Genomic Imprinting: Prader-Willi and Angelman Syndromes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
parent-of-origin effect
expression of certain autosomal genes only from the allele found on the chromosome from a specific parent
- phenotype will occur if the mutation resides on the parental chromosome which is normally expressed
- not if the mutation is on the parental chromosome that is normally imprinted
monoallelic expression
expression of a gene from only ONE of the two alleles
biallelic expression
expression of a gene from BOTH alleles
imprint reset
an individual's maternal and paternal imprinted genes are reset during gametogenesis to match the imprinting pattern consistent with their gender (i.e. imprints are erased & reestablished during meiosis )
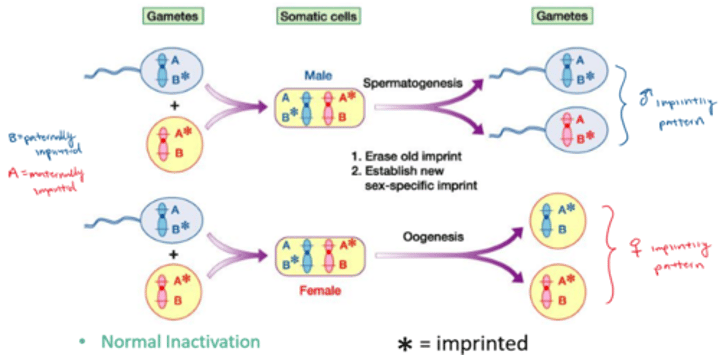
genetic imprinting
some gene alleles have different expression depending on parent-of-origin
imprinting
allele that is not expressed or "off"
- mediated by DNA methylation and epigenetic silencing
imprint & disease expression
- if disease-causing mutant allele is imprinted = disease not expressed
- if mutant allele on active chromosome = disease will be expressed
autosomal dominant paraganglioma
slowly growing, mostly benign tumors of the parasympathetic ganglia (usually in head & neck region)
- autosomal dominant
- maternally imprinted, paternally expressed (only manifests when mutation inherited from father)
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS)
an overgrowth syndrome- infants are larger than normal; growth may be asymmetric
- autosomal dominant
- paternally imprinted, maternally expressed (only manifests when mutation inherited from mother)
- most cases are spontaneous (~85%)
defective imprinting
leads to over or under expression of a gene but not in a parent-of-origin specific manner
Angelman Syndrome (AS)
lack of maternal contribution of 15q11-13
- rarely inherited thus neither dominant or recessive
- important gene: UBE3A (brain-specific ubiquitin ligase)
Angelman Syndrome (AS)
clinical presentations:
- severe intellectual disability (mental retardation)
- seizures (high risk for epilepsy)
- spasticity
- coarse facies
- short stature
- happy demeanor ("happy puppet syndrome" = derogatory)
- hyperactivity
UBE3A
brain-specific ubiquitin ligase gene implicated in Angelman Syndrome
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
lack of paternal contribution of 15q11-13
- rarely inherited thus neither dominant or recessive
- important gene: SNRPN, HB (snoRNA assembly)
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
clinical presentations:
- in infancy: poor feeding, hypotonia
- moderate intellectual disability
- polyphagia, obesity (type II diabetes)
- behavioral problems
- hypopigmentation (variable)
SNRPN
snoRNA assembly implicated in Prader-Willi Syndrome
UBE3A normal imprinting
expressed only from the maternal chromosome (paternally imprinted)
SNRPN normal imprinting
expressed only from the paternal chromosome (maternally imprinted)
OCA2 normal
biallelic gene expression
oculocutaneous albinism type 2
homozygous OCA2 loss-of-function
- autosome revessive
OCA2
gene associated with autosomal recessive oculocutaneous albinism type 2
UBE3A loss-of-function
causes Angelman Syndroms (AS) via:
- deletion of 15q11-13 on maternal chromosome
- paternal uniparental disomy = both chromosomes are paternal
- imprinting defect= paternal imprinting on maternal chromosome
- loss-of-function
SNRPN loss-of-function
causes Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) via:
- deletion of 15q11-13 on paternal chromosome
- maternal uniparental disomy = both chromosomes are maternal (maternal nondisjunction = more common)
- imprinting defect= maternal imprinting on paternal chromosome
- loss-of-function
Southern blot
method to detect methylation patterns using methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes
- NotI = methylation sensitive, will not cut imprinted alleles
- Xbal = no sensitive, will but either allele
- SNRPN probe (paternally expressed = unmethylated = cut by NotI; maternally imprinted = methylated = not cut by NotI)
uniparental disomy (UPD)
inheritance of 2 copies of a chromosome from one parent
trisomic rescue
mechanism by which UPD occurs
- trisomic conceptus occurs due to nondisjunction during parental meiosis
- trisomic cells can undergo several more divisions resulting in daughter trisomic cells
- if a mitotic nondisjunction then occurs, then it will result in disomic and tetrasomic daughter cells
- only the DISOMIC cell will develop into an embryo
uniparental isodisomy
UPD in which the 2 chromosomes from the same parent are identical
- the original nondisjunction occurred in meiosis II
- can result in homozygosity for a recessive allele with only on heterozygous parent
uniparental heterodisomy
UPD in which the 2 chromosomes from the same parent are different
- the original nondisjunction occurred in meiosis I
- if contributing parent is heterozygous, offspring will also be heterozygous
- no chromosome are contributed from the other parent