Anatomy - intro lectures
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
Head, eyes , and toes are pointed anteriorly (forward)
Anatomical position
Upper limbs are at the sides with the palms facing anteriorly
Anatomical position
Reference position when discussing the body
Anatomical position
Starting position for range of motion measurement (ROM)
Anatomical position
4 planes of motion
median (mid-sagittal)
Sagittal
frontal
Transverse (axial)
This plane passes longitudinally through the midline of the body and divides it into equal ___ and ____ halves.
■ The foot and the hand have their own median planes (3rd toe and digit)
■ Can also be called the mid-sagittal plane
Right , Left
Median
Planes run ____ to the ____
■ Create infinite cross-sections of the body
■ The median plane is a ____plane located at the midpoint of the body
parallel, median
Sagittal
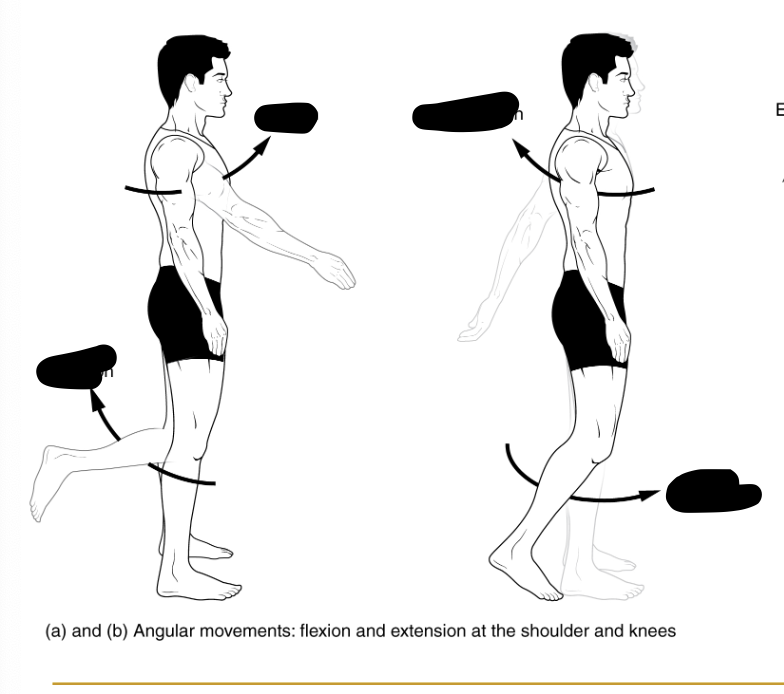
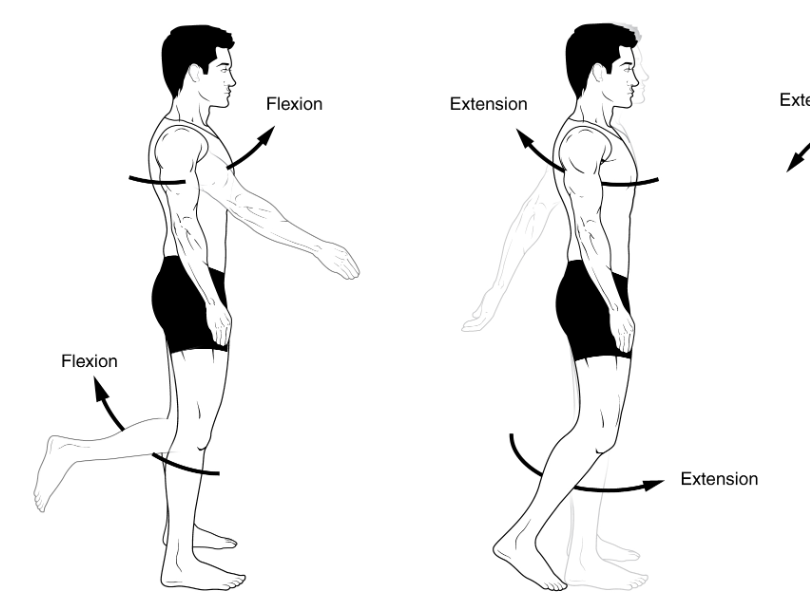
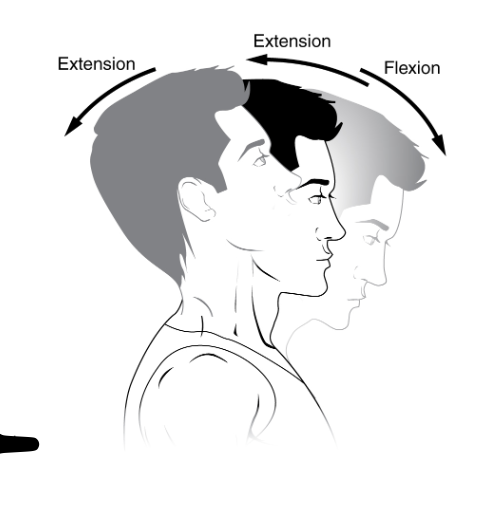
increasing the joint angle between body parts
Extension
decreasing the joint angle between body parts
flexion
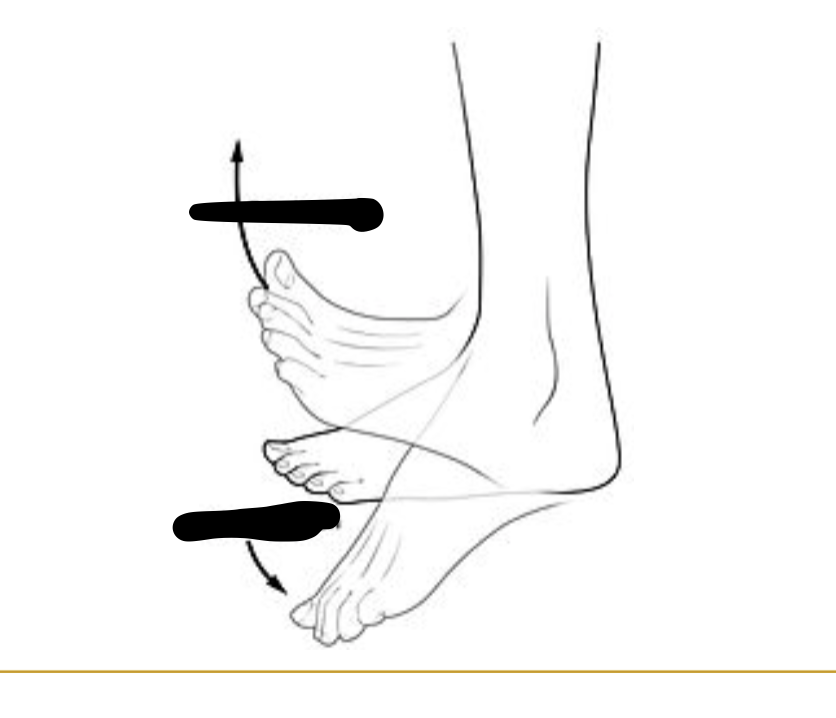
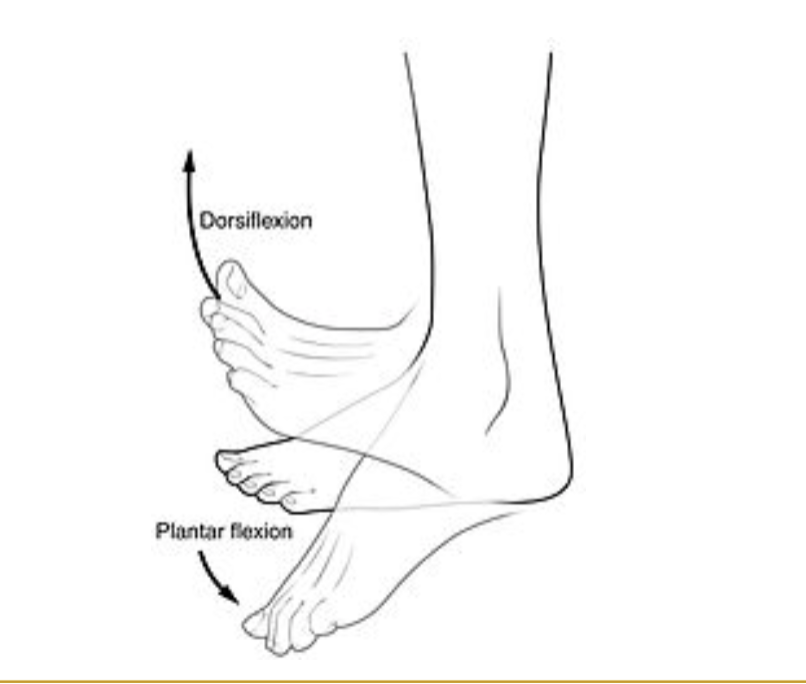
Occur specifically at the ankle
Dorsiflexion and Plantar flexion
sagittal plan movements (4)
Flexion
Extension
dorsiflexion and plantarflexion
Runs from top of the head to bottom of the feet and divides the body into ____ and
