memory unit 3
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
sensory definition
the physiological process involving sensory receptors decting/responding to stimuli
stages of sensation
reception, transduction, transmission
reception
the stimulation of sensory receptor cells
the presence of physical stimuli is detected by sensory organs
transduction
converting energy of the stimuli into electro-chemical signals
e.g. kinetic energy from a ball that hit someone converts into electro-chemical signals
transmission
the delivery of neural information to the brain for processing
e.g. transferrring info from electro-chemical signals abt being hit by a ball to parietal lobe
perception definition
the mental process of organising and interpreting sensory stimuli so that is it meaningful
stages of perception
selection, oganisation, interpretation
selection
the brain filters stimuli selecting important features for further processing while ignoring unimportant features that will receive no further processing
e.g. looking out a window and seeing a bird, filtering out a person running
organisation
the stimuli chosen to be attended to is arranged into patterns that are meaningful and easy to understand
interpretation
assigning meaning to experiences using mental structures
interpretations are determined by beliefs, experience, needs, values, involvement
subjective
perceptual expectancy
past experiences that leads to built up expectations on how to perceieve and respond to a certain stimuli
selective attention
the process of focusing on a particular object in the environment for a certain period of time
allows to tunes out unimportant details and forcus on what matters
divided attention
where mental effort is divided between two or more tasks or stimuli simultaneously
e.g. driving a car
cocktail party effect
cherry 1953
cocktail party effect aim
to study the human ability to selectively focus on one auditory message while filtering out other competing sounds
CPE fidnings
we have the ability to selectively attend to certain stimuli while filtering out other stimuli
ppl have the ability to switch their attention back and forth between selected stimuli
unattended auditory info reieves little processing
CPE contributions
to the study of how we are able to select what we need to pay attention to and how we process auditory stimuli
CPE criticism
oversimplification of what happens in real world
—> there will be more stimuli to select where to put attention to
memory
The internal record of some previous event, a process in which info is encoded, stored, and retrieved
Aspects of memory
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Encoding meaning
Conversion of info into a form that can be stored by the brain
Storage meaning
Info that is held for various amounts of time
Retrieval meaning
The process that locates stored info and returns it to consciousness as required
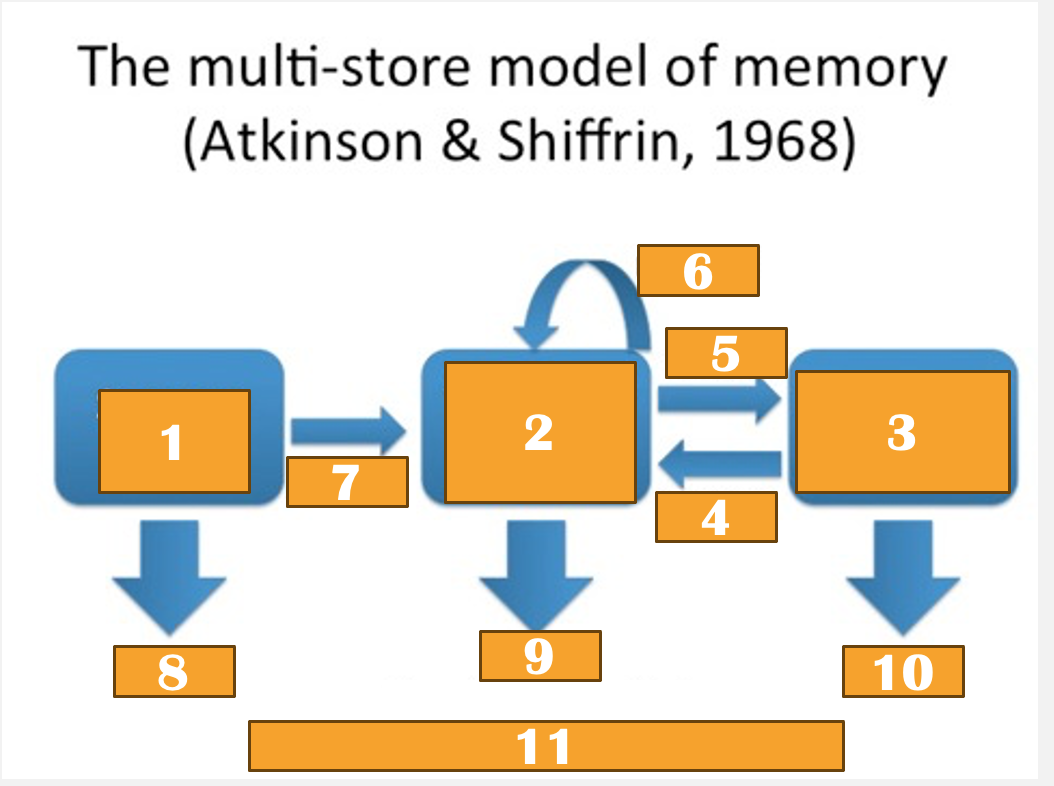
Multistore of memory
Atkinson + Shirrin 1968
Multistore of memory stages
sensory store
short-term memory
long-term memory
sensory store overview
where everything is kept until 1st stage of perception (selection)
info from senses
main function is to hold incoming info long enough to be processed further
5 separate sensory registers act as storage bins for different senses, such as iconic memory (visual), and echoic memory (auditory)
sensory store capacity, duration, encoding
capacity: unlimited, stores all incoming sensory info in the memory registers from the 5 different senses
important info that is needed to be attended to is passed to STM
duration: up to 3 seconds + quickly fades
