Radiology Cancer Test 1
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
270 Terms
What is the most common malignant tumor of bone?
-Metastasis
80% of Metastasis is from?
-Prostate
-Breast
-Kidney
-Thyroid
-Lung
Most common way metastasis spreads?
-Hematogenous
Most common Metastasis in an adult female come from?
-Breast cancer
Most common Metastasis in an adult male come from?
-Prostate
Demographic of people with metastasis?
-50 to 75 years old
Symptoms of Metastasis
-Nocturnal bone pain
-Unexplained weight loss/cachexia
-Low grade fever
-Anemia
-Pathologic fracture with progressive deformity and soft tissue mass is typically a late finding
Common distribution of metastasis
-Axial skeleton is involved 80%
-Skull
-Proximal extremities
What is rare distribution in metastasis?
-Rare distal to elbow (referred to as acral metastasis)
General osseous features of Metastasis
-Medullary > cortical
-Pathologic fracture
-Soft tissue mass and periosteal reaction much less common than primary osseous neoplasms
Metastasis in skull features
-Non-uniform size/shape of lesions
Metastasis of Spine features
-Osteopenia (Blastic change)
-Compression fracture
-Pedicle destruction
Metastasis in chest wall features
-2nd most common cause of extrapleueral sign after rib fracture
Pattern of disease for Metastasis
-Osteolytic in about 75%
What metastasis can be both blastic and osteolytic?
