8. Evaluation and therapeutic surgical methods for eye diseases diagnosis and therapy.
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Outer coat (cornea, sclera)
Middle coat (uveal tract: iris, ciliary body, choroid)
Inner coat (retina)
Lipid (from meibomian glands)
Water (from lacrimal glands)
Mucin (from conjunctival goblet cells)
What is the function of cranial nerve II (optic)?
Sensory to the central nervous system (vision)
What is the function of cranial nerve III (oculomotor)?
Motor. Innervates the dorsal, medial, and ventral rectus muscles and provides parasympathetic innervation to the iris (constriction)
What is the function of cranial nerve IV (trochlear)?
Motor. Innervates the dorsal oblique muscles
What is the function of cranial nerve V (trigeminal)?
Sensory and Motor. Provides sensation from the eye (cornea, conjunctiva, lacrimal gland) and skin around the eye
What is the function of cranial nerve VI (abducens)?
Motor. Innervates the lateral rectus and retractor bulbi muscles
What is the function of cranial nerve VII (facial)?
Motor and sensory. Controls the ability to blink (n. facialis → n. auriculopalpebralis)
What are the stages of an ophthalmologic examination?
Signalment
Anamnesis
Examination
Whether the problem is bilateral or unilateral
If a whole litter is affected
Duration of the problem
Specific details about the problem
Any prior treatments
Assessment of visual impairment (orientation)
Presence of other illnesses
Any incoordination/weakness/personality changes
Current medications
Changes in food/water intake
What are examples of specific ophthalmologic examinations?
Neurological tests
Schirmer’s tear test
Tonometry
Tear film quality
Microbiological and cytological exam
Fluoresceine stain
Jones test
Gonioscopy
Seidel test
Ophthalmoscopy
Vision tests
Cotton test
Maze test
Menace response
Neuroophthalmic tests
Palpebral reflex
Pupillary light reflex and dazzle reflex
Corneal reflex
Basal reflex
How is the cotton test carried out?
Can perform by testing each eye by covering the other with a hand, but this often distracts the dog too much and ruins the result. Better just drop cotton on each side of the head
How is the maze test carried out?
Place obstacles in the way and call the pet to navigate through them. Repeat in both light and dark environments
How is the menace reflex test carried out?
Move hand or object in front of eye in a manner to not disturb the air or fur. Blink response.
Absent in young animals → learnt response seen at 2 months and older
How is the palpebral reflex tested?
Touch medial and lateral canthus of the eye elicits a blink
How is the pupillary light reflex assessed?
Constricts the pupil in response to light.
Direct (pupillary response to light in same (ipsilateral) eye) and consensual (pupillary response to light in contralateral eye).
Optic nerve (CN II) and oculomotor nerve (CN III) function. Lack of response can indicate damage to these nerves, the brainstem, or the influence of depressant drugs.
DOES NOT ASSESS VISION!
What is the dazzle reflex?
It is manifested as a bilateral, partial blink reflex in response to a bright light. The anatomical pathway responsible for this reflex is poorly understood. However, this test is a very useful substitute for the PLR in cases when the pupils can't be seen, such as in cases of severe corneal oedema or hyphema
How is the corneal reflex assessed?
Blink reflex when cornea is touched with a cotton-tipped applicator moistened with 0.9% saline
How are basal tears evaluated?
The Schirmer tear test performed after application of local anaesthetic to the eye
How is the Schirmer tear test carried out?
Paper strip is folded (while in plastic -DO NOT TOUCH-) & hooked over lower eyelid. Tears begin to “travel” up filter paper.
