ch 23 - Brain Development and Plasticity
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
what are the three main approaches to studying brain development?
looking at the maturation of different brain structures and correlate that development with the emergence of specific behaviors
observe behaviors that emerge and make predictions about the neural changes that would support that behavior
identify factors that influence the development of both the brain and behavior
when does the neural plate fold into the neural tube?
21-25 days gestation
the neural tube is a rolled up sheet of cells that will form the ___
brain and spinal cord
after the neural tube forms, what structures begin to develop?
forebrain, midbrain, and hind brain
what is the major developmental point at 100 days (14ish weeks)
the brain has normal shape (no gyri/sulcu)
sulci and gyri start to develop at ___. full gyrification is present at ___
sulci and gyri start at 7 months gestation, gyrification present at 9 months gestation
what is different about a brain at 9mos gestation and an adult brain?
cellular structure (but gyrification is the same)
what are the two principal features of brain development?
cell destination and function are predetermined
development moves from overabundance to pruned efficiency via apoptosis
when does neurogenesis (and cell migration) occur? synaptogenesis?
neurogenesis and cell migration are largely complete by birth. synaptogenesis begins before birth and continues (along with neuronal maturation and myelination) for the first several months after birth
how do the different brain regions differ developmentally?
developmental changes take place at different rates in different brain regions
what major brain region is the first to develop and finish pruning?
sensorimotor cortex
what major brain region is the last to finish developing and finish pruning?
prefrontal cortex
list the stages of brain development
cell birth (neurogenesis + gliogenesis)
cell migration
cell differentiation
cell maturation
synaptogenesis
cell death and synaptic pruning
myelogenesis
in which developmental stage does dendrite and axon growth occur?
in the cell maturation (4th) stage
where do neural stem cells grow out of?
neural tube
what are progenitor cells? what are they produced from and what do they produce?
progenitor cells are precursor cells. they are produced from neural stem cells. progenitor cells produce neuroblasts and glioblasts that mature into neurons and glial cells.
do neuroblasts and glioblasts divide?
no
what lines the subventricular zone in adults?
stem cells
where does neurogenesis occur in adulthood?
olfactory bulb/caudate and in hippocampus.
describe the first stage of neurodevelopment.
1: neurogenesis
neural stem cells grow out of the neural tube and produce progenitor cells that mature into neurons and glia
during cell migration, cells migrate along ___ from the ___ to the ___
cells migrate along radial glial fibers from the subventricular zone to the surface of the brain
cortex is built from
inside out
outside in
inside out
___ has “map” of cortex and ___ are like roads headed there
ventricular zone is map, radial glia are roads
cortex is formed by ___ but cell migration continues to about ___
cortex formed by 4.5 months gestation, but cell migration continues to about 8 months after birth
brain has an increased sensitivity to trauma in what phases of neurodevelopment?
stages 2/3: cell migration and differentiation
disturbances to cell migration usually leads to
seizures, dyslexia, other neurodevelopmental disorders
what animal is used in research for a model of when cortex is built outside in?
reeler mouse
describe the second and third stages of neurodevelopment.
2/3: cell migration and differentiation
cells migrate along radial glial fibers from the subventricular zone to the surface of the brain, building the cortex from inside out. neurons differentiate and migrate to the associated location (ex. visual cortex neuron → occipital lobe)
what are the steps of neural maturation?
dendritic development
axonal development
how is cell maturation determined by the dendrites (think about a neuron stain)
during the maturation process, neurons develop more dendritic arborization and dendritic spines
compare and contrast dendritic growth and axonal growth
dendritic: slow process
axonal: faster process
what is the purpose of dendritic arborization and developing dendritic spines?
increase surface area for synapses with other cells
why is is important that axons grow faster than dendrites?
axons have a further distance to go. it allows dendrite and axon to reach synapse at same time
failure of the axon to reach appropriate target results in
death of the neuron (the whole neuron, not just axon)
axonal growth can be disrupted by
blocked path (like from scar tissue), abnormal development, damage to axon’s target
athetosis
slow involuntary movements. can result from incorrect pathway formation during the axonal growth stage.
dystonia
imbalances in muscle tone. can result from incorrect pathway formation during the axonal growth stage.
as a way for axons to overcome obstacles to reach their targets: if spinal cord is damaged, ___ axons can cross to undamaged side and recross
pyramidal tract
describe stage 4 of neural development
4: neural maturation
cells have migrated and are in place. now they develop their dendrites (slow process), then their axons (fast process). the dendrites and axons mature at their separate paces in order to meet their targets at the same time.
___ guide the formation of synapses (3 things)
genes, cues, and signals
what are the five phases of synapse formation?