-Lung
-Breast
-Prostate
-Colon
Osteolytic Metastasis imaging features
-Winking owl & blind owl sign
-Cookie bite sign
-Pancake vertebrae/vertebra plana
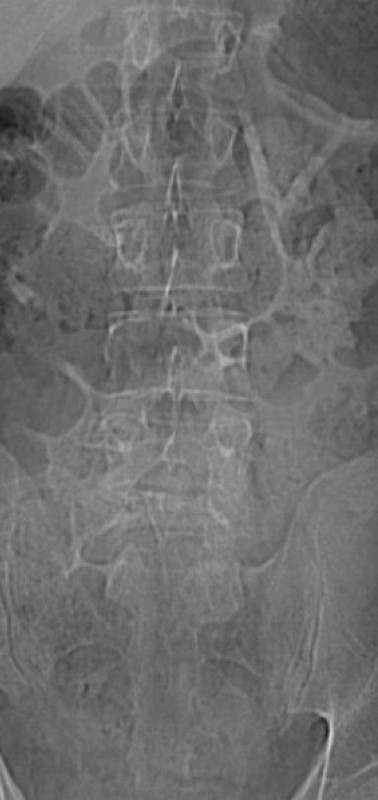
Winking/Blind Owl
-Metastatic disease affects posterior elements more often than its differentials. Pedicle involvement is suggestive of metastatic disease
-1 pedicle = winking
-2 pedicle = blind
Winking owl sign on x-ray
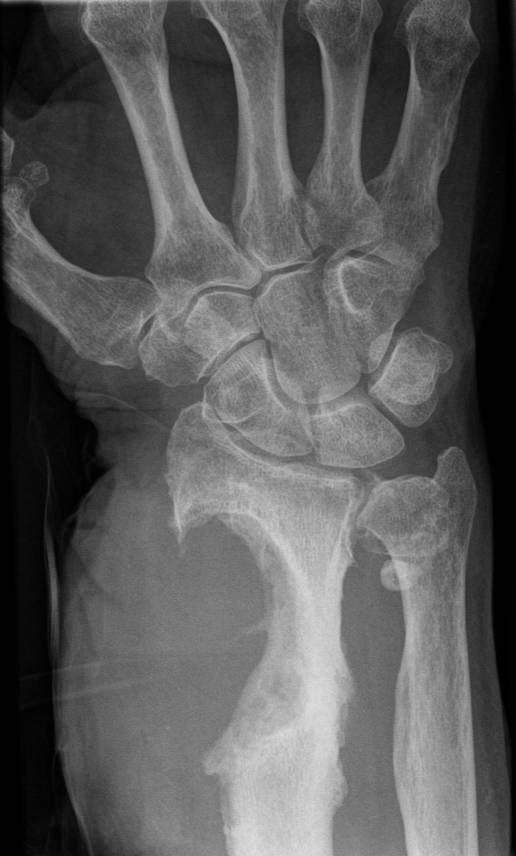
Cookie Bite Sign
-Focal eccentric lytic destruction involving the cortex
-Classically seen in lung cancer metastasis
Cookie Bite Sign on X-ray
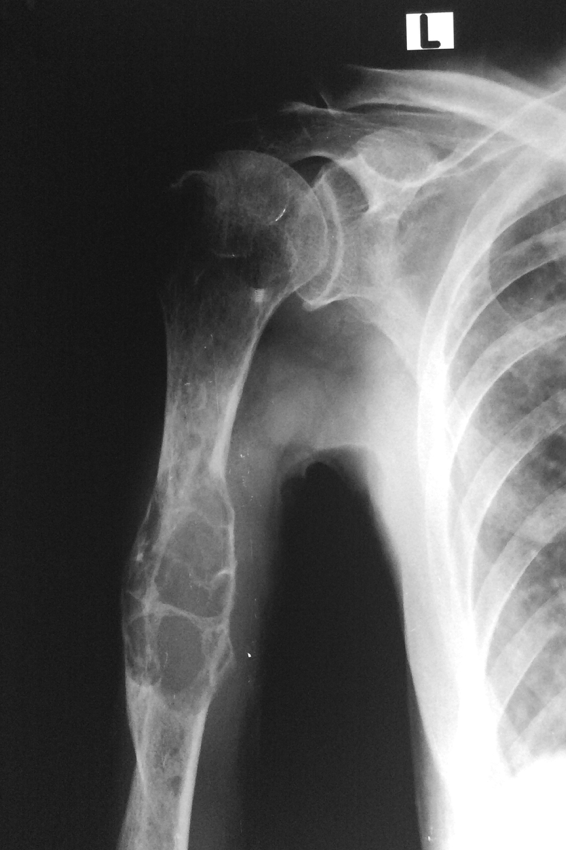
Blowout metastasis
-Rapidly expansile focal lytic lesion that may a soap bubbly appearance
RATS for blowout METs
-Renal
-Adrenal
-Thyroid
-Skin
Blowout METs on X-ray
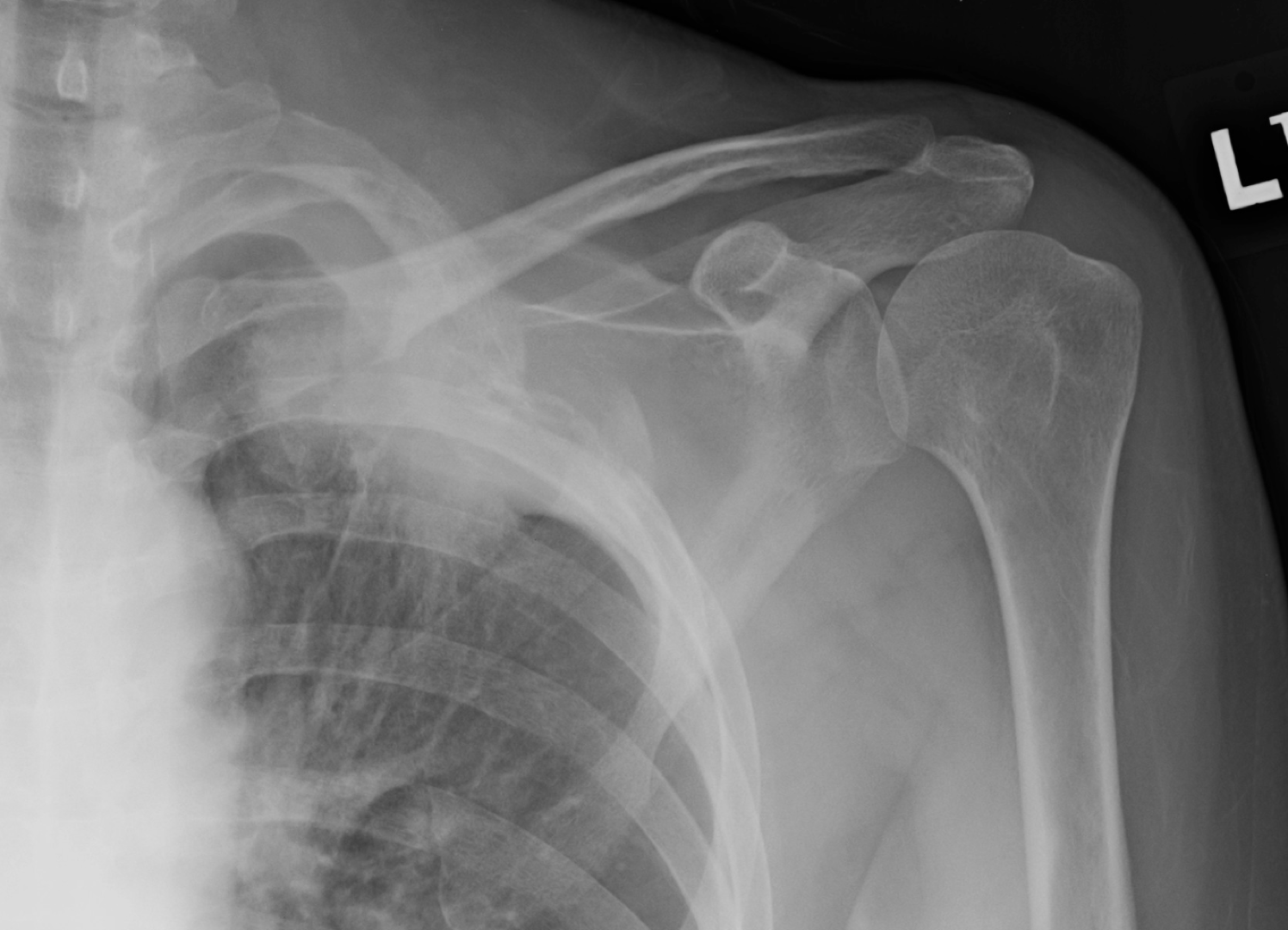
Vertebra Plana
-AKA pancake vertebra
-Relatively more common in multiple myeloma, but is much less common than metastasis
-Discs are maintained
Pancoast Tumor on X-ray
Osteoblastic Change in metastasis is more common or least common in comparison to Lytic change?
-Least common (15%)
Osteoblastic Pattern of disease Mets from?
-Brain
-Breast
-Bronchial
-Bowel
-Bladder
-Lymphoma
-Prostate
The skull vault is almost always?
-A lytic pattern
Osteoblastic METs On imaging
-Ivory vertebrae
-Filling in of Kohler’s Tear Drop
