D1- Histology 1.6 Exam 1 Nervous Tissue and Peripheral Nerve Histology: Key Concepts and Structures
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
What are the two primary cell types found in nervous tissue?
Neurons and glial cells
What is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
Neuron
What are the main components of a neuron?
Dendrites, cell body, axon, and nerve endings
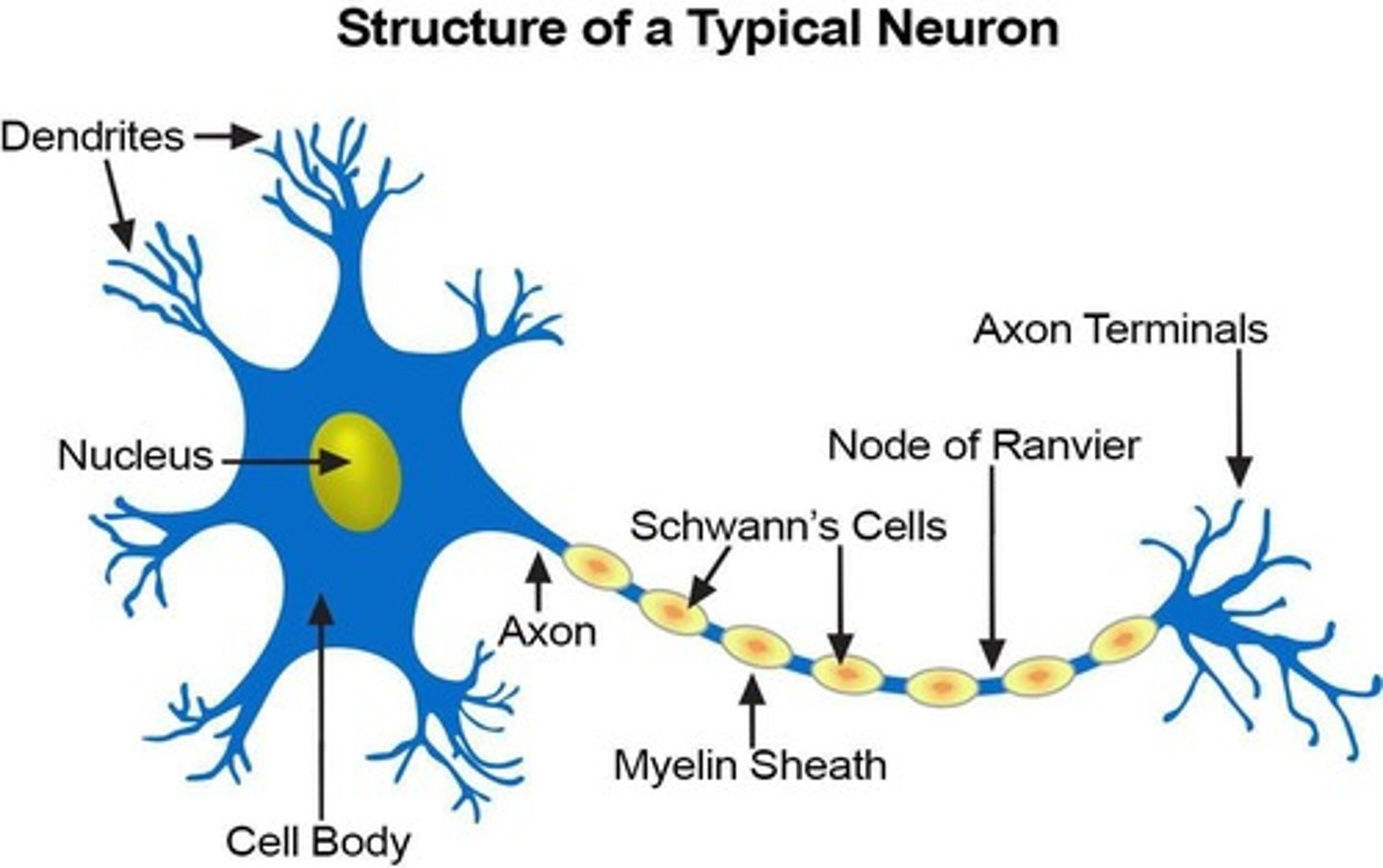
What is the role of neurotransmitters in neurons?
They stimulate other neurons in response to stimuli.
What are synapses?
Specialized structures at axonal terminals where neurons communicate.
Can neurons divide or regenerate?
Neurons are terminally differentiated and do not divide, but axon regeneration is possible.
What is the function of neurons?
Generate and carry out nerve impulses, respond to stimuli, and facilitate communication and integration.
What is the soma in a neuron?
The cell body that contains the nucleus and cytoplasm.
What are the four types of neurons based on structure?
Multipolar, bipolar, unipolar, and pseudounipolar neurons.