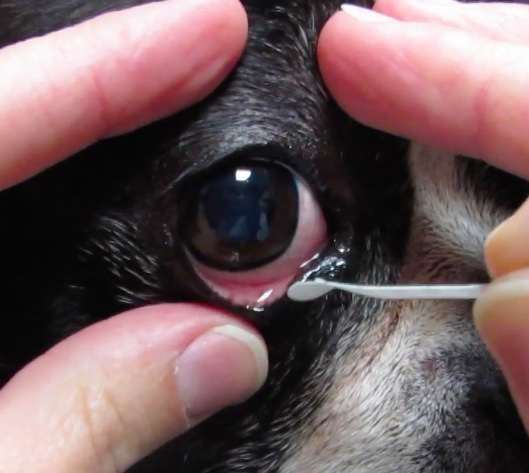
When should the Schirmer tear test be performed in relation to other ocular tests?
Before other ocular tests to get an accurate value before lacrimation is induced. Note whether the test is performed with the eye open or closed, ensuring consistency between both eyes.
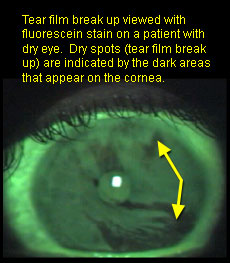
How is the tear break-up time measured?
Put fluorescein into the eye, close & then open. See how long fluorescein will remain green. As soon as the green colour breaks, the calculation is stopped
How many times should the Tonovet be touched on the cornea?
6 times
What are the types of preparation of fluorescein stain?
Eyedrops
Strip
What is the problem with fluorescein eyedrops?
Large containers have high Pseudomonas infection risk as they proliferate in the fluid.
Smaller, one-time-use containers are available and safe to use
Use of fluorescein to assess the integrity of the nasolacrimal duct. It will flow from the eye to the nose
What are the types of ophthalmoscopy?
Direct
Indirect
B. Direct ophthalmoscopy provides a direct, non-inverted image.
C. Indirect ophthalmoscopy provides an indirect, inverted (horizontally and vertically flipped) image.
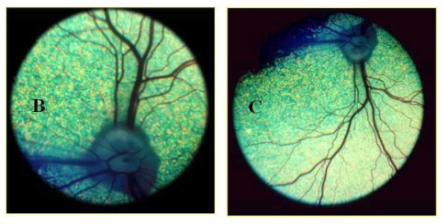
What conditions can be investigated with ophthalmoscopy?
Anisocoria (one pupil larger than the other)
Reflections (absence can indicate cataracts)
Opacities (pigment, corneal oedema)
Aphakia (aphakic crescent indicating lens luxation).
What are the surgical treatments for the eye and eyelids?
Eye globe removal (enucleation – transpalpebral or trans/subconjunctival)
Conjunctival graft
Corneal-scleral transposition
Penetrating keratoplasty
Gonioimplantation
Lens removal (phacoemulsification, intracapsular/extracapsular extraction)
Eyelid laceration repair
Temporary tacking suture for entropion, Y-V or modified Kuhnt for ectropion
Excision of eyelid tumours
Permanent lateral tarsorrhaphy (entropion)
Temporary complete tarsorrhaphy (proptosis).
Antibiotics (gentamicin, neomycin, cephalexin, chloramphenicol)
Corticosteroids (dexamethasone, prednisolone)
Antifungals (itraconazole)
NSAIDs (flunixin)
ACE inhibitors (demacolin, neostigmine)
Glaucoma medications (carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, beta blockers, diuretics, mannitol).
When are corticosteroids contraindicated in the eyes?
In case of broken epithelium, may lead to release of collagenase and proteinase → eye damage
What can you use to check retinal activity?
Electroretinography
When is USG used?
When there is opacity and the inside of the eye cannot be seen
What diseases can cause exophthalmus?
Teeth abscess, tumours behind the eye, trauma, haemorrhage
Are there any autoimmune diseases affecting the eye?
Masticatory myositis
Pannus

How can the fundus be assessed?
Dilate pupil (tropicamide; short-term mydriasis) then use ophthalmoscope
What is the commercial name for a tonometer?
Tonovet
What is the name of the surgical treatment for lens luxation?
Phacoemulsification