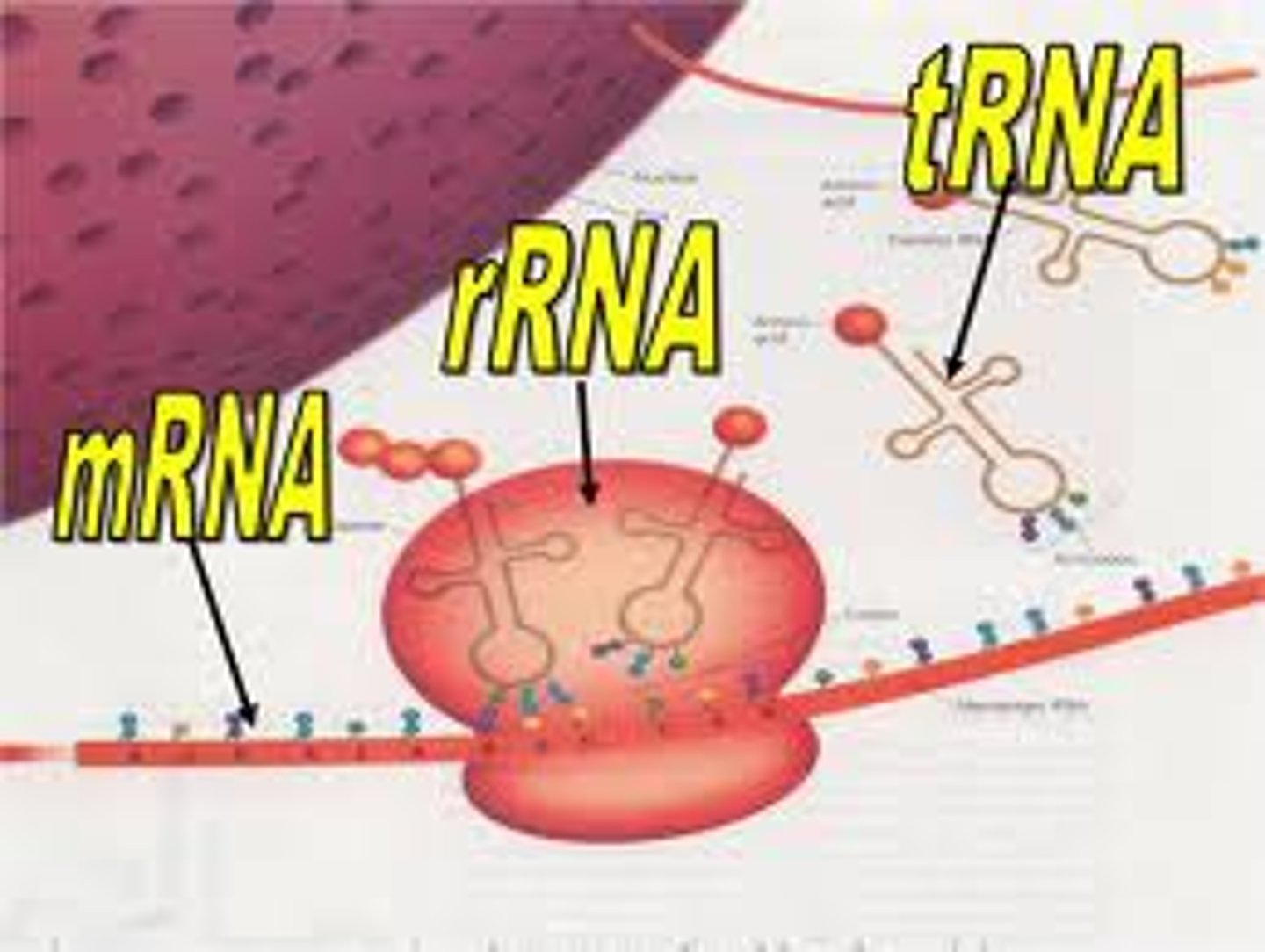
mRNA
Messenger RNA; carries code.
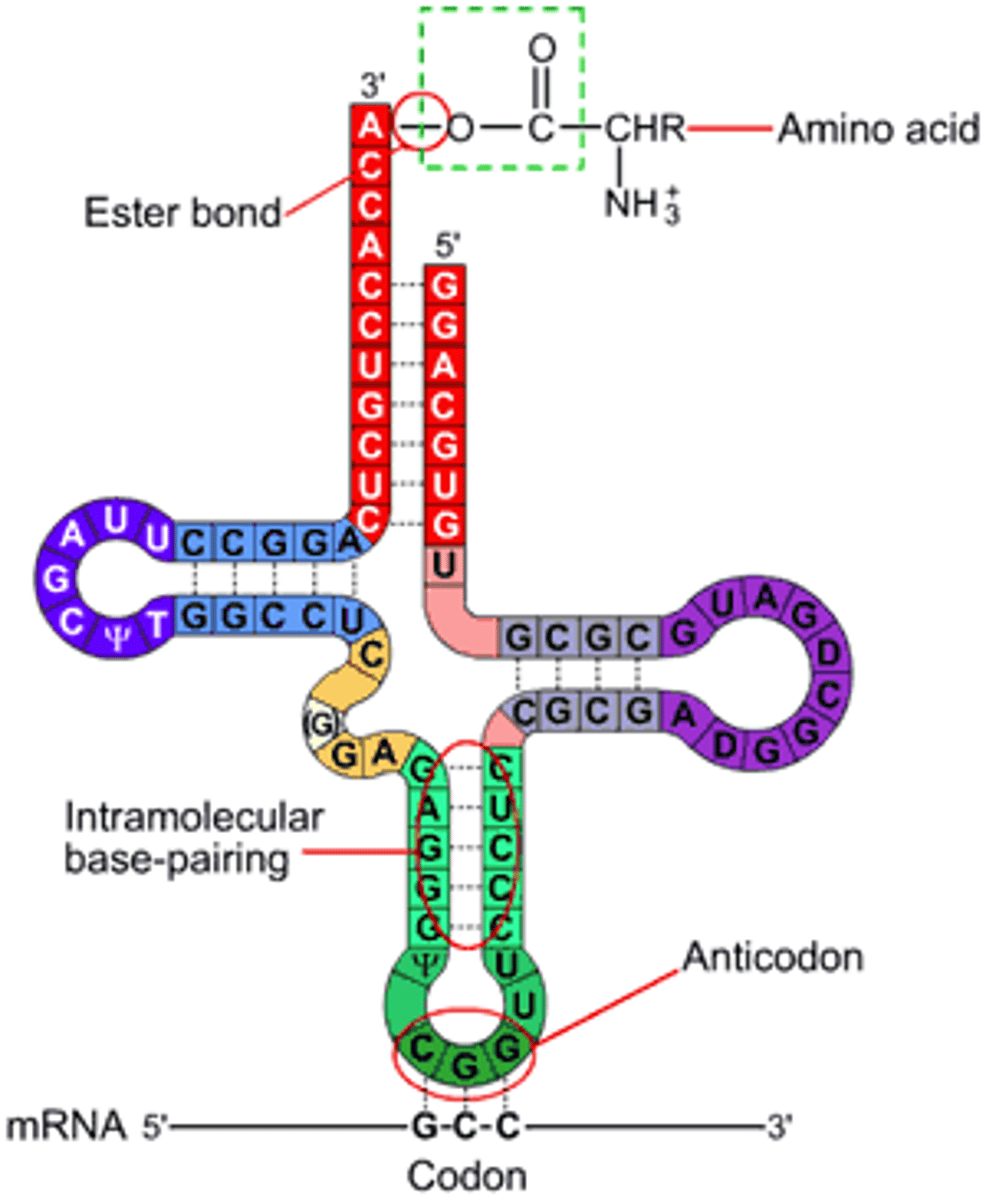
tRNA
Transfers amino acids.
rRNA
Makes ribosomes.
Transcription
Copy DNA to mRNA.
Translation
Make protein from mRNA.