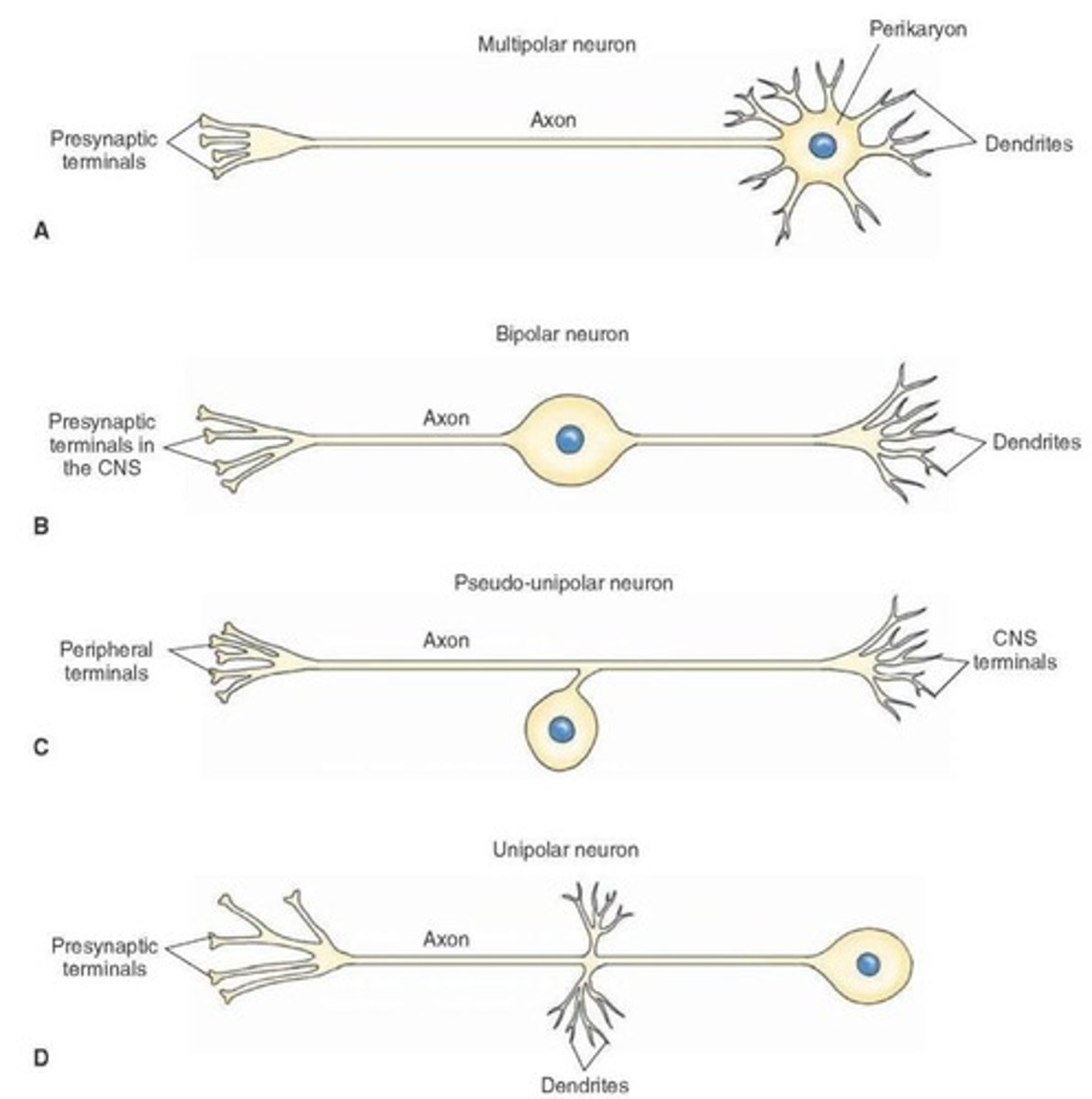
What type of neuron is most common?
Multipolar neuron
_____ are single dendrite opposite axon. Seen in receptor neurons of retina
Bipolar
_____ doesn't have dendrites on some, axon only. An example is sensory neuron
Unipolar
_____ are single dendrites and axon fuse; soma off to one side. An example is dorsal root ganglia
Pseudounipolar
____ constitute most sensory receptors, conducting pathways and integration centers
Neurons
________ cells provide physical support and protection, electrical insulation, metabolic exhange
Supporting
What are the supporting cells in the nervous system called?
Glial cells
What are the three categories of supporting cells?
Neuroglia in CNS, Schwann cells in PNS, and satellite cells in ganglia.
What is the function of the neurilemma?
It is the plasma membrane surrounding the neuron.
Most neuron cell bodies are located in _____
CNS
______ are highly branched neuron, processes received stimuli from other neurons or environment
1 or more dendrites
______ transmits stimuli to other neurons or effector cells
Single axons
Axon arises from _____, terminates in distal swelling called terminal bouton
Axon hillock
What is axonal transport?
The movement of products down the axon.
