Week 2 - Main Challenges of Food Security
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what are the 10 main challenges to global food security

why is the rising human population a problem?
need more food to feed more people → placing further pressure on our limited resources
but producing more food cannot tackle the vast amount of food wasted before and after reaching our plates
what is the current world population
over 8.2 billion people
how much more food is needed to feed the world’s population is 2050
~50% increase in global food production
how is rising income a food security challenge?
↑ economies
transition toward westernized diets
∆ in food purchasing & marketing = ↑ prices
→ socio-political issues
western diet vs traditional diets
more grain-intensive livestock & poultry products
Issues with this
↑ meat = ↑ greenhouse gas emission
Which animal meat has best feed conversion ratio?
fish > poultry > pig > beef
what are the 3 main sources of water usage
Mainly agriculture → pressure on freshwater resources
Household
Industrial use
what are the 3 reasons for water scarcity
Population growth
Socioeconomic growth → shifting diets
Climate change → melting glaciers
how is foodless days a food security problem?
Used to be dominated by surpluses → Now: scarcity
(the world’s poorest are not eating at all on some days to cope with ↑↑ grain prices)
what is the problem with soil erosion?
losing topsoil faster than new soil is forming
this reduces land fertility
threatening future food production
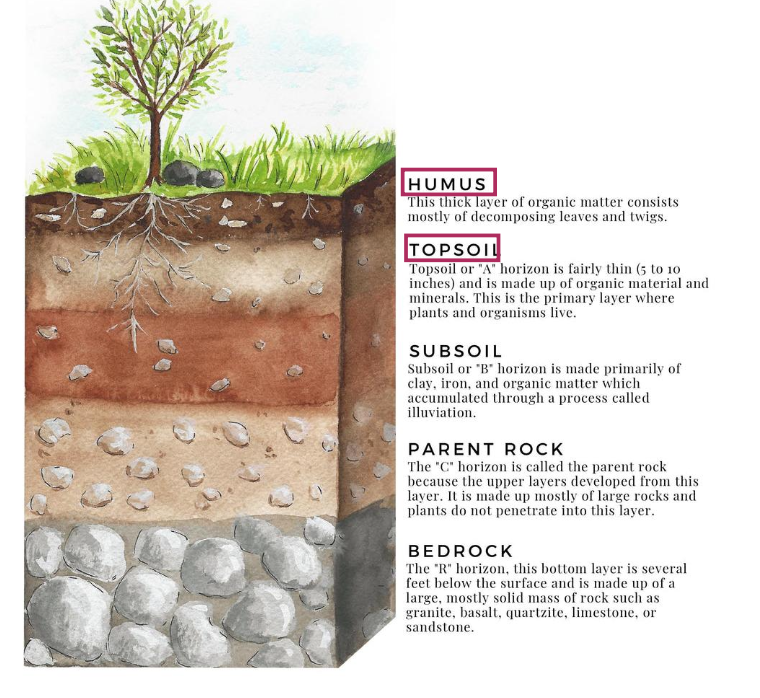
humus vs topsoil
humus = thick layer of organic matter - consisting mostly of decomposing leaves & twigs
topsoil = thin. makde up of organic material & minerals. this is the primary layer where plants & organisms live
what is the issue with flattening yields
Use of fertilizer + GMO → ↑↑ grain yield BUT reaching plateau
rice & wheat & corn
how do climate change and food production affect each other
food production affected by increased frequency of storms, droughts & other extreme weather events
climate change is worsened by greenhouse gas emissions, water scarcity & wider biodiversity issues
how does climate change affect our global food security?
affect crop & livestock production (e.g., yield reductions, especially in tropical areas)
negatively impact fisheries & aquaculture (50% of animal protein)
negative impact on food availability, rural incomes & access to food
will the impact of food production be the same across all regions of the world?
Impacts will be location specific & vary strongly across crops & regions
Up to a certain point, warmer temperatures may benefit the growth of certain crops in some parts of the world
In general, higher latitudes will tend to see smaller yield losses, or even yield gains, while yield losses in lower latitude regions are expected to be greater
how is overconsumption & waste a food security problem?
↑ pressure on food system
↑ obesity & diet-related illnesses
how much of the world’s food is lost or wasted world wide
⅓ of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted world wide
how is cost & availability of healthy diet a food security issue?
The high cost of healthy diets is associated with
increasing food insecurity
different forms of malnutrition (including child stunting & adult obesity)
how are pandemics a threat to food security?
Lockdown → economic threat to food security
Rising food inflation
Food trade restrictions (supply chain disruption)
Economic decline & instability
what are some potential solutions to food insecurity?
Science, innovation & technology
Distribution
Local food systems
Strong regulations
Willingness to act
what is the “Farm-to-fork/table” strategy
= creating a sustainable food system that covers all stages from food production on farms to consumption on plates.
Published by EU Green Deal.
Link healthy people, healthy societies & healthy planet
Improve lifestyle, healthy & environment
what are the objectives of the “farm to fork/table” strategy
reduce the environmental & climate footprint of the food system
strengthen resilience to ensure food security in the face of climate change & biodiversity loss
lead a global transition towards competitive sustainability from farm to fork
tapping into new opportunities (research & innovation)
what are the EU’s targets for 2030 for sustainable food production
reduce use of pesticides
reduce nutrient losses
reduce use of antimicrobials (for farmed animals & aquaculture)
increase percentage of organic farming