____ halves
■ Can also be called the coronal plane
■ The feet have their own ____ plane
front and back
frontal
Movement away from the median plane
Abduction
Movement toward the median plane
Adduction
The median for the hand is ___ digit and the foot is __ toe
3rd (middle finger )
Frontal Plane Movements (2)
abduction and adduction
Runs horizontally through the body and divides the body into
____and _____ (top and bottom)
■ Can also be called the axial plane
superior and inferior
Transverse
occurs about a vertical axis
❑ The direction of movement is horizontal and, therefore, in the _____ plane
Rotation
transverse
Traverse plane movement (1)
Rotation
(supination and pronation, inversion and eversion) included
Moving from the surface of the body inward (3)
superficial, intermediate, deep
closer to midline
medial
farther from median plane
lateral
in front of
anterior
behind
posterior
closer to center of body
proximal
farther from center of body
distal
higher on body
superior
lower on body
inferior
closer to the front surface of body
ventral
closer to back surface of body
dorsal
towards the head of the body
cephalad
toward the tail of the body
caudad
same side
ipsilateral
Opposite side
Contralateral
below and toward the midline
inferomedial
above and towards the midline
superolateral

Movement of the forearm and the hand that rotates the radius laterally around the longitudinal axis
❑ Bones of the forearm are parallel
❑ Palm of the hand faces anteriorly
❑ Also used to describe combination of movement of the foot
Supination
Movement of the forearm and the hand that rotates the radius medially around the longitudinal axis
❑ Bones of the forearm are crossed
❑ Palm of the hand faces posteriorly
❑ Also used to describe combination of movement of the foot
Pronationlea
leaning weight on pinkie toe (sole of foot inwards up)
inversion
leaning weight on big toe (sole of foot outwards up)
eversion
Movement of the scapula anteriorly
❑ Imagine the scapula moving anteriorly along the rib cage
top of push up
Protraction
Movement of the scapula posteriorly
❑ Imagine the scapula moving posteriorly along the rib cage
bottom of push up
Retraction
Location of muscle attachment for the stationary bone
origin
Location of muscle attachment for the bone that it moves
Insertion
Movement(s) a muscle makes
action
Nerve supply to a muscle
innervation
using one’s hands to feel or examine structures within the body
palpation
prominent features within body structures that assist in the identification of those or
other structures
landmarks
Connective tissue composed of (3)
cells - fibroblasts (build), immune cells (protect/clean up), adipocytes (repair), etc
fibers - Collagen, Reticular, Elastic
ground substance - liquid around cells contain water, minerals, proteins, etc.
