waves
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
what are waves
waves tranfer energy nad info. Waves are described as oscilations of movment or vibrations about a fixed point.They transfer energy and information from place ot place without transfering mater- it is hte wvae not the matter that travels
Features of a wave:
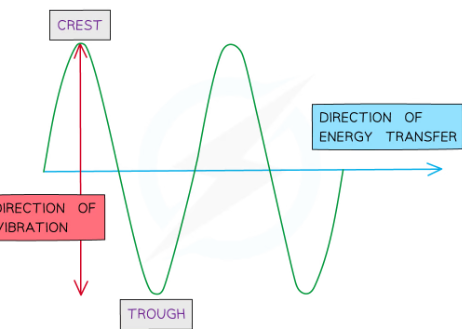
-Crest/peak: the highest point on a wave above the equilibrium or rest position
-Trough: the lowest point on a wave below the equilibrium or rest position
-Amplitude: the distance from rest position to the peak/trough of a wave. Its the max/min displacement from the undisturbed position. Measured in metres (m)
-wavelength: distance from one point on the wave to the same point on the next wave. Length of one complete wave. In longitudinal measures from the centre of one compression to centre of next. In a transverse wave its measured from one point on the wave to the same point on next wave. Metre (m)
what si frequency?
num of complete waves passing a point in a sec
Si unit= Hertz (Hz) 1Hz is 1 wave per second
whatsn i sdispalcement
hwo far a point on the wave is away from the rest position (middle point) Max dispalcement woulkd be the top of the crest to the rest position or the trough to the rest position
hwo is speed measured in waves
measured in metre per second. how far the wave has traveled in a sec.
speed= frequency x wavelength
hwo frequency afefcts wave
as long as th speed is constant if we icnrease the freq we decrease the wavelength or if we decrease the freq we increase the wavelength
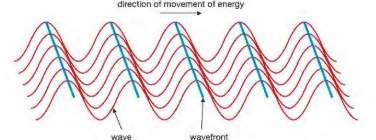
what si wavefornt?
it is an imaginary line that cut across all teh waves and joins all parts of a wave that are in step with eachother together if they are movign in the same position an dmovign in the same direction. The space between each wavefront represents the wavelength. When the wavelength are close togher they represent short wavelenghts
what is the period (T)?
it is the time it takes (in s) for one complete wave to pass a point eg a wave with period 0.002s has a frequency of 1/ 0.002= 500 hz
how to calcualte frequency
frequency= 1/ period (t)
or frequency= (number of waves) / period
what are transfverse waves
waves where the points along its length vibrate at 90 degrees to the direction of energy transfer/wave is moving
transfervse waves characterisitics
energy transfer is in the same direction as the wave motion
-they transfer energy but not particles of the medium
-can move in liquid or solid only
-can mvoe in a vacum-fastest in a vacuum
-oscilation up and down or side to side
-oscillation at right angles to the direction of travel
-pressure constant
exampels of transfverse waves
-rippels on water-water waves -electromagnetic wave eg radio,light,x-rays
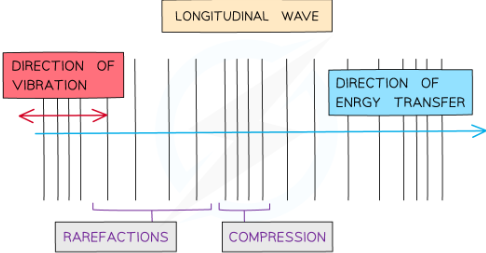
what are longitudinal waves?
waves where the points along its length vibrate parallel/along to the direction of energy transfer/direction in which wave is moving.
chaarcteristics of longitudianl waves
-energy transfer same direciton as motion
-can move in solids,liquids and gases
-Fastest in a solid
-cant move in a vacuum
-transfer energy but not particles of the medium
-oscillations are abckwards and forwards -vibrations parallel to direction wave travel
-changes pressur -they have compressiosn(where points are clsoe togheter) and rarefractions (points spaced apart)
exmapels of longitudinal waves
-sound waves -pressure waves caused by repeated movement in liquid or gas
do waves transfer matter?
All waves carry and transfer energy eg soudn waves cna make things vibrate or move. Waves cna also be used as signals to transfer info form one place to another. When a wave travels between two points, no matter actually travels with it, the points on the wave just vibrate back and forth about fixed positions
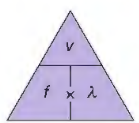
what si wave equation
wave speed (v) =frequency (f) x wavelenth
-unti for wave speed= m/s
-unit for frequency= Hz
-units for wavelength= m
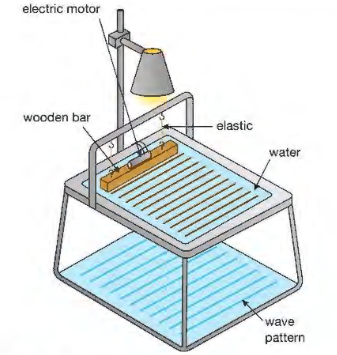
hwo cna reflection and wavelngth be shown by rippel tank?
