Infection test (med-tech)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Gram -ve
thin peptidoglycan layer; outer membrane; do not retain the crystal violet stain; appear pink under a microscope after a Gram stain.
Gram +ve
thick peptidoglycan layer; no outer membrane; retain the crystal violet stain; appear purple under a microscope after a Gram stain.
Coccus
Spherical or round-shaped bacteria
Bacillus
Rod-shaped bacteria
Spirilla
Spiral or helical-shaped bacteria
Immersion oil use and how it works:
used when lens on 100x; same refractive index as glass, which reduces light refraction, allowing more light to enter the lens (improving image clarity and resolution)
What are nosocomial infections?:
Infections that are acquired during a patient's stay in a hospital or healthcare facility.
What is the criteria for a classification of a nosocomial infection?:
infection must not be present at the time of admission
infection must manifest after 48-72 hours of hospitalization
must be associated with healthcare interventions, such as surgeries, IVs, or catheters
What type of settings are they usually found in?:
Typically found in hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, and other healthcare settings.
How are they prevented?:Hand hygiene (hand washing/sanitizing)
Hand hygiene (hand washing/sanitizing)
Proper sterilization of medical equipment
Use of PPE
Isolation precautions for infected patients
Regular cleaning and disinfecting of healthcare environments
What is a gram stain?
laboratory technique used to differentiate bacterial species into two groups (Gram-positive and Gram-negative) based on their cell wall structure
critical step of the gram stain?:
Decolorization step (using alcohol or acetone), which differentiates Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
What is an MRSA infection?:
a type of bacterial infection resistant to certain antibiotics (can cause minor things like a skin infection into a serious infection like bloodstream)
How can they be spread/prevented (Think about the 5 C’s)
Contact: Avoid skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals
Crowding: Avoid overcrowded environments
Cuts: Keep cuts and abrasions clean and covered
Cleanliness: Regularly wash hands and disinfect surfaces
Common items: Avoid sharing personal items (towels, razors, etc.)
Causes: Overuse and misuse of antibiotics in healthcare can contribute to antibiotic resistance, making infections harder to treat
Difference between infection and colonization, and do both need treatment?:
Infection: The invasion and multiplication of microorganisms that cause damage to the host (needs treatment)
Colonization: The presence of bacteria in or on the body without causing disease (doesn’t usually require treatment)
How are most staphylococcus infections spread?:
Most are spread through direct contact with infected skin or surfaces, via droplets, or by sharing contaminated personal items
What is a differential diagnosis?:
Process of distinguishing between two or more conditions that share similar symptoms, and narrowing it out to see what the disease really is
VINDICATE mnemonic meanings/definitions?:
V: Vascular (e.g., blood flow issues)
I: Infection (e.g., bacterial, viral)
N: Neoplasm (cancerous growth)
D: Degenerative (e.g., arthritis, dementia)
I: Intoxication (e.g., alcohol, drugs)
C: Congenital (e.g., birth defects)
A: Autoimmune (e.g., lupus)
T: Trauma (e.g., injury, physical damage)
E: Endocrine (e.g., thyroid disorders)
Vector borne diseases- what are they?
How have we (as the human race) made them worse?:
Illnesses transmitted by vectors (bugs) such as mosquitoes, ticks, or fleas
Climate change has expanded the habitats of vectors, allowing them to spread to new regions. Increased travel has led to faster transmission across borders