encoding: rapid, based on physical properties of stimulation (e.g. sound)
as a sense + attention
helps w experiencing constant flow of info
selective attention focuses mental resources on only some of the sensory stimuli
echoic memories fade slower than visual
short term memory overview
conscious info (current thoughts, words & images available for decision making and problem solving
STM capacity, duration + encoding
capacity: 5-9 chunks of info
greater for digits
better for echoic info than iconic
better for echoic than iconic information
duration: ~ 30 seconds
5-18 seconds w/o rehearsal
adaptive by getting rid of useless information
encoding: rehearsal (allows transferral of materials to LTM)
maintenance rehearsal
elaborative rehearsal
chunking
maintenance rehearsal
remembering info for immediate use, not to transfer to LTM
often repeating
e.g. remembering a numberplate to report for a hit and run
elaborative rehearsal
active processing and encoding of info by associating it w other info in LTM (assimilation/accommodation) to make it more meaningful so it can be stored in LTM for later use
e.g. relating psych course content w events of life
chunking
process of combining info into larger, meaningful groups based on patterns
more info to hold as STM holds 5-9 meaningful info
used to increase STM capacity along side using rehearsal and elaborative memory
e.g. remembering a phone number with the first 4 digits being a birthday
Long-term memory overview
relatively permanent store of info
info moves from STM —> LTM through physical changes in neurons and neural networks to make associations, therefore sotrage is permanent
2 types: procedural and declarative
procedural memory
the way things are done- “how to” memory
memory of actions & skilled learned
not conscious memory process & mainly refers to learning of motor skills (implicit memory)
requires little effort to retrieve (autonomic) as skills are well established and learned
e.g. riding a bike, swimming, holding a pen
declarative memory overview
memory declaring how things are or what is remembered
requires conscious effort for retrieval (explicit memory)
2 types: episodic + sematic
episodic memory
memory of past experiences
interpretation of experiences in life + remembered bc of personal importance
linked to feelings and sensations to a particular time
e.g. the birth of a younger sibling
sematic memory
memory of facts and info based on understanding and interpretation
often spoken or written material
e.g. remembering the lobes of the brain and their functions
LTM storage capacity, duration, encoding
capacity: unlimited, but subject to distortion
memories can be remembered remarkably well after long periods of time
duration: >30 seconds- forever BUT can decay
encoding: physical changes to neurons
often a result of conscious processing (usually semantic coding where details are left out in favour of the more general meaning of the infornation
this means mistakes can be made about details
1st working memory model
baddeley + hitch 1974
2 slave systems
slave systems: the workhorses of memory + executive drives the memory
central executive: responsible for organising infon+ coordinating slave systems
directs attention to relevant info + supporesses irrelevant info
pholological loop, central executive, visuospatial sketchpad
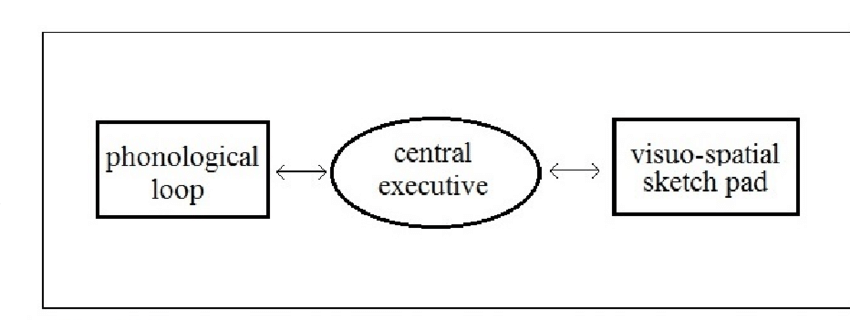
phonological loop
stores and processes sounds of language (phonological info) and rehearses it silently
visuospatial sketchpad
stores iconic and spatial info, constructs and manipulates visual images including details of shape, colour, motion, pattern and position, and representation of mental maps