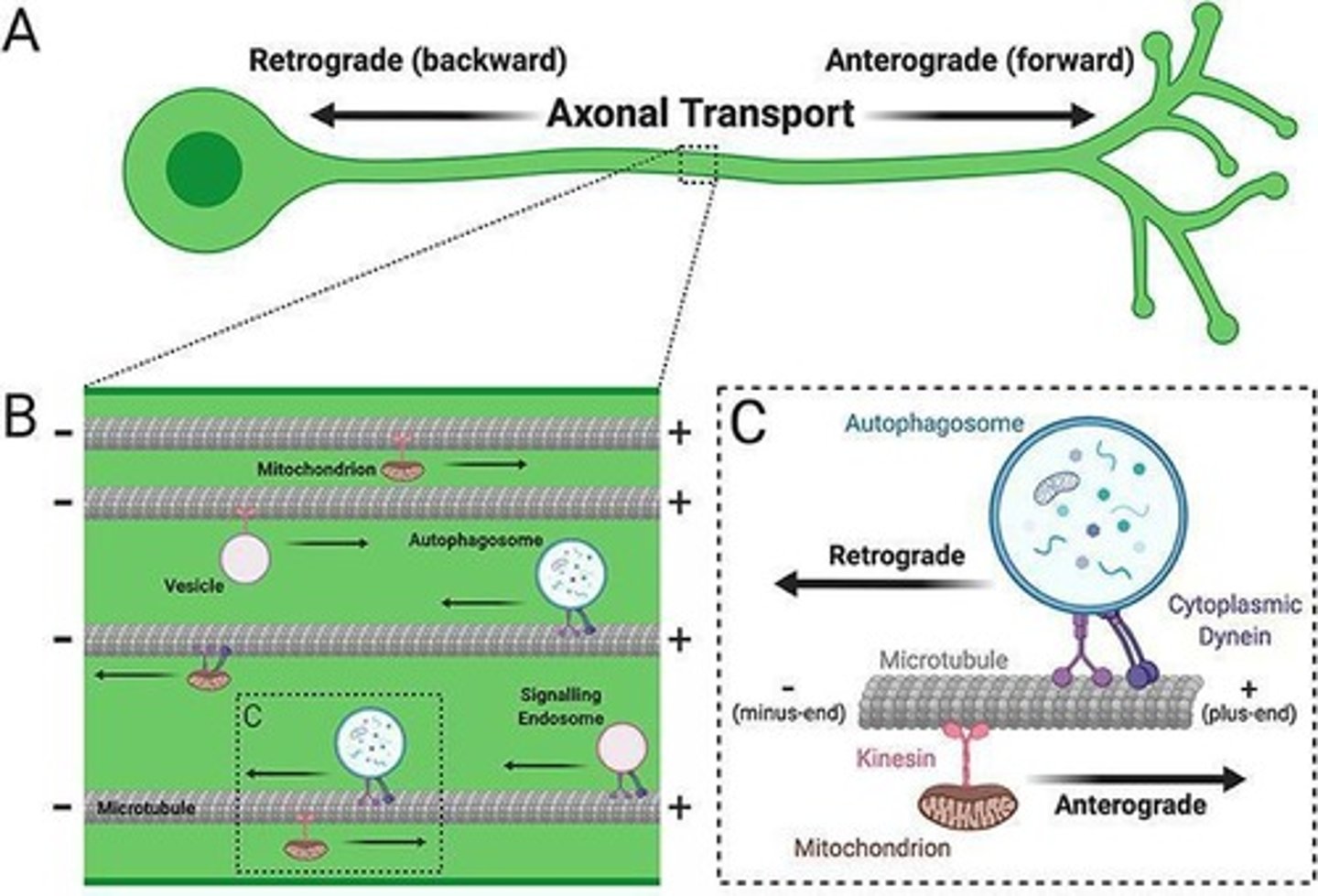
What are the two types of axonal transport?
Anterograde transport and retrograde transport.
______ carries cytoskeletal elements, and usually used for not crucial things
Slow axonal transport
______ carries membrane-bound organelles and used for crucial things
Fast axonal transport
Anterograde transport uses _____
Kinesin
Retrograde transport uses ______
Dynein
Viruses uses what type of transport to get to the nucleus?
Retrograde
What initiates an action potential in a neuron?
A strong enough stimulus that reaches the threshold.
What happens during depolarization of a neuron?
Voltage-gated sodium channels open, allowing Na+ ions to rush into the neuron.
What occurs during repolarization of a neuron?
Voltage-gated potassium channels open, allowing K+ ions to exit the neuron.
What is the role of the perikaryon?
It refers to the cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus in a neuron.
Where are most neuron cell bodies located?
In the Central Nervous System (CNS).
What is the significance of Nissl substance in neurons?
It is associated with rough endoplasmic reticulum and indicates protein synthesis.
What is saltatory conduction?
The process by which action potentials jump from one node of Ranvier to another in myelinated neurons.
What is the role of the sodium-potassium pump during the refractory period?
It restores resting potential by moving sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell in a 3:2 ratio.
