Chapter 18.1-CHM 114: Metabolism, energy and ATP
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Metabolism
the term that is used to describe all of the chemical reactions that take place in an organism
Metabolites
small molecule reactants and products for the numerous chemical reactions of metabolism
catabolism
The breakdown of large molecules in metabolism
generally involves breaking bonds within large molecules and also oxidizing the molecules.
gives off a tremendous amount of energy. When our bodies metabolize fuels as a part of catabolism, most of the energy is stored in the forms of ATP, NADH, and FADH2
anabolism
consists of the reactions that produce large molecules
The reactions that produce sugars, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids are all a part of anabolism.
REQUIRES the input of energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2 to provide the energy needed to make the bonds in larger molecules. Thus energy is needed to produce fats, sugars, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Photosynthesis
an anabolic process whereby plants can take solar energy and use it to produce sugars, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Plants continually add more energy to the cycle of catabolism and anabolism and are thus an indispensable part of life on our planet.
ATP
used as an energy source for many biological reactions.
In our bodies, ATP powers our active transporters (which in turn allow for nerve impulses and membrane transport), powers muscle movement, and allows for the biosynthesis of large molecules.
there are four reasons why the products of ATP are more stable than the reactants:
1. Decreased negative charge repulsion
2. Increased entropy
3. Increased hydrogen bonds to water
4. Increased number of resonance structures
Combustion of fuels in metabolic pathways
Our bodies carry out the combustion of organic molecules like sugars and fats into carbon dioxide and water.
C6H12O6 (𝑔𝑙𝑢𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑒) + 6O2 → 6H2O +6CO2
metabolic pathway.
a series of linked chemical reactions where the products of one reaction are used as the reactants for the next reaction.
In a living organism, when fuels are catabolized, this is done as a part of a stepwise process
biological systems STORE the energy released from catabolism in the forms of:
ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
central metabolism
These metabolic pathways produce starting compounds for the production of all biological molecules and because all other molecules eventually get degraded into a metabolite that is found in central metabolism.
Our cells' main way of producing the energy that is needed for all of the other biological processes that our cell performs.
A collection of three different processes called glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Kinases
enzymes that transfer phosphates from ATP to another substance
Sometimes kinases are named for the reverse reaction and will thus appear to transfer a phosphate from a metabolite to ADP to generate ATP
Dehydrogenases
enzymes carry out oxidations using either NAD+ or FAD
produce either NADH or FADH2
Glycolysis
a metabolic pathway that starts with glucose and ends with two molecules of pyruvate
Glycolysis is typically divided into two phases.
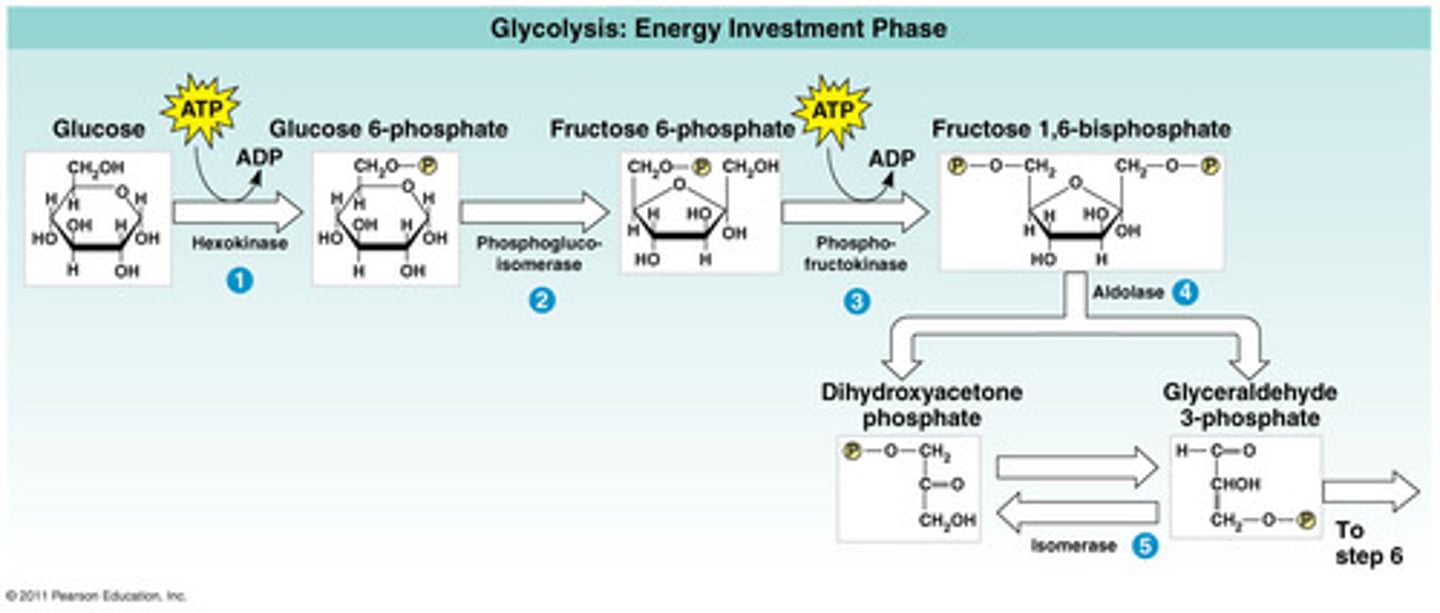
The first phase of glycolysis
expends energy in the form of ATP and ends with the splitting of glucose into two 3-carbon molecules called glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate.