When the motor is turned on, the wooden bar vibrates creating a series of ripples or wavefronts on the surface of the water. A light placed above the tank creates patterns of the water waves on the floor. By observing the patterns we can see how the water waves are behaving.
Wavelngth :
-using a ruler measure the length of the screen
-dividing this distance by the num of wavefront
Frequency:
-timing how long it takes for a given num of waves to pass a particular point
-Dividing the num of wavefront byt eh time taken
what is wavelength of different frequencies liek when mtor adjusted?
The motor can be adjusted to produce a small number of waves each second.
-The frequency of the waves is small and the pattern shows that the waves have a long wavelength.
-At higher frequencies, the water waves have shorter wavelengths. The speed of the waves does not change.
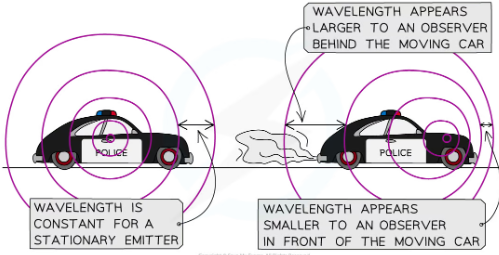
what is the doppler affect?
The apparent change in wavelength and frequency of a wave emitted by a moving source
exaple of doppler affect
when police car is moving the wavefront is no longer evenly spaced. Ahead of the car the wavefronts will be compressed as the car is moving in this direction. The waves will have a shorter wavelength and a higher frequency. Person infront therefore hears a sound that has a higher pitch than when the car was stationary. Behind the car the waves are stretched out so person behind hears a sound with a longer wavelength and lower frequency - that is, the pitch appears to have decreased.
why does the doppler effect occur?
usually when a stationary objects emits waves the waves spread out symmetrically. If the object emitting waves begins to move, the waves can get squashed together at one end of the object and stretched at the other end.
The waves at the front of the moving vehicle appear to be squashed together:
This means the wavelength decreases (and the frequency of the waves increases)
The waves behind the moving vehicle appear to be stretched out:
This means the wavelength increases (and the frequency of the waves decreases)
The faster a wave is moving away from you the longer its wavelength will be
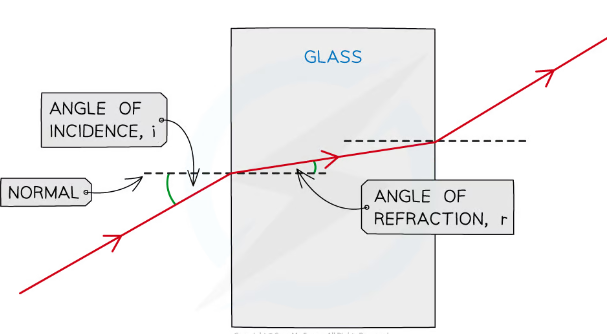
what is the normal
This line is perpendicular to the surface of the boundaries and is usually represented by a straight dashed or dotted line
what is refraction
when wave passes a boundary between two different trasnparent media and undergoes a change in direction
how ripple tank used to investigat reflection?
-reflection can be shown by the waves hitting a plane (stright) surface such as a wall or mirror -A vertical surface is put in the path of the waves. The waves are reflected from the surface at the same angle they strike it -follows law of angle of incidence
why does refraction occur?
refraction occurs due to the change in speed of the wave from one material to another due to their different densities. Em waves travel mroe slowley in denser emdia and sound waves travel faster in denser substances
what happens as waves travel from shallower water to deep water-
-wave speeds up
-bends away from nromal
-wavelgnth increase
-freq remains same
what happnes to direction when moves from less dense to more dense (e.g air to glass)?
light slows down and bends towards the normal
what happnes to direction when mvoes from mroe dense to less dense eg glass to air?
light bends away from normal
what properties change durign refraction?
speed and wavelength – the frequency of waves does not change
hwo is refraction shown using ripple tank?