Toxoplasmosis
- Parasitic infection
- eating undercooked meat, contact with cat feces (poop) or contaminated soils
Hepatitis C
- Viral infection
- transferred through blood-to-blood contact (not likely: through sexual contact or mother to child during birth)
Ringworm
- Fungal infection
- contact with an infected person or animal, contaminated surfaces/objects
Meningitis
- Can be bacterial, viral, or fungal
- Droplet transmission (through coughing or sneezing)
- Airborne and bloodborne spread for some
Strep Throat
- Bacterial infection
- Droplet transmission (coughing or sneezing)
Pinworm
- Parasitic infection
- Fecal-oral transmission, often through ingestion of eggs
Necrotizing Fasciitis
- Bacterial infection
- Contact with infected tissue (breaks/cuts in skin)
Tetanus
- Bacterial infection
- Contact with contaminated soil or objects
- Affects your nervous system
Signs
Something you can see/observe (like a rash)
Symptoms
things that are felt by the pt (like chest pain or headache)
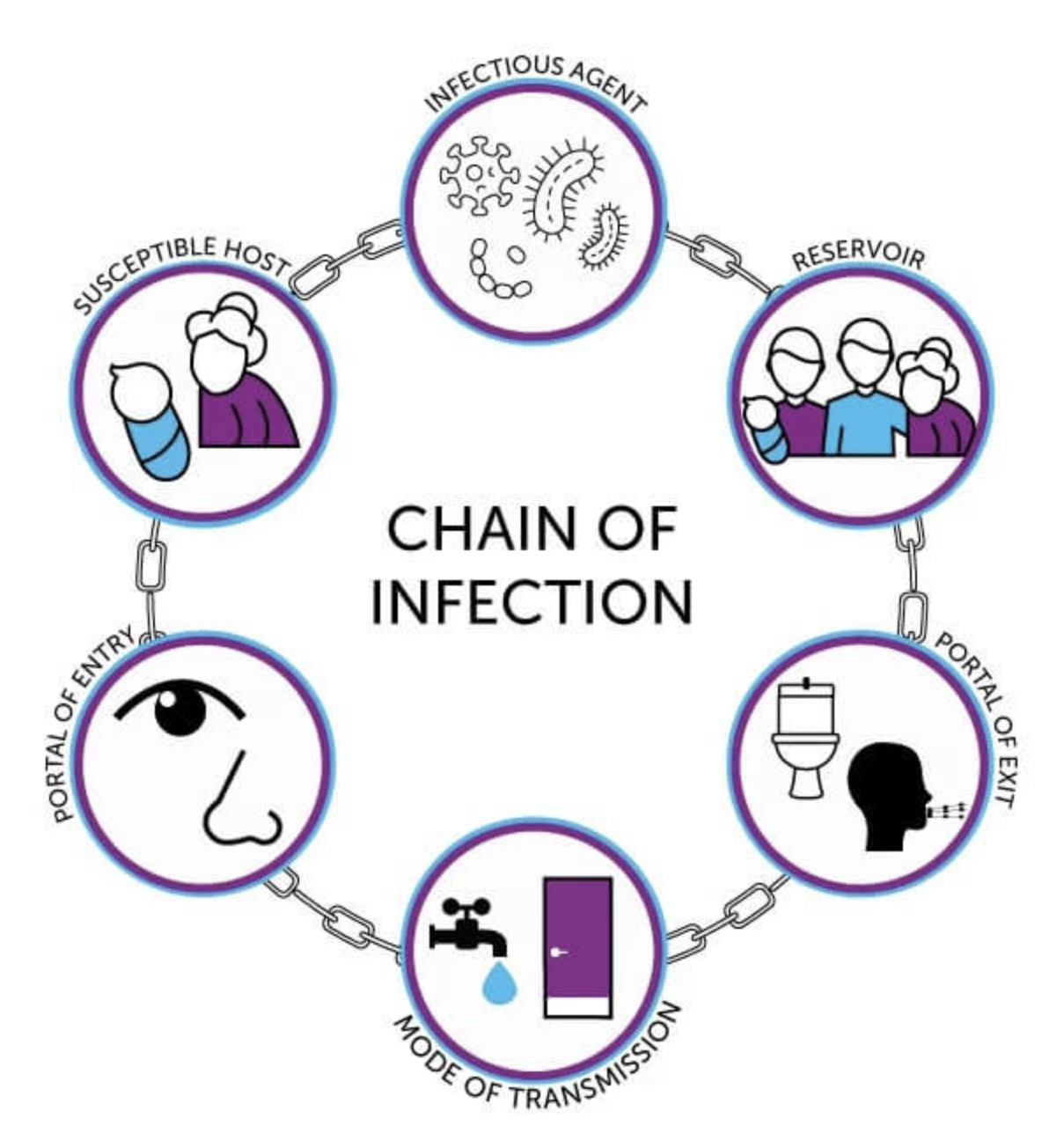
Chain of Infection:
Infectious Agent (any microorganism)
Reservoir (where it hangs out/live; in the soil, water, animals)
Portal of Exit (from the water supply contaminated food, sneezing, coughing)
Mode of Transmission (transmit to the next host; contact, blood, contaminated food and water, inhalation, transplacental)
Portal of Entry (how does it go into the next person; eye, nose, mouth, skin/cuts)
Susceptible Host (cause the disease itself)
Category I:
Category II:
Category III:
Tasks that have a chance of exposure to bodily fluids and blood (assisting in minor surgical procedure)
Tasks that don’t usually have a change of exposure to bodily fluids and blood (like CPR); however precautions must be taken
Tasks do not require any PPE (taking vital signs, like blood pressure)
Disinfection, Sanitization and Sterilization (differences and order):
Sanitization: Reduces microorganisms to safe levels, often through cleaning methods (hand sanitizer in a public bathroom)
Disinfection: Kills a high percentage of pathogens, but does not necessarily remove all microorganisms (using disinfectant wipes)
Sterilization: Completely destroys all microorganisms, including spores (using chemical sterilants for medical devices/surgical instruments)
Order of Cleaning:
Clean (remove visible dirt and debris)
Rinse (if necessary, to remove cleaning agents)
Disinfect (kill pathogens)
Sanitize (reduce microbial load to safe levels)
Sterilize (eliminate all microorganisms, if required)
Autoclaving Temps and Time:
- must reach between 250° and 270° F.
- unwrapped items are sterilized for 20 min
- wrapped items for 30 min
OSHA guidelines for exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens:
Exposure Control Plan: Written plan identifying risks and how to mitigate them
Universal Precautions: Treat all blood and OPIM as infectious
PPE: Provide personal protective equipment (gloves, gowns, masks, etc.)
Hepatitis B Vaccination: Offer the vaccine to at-risk employees
Post-exposure care: Provide medical care and follow-up after exposure
Training: Regular training on bloodborne pathogen safety for at-risk employees
Sharps Safety: Implement safer needle devices and proper disposal methods
Waste Disposal: Proper handling and disposal of contaminated materials
Recordkeeping: Maintain records of exposures and training for future reference.
Medical Asepsis
is about reducing the spread of microorganisms, and is often used in routine healthcare settings and non-invasive procedures (disinfecting, hand washing)
Surgical Asepsis
is about completely eliminating all microorganisms to prevent infection during surgical or invasive procedures (sterilization)