10: Articular Cartilage
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
types of cartilage
elastic, hyaline, fibrocartilage
elastic cartilage
protein: elastin
ex: epligottis, layrnx, ear
has the MOST ECM, very elastic!
hyaline
primary component of articular cartilage
fibrous cartilage
ex: has the LEAST ECM and MOST collagen
ex: IVD, pubic symphysis, meniscus
articular cartilage development begins to develop around the ___ week of gestation
5th
_______ stem cells producing cartilage are _______________
mesenchymal ; pluripotent
limb development is called what considering articular cartilage?
endochondral ossification
steps of limb development
1) cartilage scaffolding
2) chondrocytes form at the articular and transient cartilage and transient cartilage at the end of the opposing bones
3) chondrocytes undergo hypertrophic differentiation in the middle of the limb bud
4) limb bud layers mesenchyme over layer of ectodermal cells forming a ridge (AER)
AER
apical ectodermal ridge
AER has what 2 functions
1) allows the mesodermal cells to replicate
2) protects the cells allowing for limb growth
AER is controlled _ dimensionally... explain
3
proximal & distal
anterior & posterior
dorsal & ventral
zone of ________________________ - controls the anterior -> posterior (formation of the digits)
zone of polarizing activity
zone of polarizing activity is controlled from what gene
the sonic hedgehog gene
role of articular cartilage
covers articular surfaces (except TMJ)
4 functions of articular cartilage
1) distribute joint load over wider area (cushioning/shock absorption)
2) allow relative movement of the opposing joint surfaces with minimal friction
3) improve fit of articular surfaces
4) provide lubrication of articular surfaces
characteristics of articular cartilage
avascular
no lymph drainage
not innervated
very few cells (chrondrocytes)
main cells of articular cartilage