Ivory vertebra present could be? (Blastic pattern of disease)
-Idiopathic
-Hodgkins Lymphoma
-Osteoblastic Metastasis
-Paget’s Disease
Hodgkins Lymphoma with Ivory vertebra
-Ages 10 to 80
-May have anterior vertebral body scalloping due to enlarged paraspinal lymph nodes/masses causing pressure erosions
Ivory Vertebra w/ anterior scalloping on X-ray

Osteoblastic Metastasis w/ Ivory Vertebra
-Over 50 years old
-No anterior scalloping
-No osseous enlargement
Osteoblastic METs in spine on X-ray
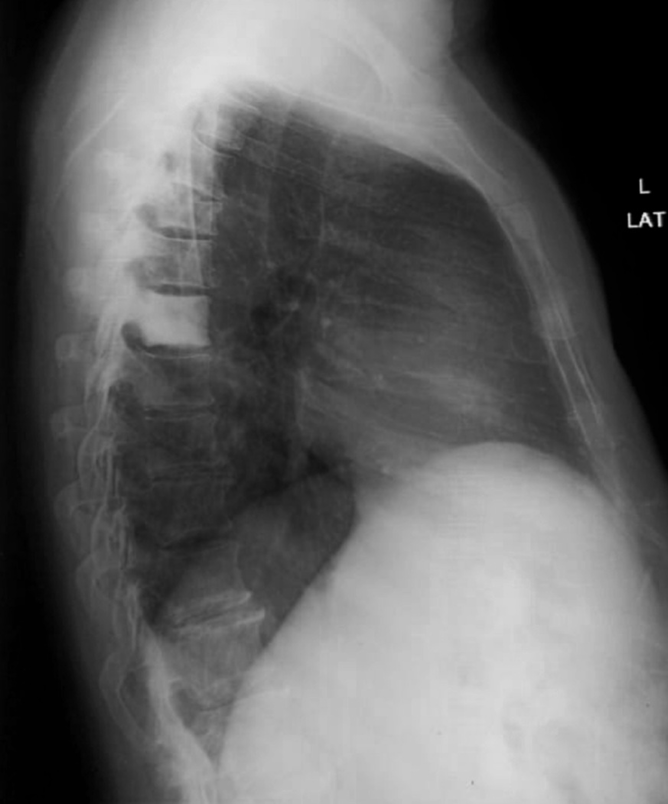
Ivory vertebra w/ paget’s disease
-over 50 years old
-Triad of: Osseous enlargement, Cortical thickening, Trabecular accentuation
Paget’s disease in spine on X-ray
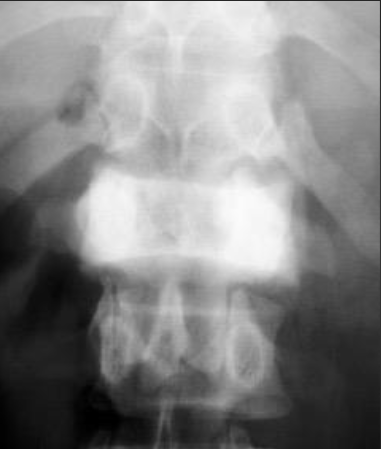
Filling in of Kohler’s teardrop indicates?
-Hodgkins, Osteoblastic METS, or Paget’s
How much bone destruction is necessary for visualization on X-ray
-30 to 50 %
Neuroblastoma
-AKA sympatheticoblastoma
-2nd most common abdominal tumor after nephroblastoma
-Metastasizes mostly in adrenal gland
-Most commonly occurs in children under 2.5 years of age
Neuroblatoma Metastasis on Imaging
-May see abdominal » mediastinal > paraspinal soft tissue mass
-60 to 85% show stippled calcification within soft tissue mass
Osseous Metastasis
-Multifocal, fairly symmetric osseous lesions that are usually non-specific, but may show lucent metaphyseal bands paralleling the physis