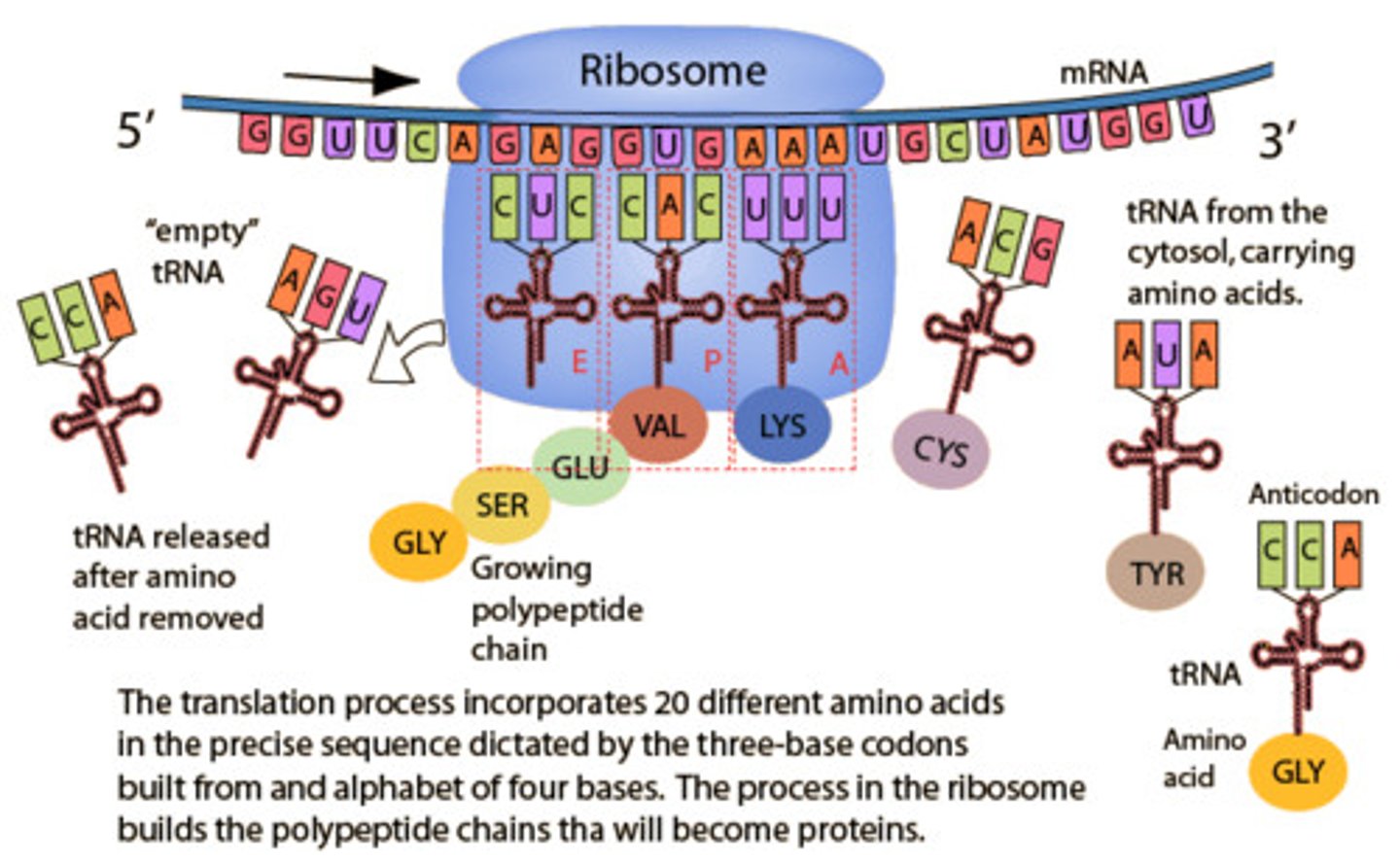
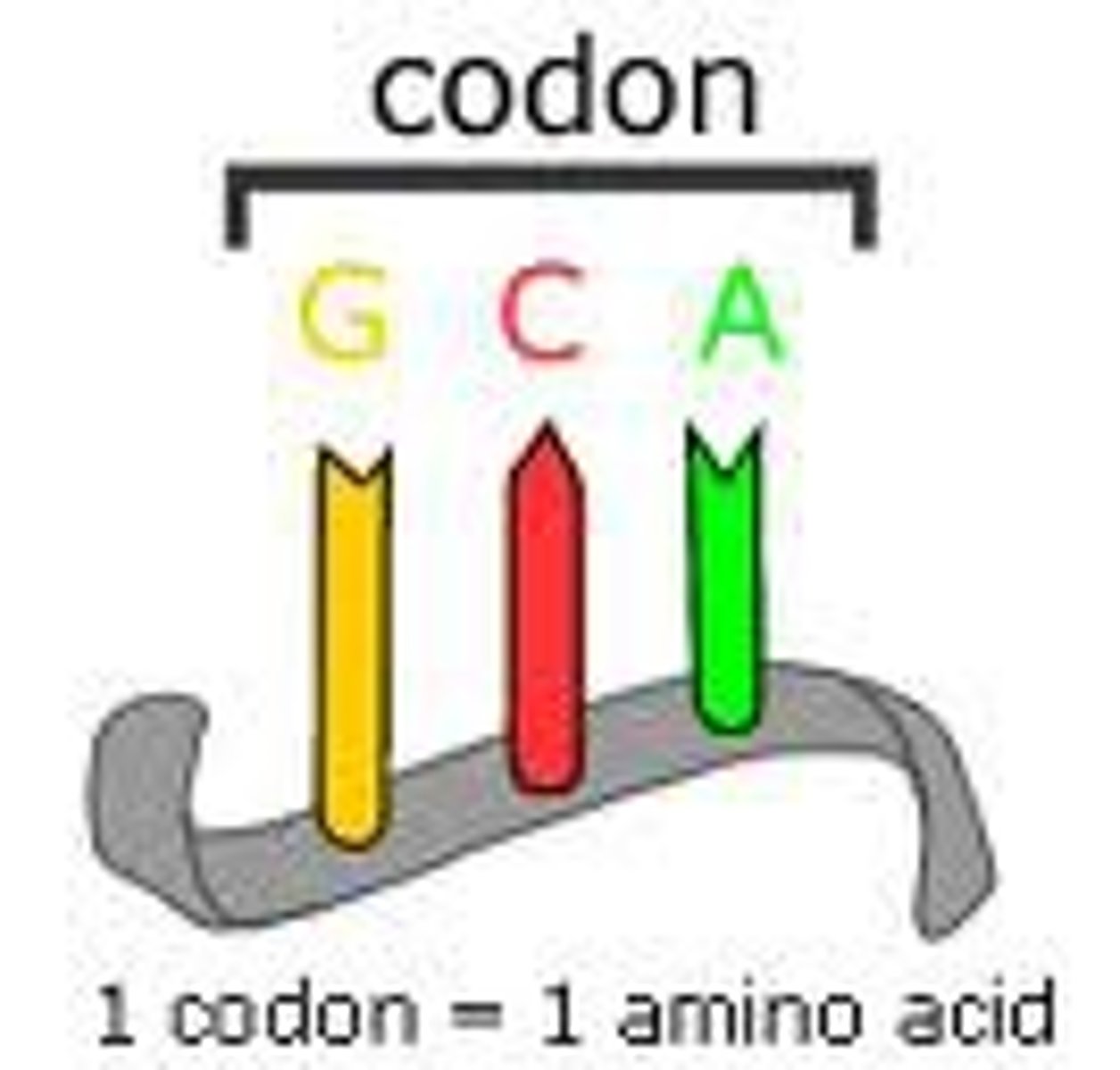
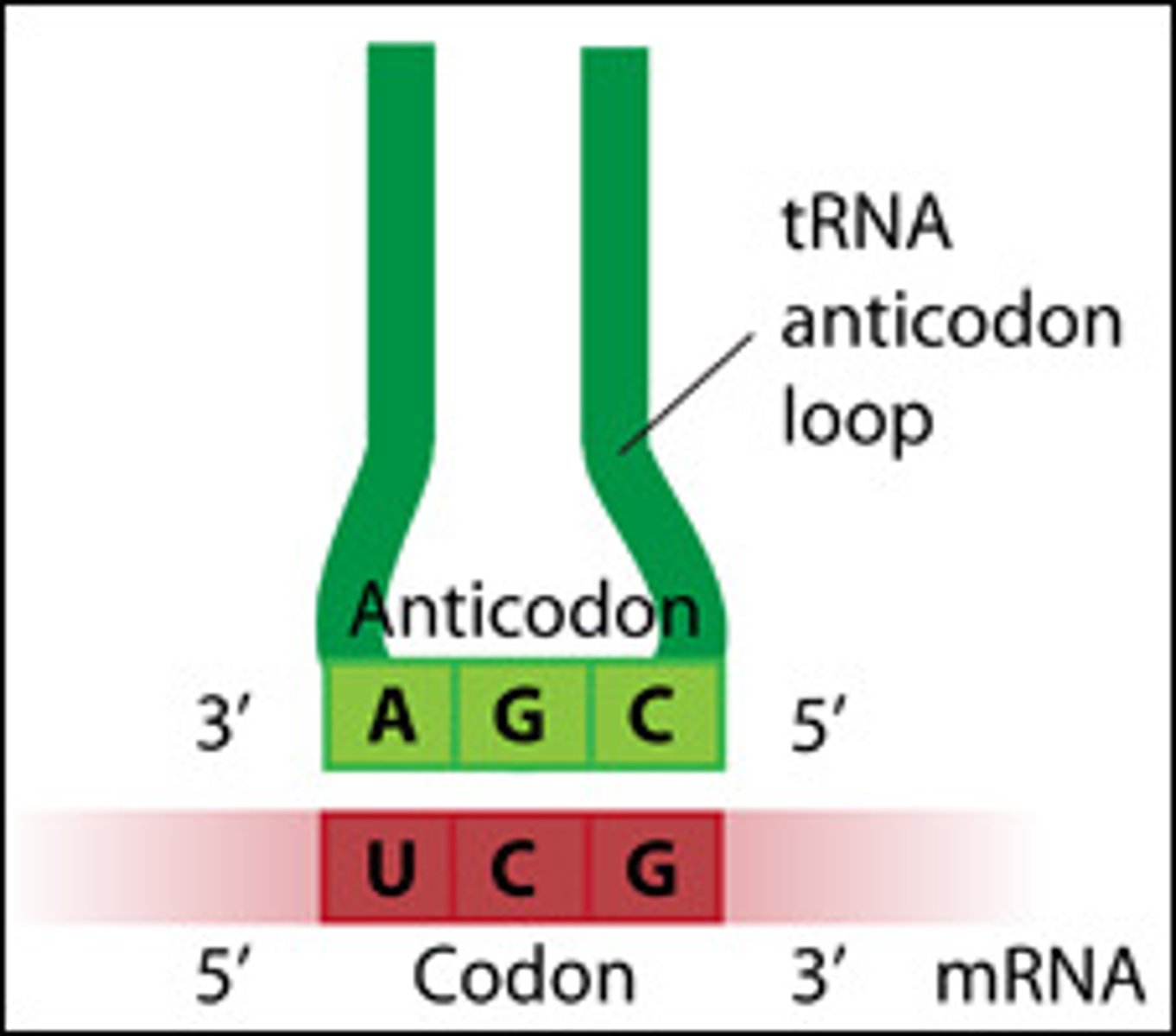
Codon
3 mRNA bases (occurs during protein synthesis)
Anticodon
Complementary tRNA triplet.
Point mutation
Substitution.

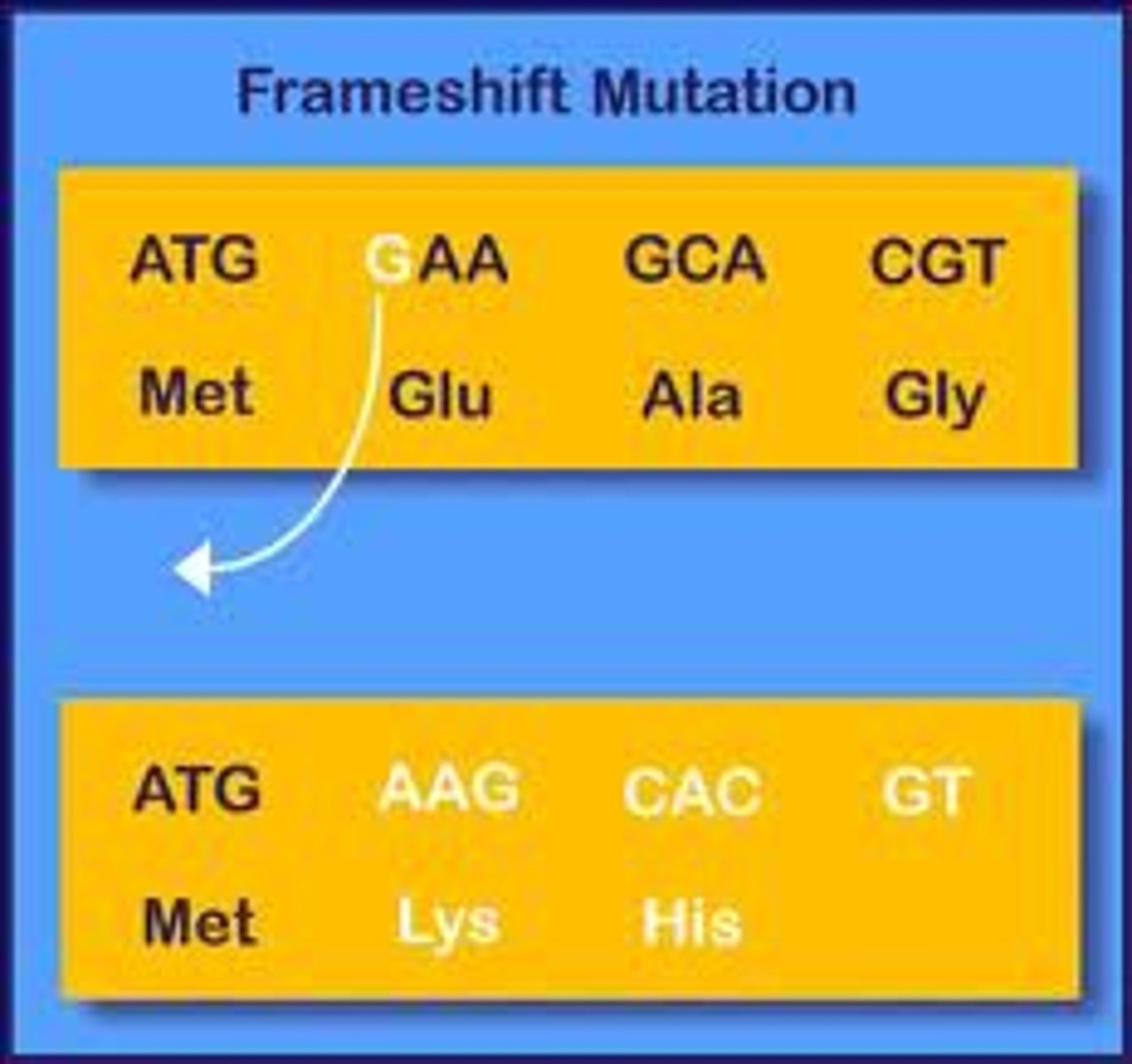
Frameshift
Insertion/deletion.