episodic buffer
links info across domains to form intergrated units of visual, spatial, and verbal info w time such as memory of a story or movie
2000 updated model
hippocampus overview
curved shaped deep w/in each temporal lobe
acts as a hub, consolidating various elements of memory into cohesive memory representations
an early storage place for new LTM and invovled in the transition of LTM to more permament ones
interacts w other brain regions to create memories
hippocampus memory formation
important in organisation of storage of new memories, especially declarative
makes memories stronger by connecting sensations and emotions (works with amygdala)
hippocampus storage of memories
memories temporarily stored in hippocampus before being transferred to pre-frontal cortex
info circulates whist neurons start to encode info through long-term potentiation
form of neural plasticity
strongest circulating info returns to brain area it originated from to turn stm-ltm
spatial memory and navigation
hippocampus
rear part involved in processing spatial memories
to encode environment around us and remember where everything is (contains cognitive map)
Henry Moliason procedure
scoville peformed in 1953
partial medical temporal lobe resection
removes medical portions of temporal lobes
extends 8cm toward the back of the brain in each lobe
removed the pair of amygdala and majority of the hippocampi in each lobe
goal was to control seizures
HM post surgery
demonstrated regrograde and anterograde amnesia
suffered from retrograde for the 11 year period before surgery, childhood memories unaffected
demonstrated inability to form declarative memories
at the time of surgery medical community did not know what the hippocampus did
HM conclusions and contributions
until the surgery, the hippocampus was not know as essention for making memories
case indicated procedural memories are not controlled by hippocampus & amygdala
inability to form declarative memories left to conclusion that hippocampus is vital
cerebellum overview
located under cerebrum
involved in balance, coordination skills of fine motor skills and judging distance
invloved in the formation and storage of procedural memory
cerebellum formation of memories
formation of procedural memories
unconscious/implicit memories (such as motor skills)
e.g. how to draw a certain shape
cerebellum sotrage of memories
involved in storage of procedural memories
specifically sensorimotor skills
amygdala overview
collection of nuclei deep within each temporal lobe
involved in processing emotions and memories associated eith fear
has high connections to other brain functions-can link areas to process higher cognitive information with systems that control lower functions
fight or flight
amygdala formation of memories
fearful memories established w only a few receptors
attributes emotions to memories, the more emotive memories are, the easier to remember
amygdala storage of memories
strenghtens episodic memories stored in other regions of the brain (has connections to other brain functions)
bidirectional connections w hippocampus
current understanding is suggested that it does not sore memories
CPE method
presenting participants with 2 different audios simultaneously rhough headphones, asking them to repeat one message while ignoring the other. This is to test their ability to selectively attend to a single stimulus
sensory memory
working memory
long term memory
retrieval
encoding
rehearsal
attention
interference
interference
decay
memory loss
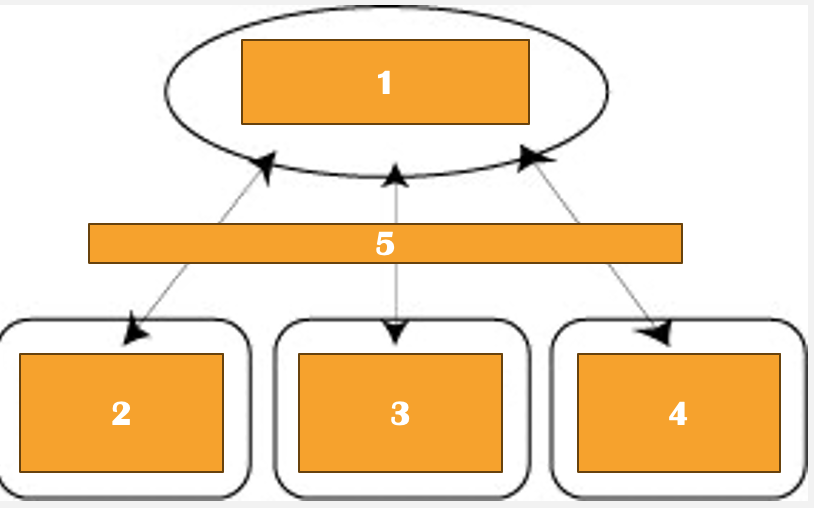
central executive
phonological loop
visuospatial sketchpad
episodic buffer
rehearsal