-a flat epice fo plastic/glass block placed in tank. Glass block should sit below the surface of the water covering only soem of the tank floor -the depth of the s
analysis of results
-as the light passes from the air into the block (a denser emdium) it bends towards hte normal. This is bcs it slows down i > r
-when the light reaches the boundary on the other side of the block its passing into a less dense medium so it speeds up and bends away from the normal i < r
-the light ray that emerges on the other side of hte block is now trvelling in the same direction as it was to begin with0its been refracted towards the normal and hten back again by the same amount
Evaluating the Experiment
Systematic Errors:
An error could occur if the 90° lines are drawn incorrectly
Use a set square to draw perpendicular lines
Random Errors:
The points for the incoming and reflected beam may be inaccurately marked
Use a sharpened pencil and mark in the middle of the beam
The protractor resolution may make it difficult to read the angles accurately
Use a protractor with a higher resolution
what happens if wave hits boundary face on or at an angle?
If the wave hits the boundary face on eg elong the normal it slows down but carries on in the same direction -doesnt bend so no refraction i=r. But if the wave meets a differnt medium at an angle the top part of the wave hits the denser layer first and slows down while the bottom part carries on at the first faster speed. SO the wave changes direction-its been refracted
how to draw a ray diagram for a refracted wave?
a ray diagram shows hte apth that a wave travels:
1) Draw the boudnary between your two materials and the normal
2) Draw an incident ray that meets hte normal at the boudnary
3) The angle between the ray and the normal is hte nagle of incidence
4) Draw the refracted ray on other side of boundary. The angle between the refracted ray and the normal is the angle of refraction
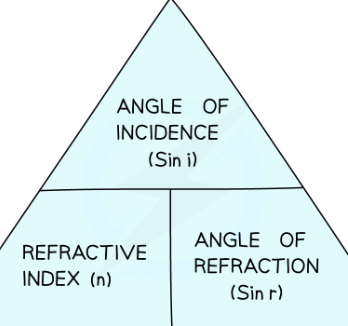
what is snells law?
-if light travels form a less dense to a more dense medium angle of Incidence bigger then the angle of reflection (bends towards normal)
-if ligth travels from a more dense to less dense medium angle of reflection bigger then angle of incidence (bends away fom normal)
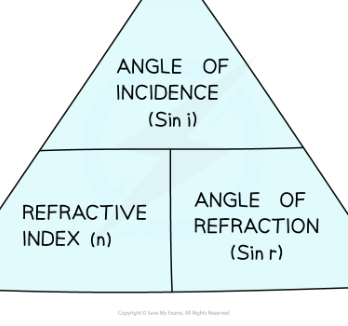
formual for snells law
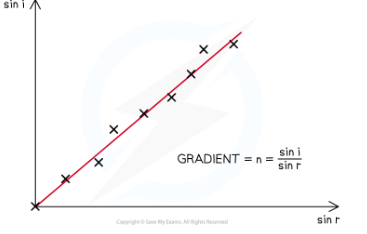
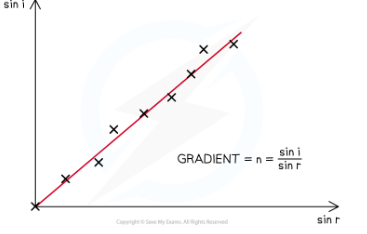
n= sin i / sin r
n = the refractive index of the material
i = angle of incidence of the light (°)
r = angle of refraction of the light (°)
what is refractive index?
the refractive index is the amount of bending that occurs when light travels from oen amterial to another and how fast light travels in the material. speed of light in material is always less then speed of light in vaccuum
what is refractive index of water an dair?
refractive index of glass is high- 1.5 so light slows down a lot in glass. The refracted index of air is 1.00-speed of light in air is about same as in a vacuum
what is high and low refractive index
The refractive index is a number that is always larger than 1 and is different for different materials
Objects which are more optically dense have a higher refractive index, so light slows down quite a lot
Objects which are less optically dense have a lower refractive index,
what is refractive index fromula
refractive index= speed of light in vacuum/ speed of light in material
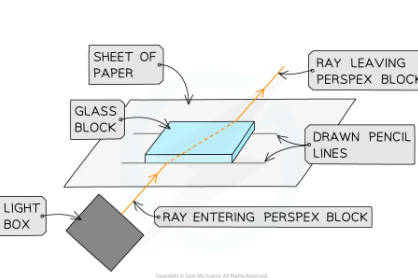
Place the glass block on a sheet of paper, and carefully draw around the rectangular perspex block using a pencil
Draw a dashed line normal (at right angles) to the outline of the block where the points are
Use a protractor to measure the angles of incidence to be studied and mark these lines on the paper