1 and 2: synapses generated independently of experience (in utero)
3: rapid growth from birth to age 2
4: plateau and rapid elimination through puberty
5: another plateau in middle age, then steady decline with older age (experience dependent)
___% of synapses lost through puberty
50%
experience expectant synapses
development depends on the presence of sensory experiences (phases 3 and 4 /birth-puberty)
experience dependent synapses
generation of synapses that are unique to the individual (phases 3, 4, 5/everything post birth)
experience expectant and experience dependent are both types of
plasticity
experience-(expectant/dependent): visual cortex synapses depend on exposure to features such as line orientation, color, movement
expectant
experience-(expectant/dependent): Visual system synapses correspond to learning of specific visual info (ie., facial features)
dependent
dendritic spine loss (pruning) continues in the ___ until the 30s
PFC pyramidal neurons
___ areas lose synapses before PFC does
primary sensory
spine density on pyramidal neurons in the DL PFC peaks around age ___
5
describe stages 5 and 6 of neural development
5/6: synapse formation and pruning
synapses form in utero and after birth (until puberty), then pruning of synapses occurs throughout the lifespan. formation and pruning occurs at different rates for different areas of the brain.
when does glial development begin and end?
it begins after neuronal development and continues throughout life
when does myelination begin and end?
myelination begins after birth and continues into adulthood.
rough marker of cerebral maturation
myelination
what cortical area is myelinated first? which is last?
sensory areas first, association cortex last
which scientist produced a map that shows the progress of myelination?
Flechsig
areas early to myelinate control ___. areas later to myelinate control ___.
early - simple movement or sensory analyses
late - higher mental functions
describe stage 7 of neurodevelopment
7: myelogenesis
astrocytes and oligodendrocytes form, and myelination begins (after birth). myelination occurs throughout life, with areas associated with higher mental functions finishing last.
anencephaly
cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, and midbrain are absent
holoprosencephaly
cortex forms as a single undifferentiated hemisphere
lissencephaly
brain fails to form sulci and gyri and corresponds to that of a 12 week embryo
micropolygyria
gyri are more numerus, smaller, and more poorly developed than typical
macrogyria
gyri are broader and less numerous than typical
microencephaly
development of the brain is rudimentary and the person has low intelligence
porencephaly
cortex has symmetrical holes where the cortex and white matter should be
heterotopia
displaced islands of gray matter appear in the ventricular walls or white matter, caused by aborted cell migration
callosal agenesis
entire corpus callosum or a part of it is absent
cerebellar agenesis
parts of the cerebellum, basal ganglia, or spinal cord are absent or malformed.
adolescence is characterized by
rapid pruning and rapid growth of new connections
gray matter loss is from ___, white matter gain is from ___
neuron and synapse pruning, myelination
spatial and language regions mature at ___
puberty (11-13y)
physical and hormonal changes are related to
patterns of brain maturation
vocabulary scores correlate (negatively/positively) with thickness of the cortex during development
negatively
(more cortical thinning = better vocab development)
vocab findings are more ___ in left hemi and ___ in right hemi
more widespread in left, focal in right
how does prefrontal-subcortical circuitry change throughout the lifespan?
overall, the connections between prefrontal and subcortical areas become stronger.
go from more subcortical-subcortical connections to cortico-subcortical circuits
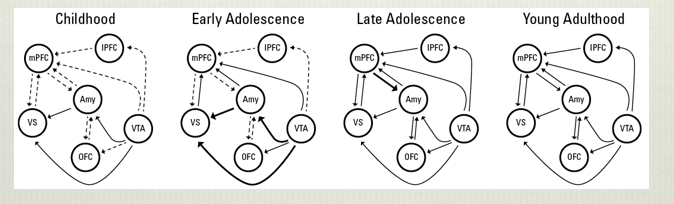
studies of white matter connectivity showed that ___ fibers develop before ___
interhemispheric before intrahemispheric
children with ADHD have a reduced volume of ___ matter in the ___
gray matter in PFC
sometimes, kids with ADHD have a decrease in PFC gray matter volume that is not permanent, but instead represented ___
a delay of about 2.5 years for the development of gray matter compared with non-ADHD controls
The brain regions associated with response inhibition were significantly larger in ___ than ___
larger in children than adults
brain growth spurt periods line up fairly well with ___
Piaget’s stages of cognitive development
theres a ___% increase in brain weight in each growth spurt
5-10%
Both human and monkey infants learn the discrimination task earlier than the non-match to sample task. this suggests…
brain regions that support the easier task must develop sooner than those that support the harder task
in utero environmental effects on brain development
mother’s exposure to stress, prescription drugs, recreational drugs, caffeine
microbiome
epigenetics
lead poisoning
SES
Kennard Principle
Functions are spared when injury occurs during infancy, the earlier the better for regaining function (more plastic)
how was the Kennard principle modified by Hebb?
found that injury too early is also bad
what age has the best prognosis for brain injury?
1-5 years