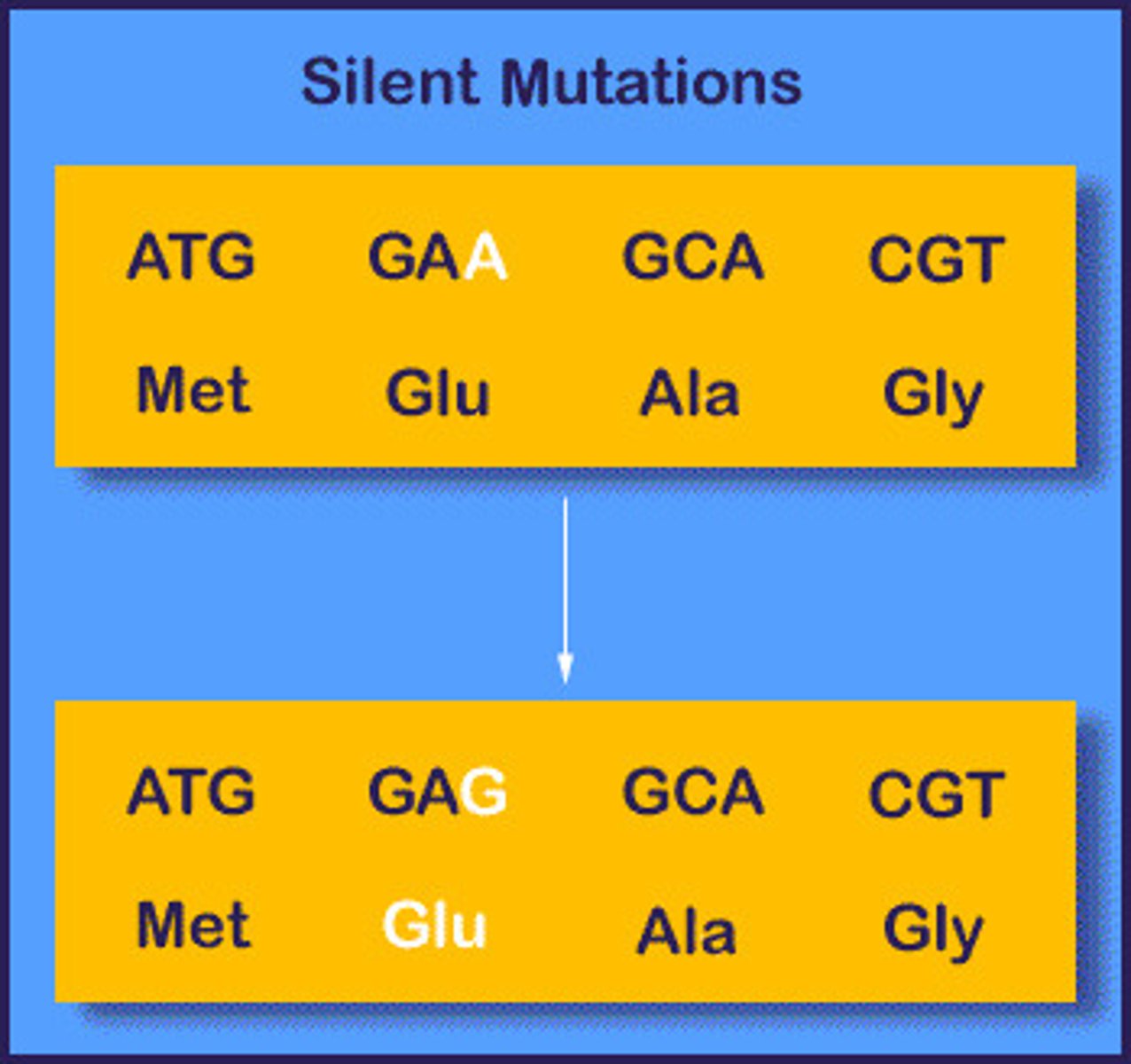
Silent/Neutral mutation
No effect.
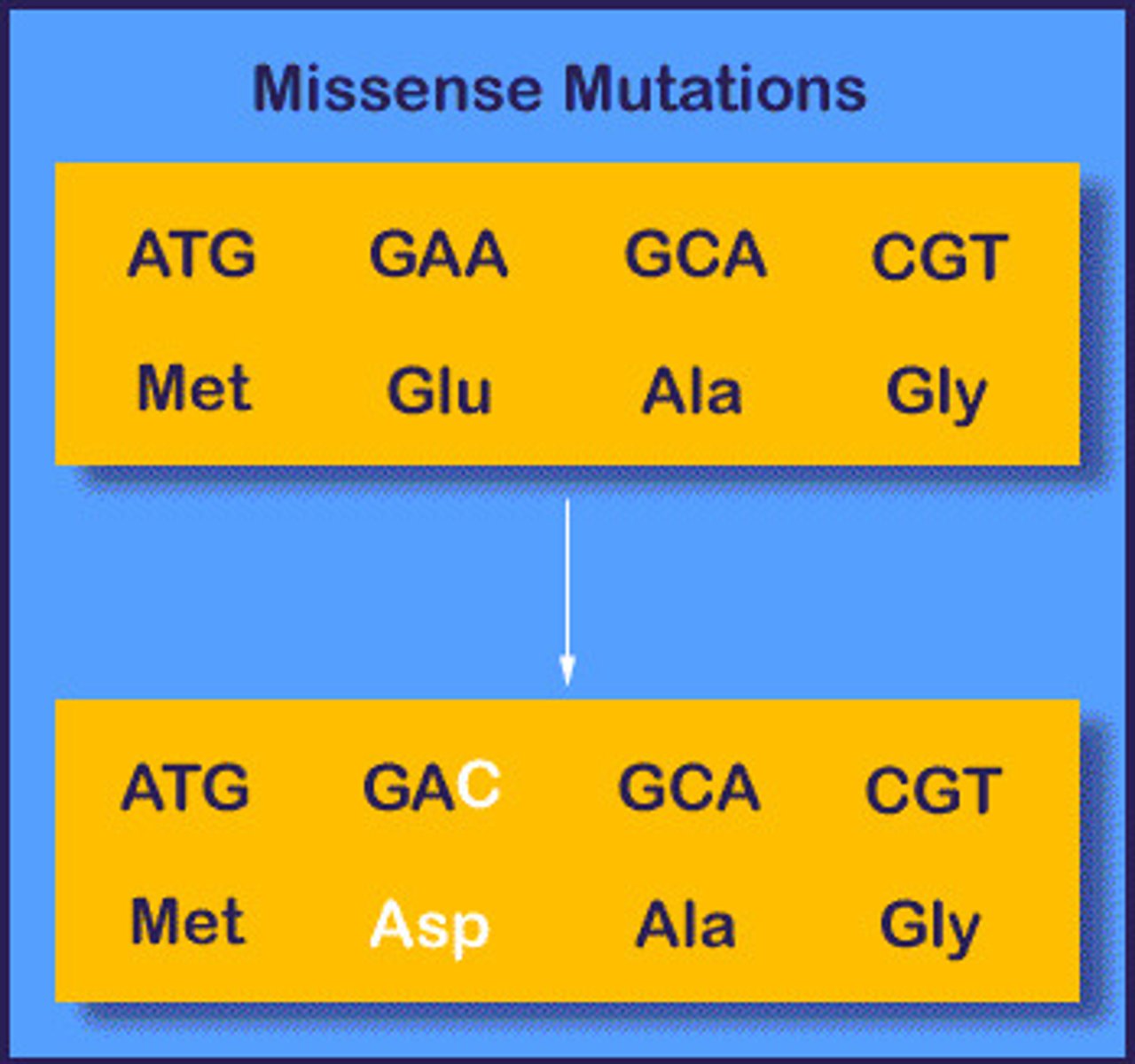
Missense mutation
Wrong amino acid.
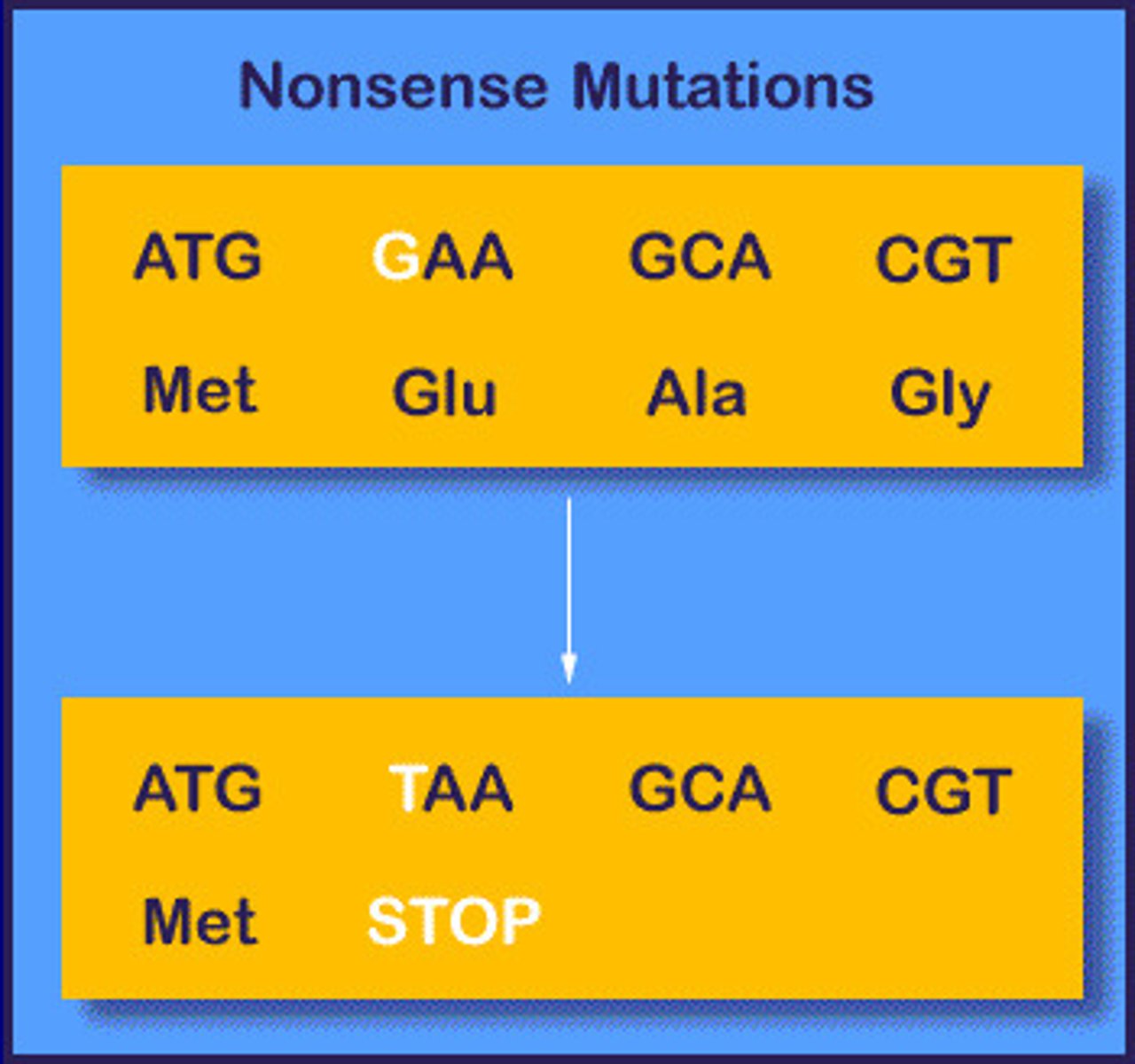
Nonsense mutation
Stops early.