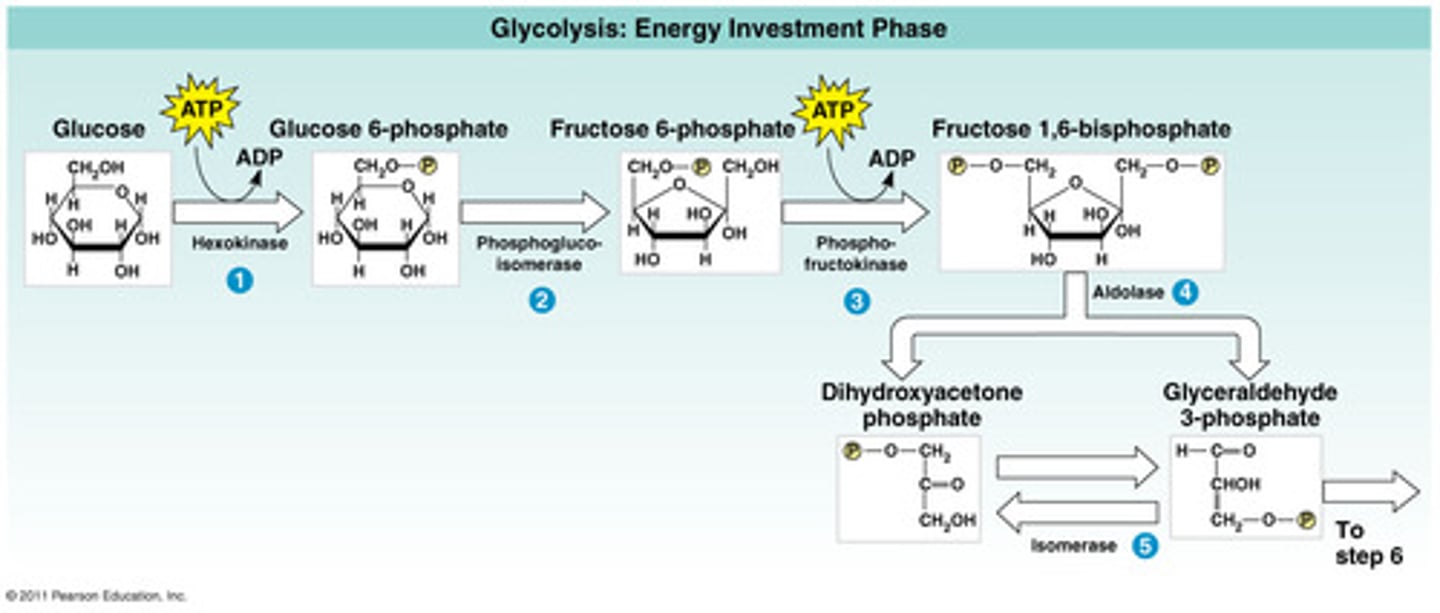
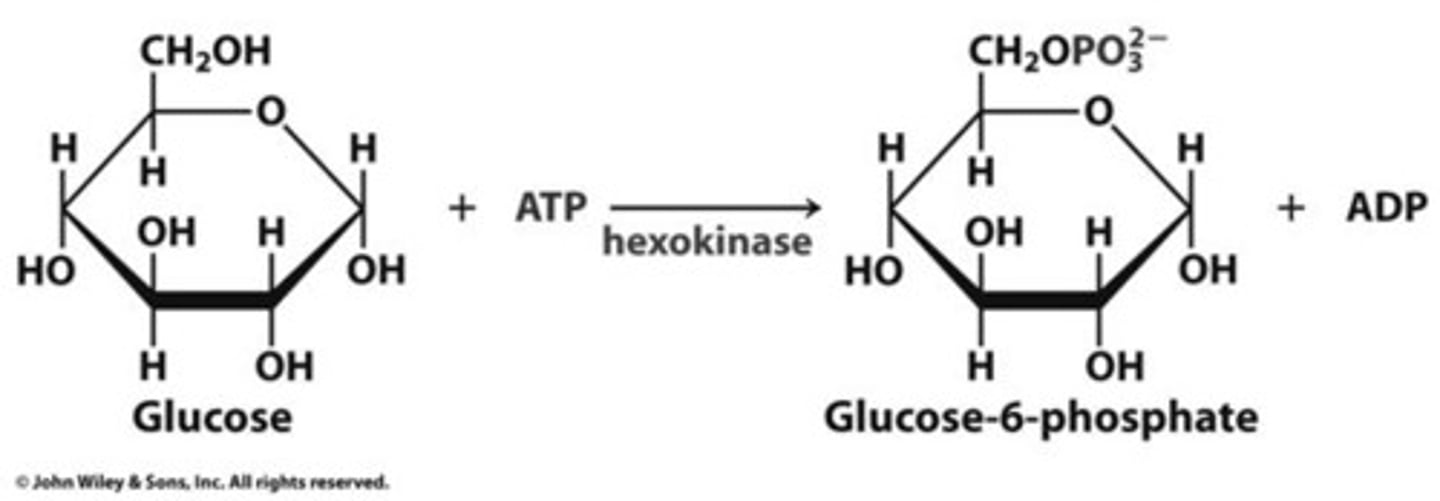
hexokinase
The first molecule of ATP is used in the very first step which is catalyzed by this enzyme.
uses ATP to convert glucose into glucose-6-phosphate.
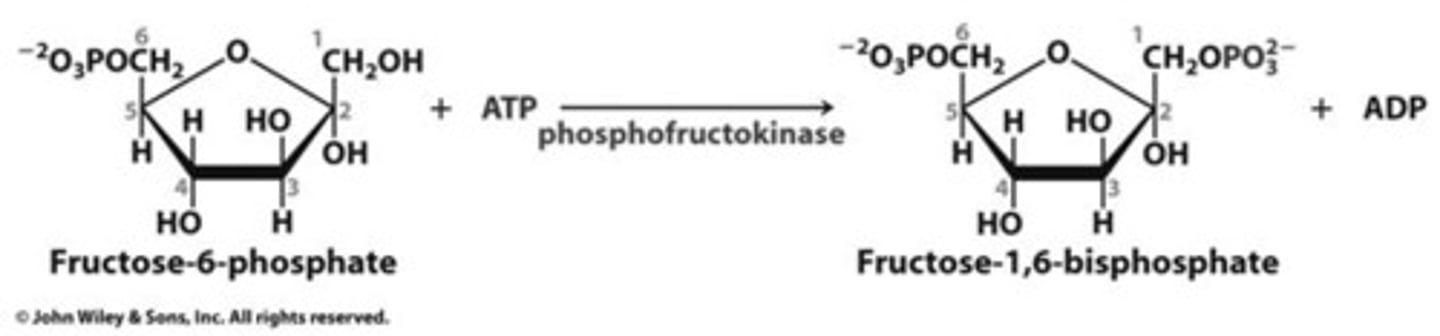
phosphofructokinase
after glucose-6-phosphate gets isomerized to a fructose-6-phosphate molecule in a previous step.
This enzyme adds a second phosphate onto the sugar, forming fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and primes it for splitting into two 3-carbon compounds in the next step.
The step after that ensures that both 3-carbon compounds are identical (glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate).
The first phase of glycolysis
involves an input of energy in the form of two ATPs. It also splits the 6-carbon molecule into two 3-carbon molecules.
The second phase of glycolysis
transforms these two 3-carbon molecules into two molecules of pyruvate.
Along the way, energy will be harvested in the form of 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules.