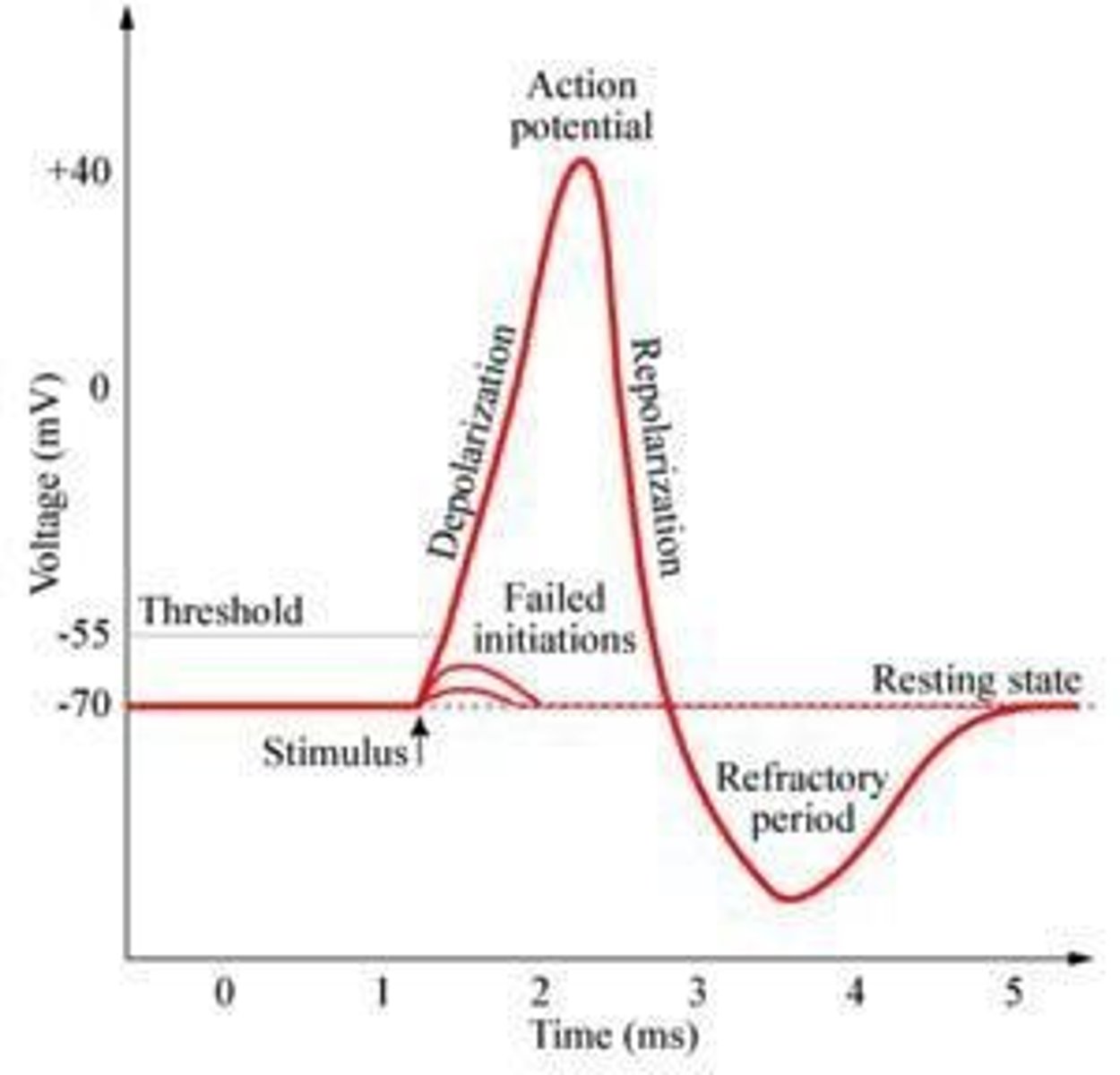
What happens to sodium channels during the refractory period?
Sodium channels close and cannot reopen for 1-2 milliseconds, resulting in a period where the neuron is unresponsive to stimuli.
How is an action potential conducted to an effector cell?
It is conducted via neurotransmitters at the synapse.
What is the directionality of synapses?
Each synapse is unidirectional, and the response to a stimulus may be either excitatory or inhibitory.