Switch on the ray box and direct a beam of light at the side face of the block at the first angle to be investigated
Mark on the paper:
A point on the ray close to the ray box
The point where the ray enters the block (incident ray)
The point where the ray exits the block (emergent ray)
A point on the exit light ray which is a distance of about 5 cm away from the block
Remove the block and join the points marked with three straight lines to show the incident ray,emergent ray and refracted ray
Use a protractor to measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
Replace the block within its outline and repeat the above process for a rays striking the block at the next angle
Find refractive index using snells law
graph of snells law
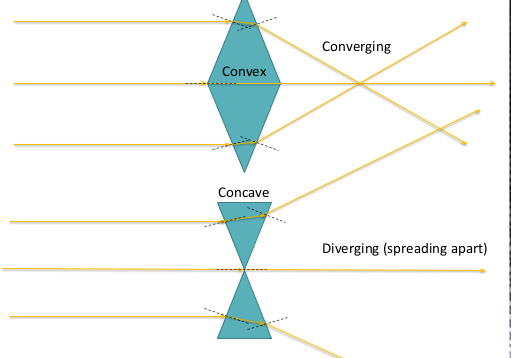
what does it mean when rays paralle,converging or diverging
-Paralle l@ if rays of light same distance apart -Converging: if rays coem toghether -Diverging: if rays movign apart
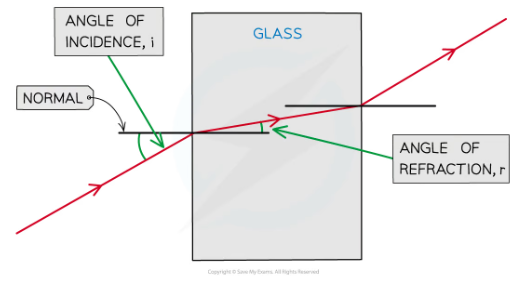
names of ray and angles
-incoming ray form ray box iincident ray with arrow towards boundary
-the outgoing ray that bounces off the mirror is called th refelcted ray
-the line at 90 degrees to the mirror where the icnident ray htis the mirror is calle dthe nromal
-angle appraochign boudnary formed between the incident ray and teh normal is called the angle of incidence
-the angle of wave leavign the boudnary between the reflected ray and nromal is angle of reflection
what is reflection?
A wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but instead stays in the original medium
how does reflection help us see thigns?
visible light is a transfverse wave and its reflection allows us to see things as light bounces off obejcts into our eyes
what happens when object reflects form an uneven surface?
the light reflects off at all different angles and you get a diffuse reflection
what happens when objects reflect from eben surface?
then its all reflected at the same angle and you get a clear reflection
characteristics of reflection in a palne mirror
when an object place din fornt of amirror an image of htat object can be seen in the mirror The image will be:
-same size as obejct
-same distacne behind the mirro as the obejct in front of the mirror
-upright
-directly in line with obejct
-virtual: no ray of ligth actually pass throguh them and image cnat be formed on screen. Formed when the light rays bouncing off an object onto a mirror are diverging so appea to be coming from a completely different place.
-laterally inverted: the image left is obejct right
-the lien joinign equivalent poitns on obejct and iameg passes throguh the mirror at right angles
what is law of refelction?
angle of incidence= angle of reflection
Angles are measured between the wave direction (ray) and a line at 90 degrees to the boundary-the normal
The angle of the wave approaching the boundary-between incoming wave and normal- is called the angle of incidence (i)
The angle of the wave leaving the boundary-between the reflected wave an dnromal is called the angle of reflection (r)
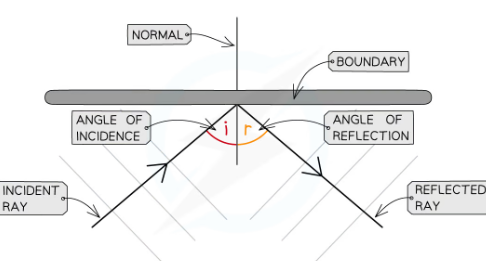
how to draw refelction ray diagram?
When drawing a ray diagram an arrow is used to show the direction the wave is travelling
An incident ray has an arrow pointing towards the boundary
A reflected ray has an arrow pointing away from the boundary
The angles of incidence and reflection are usually labelled i and r respectively and measured from the normal
uses of reflection
-in periscopes: using reflection to allow us to see over obstructions and around corners. This uses TIR- ti consists of two right angles prisms. Light TIR in both prisms . Reclecion by right ngles prisms -in mirrors to allow us to see behind us in cars
speed of ligth in air
300,000 km/s
what happens when beam of lgith passed throguh prism?