What are the 4 most common malignancies?
-Multiple myeloma
-Osteosarcoma
-Chondrosarcoma
-Ewing’s Sarcoma
What are the most common malginancies in children?
-Osteosarcoma
-Ewing’s Sarcoma
-Lymphoma
What are the most common malignancies in adults?
-Multiple Myeloma/Plasmacytoma
-Chondrosarcoma
-Fibrosarcoma
-Lymphoma
-Chordoma
Multiple Myeloma
-Most common primary malignancy of bone
-Plasma cell infiltration of bone
-Occurs in 50 to 70 years of age
-More common in Males
What is the most common overall malignancy
-Metastasis
Diagnostic Criteria of Multiple Myeloma
-10% abnormal, atypical, or immature plasma cells in bone marrow PLUS one of the following:
-Serum M-Protein Spike
-Urine M-protein spike or Bence Jones proteinuria
-Osteolytic bone lesions
-Osteoporosis
-Biopsy proven plasmacytoma
Clinical Presentation of Multiple Myeloma
-Bone pain (Intermittent → constant and better at night)
-Fatigue/weakness
-Fever
-Weight loss
-Bleeding
-Pathologic fractures common
Multiple Myeloma Present with what on labs?
-Reversal of A:G ratio (globulin:Albumin)
-Myeloma spike (M spike) on electrophoresis
Bence Jones’ Proteinuria
-light chain immunoglobin that clump together and damage the glomeruli as they pass through, leading to progressive ‘myeloma kidney’ and contribuiting to amyloidosis
Multiple Myeloma Osseous involvement which is the most common?