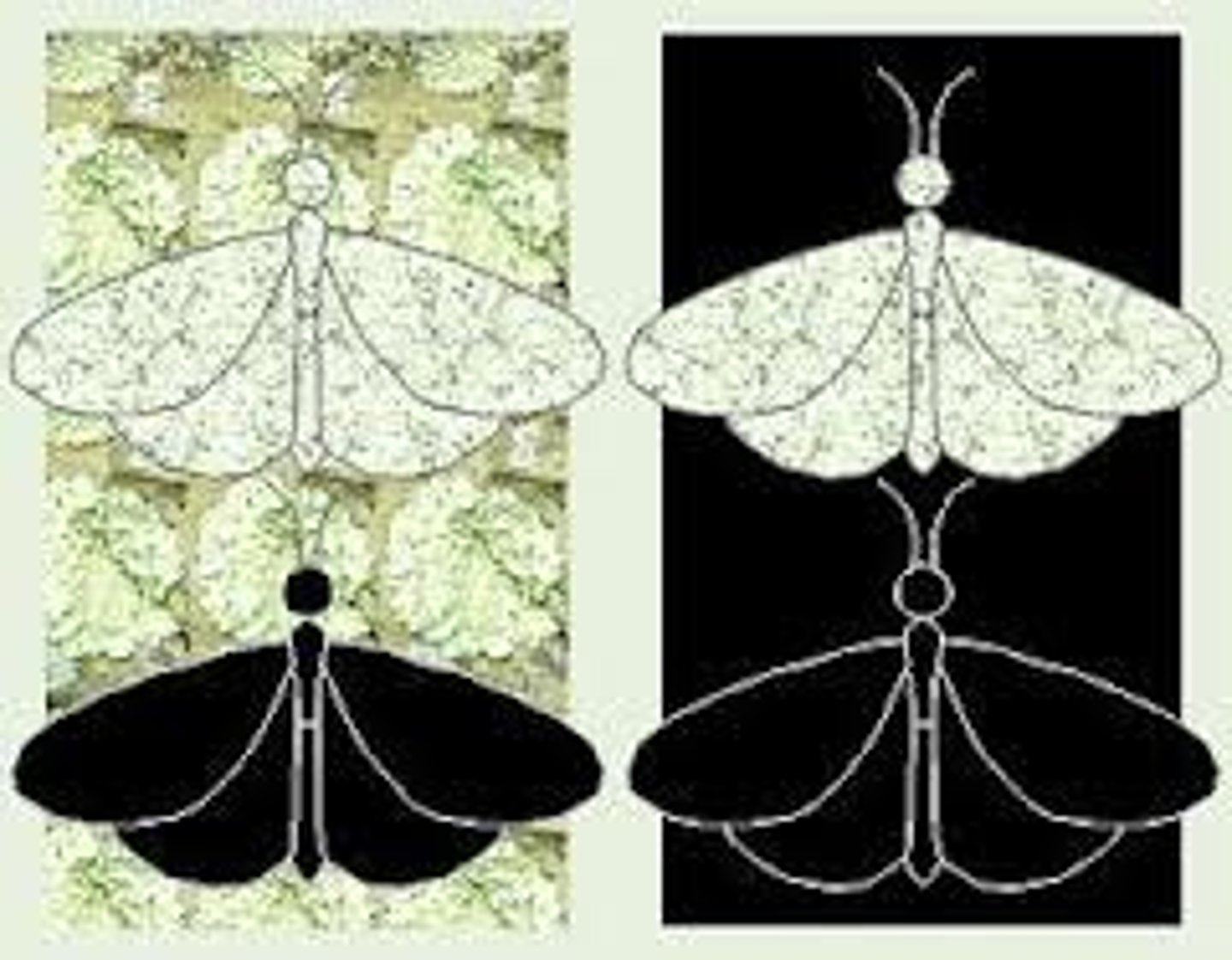
Natural Variation
Variations increase survival/reproduction → pass on traits.
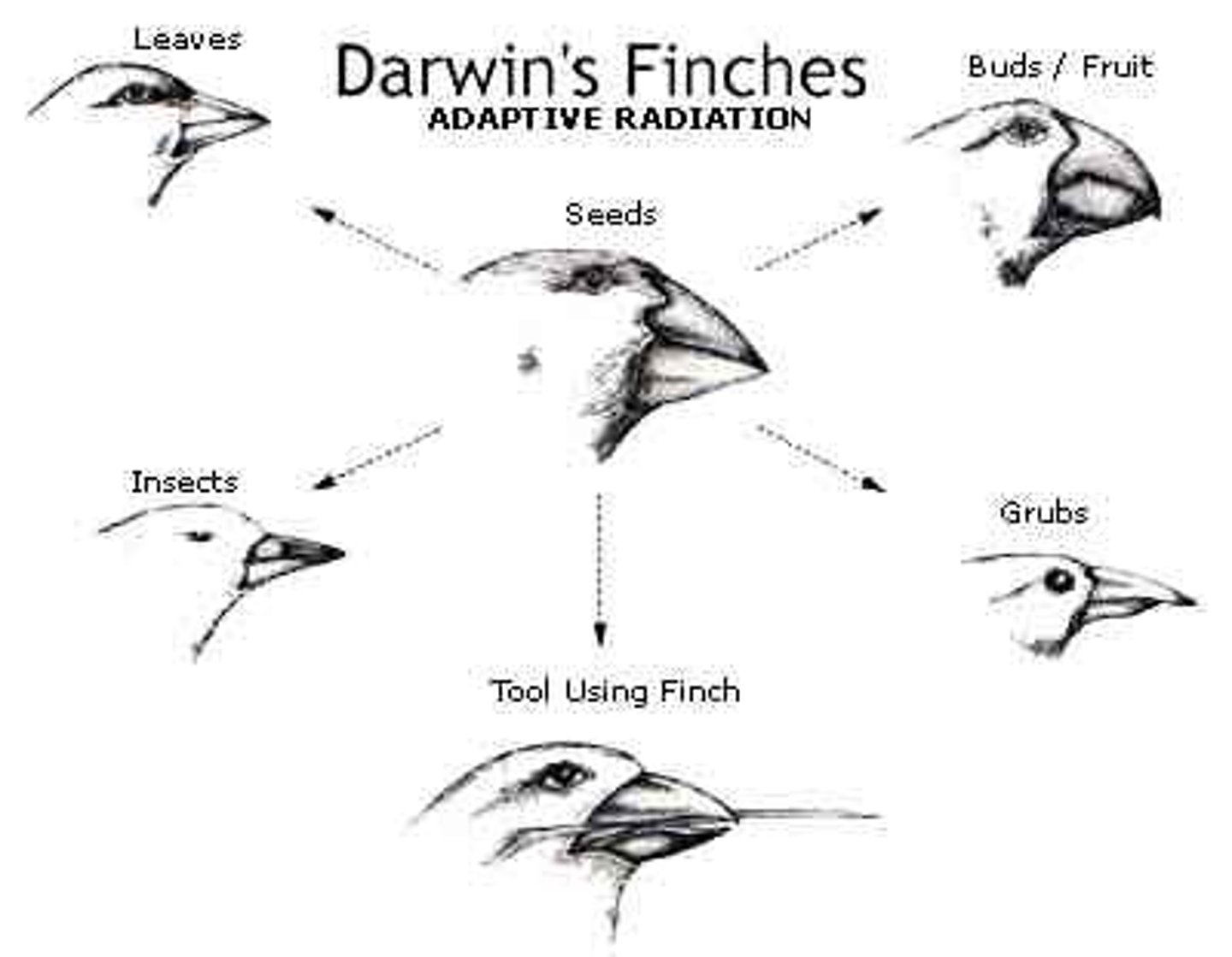
Adaptation
Trait that improves survival/reproduction.

Fitness
Reproductive success.