fibers and ground substance referred to
extracellular matrix
Connective Tissues - FIBERS are
collagen
long strands of protein that offer tensile strength and flexibility
over 28 types
collagen
Most common
■ Found in tendon, ligament, muscle and bone
strongest type
Type I collagen
Found in articular cartilage
Type II
Found in pliable tissues such as blood vessels and in wounds
Type III collagen
thin, branching proteins that are comprised of a specific kind of Type III collagen fibers
reticular fibers
Acts as a supporting net in soft tissues and organs
Reticular fibers
Wavy bundles of the protein elastin that can tolerate stretch
Elastic fibers
Allows tissues to return to original shape following stretch
Elastic fibers
Nerves
■ Bones
■ Muscles
■ Tendon
■ Ligament
■ Synovium
■ Cartilage
■ Fascia
Specialized tissues
Made up of neurons and support cells
Nervous Tissue
Neurons conduct ______ impulses
electrical
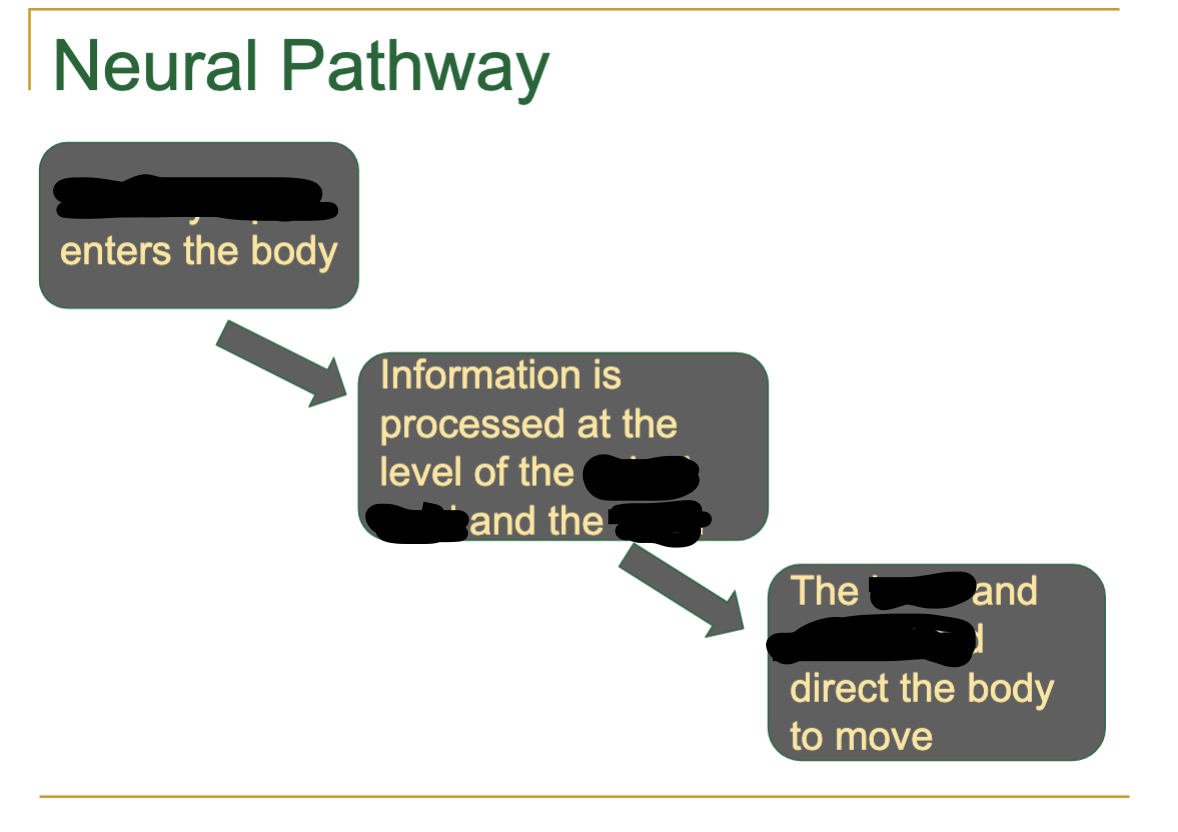
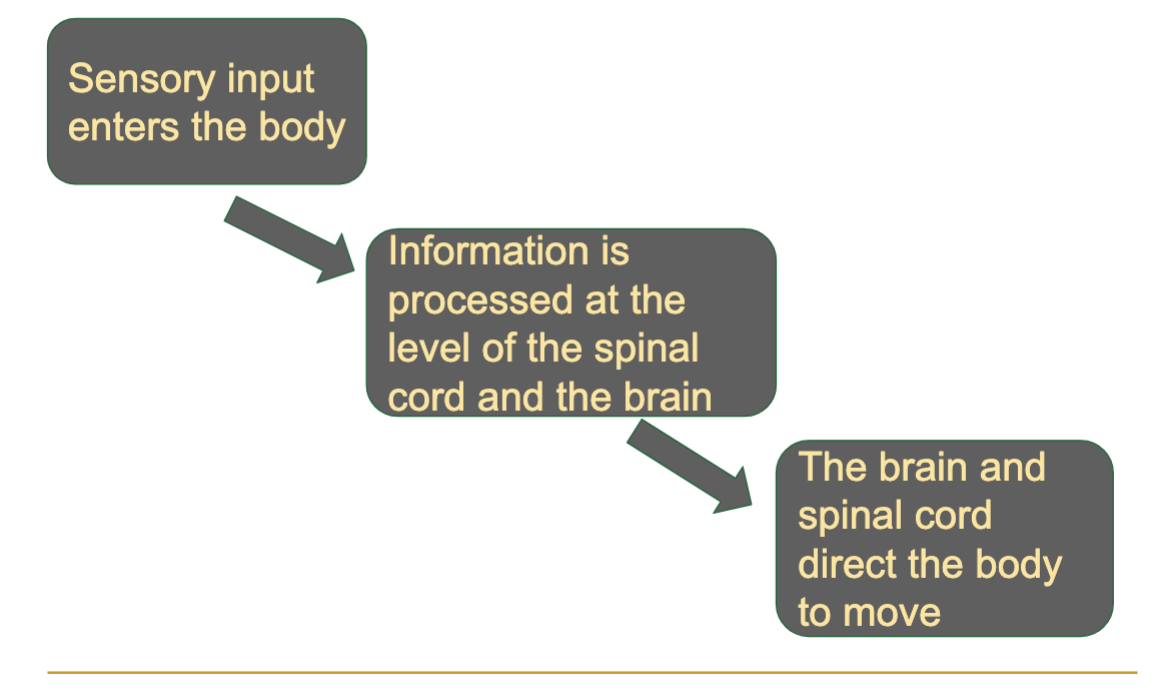
electrical impulses From the environment to the brain
this is a ??
sensory input
dendrite
electrical impulses from the brain to the body
motor ouput
nervous tissue Includes the ____ and _____ nervous systems
central and peripheral
In the CNS, divided into ____ ____ (cell bodies) and _____ ____ (axons)
grey matter
white matter
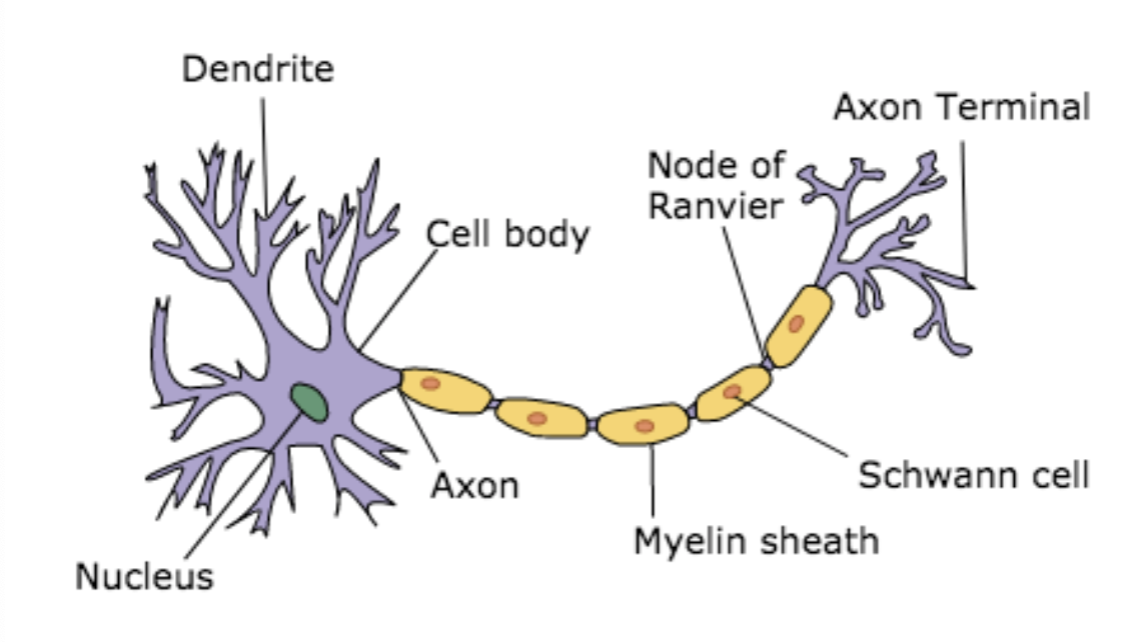
structure of neuron (3)
dendrites
cell body
axon
support cells - glia
“input” portion of the cell
dendrites
information processing portion of the cell contains organelles
this is a ??