What is entrainment in the context of synapses?
The phenomenon where the more a pathway is used, the easier it is to access.
What separates the terminal bouton from the effector cell?
The synaptic cleft.
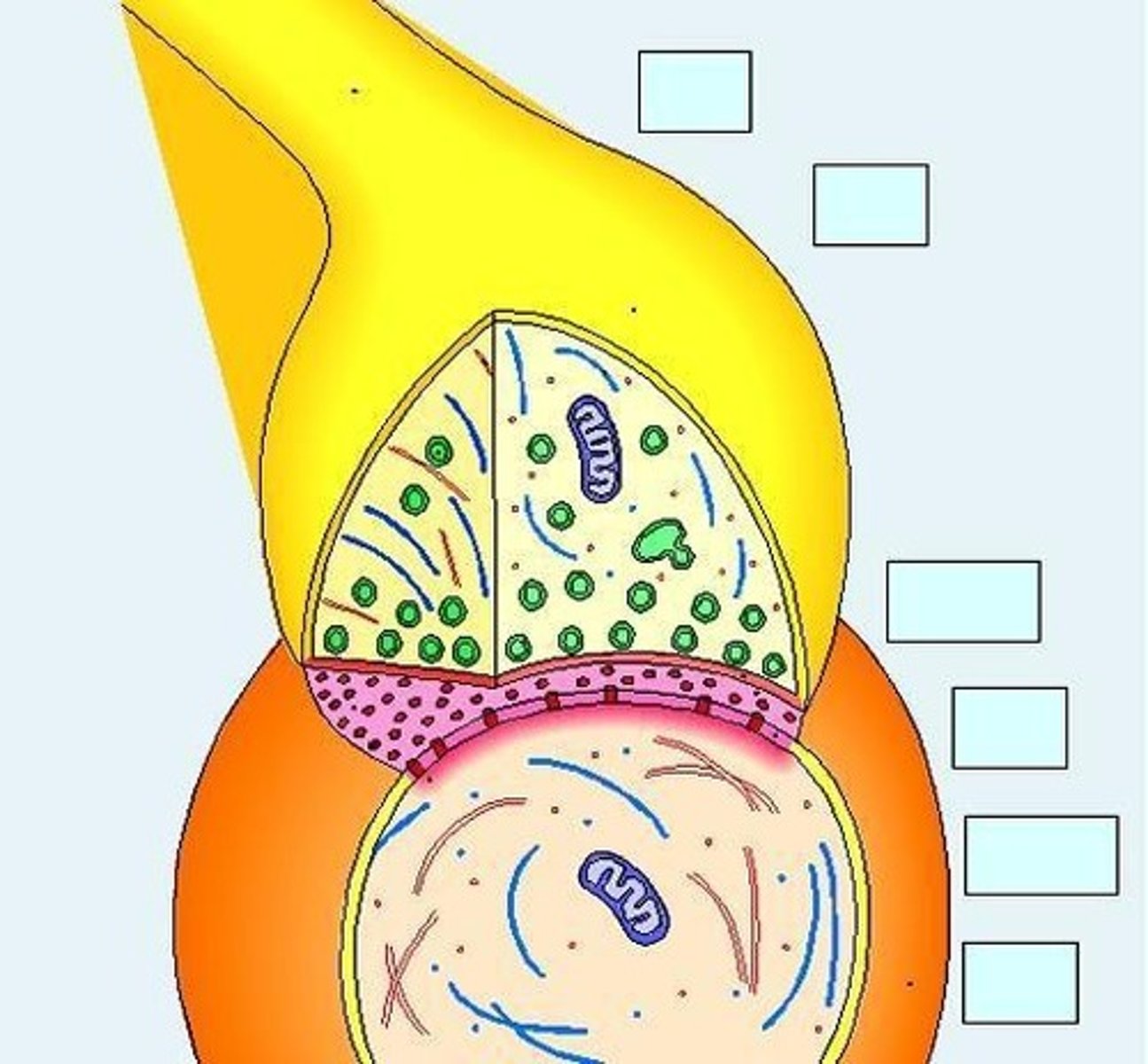
What do synaptic vesicles contain?
Chemical neurotransmitters that are released from the presynaptic membrane.
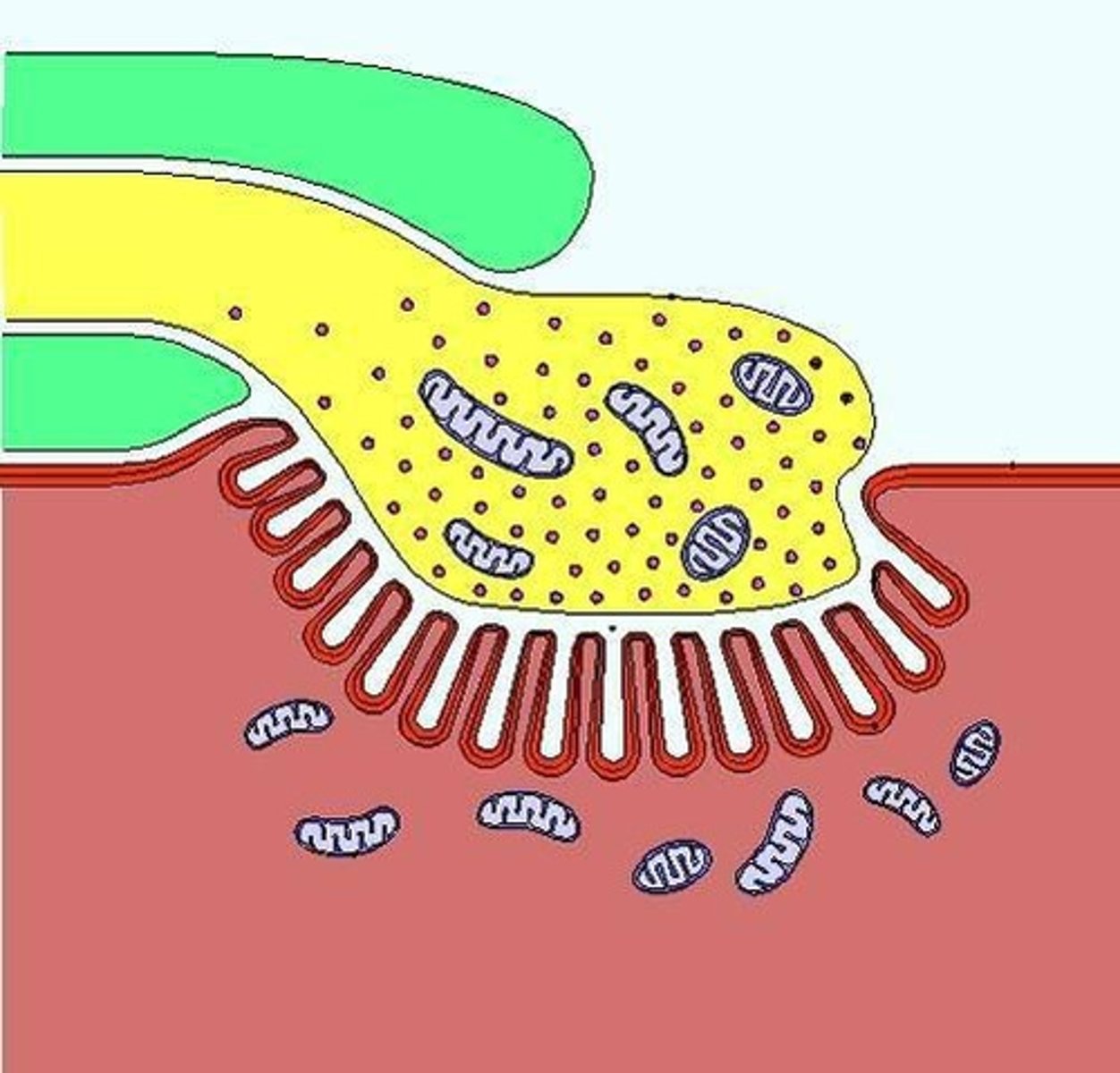
What happens to neurotransmitters after they are released?
They diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules on the postsynaptic membrane.
What is the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)?
It is the junction where a motoneuron embeds itself in a skeletal muscle cell.
What are the two main neurotransmitters used in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Acetylcholine and norepinephrine.
What is the role of norepinephrine in the sympathetic nervous system?
It acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in the 'fight or flight' response. Adrenergic
What are the neurotransmitters used in CNS?
GABA, dopamine, serotonin.. etc
What neurotransmitter is used in the parasympathetic nervous system?
Acetylcholine, which promotes relaxation. Cholinergic
What enzymes are found on the postsynaptic membrane?
Hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes, such as acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase (MAO).
What is the function of acetylcholinesterase?
It inactivates neurotransmitters between consecutive impulses to prevent continuous stimulation.
What are the structural components of a nerve in the PNS?
The nerve is organized into epineurium, perineurium, and endoneurium.
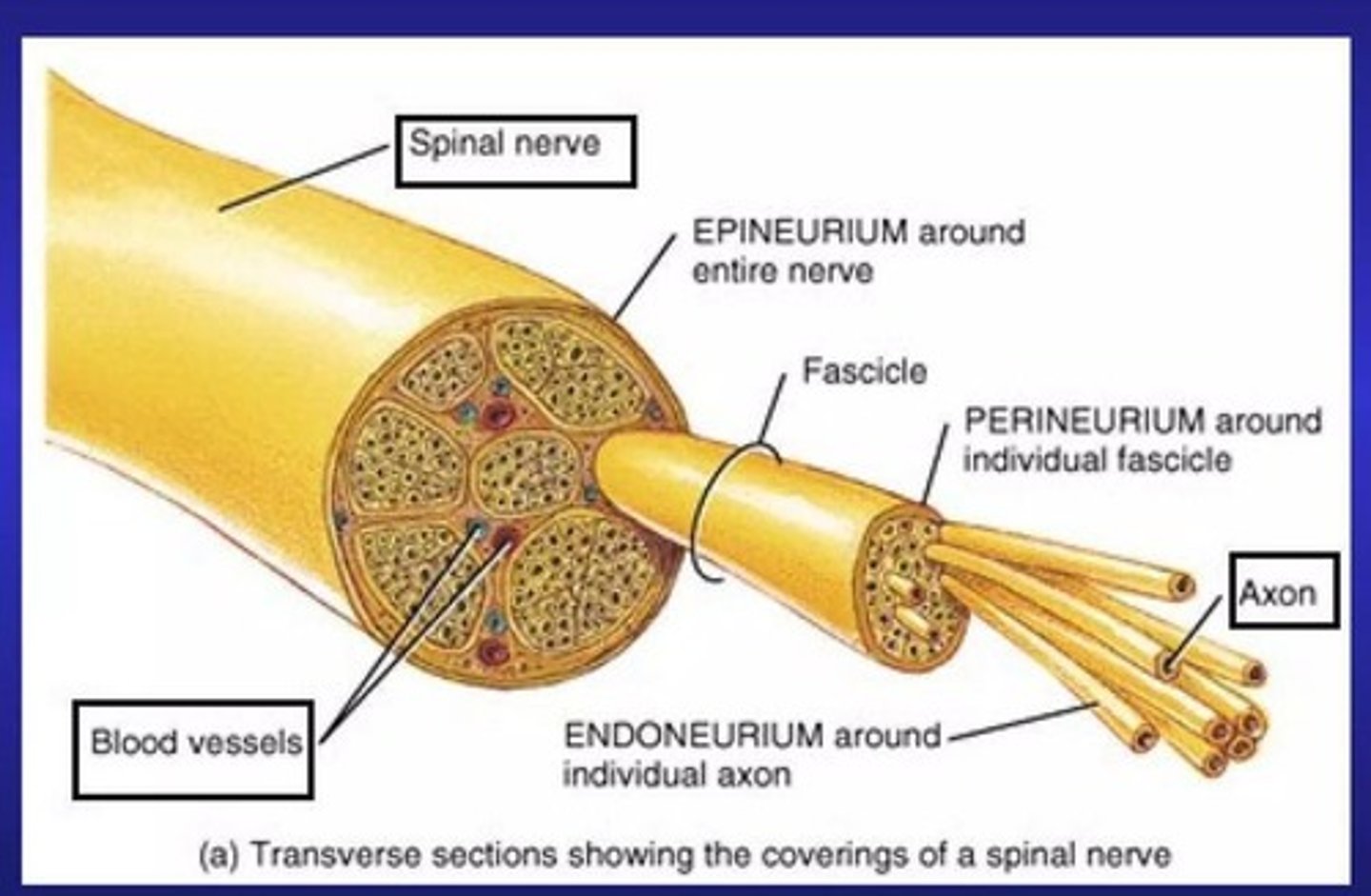
What surrounds individual axons in peripheral nerves?