if a narrow beam of light passed throguh a prism it splits it up into a range of colours which forms a spectrum. This is becasue the different wavelenghts from which white ligth are made are refracted by different amounts. so white light disperses into different colours as it enters the prism (simialr if elaves prism too) each colour travels through glass at slightly different speed. Violet travelign slowest it has hte smallest wavelength (and therefore greates frequency and energy) so is refracted the msot while red light refracted elast
features of light
-ligth is a form of radiation. a narrow beam of light to show which way its travellign is called a ray -travels in straight lines -transfers eenrgy -travel as waves-radiate from surface -wavelegnth very samlll -can travel through vaccumm -fastest thing there is
what is monochromatic light
single wavelngth or frequency and same colour eg lasers
what si the spectrum
red,orange,yellow,green,blue,indigo,violet
what si frequency and wavelngth liek in spectrum
-red has longest wavelength and lowest freq and energy -vioelt has shortest wavelength and highest frequency and energy -wavelenth increases as you go up the spectrum
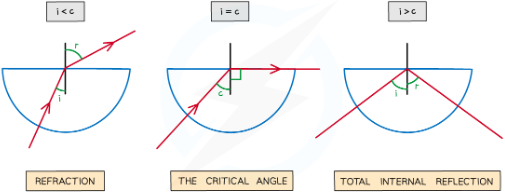
what si total internal reflection
when light moving from a denser medium towards a less dense one, instead of being refracted all of the light is reflected inside the dense material. Occurs when angle of incidence is larger then then critical angle and the incident material is dneser than the second material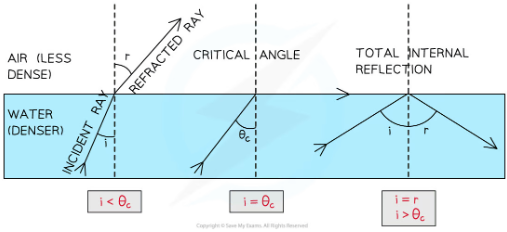
whta is criticla angle
As the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases until it gets closer to 90°. Critical angle is when the angle of refraction is exactly 90 degrees the light refracted along teh boudnary.At this point, the angle of incidence is known as the critical angle c
how to calcualte critical anfle
Sin C = 1 / n
n= refractive index of material
-the higher the refractive index, the lower the critical angle
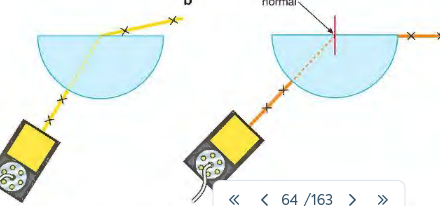
how to use semicircular blocks to show total internal reflection? see pg 35 of cgp
1) inctead of using a rectangular block liek previously use a semi circular block
2) the incident ray is directed at centre of straight side of the block so that it always enters at right angles to the edge. This means it doesn’t bend as it enters the block-only when it leaves from the straight edge.
3) To investigate the critical angle C marke the positiosn of the rays and hte block on paper and use a protractor to measure i nd r for different angles of incidence. By carefully increasing and decreasing the angle at which the ray strikes the flat edge of the glass block, we can discover the smallest angle at which most of the light is refracted along the edge of the glass block (see Figure 12.12b). This angle is the critical angle.
conditions for TIR
-angle of icnidence larger then critical angle
-incident material denser thean second amterila
TIR uses in medicine
-Optical fibre: very thin,flexible rods made of special glass/transaprent palstic. It consists of a central core surrounded by lcadding with a lower refractive index. Light put in one end and is TIR evenry time it hits the edge of the fibre until it comes out the other end as core of the fibre is so narrow that light signals passing through always hit the core cladding boundary at angles higher than critical angle. Used in endoscope to help surgeons look inside body,communcation,deocrative lamps,
uses of prism
risms are used in a variety of optical instruments, including:
Periscopes
Binoculars
Telescopes
Cameras
They are also used in safety reflectors for bicycles and cars, as well as posts marking the side or edge of roads
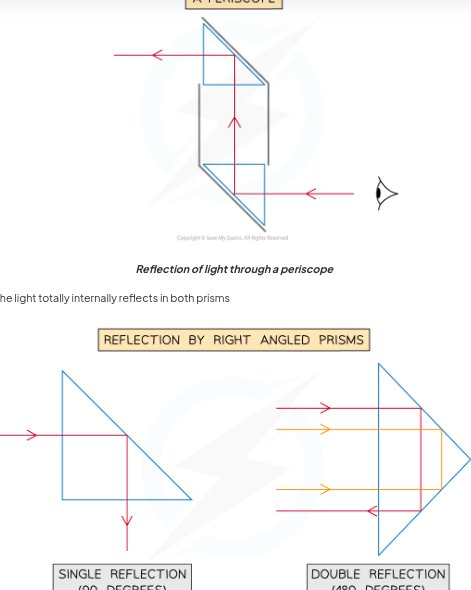
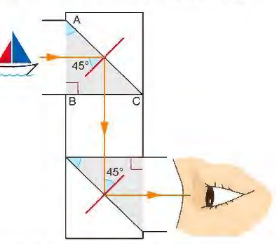
how is total internal reflection use dinperiscope
Total internal reflection also allows us to use prisms to see objects that arent in our direct line of sighnt. A periscope is a device that can be used to see over tall objects
.It consists of two right-angled prisms The ray of light travels into one prism where its totally internally reflected by 90 degrees
It then travels to another prism lower down and is totally internally reflected by another 90 degress
the ray is now travelling parallel to its inital path but at a differnt height
how is TIR used in binoclulers
Each side of a pair of binoculars contains two prisms to totally internally reflect the incoming light. Without the prisms, binoculars would have to be very long to obtain large magnifications and would look like a pair of telescopes.
what are light waves like?