Natural Selection
Nature selects traits best fitted for environment
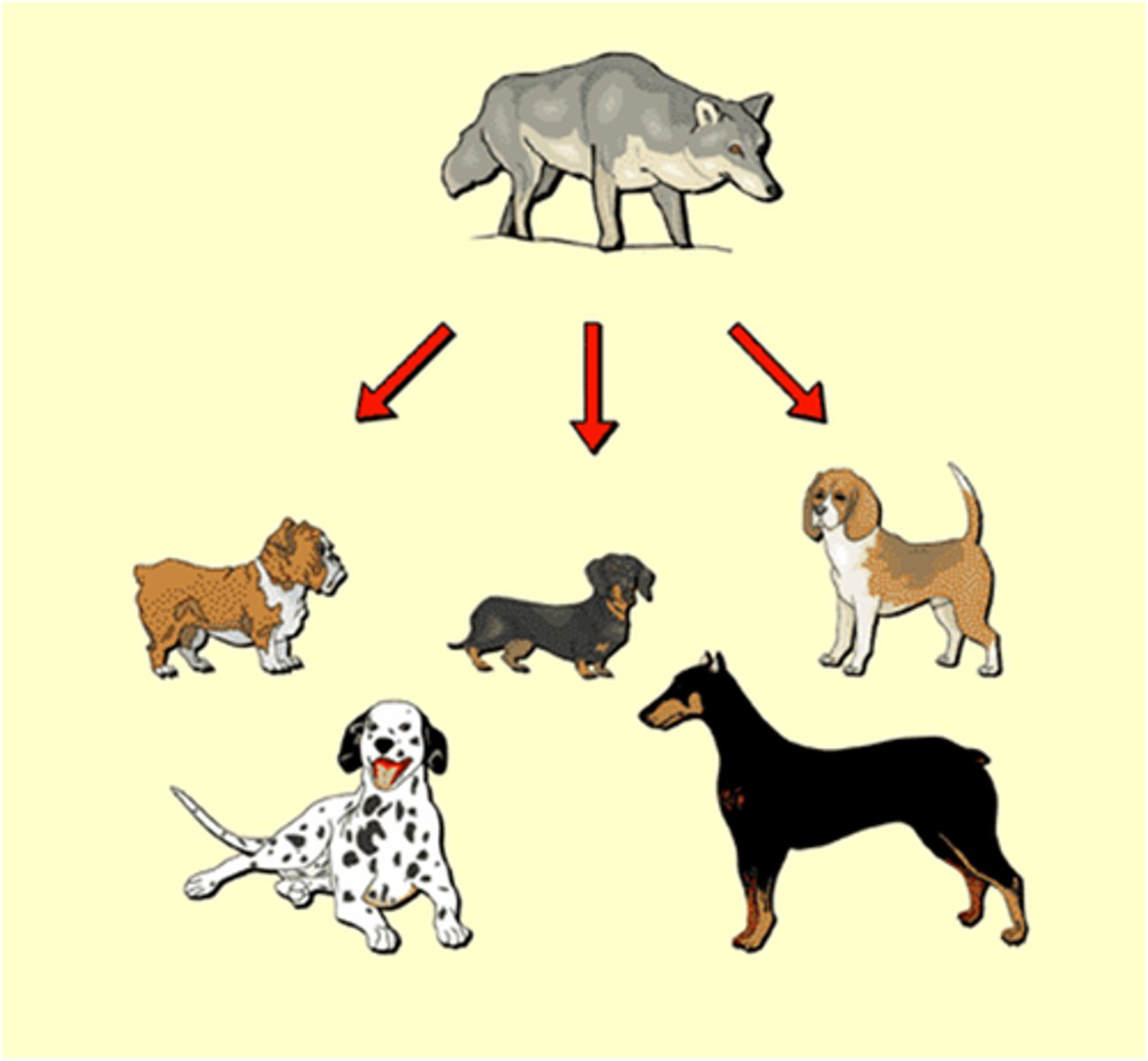
Artificial Selection
Humans select traits (e.g., dog breeding).
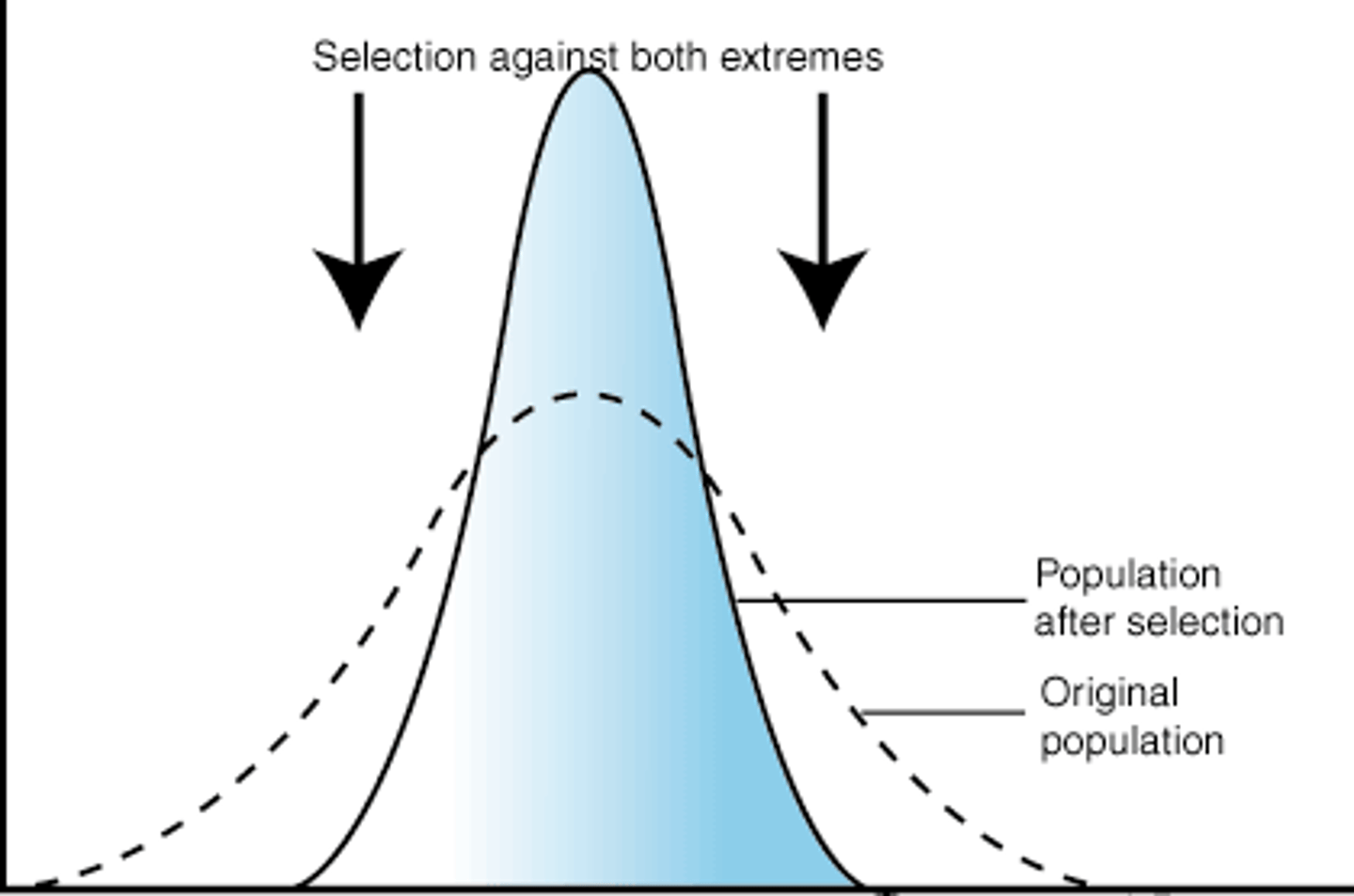
Stabilizing Selection
Average favored.
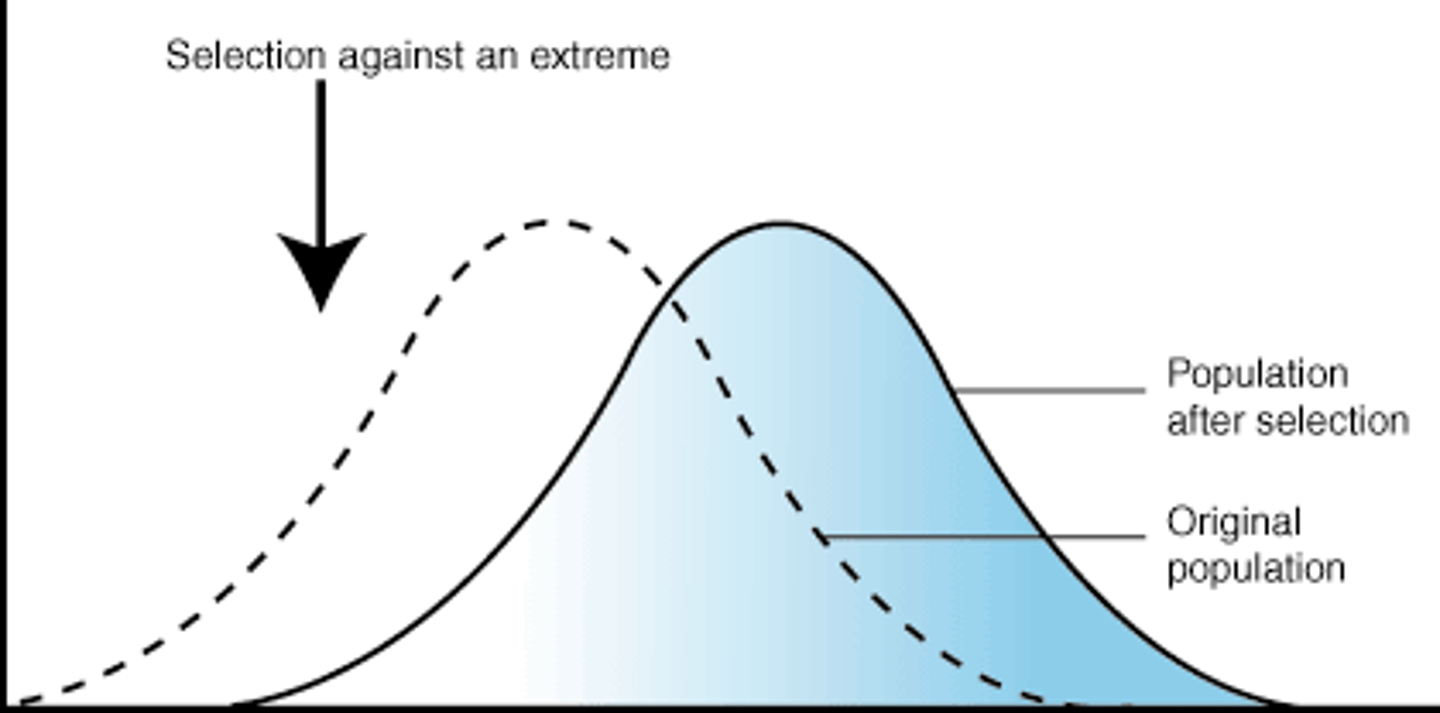
Directional Selection
One extreme favored.