-Vertebrae 69%
-Ribs 59%
-Skull 40%
-Pelvis 40%
-similar distribution as METS
Multiple Myeloma Imaging Features
-Classically lytic and cold on bone scan due to plasma cells releasing large amounts of osteoclasts activating factor
-Initial presentation is severe osteopenia but progress to lytic destruction
Multiple Myeloma in spine on X-ray
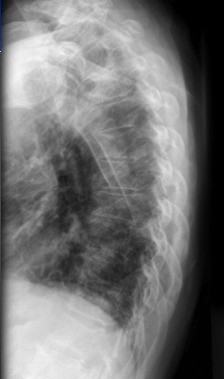
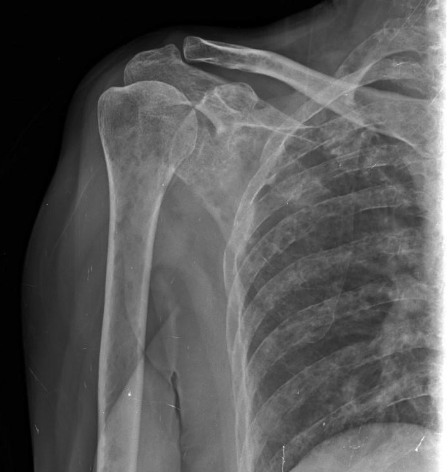
Punched out lesions & motheaten pattern =
-Multiple Myeloma
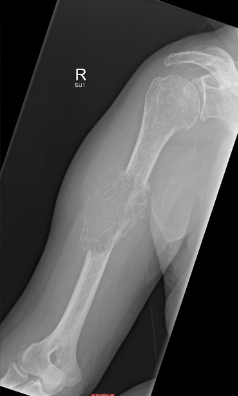
Multiple Myeloma in proximal humerus on X-ray
Raindrop Skull
-Relatively uniform and well-defined foci of lytic destruction
-Indicates multiple myeloma
Raindrop skull on X-ray
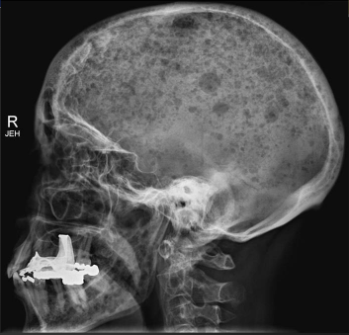
Metastasis in skull on X-ray
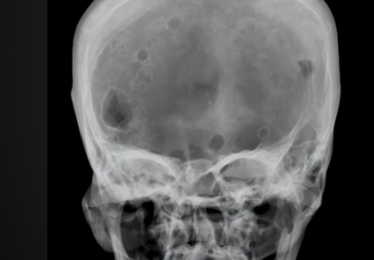
If you see diffuse osteoblastic change where should multiple myeloma be on DDX
-very low
If you see lytic destruction what are your differentials?
-Multiple Myeloma, Osteolytic metastasis, lymphoma (MML)
Plasmacytoma
-Solitary form of multiple myeloma (70% will develop multiple myeloma)
-Slightly younger presentation than multiple myeloma (40 to 75 years old)
Clinical Presentation of Plasmacytoma
-May be silent
-Symptoms related to region of involvement
Imaging Feature of Plasmacytoma
-Soap-bubbly, expansile, lytic destruction
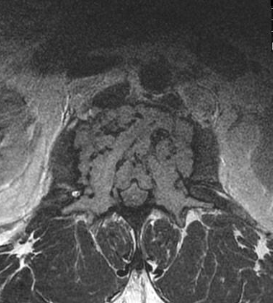
-Mini-brain appearance in vertebral body on advanced imaging
Plasmacytoma on X-ray
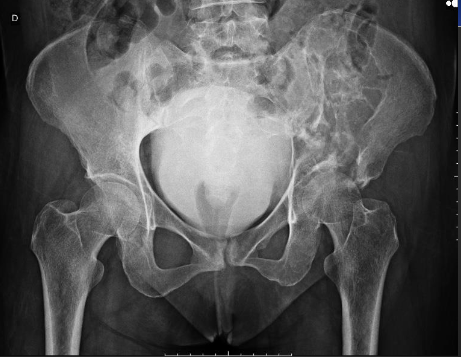
Plamacytoma Pelvic view on X-ray
Plasmacytoma in humerus on X-ray
“mini Brain” on imaging
Osteosarcoma
-2nd most common primary osseous malignancy
-Most common primary osseous malignancy under 25 years old
-Bone producing tumor with pathogenesis from osteoprogenitor cells
What is the most common primary osseous malignancy under 25 years old?