cell body
“output” portion of the cell
axon
structure of spinal nerve
Bundles of _____,
____ vessels, and
_____ tissue
entering and exiting the spinal cord
nerves
blood vessels
connective tissue
osseous tissue =
bone tissue
Bone is comprised of (2)
collagen
mineral deposits
Purpose of Bone:
❑ Storage of _____
❑ Formation of ____ cells
❑ Protection of vital ___
❑ Support for body and mechanical basis for movement
Ca++
blood
organs
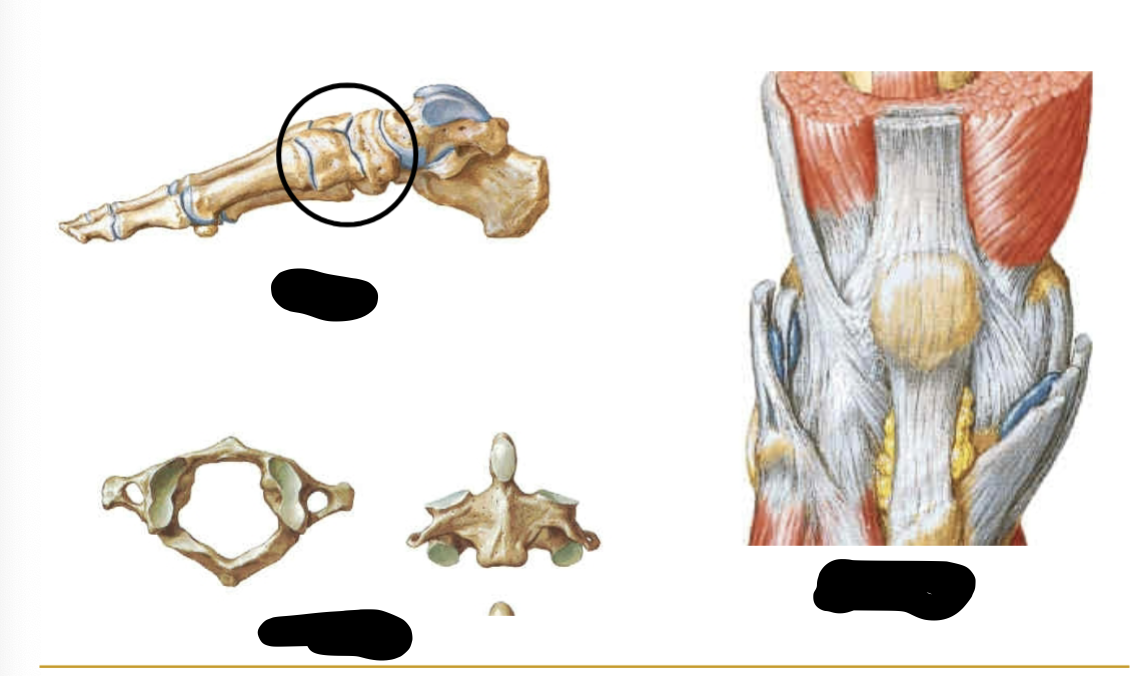
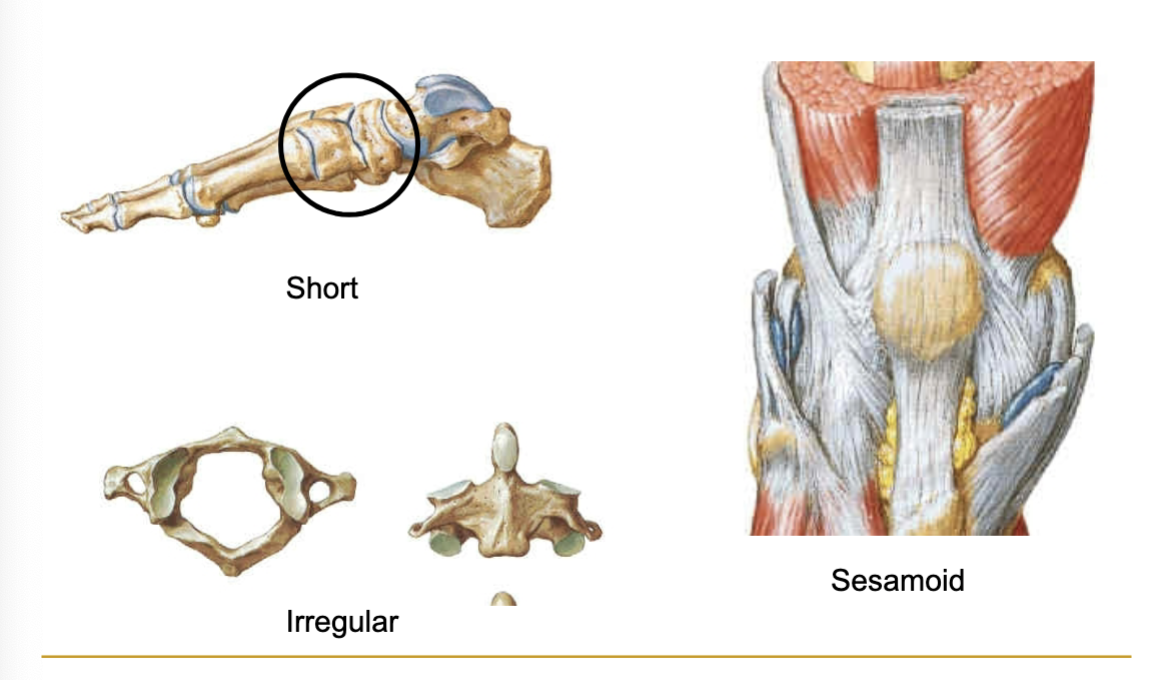
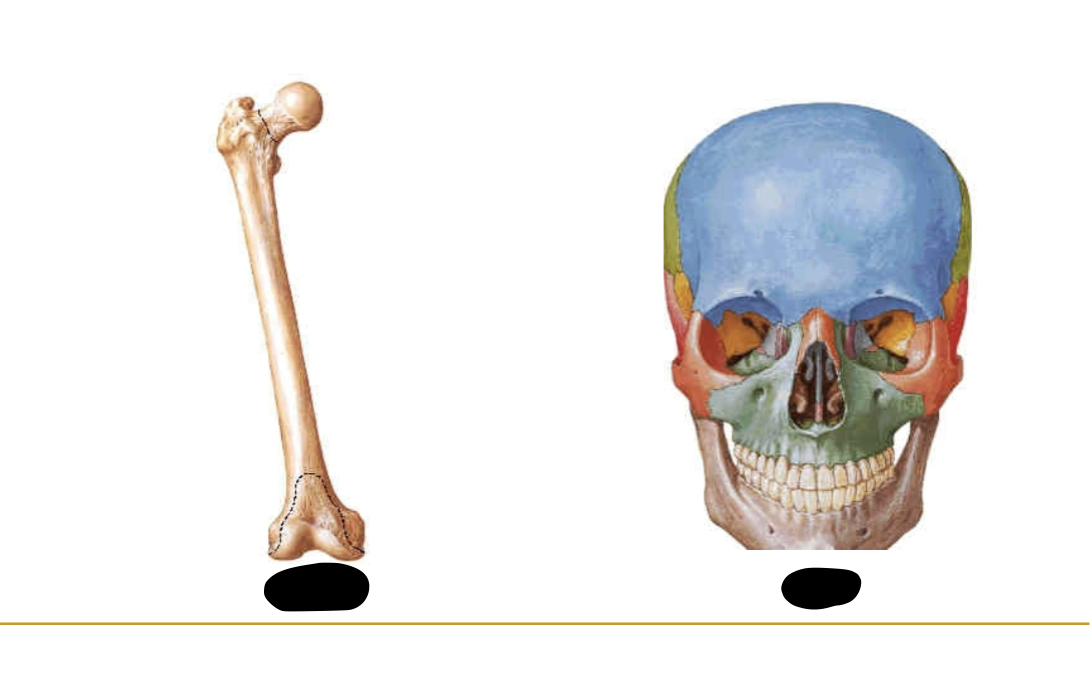
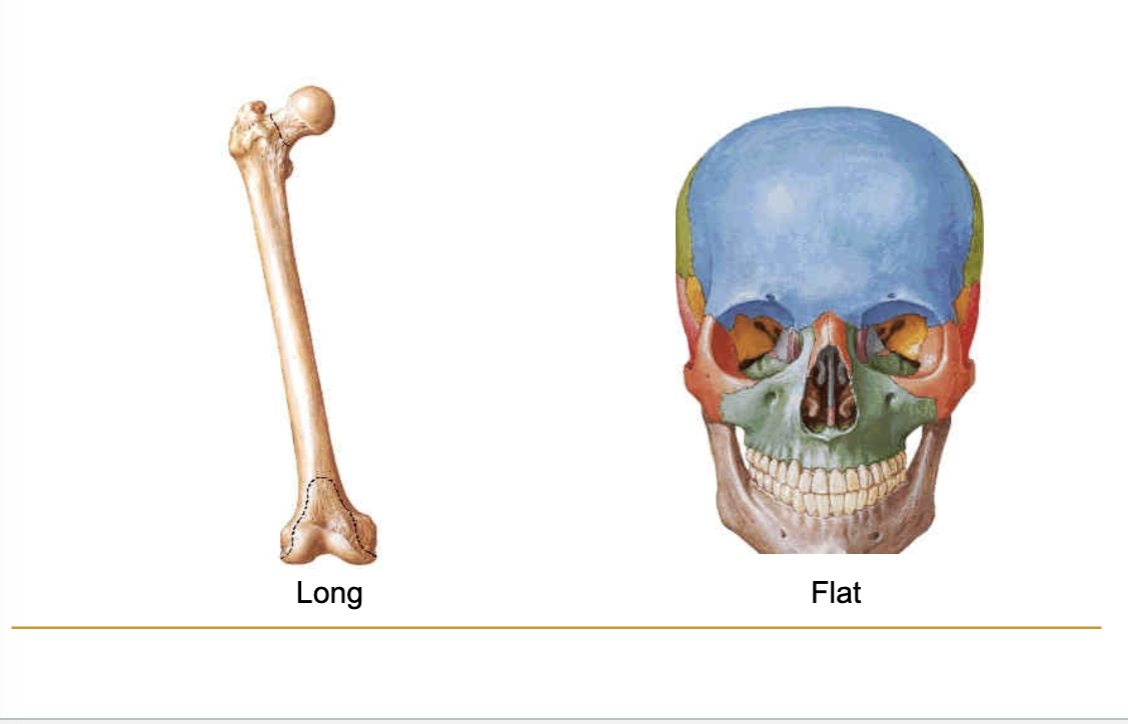
WHAT BONE? Tubular (e.g. Humerus and Femur)
Long
WHAT BONE? Cuboidal (e.g. Carpals and Tarsals)
Short
WHAT BONE ? Protective function (e.g. bones of cranial vault)
Flat
WHAT BONE? Bones of the face and vertebral column
