BIN300 W9 - Equivalent BLUP models for genomic selection
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Two BLUP models for genomic selection
Marker based model (SNP-BLUP)
G-matrix based BLUP model (GBLUP)
Marker based model (SNP-BLUP)
Estimates effects of markers
assumes markers are NIID distributed (normal independently identical distributed)
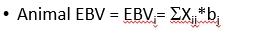
G-matrix based BLUP model (GBLUP)
estimates effects of animals
animals are related through genomic relationships
no marker effects, may be obtained with some difficulty
SNP based model (SNP-BLUP) - formula
• var(b) = total genetic variance divided by the number of markers (m). No dividing by heterozygosity is needed here (contrary to previous lecture) because Xij is standardised (ie. divided by heterozygosity).
•
•genotypes are standardised so that mean is 0 and standard deviation is 1. This is done by substracting the mean of mij, ie. 2pj, and dividing by its standard deviation √(2pj(1-pj)).
SNP-BLUP GEBV
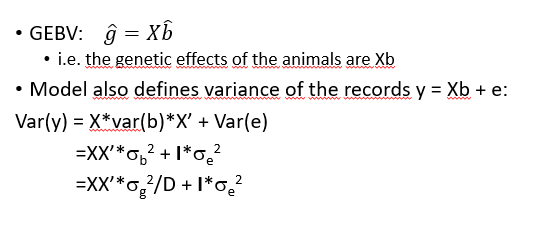
Gmatrix based model (GBLUP
•var(b) = total genetic variance divided by the number of markers (m)
•
•genotypes are standardised so that mean is 0 and standard deviation is 1. This is done by substracting the mean of mij, ie. 2pj, and dividing by its standard deviation √(2pj(1-pj)).
•
•If two models are equivalent means that they are perhaps parameterized in a different way, but for the same parameters, eg. EBVs, they give exactly the same solution. In case of linear models, the models are equivalent if they assume the same mean (here : 0) and the same variance (Var(y)) for the records.

GBLUP and SNP-BLUP are equivalent
Give the same GEBV estimates
no. of equiations to solve differs
GBLUP: n = number of animals
SNP-blup: number of markers
SNP=BLUP estimates of SNP effects
GBLUP: needs inverse of (large) G matrix• Equivalent model means that the models are the same but parameterised differently. For the same parameters they give the same results, ie. they give the same genomic EBV.
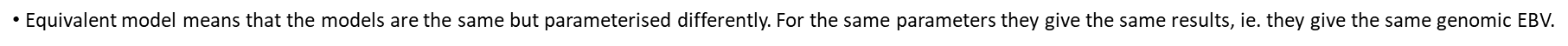

Derivation of equivalence
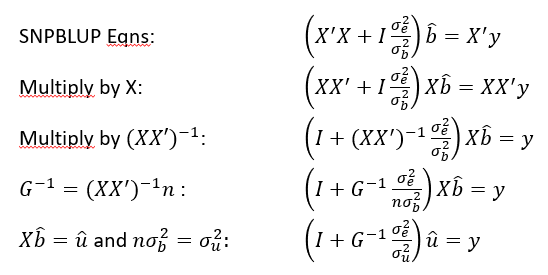
GBLUP vs traditional BLUP
Aped vs G matrix
Aped is only estimate of Atrue
G=XX’/D may be a better estimate of Atrue
given sufficient markers
So GBLUP can use same softwares as raditional BLUP
replace A by G in traditional animal model, much fewer equation than SNP-BLUP, as long as the number of gneotyped animals is small, but this is not logner the case in many species
• Eg. Relationships between full sibs: Aped=0.5 but Atrue can vary from 0.4 to 0.6 (average of many loci). At any locus the fraction of IBD alleles can vary from 0 to 1. G estimates Atrue, and the estimate will be close to Atrue if the number of markers is large.
Models are equivalent
the mean and variance of the data is the same
GEBVs are the same
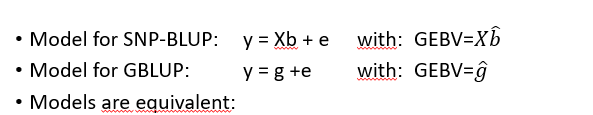
GEBV
What is a genetically estimated breeding value (GEBV)? A GEBV is a statistically generated number or score that estimates the total genetic potential of an animal with respect to a heritable trait. Traits are influenced and controlled by many different genetic regions, or loci, across the genome.
GBLUP model has fewer number of equations
as long as the number of genotyped animals is less than Nsnps
in the future: SNP-BLUP may have fewer equaionts
but number of SNPs increases also due to increasing marker density