Visible light is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum which means it is a transverse wave. This means the direction the light particles vibrate is perpendicular to the direction of the energy transfer. It can undergo reflection and refraction
what are sound waves
-sound waves are vibrations of air molecules. These vibratiosn travel as waves. The vibrations are passed through the surround medium as a series of compressions
charcateristiscs of soudn waves:
-soudn waves need a medium to travel thrgiuh-cant travel through vacuum
-they are longitudinal waves-contain compression and rarefraction. These cause changes in pressure the variation in pressure causes solid to vibrate in sync wiht soudn waves. Air oscillates backwards and forwards. when pushed together--> compressions (region sof higher density)--> air. Rarefractions are regions of lower density, pressure falls. As objects vibrate in the opposite direction an area of rarefaction forms
-can travel fastest throguh solids, liquid and slowest in gases travels at diff speeds in diff mediums
-in general the denser the medium the faster sounds travel through it.
can sound waves be reflected and refracted?
-can be reflected by hard flat surfaces. Things like carpets and curtains act as absorbing surfaces which will absorb sounds rather than reflect them. Reflected sound is called an echo
-they can also refract as they enter different media. As they enter denser material they speed up.For example, things sound louder and closer at night as durign ngith the ground cools qucikly air layers near the gorund become cooelr than thsoe above. Sound waves travel mroe slowly throguh this cooler air. As a result waves elaving ground tend to bend backwards towards it instead of upwards. Thsi change in direction bcs of change in speed called refraction
what is frequency
frequency of a wave is the number of complete vibrations it performs in 1 sec (no of waves that oasses a certain point in 1 sec 1Hz
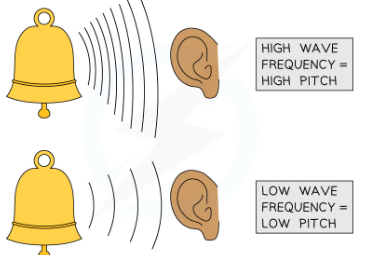
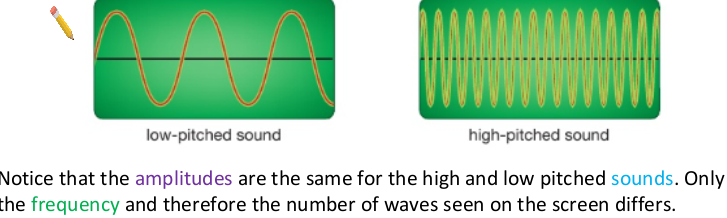
hwo does frequency relate to pitch
--sounds with high pitch have high frequency and short wavelength
-soudns with low pitch have low frequency and long wavelength
-if pitch increases by one octave, freq doubles. As the higher note has double the freq of the lower note,t eh peak occurs twice as other and closer (hald as apart)
what si hearign range
vibration sof sound waves may eventually reach eardrum. we emasure loudness of sound on decible scale. human ear can detect 20 Hz-20000 Hz- decreases as we get older. Soudn above 20,000 hetz called ultrasound while soudns below 20 hz called infrasounds
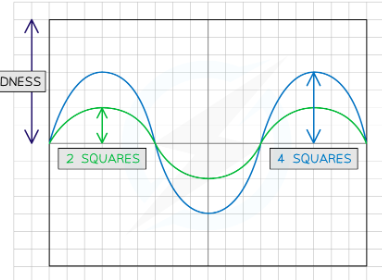
what is amplitude
amplitude of a sound wave is the distance form the rest position to teh crest and is related to its volume+ wavefront:
-sounds with large amplitude have a hgih volume-oscillation bigger and carry more enrgy
-sounds with small amplitude have a low volume
waht is pitch
-large objects vibrate slwoly producing low pitched sound/note -small objects vibrate quickly producing hgih pitched sound or note. Pithc depends on freq
what is osciliscope
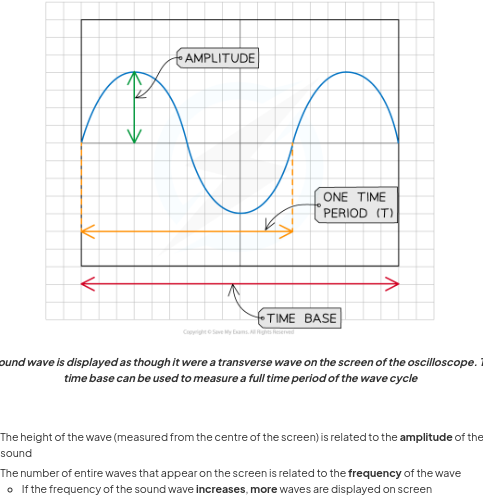
