Reservoir final exam
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
recovery stages
primary: natural drive mechanisms & fluid expansion
secondary: water flooding
tertiary:EOR
displacement efficiency factors
capillary pressure
relative permeability
displacement efficiency, ED
a measure of the effectiveness of the displacing fluid to mobilize the oil at those places where the displacing fluid contacts the oil reflected in:
magnitude of residual oil saturation, Sor
regions contacted by the displacing fluid
time scale in which Sor is reached
sweep efficiency, ES
a measure of how effective the displacing fluid sweeps out the reservoir volume (areally and vertically)
displacement efficiency formula
ES = EVS x EAS
E = ED x ES
water flooding purposes
maintain reservoir pressure
displace oil from a water injection well to the production well
viscous drive
displacement of oil by applying a viscous force between the injected water and the oil in place
fractional flow
describe the relative movement of different fluid phases within a system - the relative flow velocity of water with respect to the total flow velocity
wave classification
Spreading waves: wave becomes more diffuse on propagation
Sharpening waves: wave is self sharpening and becomes less diffuse →the wave will become a shock, even if the initial condition is diffuse
Mixed waves: Like the Buckley-Leverett wave
Indifferent waves: neither spreading nor sharpening – might appear as shocks in the absence of dissipation
shock construction methods
equal area
wedge construction
equal areas method
based on the principle of conservation of mass and involves finding the shock front position by balancing areas on the fractional flow curve
shock waves
the properties of a surface of discontinuity of a solution of a first-order quasi-linear hyperbolic system of partial differential equations.
aerial vs. vertical sweep
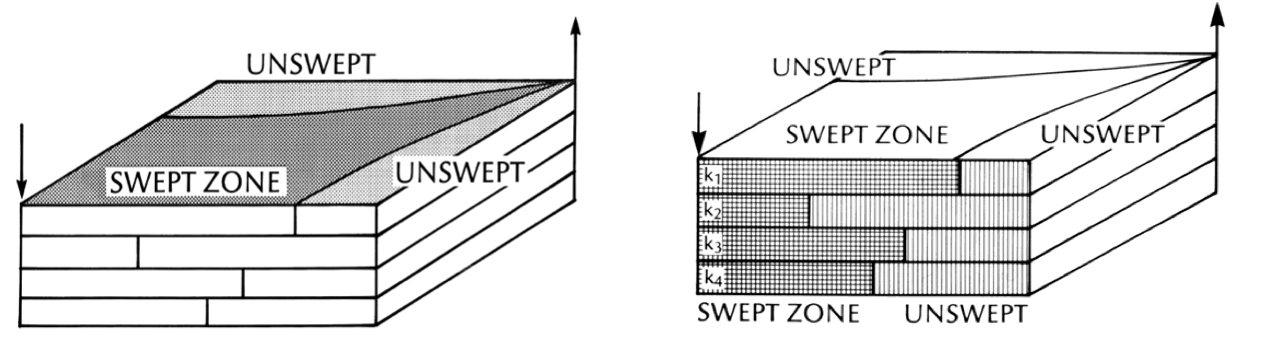
sweep efficiency factors
reservoir geometry
formation heterogeneity
displacement instability
well pattern & placement
heterogeneity types
vertical
areal
fluid movement in vertical reservoir
A reservoir is rarely homogeneous in vertical direction, thus, the injected fluid will seek the path of least resistance to flow and will move through the reservoir as irregular front. It will travel more rapidly in the more permeable zones and less rapidly in the tighter zones. => reduction in vertical sweep efficiency and and an early breakthrough.
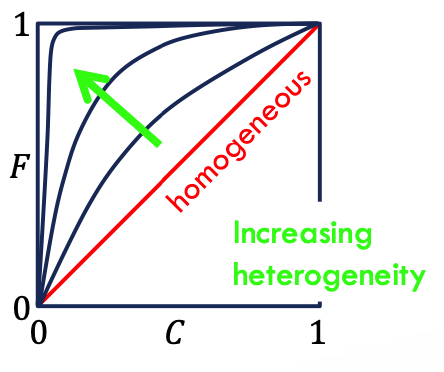
Lorenz coefficient, L
a single parameter that describes the degree of heterogeneity within a pay zone selection (0: homo - 1: het)
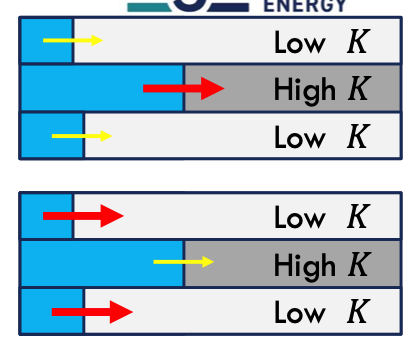
unfavourable (unstable) displacement
Middle layer is advanced front & has a higher fluid mobility than in the other layers → lower injection pressure, accepts more fluid, meaning front is running away from the main front
favourable (stable) displacement
Middle layer is advanced front & has a higher resistance flow than in the other layers → higher injection pressure, meaning main front is catching up with middle layer
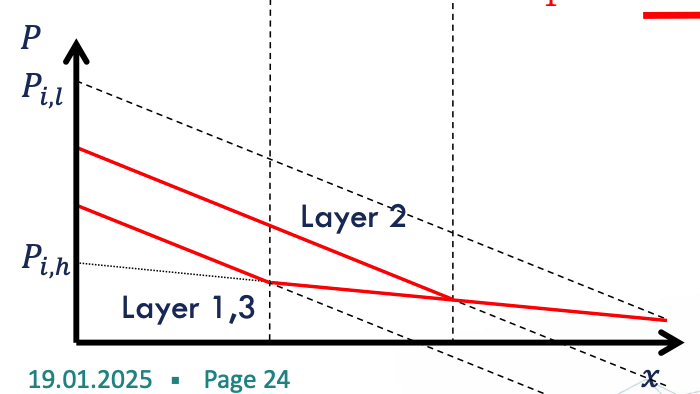
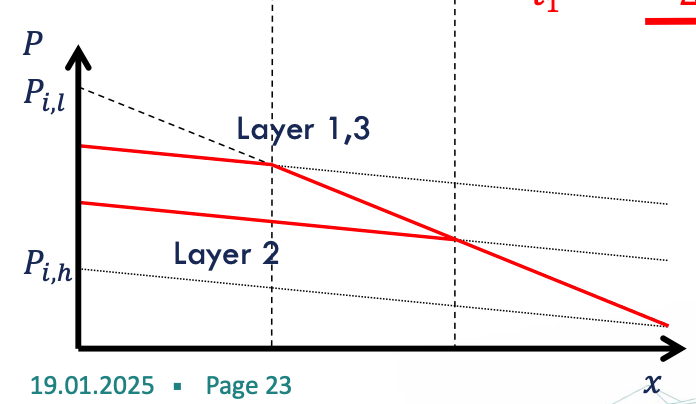
two layer system
low mobility ratio (M<1): favorable mobility ratio → high perm layer initially invaded faster than low permeable layers, but flow in high-K slows down with time due to increasing resistance to flow.
high mobility ratio (M>1): unfavorable → high-K is invaded more easily and flow resistance is decreasing with time → displacement is unstable.