irregular
WHAT BONE ? Protect tendons from wearing (e.g. patella) (resembled sesame seeds)
Sesamoid
Bone is a living, dynamic ____
■ Bone needs ____ supply to live
❑ Rich arterial supply
■ Without blood supply it will __
❑ Avascular Necrosi
tissue
blood
die
Fracture healing requires adequate _____ ____
❑ Elderly population: increased time for healing due to decreased circulation or nutrition deficits
Blood Supply
Four stages of bone healing
❑ Inflammation
❑ Soft callus formation
❑ Hard callus formation
❑ Remodeling
Length of time to heal bone variable based on
_____ type,
_____,
____ of fracture
fracture
site
size
Immobilization can range from _ weeks for smaller bones
to _+ weeks for the long bones
3
8+
Healing continues once the ___/___ is removed
❑ ___ will eventually be reabsorbed during remodeling stage of healing
splint/cast
callus
Describes bone remodeling (and tissue remodeling)
❑ Growing bone ____ to the forces placed upon it
(i.e. weight-bearing stresses and muscular contractions)
you need to put normal stress on a bone in order for it to grow !!!
“Use it or lose it!!”
adapts
Wolff’s Law
Absence of “normal stress” can lead to _____ and ____
deformity and injury
3 types of muscle
❑ Smooth
❑ Cardiac
❑ Skeletal
__% of body weight (+/-) is skeletal muscle
40
Muscles are ______, _______ working to:
❑ Pump___
❑ Move food through _____
❑ Maintain ____
constantly, unconsciously
blood
intestines
posture
Involuntary muscle lining various organs
Also called visceral muscle.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Responsible for peristalsis, which facilitates movement through the GI tract
Smooth Muscle Tissue