An oscilloscope is a device that can be used to study a rapidly changing signal, such as a sound wave and analternating current waves. It shows waves graphically usign a microphoen and oscilloscope. Sound waves enter microphone and make a crystal or emtal palte inside vibrate. \ Vibrations changes into electrical oscillations and teh oscilloscope uses these to make a spot oscillate up and down. Moves spot steadily sideways at same time to produce shape called wavefront. shows the num of waves produced in a certain lien by a particular source.The (longitudinal) sound wave is displayed as though it were a transverse wave on the screen.The time base (like the 'x-axis') is used to measure the time period of the wave
what does appearance of wave on oscilloscope show? see pg 36 of cgp
The appearance of the wave on the screen deoedns on energy energy trasnferred by the soudn and frequency and tells you whether the sound is loud or quiet and high or low pitched. The height of the wave (measured from the centre of the screen) is related to the amplitude of the sound adn shwos how loud it is.
The number of entire waves that appear on the screen is related to the frequency of the wave.If the frequency of the sound wave increases, more waves are displayed on screen.A sound with a constant frequency will produce a perfect sine curve.
how is low pitcha nd high pitch shown on oscilloscope?
how to measure the speed of sound-practical?
Use the trundle wheel to measure a distance of 100 m between two people
One of the people should have two wooden blocks, which they will bang together above their head to generate sound waves
The second person should have a stopwatch which they start when they see the first person banging the blocks together and stop when they hear the sound
This should be repeated several times and an average taken for the time travelled by the sound waves
Repeat this experiment for various distances, e.g. 120 m, 140 m, 160 m, 180 m
or could use echo method

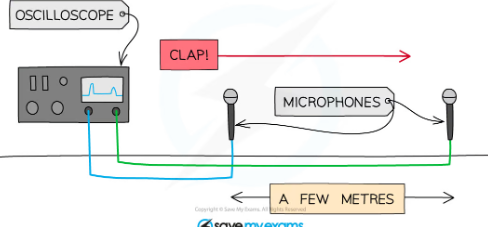
how to use oscilloscope to measure the speed of sound?
Connect two microphones to an oscilloscope
Place them about 2 m apart using a tape measure to measure the distance between them
Set up the oscilloscope so that it triggers when the first microphone detects a sound, and adjust the time base so that the sound arriving at both microphones can be seen on the screen.
Make a large clap using the two wooden blocks next to the first microphone.The detected waves at each microphone can be seen as a seperte wave on teh oscillosope
Use the oscilloscope to determine the time at which the clap reaches each microphone and the time difference between them. Measure the distance between the microphones to find the wavelength.
Repeat this experiment for several distances, e.g. 2 m, 2.5 m, 3 m, 3.5 m. Start with both microphones next to the speaker then slowly move one away until the two waves are aligned on the display but exactly one wavelength apart. Use the fomrula speed = frequency x wavelength. Frequency is whatever you set the singal generator to in the first place
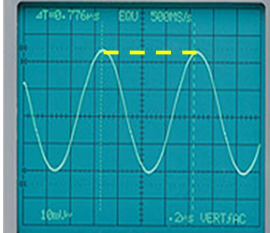
how to find the period of a wave on an oscilloscope to get its frequency?
1) The horizontal axis on the oscilloscope display is time
2) The time between each large division on the scale can be adjusted to get a clear,readable trace.
3) Adjust the time divison setting until the display shwos at least 1 complete cycle
4) Read off the period- the tiem taken for one compelte cycle see cgp pg 37
how to use an oscilloscope?
Connect the microphone to the oscilloscope as shown in the image above
Test the microphone displays a signal by humming
Adjust the time base of the oscilloscope until the signal fits on the screen - ensure that multiple complete waves can be seen. Changing time base setting will
affect the distance between crests of the transverse ways displayed.
