sport psychology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
acronym for mental skills
SCAMS
acronym for mental skill stratergies
GRIPS
two types of positive self talk
positive cue words: single words or short sentences to refocus attention and combat negative thoughts
positive emotions: used to create stronger self belief and positive emotional experiences
how does positive self talk benefit performance
reinforcing skill learning: remind athletes of performance cues
changing bad habits: cue word increase likelihood of correct response
motivating the performer: maintain or lift intensity of performance
focusing attention: key words to focus of task
building self confidence: phrases that reinforce self belief
self talk and stress
reduce stress by helping athlete feel they are good enough to meet demands of the task.
using words ‘ive done this before’ or ‘relax’ can reduce effect of stress
self talk and motivation
self talk can increase their motivation and performance ‘if i quit now the whole team will suffer
self talk and concentration
using key phrases to help maintain concentration, change level or focus on particular aspect.
self talk and arousal
can be used to increase or decrease arousal levels
motivational phrases increase
terms like ‘relax’ or ‘calm’ reduce arousal levels
methods of relaxation
an athlete needs to use technique relevant to the type of stress
progressive muscle relaxation: sequentially contracting and relaxing muscle groups
breathing techniques: promote relaxation by slow deep breathing
music: mellow tunes have calming effect
autogenic training: focus on producing sensations of warmth and heaviness in specific body areas - time consuming
self talk: stop negative self doubt, can be physical cue
massage: help relax physically and mentally
flotation tanks: create environment of minimal stimulation by reproducing weightlessness and removing sight and sound
meditation: focusing the mind on a particular thing for a period, using mantra or blank meditation
relaxation and stress
used to reduce the impact of the physical effects of stress
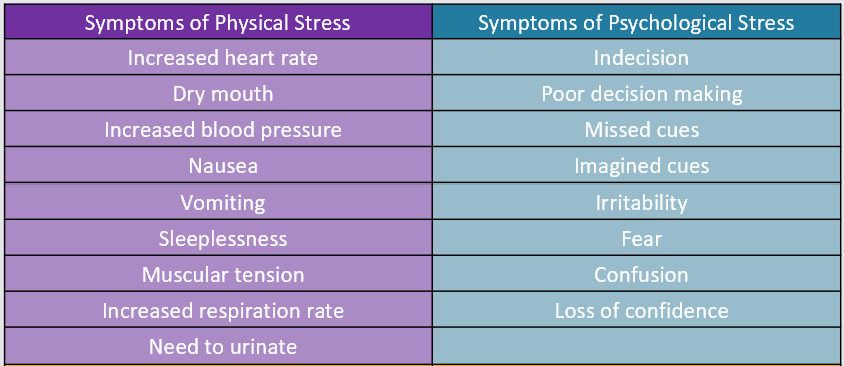
symptoms of physical and psychological stress
relaxation and motivation
athletes highly motivated can experience a decline in performance associated with trying to hard - choking under pressure
over motivated athletes use relaxation to control their thoughts and focus on their performance, rather than thinking of possible outcomes
relaxation and concentration
high level performers can shift from broad to narrow focus
over aroused have narrow focus, limiting ability to concentrate on all relevant cues
using relaxation techniques can help maintain concentration, improving performance
relaxation and arousal
over aroused athletes miss cues and don’t perform at optimal, this happens before and during performance
should use appropriate technique to lower levels
relaxation and self confidence
‘in the zone’, a taper is used to be physically and mentally fresh having increased self confidence
things to consider when making a performance routine
pre comp checklist
use positive self talk
make it repeatable
performance routine and arousal
act as ‘security blanket’ in stressful situations, increase in others
decrease from music
increase with something like Haka
performance routine and stress
reduce stress response as they give the belief that they are in full control, reducing physical effect of stress
use to focus on task not possible outcomes
performance routine and motivation
motivation can be heightened by their game day routine
performance routine and concentration
help focus on relevant cues in environment, ignoring irrelevant. allows them to control their emotions, gather thought and focus on performing task
performance routines and self confidence
can increase self confidence, can relate past successes with routine and feel future success, making them feel in control and confident
how does goal setting improve performance
focusing attention on important elements of skill
boosting self confidence through achievement of realistic targets
helping create positive psychological state
improving intrinsic motivation
improving quality of practices by making it more challenging
encouraging perseverance
enhancing playing skills, techniques and strategies
three types of goals
outcome goals: end results, times, finishing place, ranking or medals
performance goals: independent of other competitors, used to compare past and present performances
process goals: actions that the athletes must perform during a competition to achieve a performance goal
preferable to use a multi goal approach
times of goals
short term: help attain long term goals, stepping stones
long term: achieved by attaining short term goals over long period
SMARTER goals acronym
specific: need to be specific and as clear as possible to focus attention
measurable: need to be able to asses to see if progress is happening
accepted: accepted by all parties involved
realistic: need to be achievable and within athletes capacity
time phased: specific date for completion need to be set
exciting: need to be challenged and inspired
reviewed: goals are monitored and adjustment made if neccesary
goal setting and arousal
can help maintain an optimal level of arousal, resulting in improved performance. having a realistic goal to strive for increases arousal
goal setting and motivation
too easy goals will decrease motivation. effective goals will increase motivation. as short term goals are achieved, self confidence and motivation increase
goal setting and concentration
setting goals enables a performer to concentrate on performance aspect
goal setting and stress
helps reduce stress response giving performance related objectives, reducing like hood of physical stress responses
goal setting and self confidence
have positive or negative impact.