chondrocytes
chondrocytes make up less than ____-% of the tissue volume
10
role of chondrocytes
manufacture, secrete, organize, and maintain the organic component of ECM
matrix is composed of dense network collagen (type ?)
type II
how is collagen in articular cartilage distributed and layered
inhomogeneously distributed and layered

superficial zone of articular cartilage
densely packed fibers randomly woven in parallel planes to the articular cartilage
what % of weight is the superficial zone
85% of dry weight
superficial zone is the lowest concentration of
proteoglycans
superificial zone - resists ____ component of compressive load
tensile
middle zone of articular cartilage
greater distances between the collagen
middle zone - _____________ concentration of PG; _________ of cartilage
highest; workhorse
deep zone of articular cartilage
the fibers come together forming larger, radially oriented fiber bundles
deep zone - cross the _____________ insert on calcified cartilage and subchondral bone
tidemark
proteoglycan
protein polysaccharides with GAGs attached
aggrecans purpose
is to aid in structural stability
aggrecans have an affinity with ___________
hyaluronan molecules (hyluronic acid) --> attracts water
aging causes water content and car/protein ratio ______
decreases
water content in articular cartilage- what %
80%
what cations does articular cartilage contain
Na+ K+ Cl-
water in cartilage allows for ________
waste, gases, and nutrients to flow back and forth in the cartilage
how do materials move in articular cartilage
passive diffusion
the___________________ is crucial to joint lubrication
movement of water with loading
compressive loads lead to _________ controlled by PGs
deformation
fluid flows out of collagen, which leads to inc concentration of PGs, which leads to _________ negative charge, which leads to attracting _____ which ____the tissue
inc
water