Strike the tuning fork on the edge of a hard surface to generate sound waves of a pure frequency
Hold the tuning fork near to the microphone and observe the sound wave on the oscilloscope screen
Freeze the image on the oscilloscope screen, or take a picture of it
Measure and record the time period of the wave signal on the screen by counting the number of divisions for one complete wave cycle
Repeat steps 4-6 for a variety of tuning forks
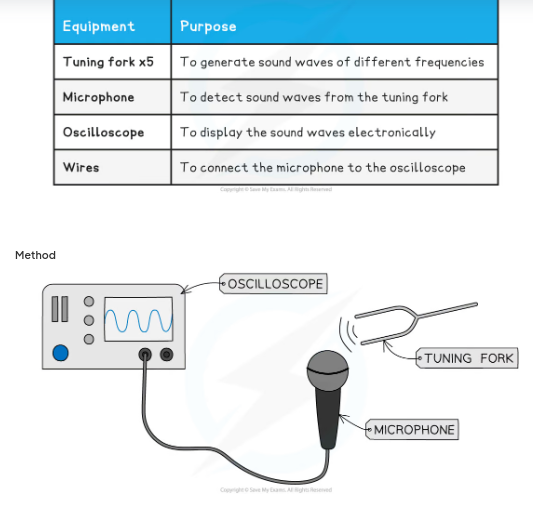
what is a tuning fork?
A piece of equipment that can produce sound of a constant frequency is called a
tuning fork. When struck, it resonates a specific number of times ever second.
what are echoes and how are htey caused
sound waves reflect off hard surfaces. we hear reflected sound as echoes (a short tiem after the orgi sound) -hard smooth surfaces very good at reflectign sound -soft, orugh surfaces good at absorbing sound
equaiton for spee dof sound using echoe
2 x distance to wall / echo time
uses of echo
-echo soudnign: can be used to emasure depth or detect obejcts underwater. A sound wave can be transmitted from the surface of the water. The sound wave is reflected off to bottom of the ocean. Equitment on the ship detects these reflected sound waves. It measures the echo time whichc an be used to calcualte the depth of the sea
what is speed of osund and what does it depend on
speed of soudn in air at room temp 330-350 m/s Depends on:
-temp of air-faster throguh hot air
-doesnt depend on pressufe of air
-differnet throguh diff materials-fastest throguh liquids tehna gases fastest in solids
what are electromagnetic waves?
Transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
what is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum (EM spectrum) is a continuous spectrum of waves, which includes the visible spectrum. At one end of the spectrum the waves have a very long wavelength and low frequency, while at the other end the waves have a very short wavelength and high frequency.
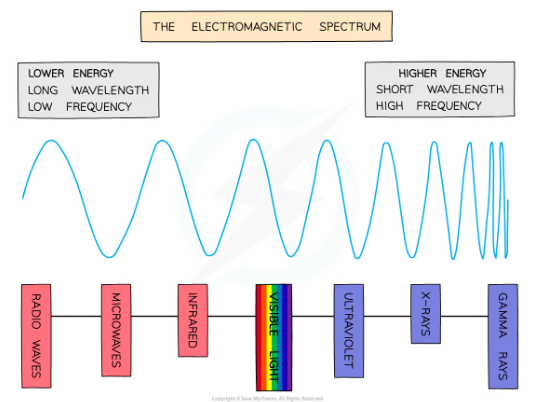
what features do all electromagnetic waves share?
They are all transverse
They can all travel through a vacuum
They all travel at the same speed in a vacuum -300 000 000 m/s
They can all be reflected and refracted.
what do different colours of visible light depend on?
the different colours of visible light depend on the wavelength- red has the longest wavelength (and lowest frequency) and violet has the shortest wavelength (and highest frequency.)
order of colours in order of increasing frequency?
-Richard-red
-Of- orange
-York-yellow
-Gave-green
-Battle-blue
-In-indigo
-Vain-violet
relationship between frequency and radiation?
The higher the frequency, the higher the energy of the radiation
Radiation with higher energy is:
Highly ionising
Harmful to cells and tissues causing cancer (e.g. UV, X-rays, Gamma rays)
Radiation with lower energy is:
Useful for communications
Less harmful to humans
relaition ship between frequencya nd energy
Frequency and energy aredirectly proportional to
each other. As thefrequency of the wave increases, so does the energy.
what is visible light?
Visible light is defined as the range of wavelengths which are visible to humans. It is the onyl part of hte spectrum visible ot humans. Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional,
what are radio waves?
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. longer then 10 cm
uses of radio waves?
Their main uses concern wireless long range communication as they can be reflected from the earths atmoshpere. Long wave radio can be transmitted a long way because long wavelengths are bent around the curved surface of the earth. Short wave radio signals can also be received at long distances from the transmitter.
-Radio waves are given out (emitted) by a transmitter. As they arrive at an aerial, they are detected and the information they carry can be received. Televisions and FM radios use radio waves with the shorter wavelengths to carry their signals.