realistic goals will increase self confidence as goals are achieved.
unrealistic goals decrease as goals wont be achieved
types of senses for imagery
kinaesthetic sense: feel our body as it moves through different actions. sensory nerves, joints and tendons give feedback
auditory senses: used to monitor the way your playing environment sounds
tactile sense: allows you to take in how your equipment feels
how does imagery improve performance
increase neural pathways between the brain and muscles
providing mental template of rehearsed sequences
slowing down complex skills so that key components can be isolated and correct movements felt
allowing potential technique problems to be identified
enabling athletes to practice and prepare for events they are likely to encounter during comp
allowing athletes to pre-experience the achievement of goals
two types of imagery
internal: you image what you would see
external: you watch your performance from external view
PETTLEP model of imagery
Physical: should be as physical as possible, correct uniform, equipment
Environment: where the imagery is performed, should replicate as closely as possible
Task: imagine the exact requirements of the task, needs to be specific
Timing: refers to the speed at which imagery is completed, imagine task being completed in real time
Learning: imagery experiences should reflect stage of learning over time
Emotion: ensure optimal level of arousal and specific emotions experienced during performance is replicated
Perspective: internal is most advantageous
imagery and stress
used to reduce stress by creating a mental picture of themselves performing the skill perfectly
stress on highly skilled athletes can improve performance
imagery and motivation
used to motivate to strive for ongoing improvement
imagery and concentration
use for particular skill, aspect of skill or game specific scenario
imagery and arousal
over aroused do not perform at optimal, missing cues, negatively impact production of physical skills
under aroused players fail to perform to potential
arousal can be increased by creating an image of aggressive or successful performance and decreased by creating a more relaxed image in athletes minds
imagery and self confidence
improve by creating mental picture of themselves performing skill perfectly
used before or during comp
group cohesion
a term used to describe the extent to which a group stays together and united in the pursuit of common goals
two factors of group cohesion
task cohesion: how committed are the team member to achieving their predetermined common performance goal
social cohesion: the degree to which team members like each other and enjoy being together
strategies to improve group cohesion
use of leadership
communication
goal setting
team building
roles and expectations
benefits of cohesion
communication and motivation within the group are extensive
increased feeling of group rather than individual
players work together to achieve team goals instead of personal goals
players enjoy each others successes
high cohesiveness is more successful
much more satisfied members
barriers to cohesion
personality clashes
unclear roles among members
frequent changes to group
lack of communication
power struggle between players
factors affecting group cohesion
social loafing: the tendency of individuals to lessen their effort when they are part of the group
leadership: the style the coach and captain use and how this affects the group cohesion
team dynamics: the collective goals of the team
traits of social loafing
decreased effort
late
missing training
expect team mates to cover form
how to minimise social loafing
develop rules of conduct
create appropriate group sizes
write a team contract (group expectations, individual responsibilities, methods of discipline)
rotate responsibility and positions
set challenging individual and team goals each training
make individuals accountable for effort by publishing results
three levels of communication
co-acting activities: little to no communication, resulting in individual scores
mixed activities: combination of co-acting an interacting activities
interacting activities: high level of interaction to achieve goal