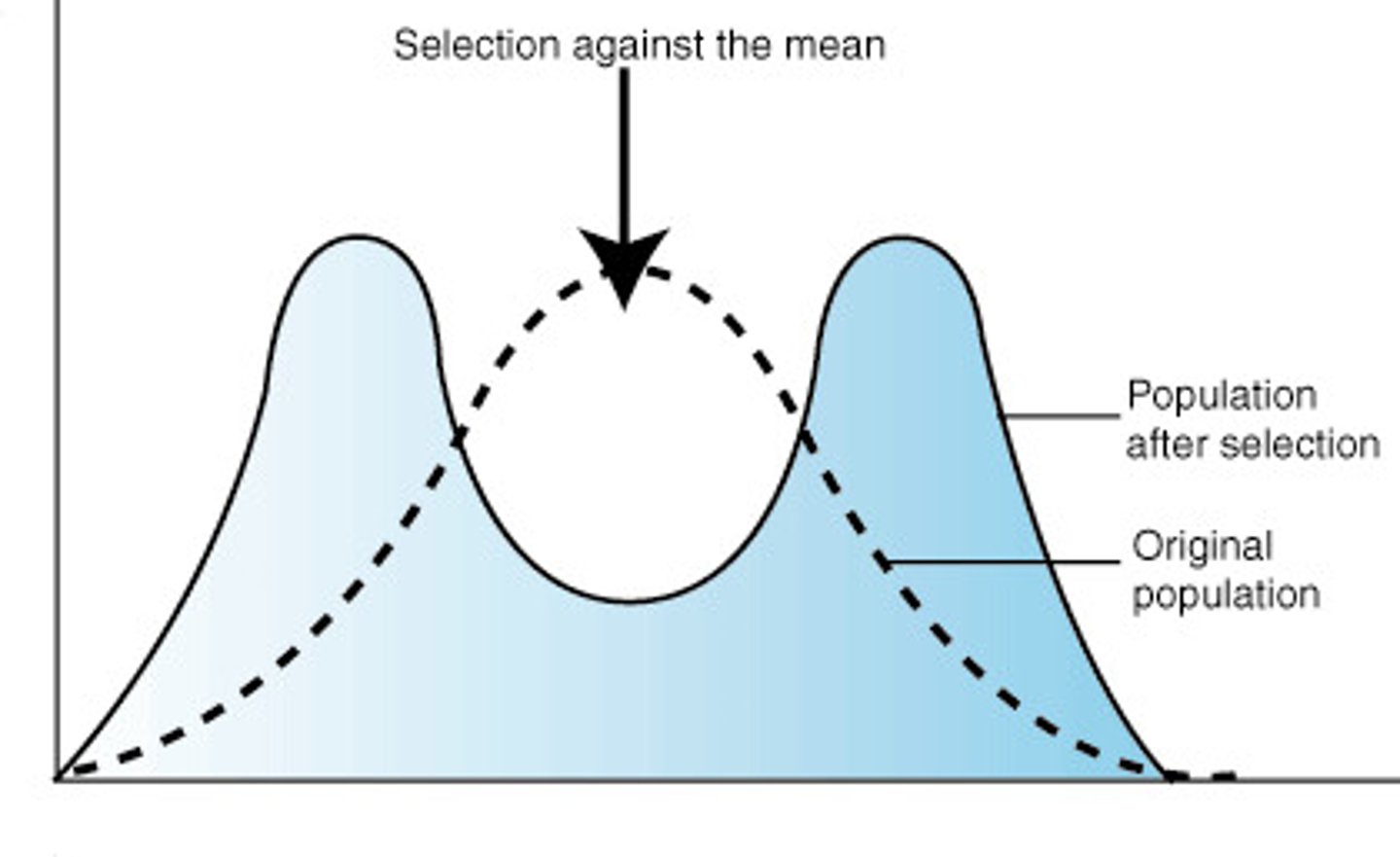
Disruptive Selection
Both extremes favored.
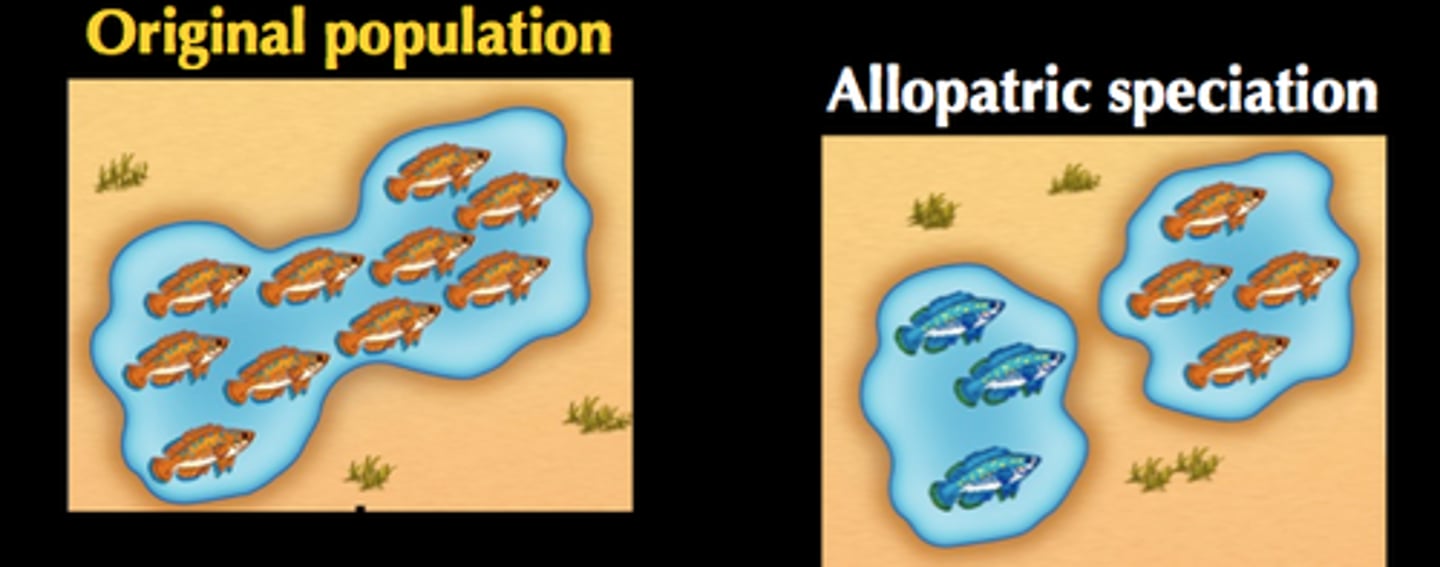
Speciation
New species form.
Genetic Drift
Random changes in small populations.

Bottleneck
Drastic reduction in population.
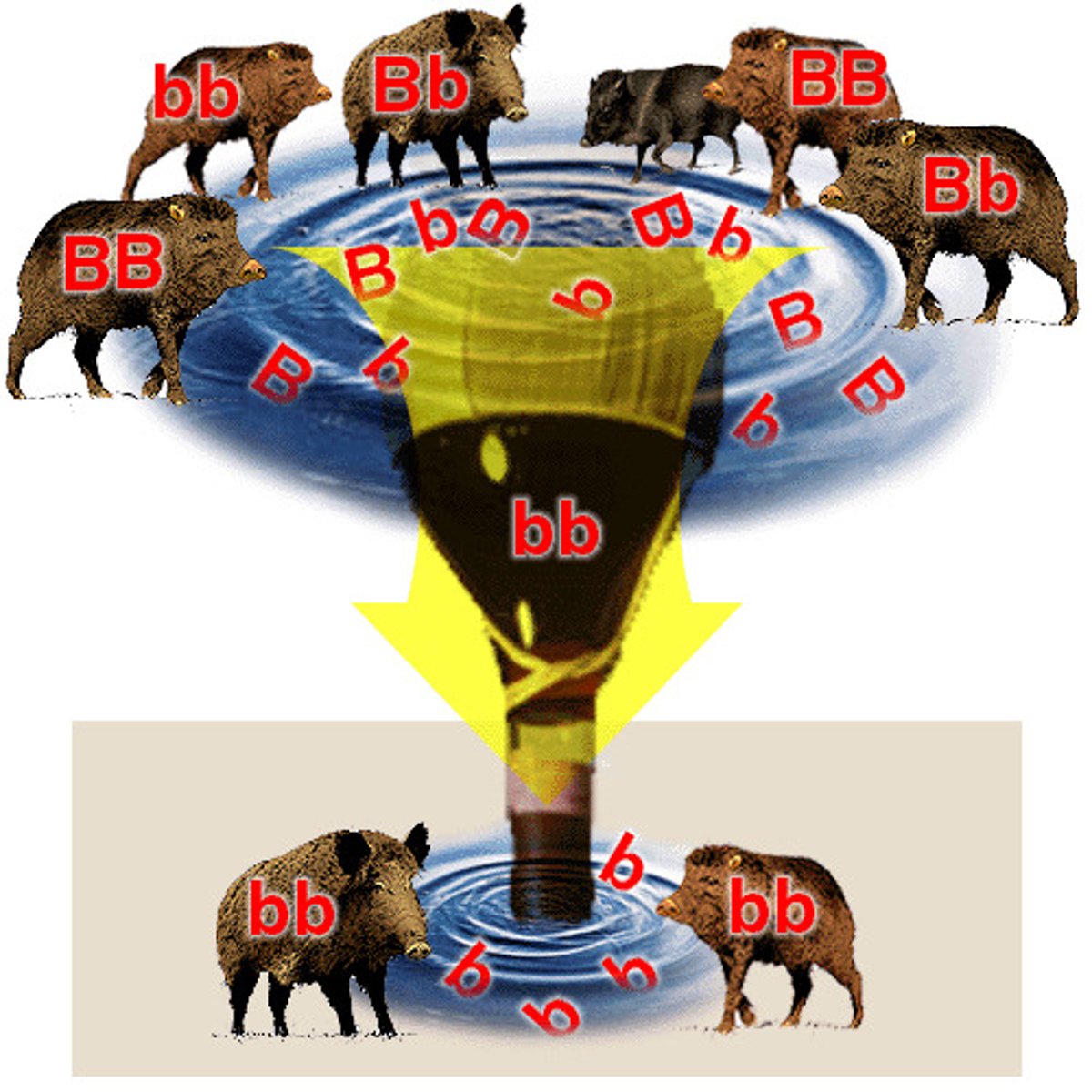
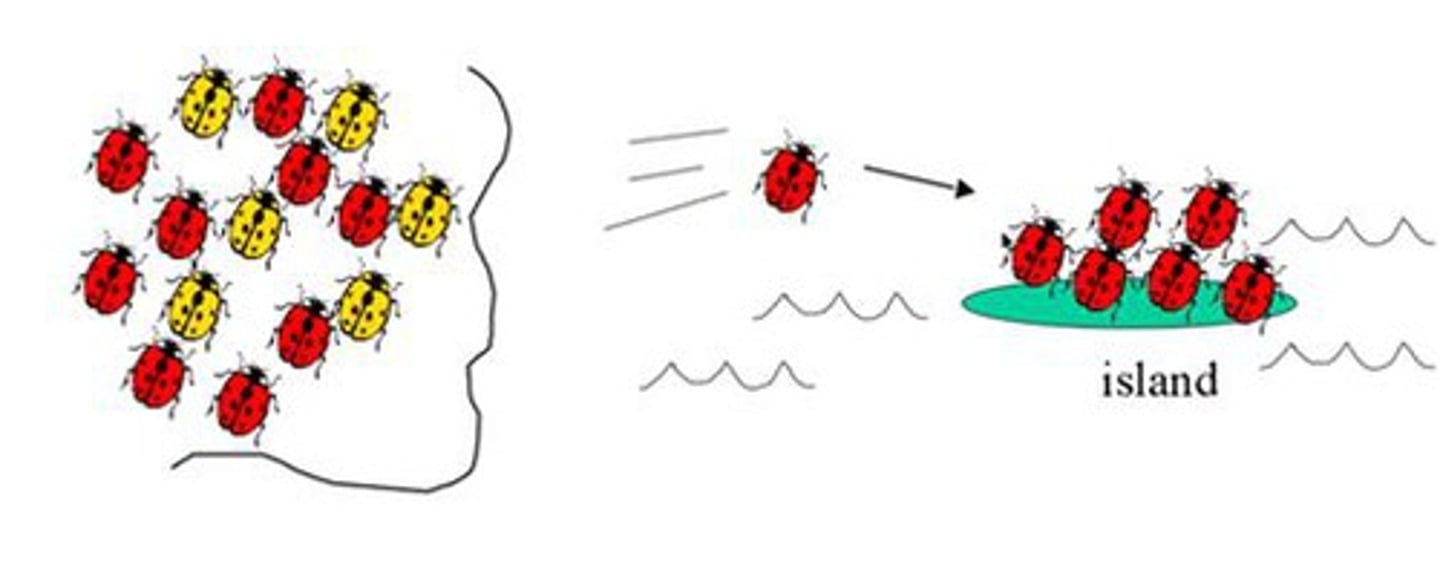
Founder Effect
New population from few individuals.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
No evolution occurs if: No mutation, large pop, no migration, random mating, no selection.