Loose connective tissue called endoneurium.
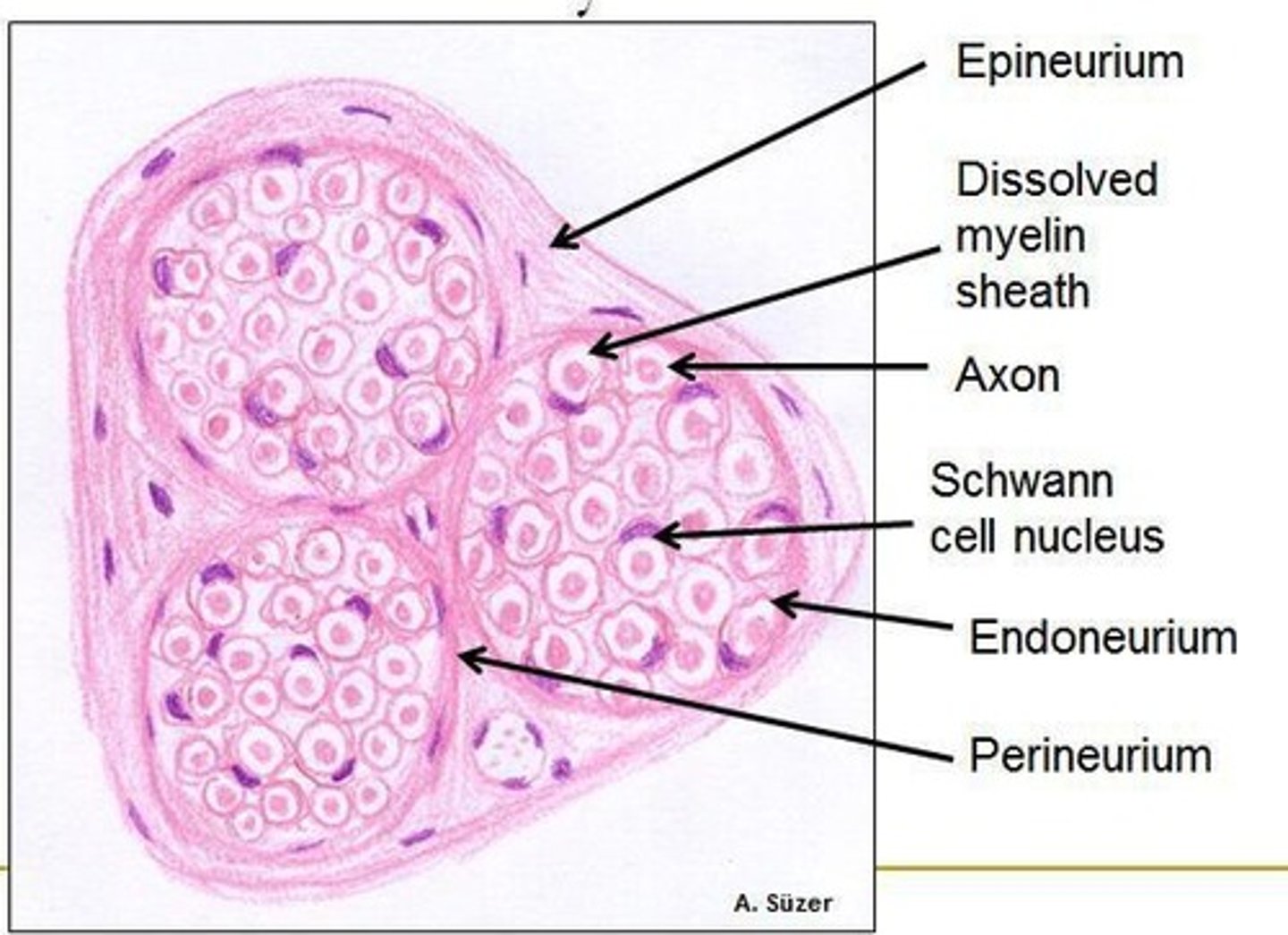
Individual axon and schwann cells are surrounded by _____
Endoneurium
What is the structure that organizes multiple axons into bundles?
Fascicles, which are surrounded by perineurium.