stiffens
other ____________improve the structural ingrity and and provide additional stiffness
PGs (biglycan, decorin)
the compressive force will lead to little deformation or volume changes -->
cells are protected and no mechanical damage to the tissue is observed
the ability of PGs to resist compression comes from (2 things)
1) the donnan osmotic swelling pressure associated with the tightly packed anionic group
2) the bulk of stiffness of the collagen PG complex
weeping
fluid exudation under compressive loads
weeping causes loss of ____-% of original fluid content
50%
tissue is very ______ = the measure of ease with which fluid can flow through a porous material
permeable
permeability is inversely proportional to the _________ of fluid flow, implying how much force does it take to get fluid moving through tissue
frictional drag
permeability changes with changes in _______ and ______________ loading
magnitude and rate of compression
permeability decreases ______ while load increases and rate increases
exponentially
once yield is quickly reached, failure occurs _____ and fracture ________
quickly, patterns vary
toe region
small because it is not reflective of de-crimping (should be nonlinear)
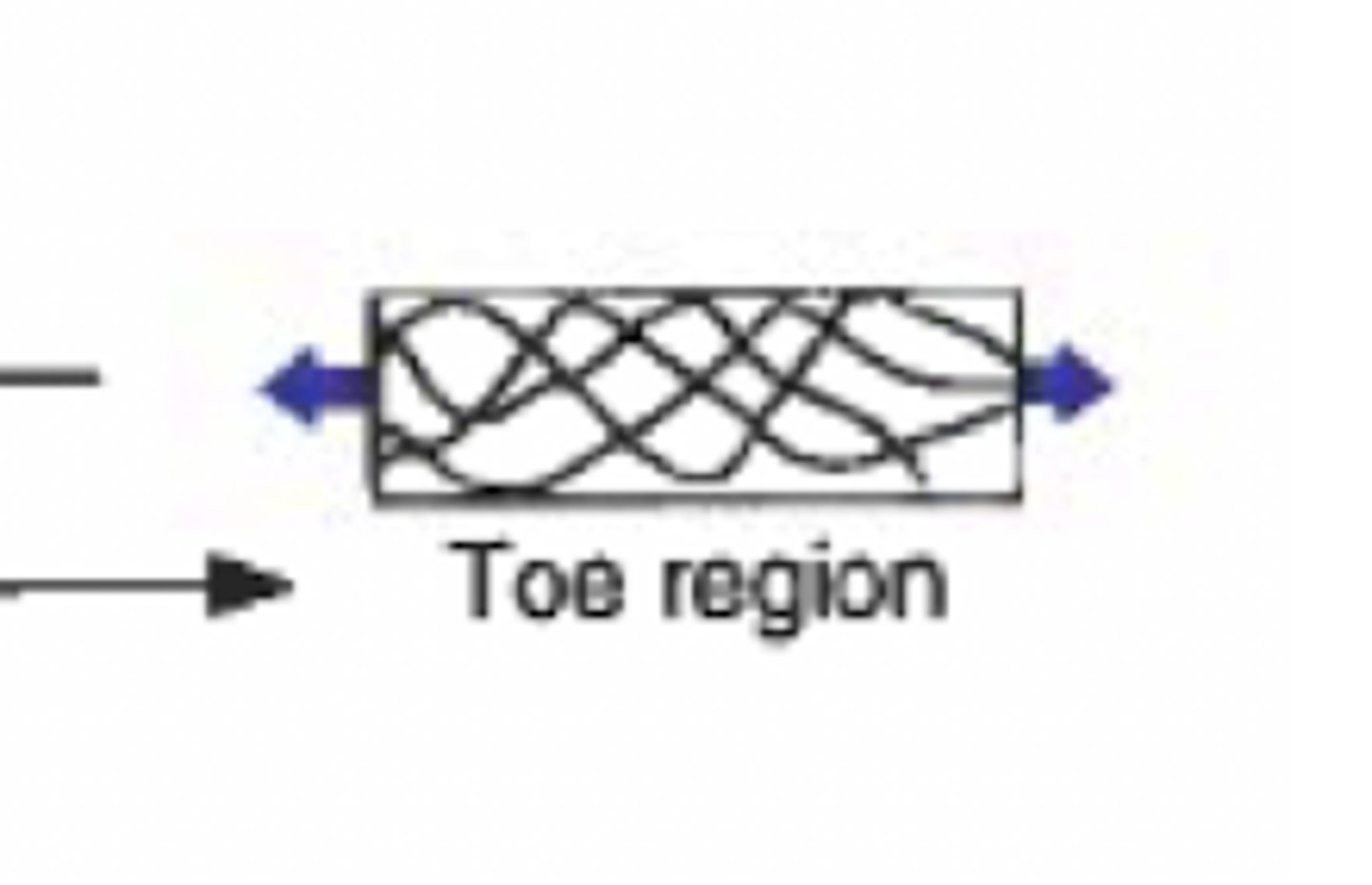
elastic region
linear region (wavy)
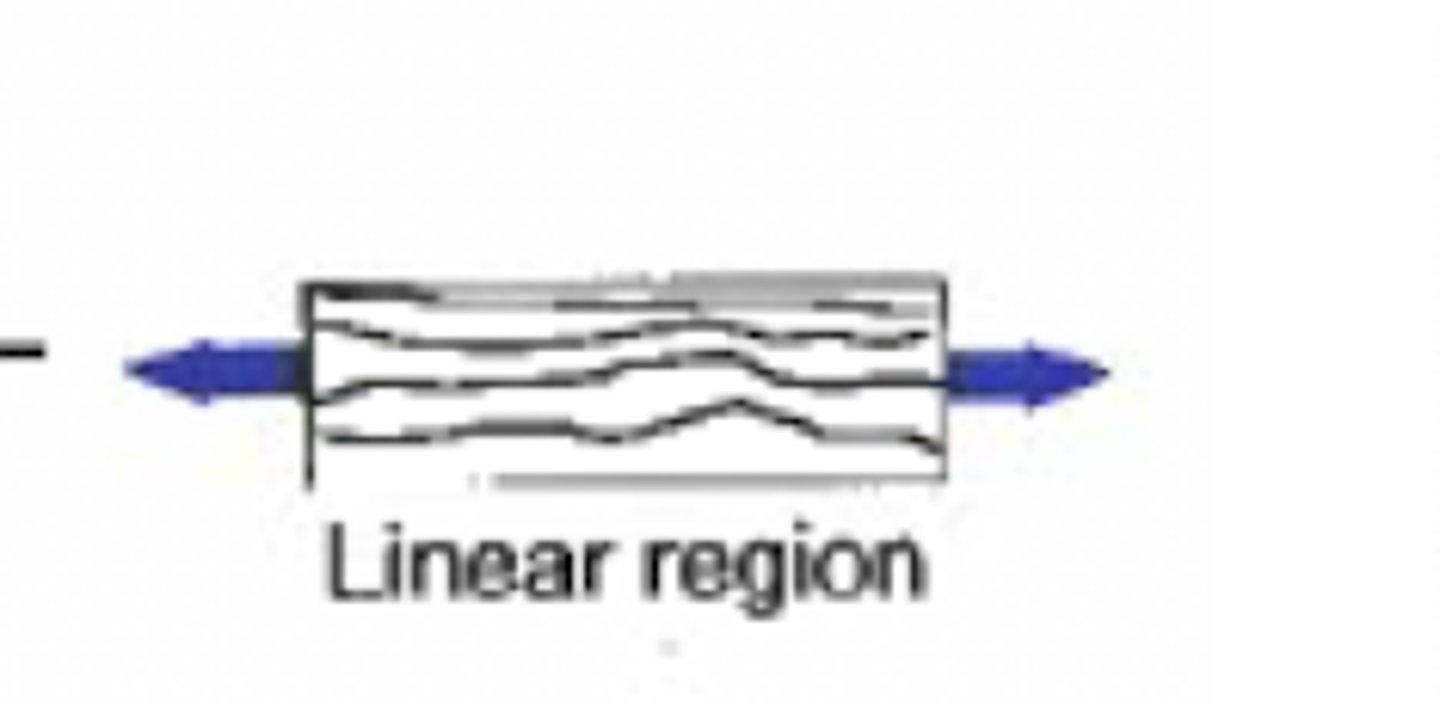
plastic region
fracture point occurs very soon after plastic region is met

what are the 3 viscoelastic behaviors
creep
stress relaxation
hysteresis
the viscoelastic properties are all _____ than in tendon/ligament
less
takes _________to reach equilibrium on creep and stress relaxation
longer
over time fluid is redistributed and allows load to spread out over __________________________________
greater surface area
takes _______ for hysteresis to reduce but the area between the curves is not any bigger than ligament/tendon
more reps
during stress relaxation ...