Coevolution
Species evolve together.

Convergent Evolution
Similar traits, different ancestors.
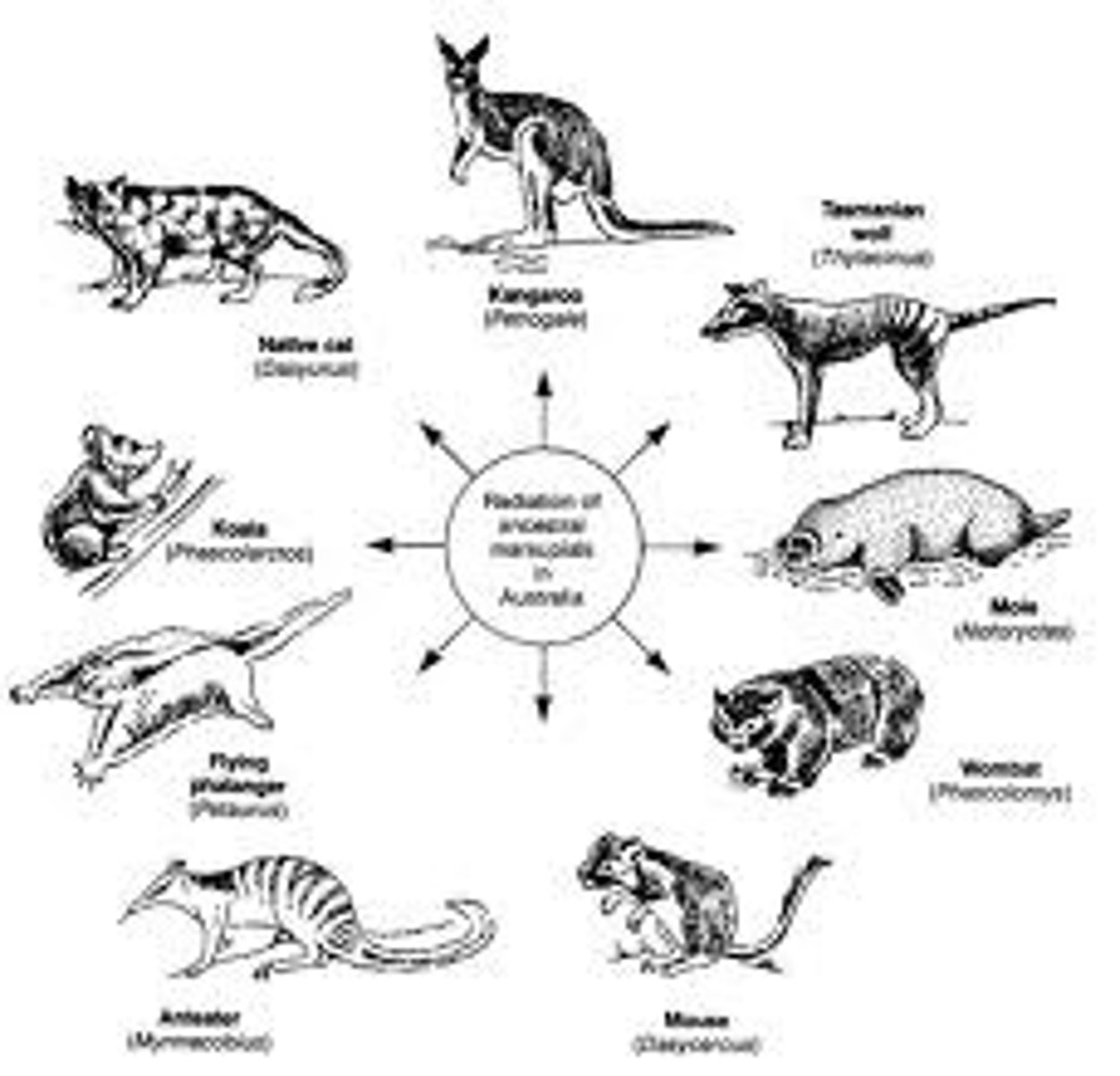
Divergent Evolution
Different traits, common ancestor.
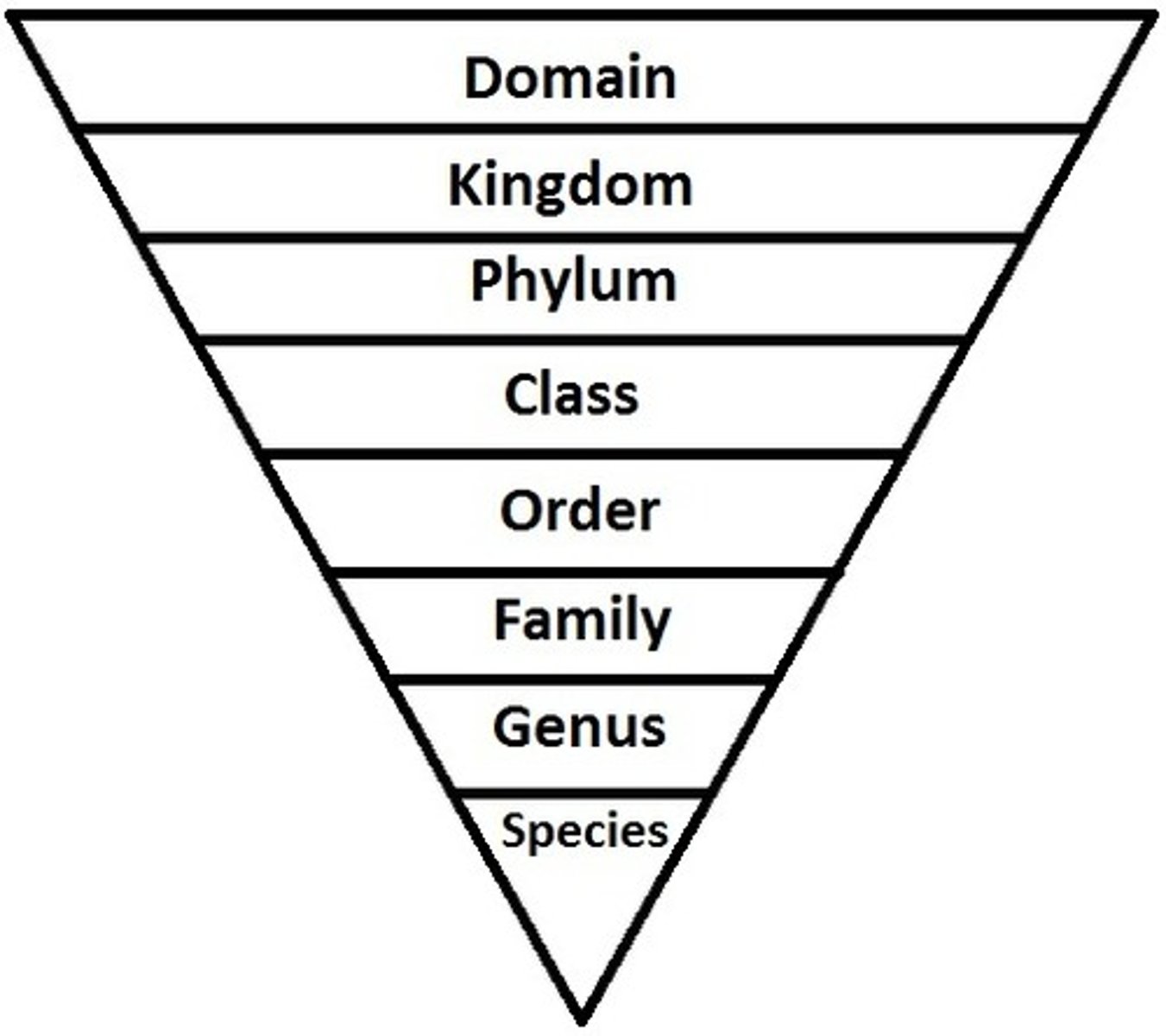
Taxonomic Order
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
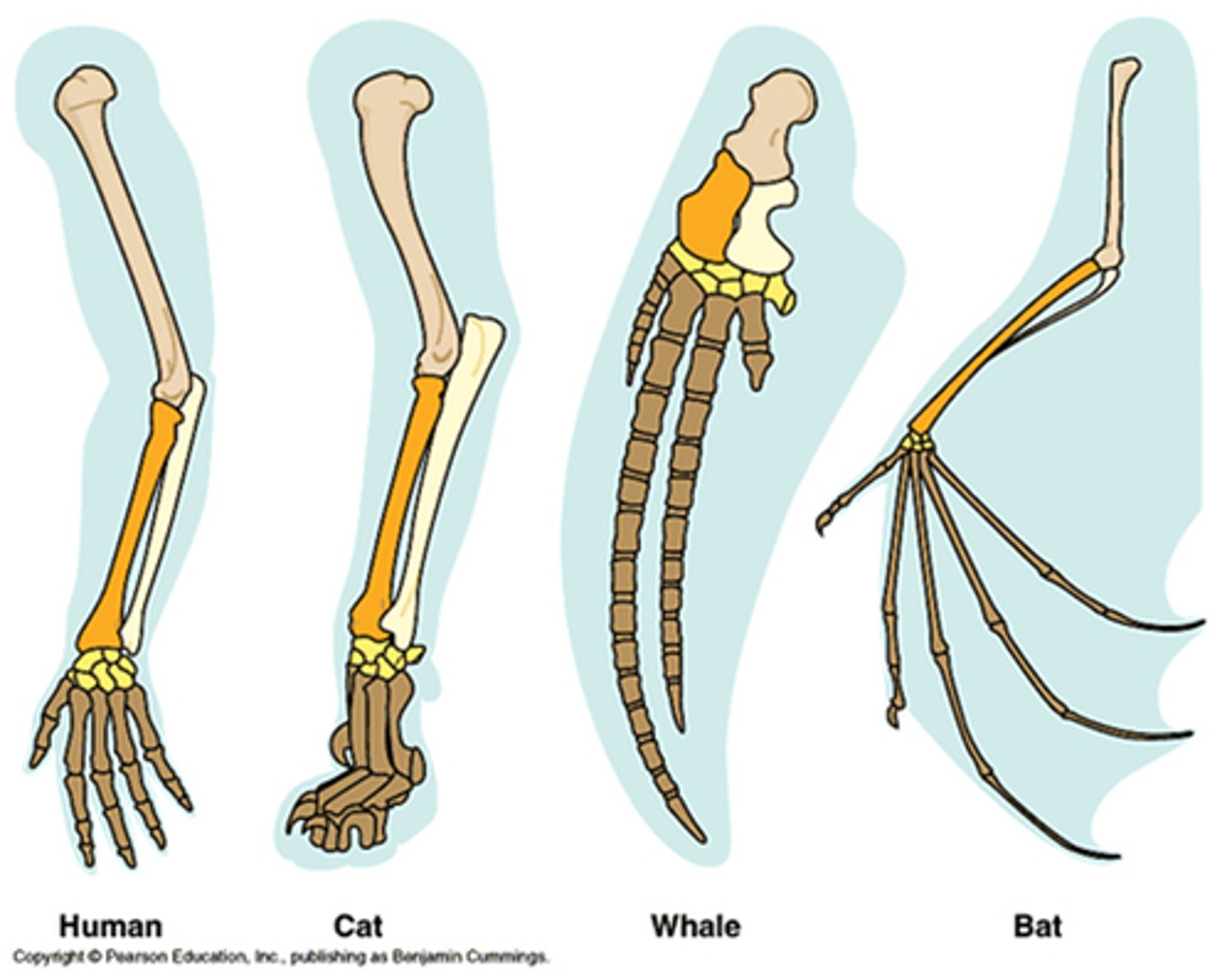
Homologous Structures
Same structure, different function (common ancestor).
