🩻Cell Quiz Review Flashcards
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key cell structures, functions, membrane properties, cell types, and transport mechanisms based on the provided lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Nucleus
The control center of a eukaryotic cell, containing the genetic material (DNA).
Nucleolus
A dense structure within the nucleus, primarily involved in ribosome synthesis.
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
A network of membranes involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage, lacking ribosomes.
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
A network of membranes studded with ribosomes, involved in the synthesis and modification of proteins destined for secretion or insertion into membranes.
Golgi apparatus
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Mitochondria
Often called the 'powerhouse of the cell,' responsible for generating most of the cell's supply of ATP through cellular respiration.
Cell membrane
A selectively permeable boundary that regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell, composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
Cytoplasm
The entire contents within the cell membrane, excluding the nucleus; includes the cytosol and organelles.
Lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris.
Chromosomes/Chromatin
Structures within the nucleus composed of DNA and proteins, carrying genetic information. Chromatin is the decondensed form; chromosomes are condensed for cell division.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis.
Centrioles
Cylindrical organelles involved in cell division in animal cells, forming the spindle fibers.
Phospholipid Bilayer
The fundamental structure of the cell membrane, consisting of two layers of phospholipid molecules arranged tail-to-tail.
Hydrophilic
Describing a substance or portion of a molecule that is 'water-loving' and tends to interact with water (e.g., the phosphate head of a phospholipid).
Hydrophobic
Describing a substance or portion of a molecule that is 'water-fearing' and repels water (e.g., the fatty acid tails of a phospholipid).
Neuron cells
Specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body.
Axon
The long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body.
Dendrites
Branching extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons.
Hypertonic solution
A solution with a higher solute concentration than the cell's cytoplasm, causing water to diffuse out of the cell.
Hypotonic solution
A solution with a lower solute concentration than the cell's cytoplasm, causing water to diffuse into the cell.
Isotonic solution
A solution with the same solute concentration as the cell's cytoplasm, resulting in no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
Active Transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy (ATP).
Passive Transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane down their concentration gradient, not requiring cellular energy.
Simple diffusion
A type of passive transport where substances move directly across the cell membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Osmosis
The passive diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
Exocytosis
An active transport process by which cells release substances to the outside by fusing a vesicle with the cell membrane.
Endocytosis
An active transport process by which cells take in substances from outside by engulfing them in a vesicle formed from the cell membrane.
Longest cell
neuron, which can be over a meter in length.
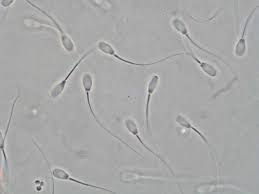
smallest cell
sperm cell, which is much smaller compared to other cells.
Widest cell
oocyte, which is larger than most other cells.
Cell that lives the longest
neuron, which can live for many years, potentially even a lifetime.
Cell that lives the shortest
red blood cell, which has a lifespan of about 120 days before being replaced.
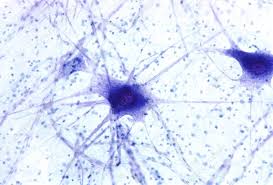
nerve cell
includes long extensions called axons and dendrites, which help transmit signals throughout the body.
muscle cell
is characterized by elongated, cylindrical shapes, striations, and multi nucleation, allowing for contraction and movement.
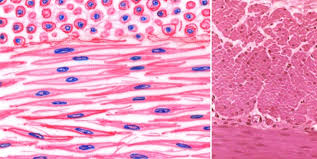
epithelial cell
is characterized by closely packed layers, varying shapes (cuboidal, columnar, squamous), and functions in protection, absorption, and secretion.
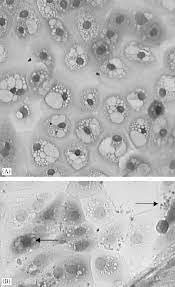
red blood cell
is a biconcave disc-shaped cell that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
sperm cell
is a motile male gamete characterized by a flagellum, enabling movement towards the ovum for fertilization.