weeping occurs initially followed by fluid redistribution
during creep....
only weeping appears to occur... takes hours to reach relative equilibrium point during creep and stress relaxation
rate of time dependent behaviors depend upon __________________
fluid exudation rate (related to the permeability of the tissue)
aligment of collagen along the axis of tension. there is a resistance of tension by the collagen strands = ?
articualr cartilage under tension
no change in volume=no intersititial fluid flow. collagen is responsible for the tension restriction = ?
articular cartilage under shear
biofilms
Colonies of bacteria that adhere together and adhere to environmental surfaces.
synovial fluid plays significant role in
lubrication
fluid film interaction
thin film of fluid that creates a surface separation like oiling
fluid film interaction probably develops as a result of ___________ of articular cartilage
weeping
part of the compressive load is supported by the pressure developed in the
fluid film layer
cartilage can carry _____ loads for _____ durations
high loads, short durations
fluid film lubrication
Movement increases the amount of fluid between articulating surfaces, thus increasing their separation
fluid film lubrication is the
first responder to compressive loads - especially fast rates of loading
over time the fluid film layer ______ with pressure application leaving high load areas _____________
thins out, unprotected
fluid film flayer is important for _________, but likely most important for ___________ as it allows nutrients in and out of articular cartilage
reducing friction
nutrition of articular cartilage
_____ is not as good as the boundary layer
coefficient of friction
boundary layer lubrication
considered a monolayer of lubrication directly on top of the articular cartilage
boundary layer consists of ________
hyaluronan
what is considered a concentrated fluid
boundary layer
boundary layer handles ____ loads, ____ speeds, ____ duration
high, low, long
boundary layer prevents _____________contact and eliminates most of the surface wear
surface to surface contact
boundary layer contains ______
independent physical properties of the lubricant and the bearing material only
boundary layer is dependent upon
chemical properties of the lubricant
boundary layer can reduce friction ______times
3-6
the boundary layer is the best ________ of all lubricating systems in the body
coefficienct of friction
both types of lubrication exist, and a shift occurs from ______ early on during activity to ____________ with sustained loading activity
fluid/film
boundary
the middle layer is the
working layer
injury leads to the __________ of random collagen fibrils
disruption
disruption causes more swelling pressure to expand the collagen network --> forms ________
vertical columns (instead of random)
injury disrupts the orientation of ____ and cells which lessen the mechanical strength of tissue
aggrecan
breakdown defined by volume of load being too high
single insult
breakdown defined by being applied too often
fatigue failure
both types of loading cause what?
unwanted removal of material from the articular cartilage by mechanical action occurring
during breakdown of articular cartilage, _____ is unable to keep up with these loads and cannot prevent tissue damage
lubrication
2 types of wearing
interfacial wearing
fatigue wear
interfacial wearing
interaction of surfaces related to friction
fatigue wear
related to deformation over time under load
interfacial wear has to do with what layer
superficial ; weight bearing surfaces come into direct contact with no lubrication
adhesions
pieces stick to each other and pull off original surface
abrasions
soft material is scraped by a harder one; leads to shredding
once injured, will adhesions or abrasions occur?
both
interfacial wear increases ________ and softening of cartilage
permeability