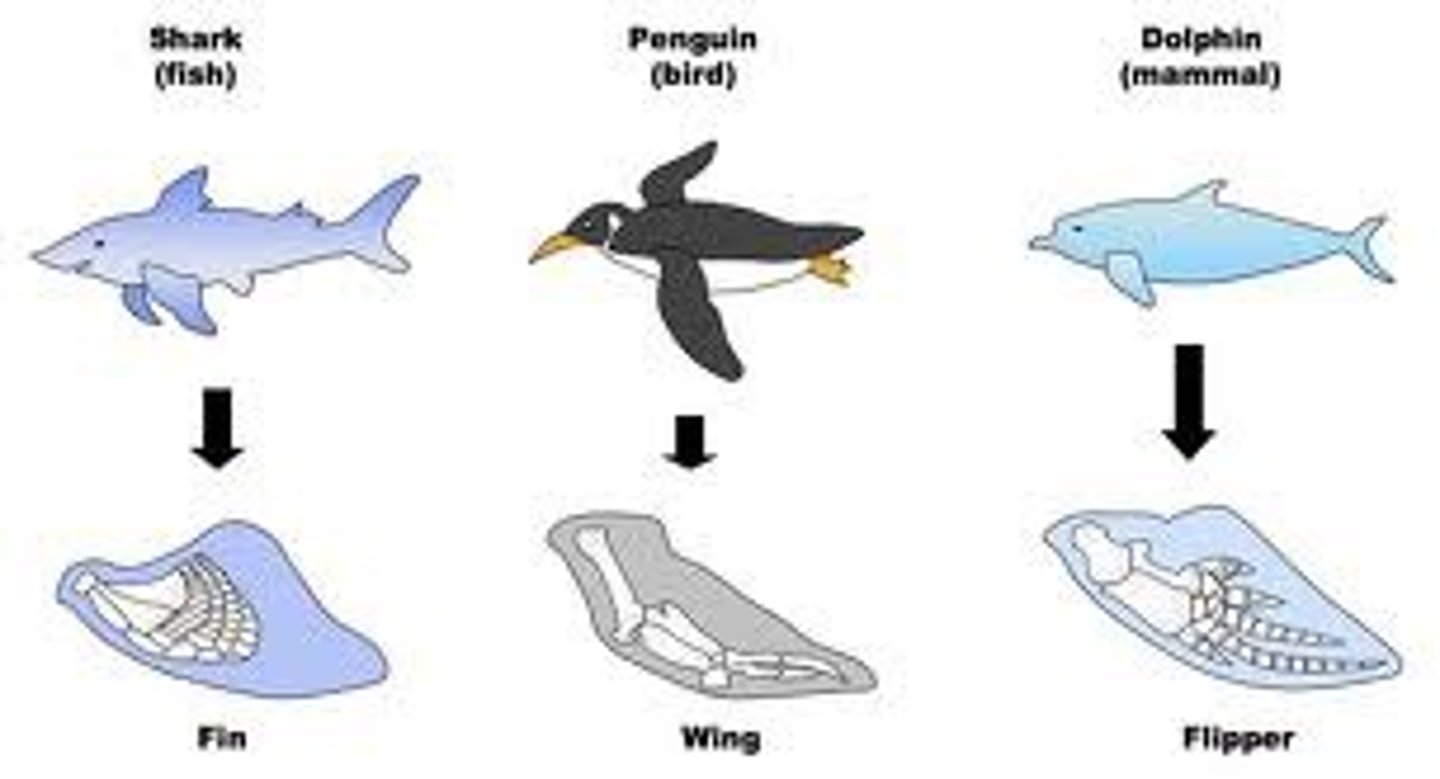
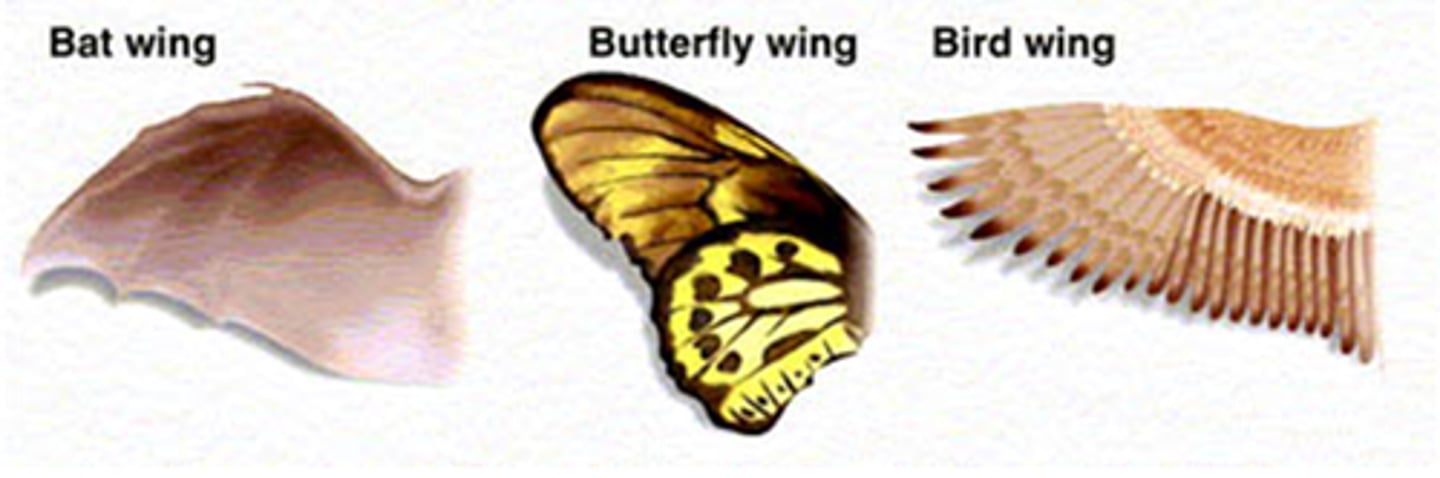
Analogous Structures
Different structure, same function (no common ancestor).
Mendel
Laws of inheritance; pea plant experiments.

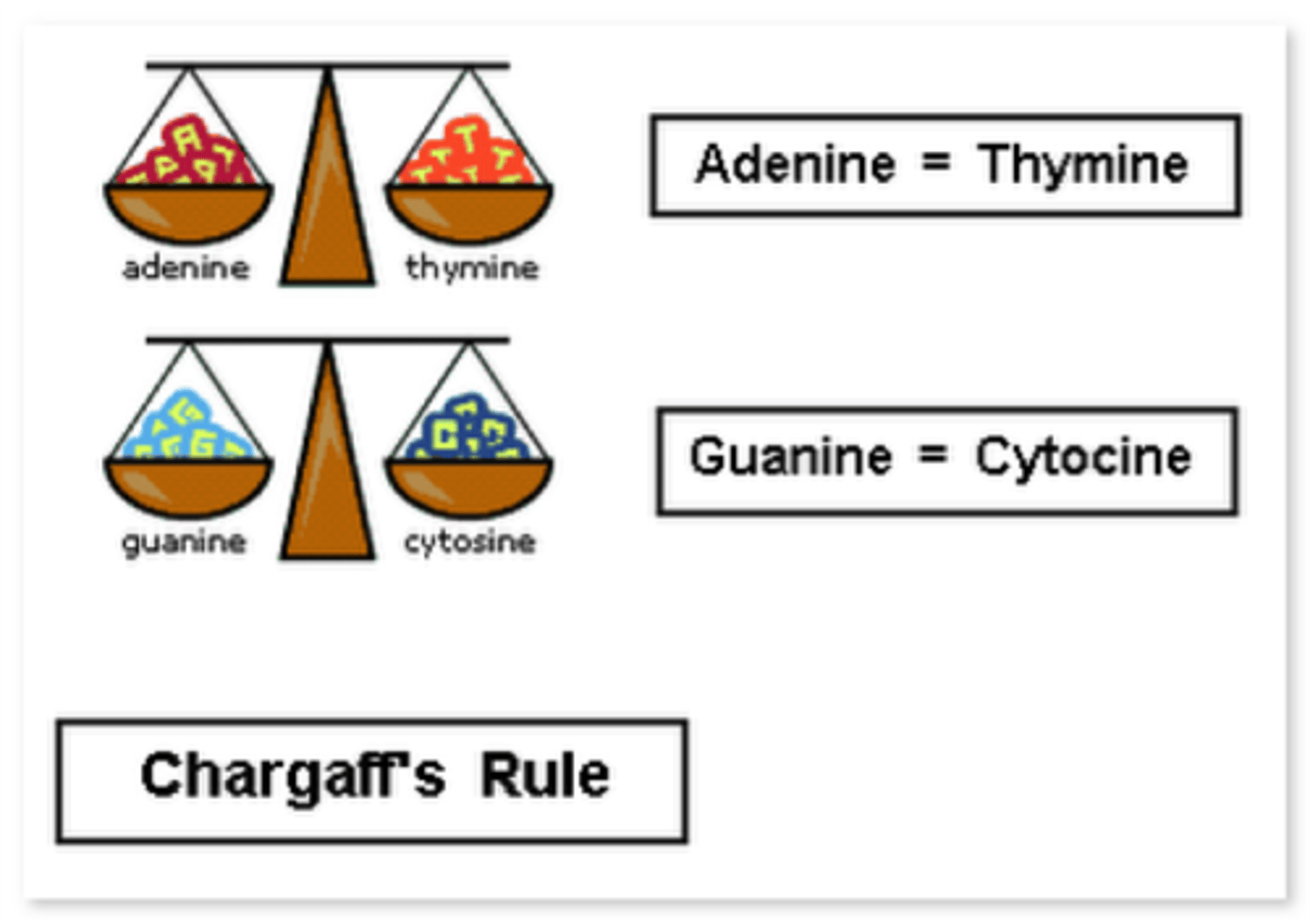
Chargaff
Base pairing rules (A=T, G=C).
Watson & Crick
Discovered DNA double helix structure.

Darwin
Natural selection theory; On the Origin of Species.

Wallace
Co-discovered natural selection with Darwin.

Lamarck
Inheritance of acquired traits (later disproven).

Hardy & Weinberg
Principle of genetic equilibrium in populations.