-Osteosarcoma
Clinical Presentation of Osteosarcoma
-Typically pain and swelling around a joint
-80 to 90 % abut a physis
-Most common in extremities
Pattern of disease for Osteosarcoma
-Blastic (50%)
-Lytic (25%)
-Mixed (25%)
What is the 2nd most common primary osseous lesion to metastasize to bone
-Osteosarcoma
Classic Presentation of Osteosarcoma on X-ray
-Blastic metaphyseal lesion, abutting a physis with “cumulus cloud” ossified soft tissue mass, spiculate/sunburst or Codman’s triangle periosteal reaction in a child
Osteosarcoma on X-ray
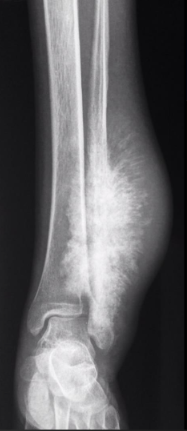
Osteosarcoma on X-ray (knee)
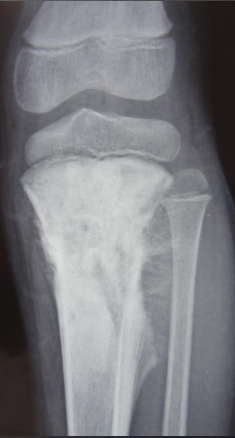
Osteosarcoma Mixed on X-ray
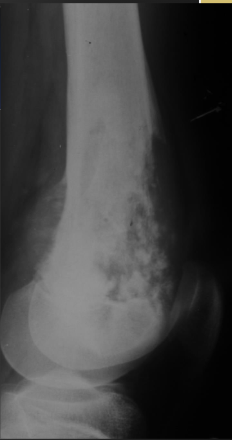
Paget’s w/ Osteosarcoma on X-ray
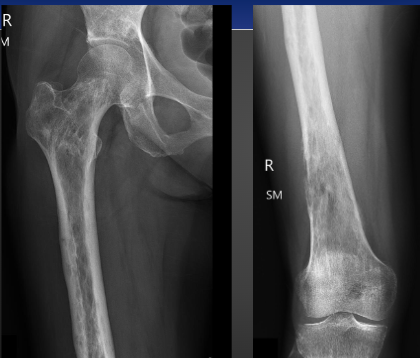
Chondrosarcoma
-3rd most common primary malignancy of bone
-Affects ages 30 to 60 years olde (peak is 45)
-10% of primary osseous malignancies
-This is a cartilage malignancy
Chondrosarcoma Clinical Presentation
-Pain occurs late in process
-Large soft tissue mass
-potential pathologic fracture
-typically metastasize late in the disease process
-Pain at site of previously known benign lesion such as osteochondroma or enchondroma (secondary - malignant degeneration of enchondroma or osteochondroma)
Location for Chondrosarcoma
-Long bones (proximal humerus is most common)
-Innominate bone
-Ribs
-Vertebrae
-Scapula
-Sternum
-LIRVSS
What is the most common primary osseous malignancy of ribs, sternum, and scapula?
-Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma on Imaging
-90% low grade and central
-ICE lesion
-2/3 show calcification (popcorn/flocculent, stippled/punctate, arcs and rings)
-Can show poorly defined lytic destruction
-Large soft tissue mass, often with calcification
-Laminated or spiculated periosteal bone reaction
ICE lesion in Chondromsarcoma X-ray
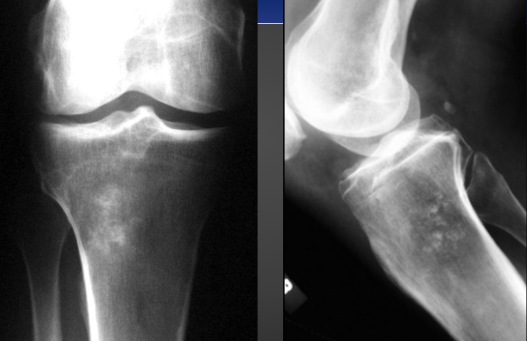
Chondrosarcoma on X-ray
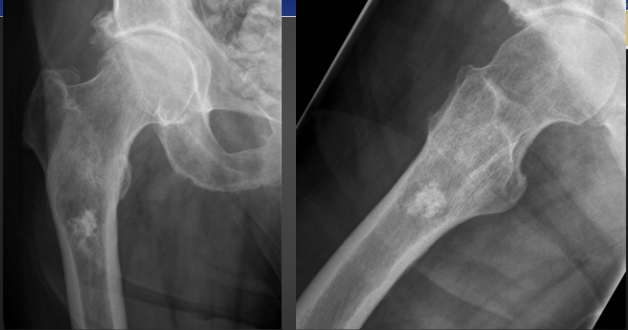
Secondary Chondrosarcoma on Xray (Enchondroma)
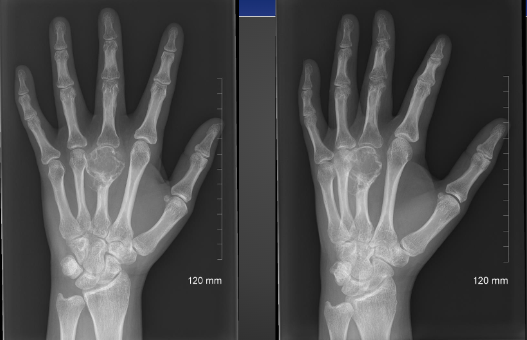
Biopsy Considerations for Chondrosarcoma
-Known to seed along biopsy needle tract (seen in osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma)
-May not show malignancy or may misrepresent grade of tumor
Chondrosarcoma > Enchondroma
-Over 40 years of age
-pain without pathologic fracture
-Over 5cm
-Endosteal scalloping > 2/3rd
-Lytic destruction or change in size
-Chondrosarcoma are rare in hands and 2x more common in long bones than enchondroma
-Chondrosarcoma are common in pelvis, whereas enchondroma rarely occur
Ewing Sarcoma
-4th most common primary malignant bone tumor
-2nd most common primary malignant bone tumor in children (after osteosarcoma)
-peak age is 10 to 25 years old
-Caucasians show a much higher incidence than other ethnicities
Common locations for Ewing sarcoma
-Femur
-Innominate
-Tibia
-Humerus
-Fibula
(in order from most common to least)
Clinical Presentation of Ewing Sarcoma
-Localized pain and swelling
-May mimic infection clinically
Classic Ewing Sarcoma
-Diaphyseal > metadiaphyseal > metaphyseal permeative lytic lesion with spiculated or laminated periosteal reaction, often with large soft tissue mass
What is the most common primary osseous malignancy to metastasize to bone
-Ewing Sarcoma
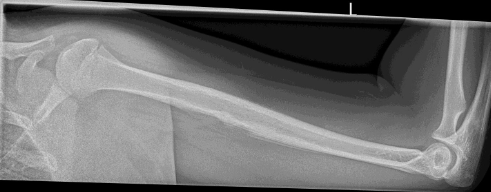
Ewing Sarcoma in Humerus on X-ray
Ewing Sarcoma on X-ray
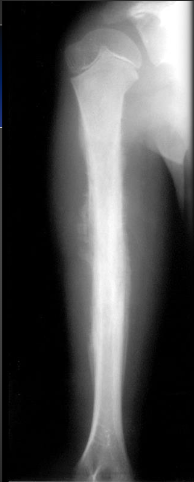
If the lesion is in the metaphysis?
-Osteosarcoma before Ewing
If the lesion is in the diaphysis?
-Ewing before osteosarcoma
If it is in the metadiaphysis and its blastic?
-Osteosarcoma before ewing
If it is in the metadiaphysis and its lytic?
-Ewing before osteosarcoma
Chordoma
-Slow growing cartilaginous tumor of notochordal origin (always in the spine/skull base)
-Locally aggressive (rarely metastasizes)
-Peak age is 40 to 70 years old
Common locations for Chordoma
-Sacrum
-Base of the skull
-C2 vertebra