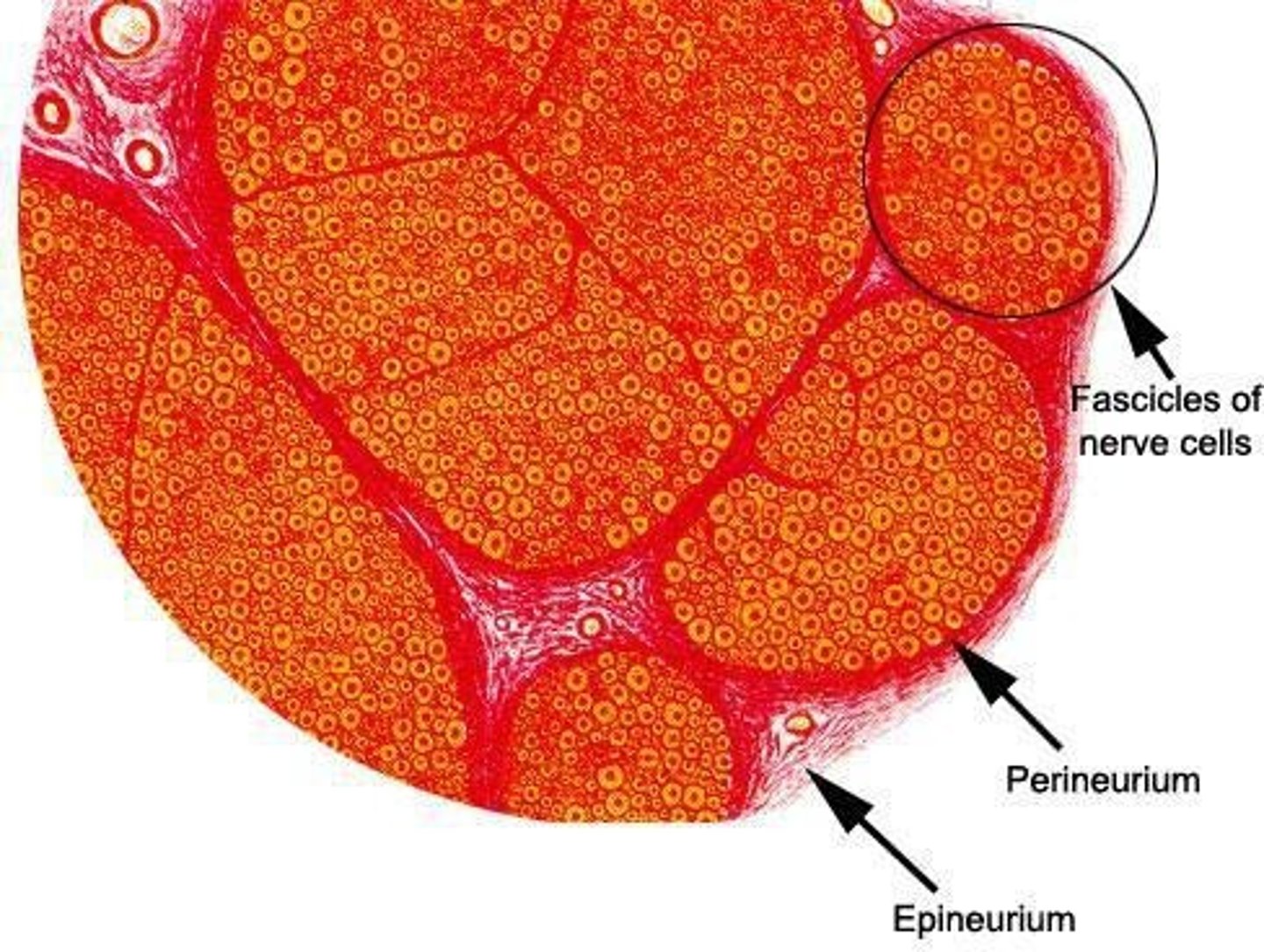
What unique features do cells of the perineurium exhibit?
Epithelioid and myoid features, which may play a role in axon regeneration.
What is the outermost layer of connective tissue surrounding larger nerves?
Epineurium.
What are the two types of fibers contained in peripheral nerves?
Afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers.
Where are the cell bodies of peripheral nerves located?
In the central nervous system (CNS) or in ganglia.
What is the role of Schwann cells in peripheral nerves?
They provide metabolic support and electrical insulation to axons.
What distinguishes myelinated nerves from non-myelinated nerves?
Myelinated nerves are insulated by concentric layers of Schwann cell membranes, while non-myelinated nerves have several axons lying in channels within a single Schwann cell.
What are the gaps in the myelin sheath called?
Nodes of Ranvier.
What type of conduction occurs at the nodes of Ranvier?
Rapid, 'saltatory' conduction.
What are the two types of neurons in the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Preganglionic (presynaptic) and postganglionic (postsynaptic) neurons.
Where are the cell bodies of preganglionic neurons located?
In the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord.
Postganglionic or post synaptic neurons with cell bodies are located in ____
Ganglia
What are ganglia?
Discrete aggregations of postsynaptic neuron cell bodies located outside the CNS.
What types of ganglia exist in the peripheral nervous system?
Sensory (dorsal root ganglia) and autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) ganglia.
What surrounds the neuronal cell bodies in ganglia?
Satellite cells, which provide structural and metabolic support.
Where are sympathetic ganglia located?
Parallel to the vertebral column, including prevertebral (ganglia located anterior spine) and paravertebral ganglia (sympathetic trunk).
What is the location of parasympathetic ganglia?
In or near effector organs, such as between smooth muscle layers of the gut wall.
Multipolar neuron is a _______ motor neuron, and is found in _______ horn
Somatic, ventral
Pseudounipolar neuron is a ________ sensory, and is found in ________
Somatic, dorsal root ganglion