Net gain (4-2)= 2 ATP
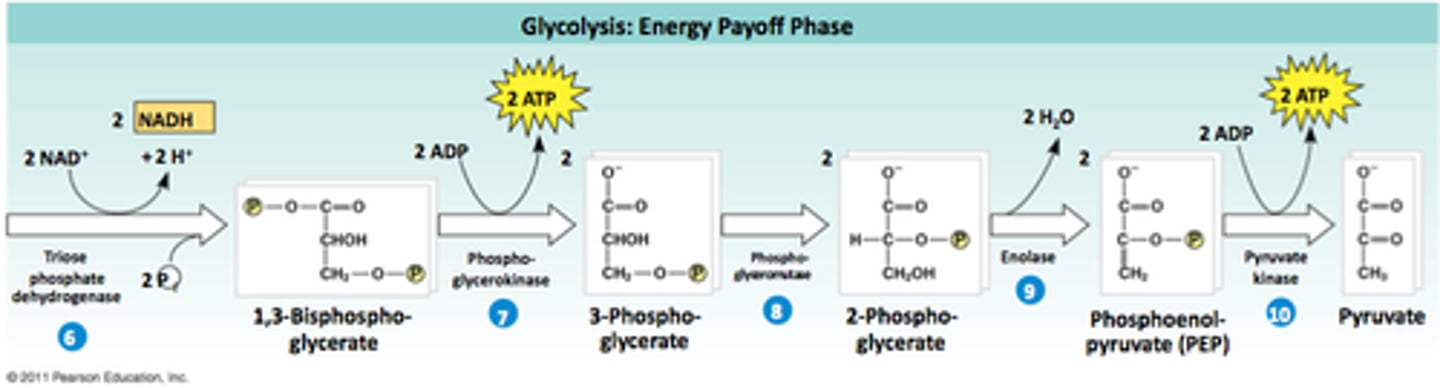
In order to make the 4 ATPs
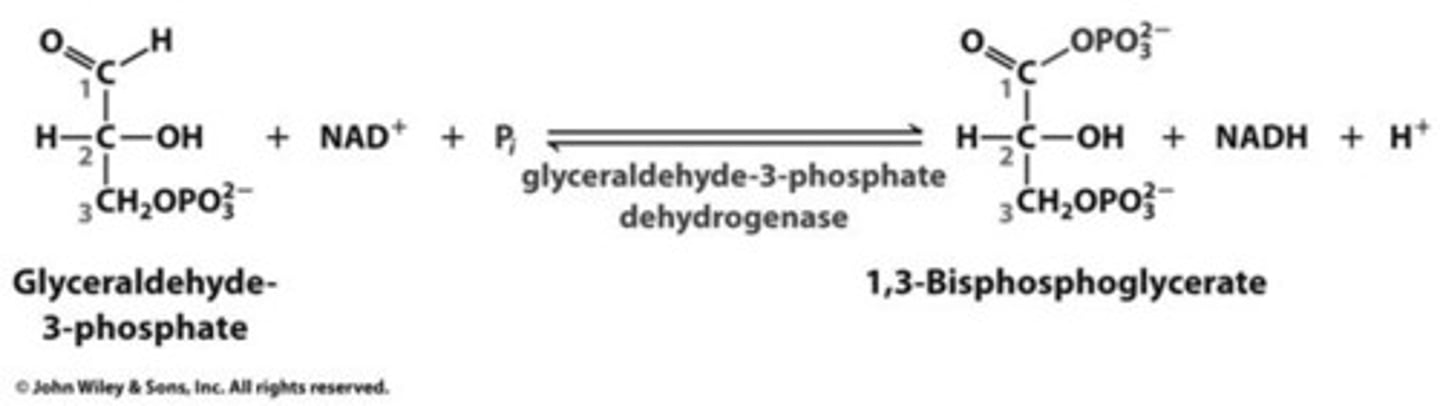
a phosphate must be transferred from a metabolite to ADP. Making 4 ATPs therefore requires 4 phosphates to be present on the two 3-carbon molecules. Two were already added as a part of the first stage of glycolysis. During the 2nd stage two additional phosphates get added at the same time that the glyceralde-3-phosphate molecules get oxidized. This reaction is the first one in the 2nd half of glycolysis and is catalyzed by the enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH).
GAPDH
The product of the GAPDH reaction is 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
This is a 3 carbon molecule with 2-phosphates.
These two phosphates are transferred to 2ADPs in reactions catalyzed by phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase
Important Enzymes
Hexokinase
Phosphofructokinase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase Phosphoglycerate kinase
Pyruvate kinase
Important metabolites
Glucose
Glucose 6-phosphate
Fructose-6-phosphate
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Pyruvate