Neurodevelopmental disorders: mechanisms and drugs
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are synapses?
highly-organized neuronal junction
when do synapses form?
- they form last when neurons are matured
what are synapse development crucial for?
- neural network formation
what are the 2 different types of synapses and what do you know about them?
Altered balance between excitatory and inhibitory synapses (E/I imbalance) in neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders
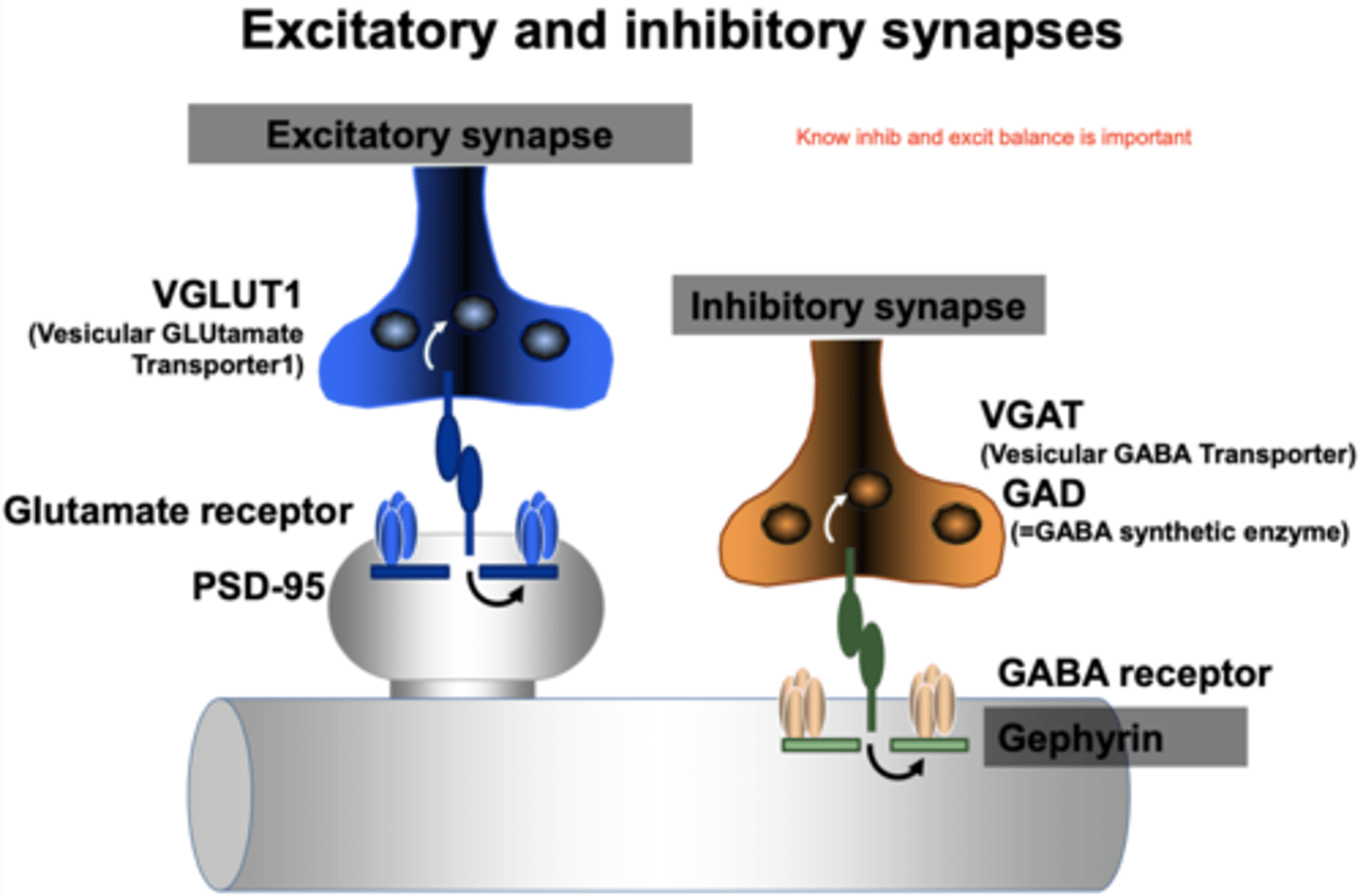
NOTE: People rarely have just one disorder, as many disorders are caused by similar things/in similar pathways
what is synaptic plasticity?
- the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity
what is cognitive inflexability and what are the results?
- do not have flexibility in neurocircuits which can disrupt learning, attention, responses, etc
+ Mutations in synaptic molecules associated with neurodevelopmental disorders can potentially alter synaptic properties.
what type of disorder is autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
- Continuum of neurodevelopmental disorders with complex etiology
what is the best way to study/examine ASD?
As a developmental disorder, it may be more informative to examine heterogeneity in developmental course than cross- sectional variation
+ Twin studies important in establishing the genetic nature of causation of ASD.
what causes ASD?
Numerous possible genetic factors (both heritable and de novo mutations) likely account for very diverse subtypes of ASD manifestation.
what genes are involved in ASD?
Genes that affect transcription, and genes that directly affect synaptic function, are the 2 main types of genes associated with ASD
What proportion of ASD is based on genetics?
Genetics count for 50 - 80% of ASD presentation
what do you know about ASD etiology?
Etiology can change over time.
+ People can "outgrow" their autism, some it gets worse
what are the characteristics of ASD?
- Social interaction deficits
- Social communication deficits
- Restricted interests
- Inflexibility
- Repetitive behaviour or speech
- Maybe co morbid with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) , Anxiety disorders, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- High probability of Intellectual Disability
what are the main diagnostic measures for ASD?
Autism Diagnostic Interview - Revised (ADI-R)
Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) - most used in Canada
• Other
- Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
- Diagnostic Interview for Social and Communication Disorders (DISCO)
what are the two therapy types for ASD?
- behavioural intervention options
- pharmacotherapies
what behavioural intervention options exist for ASD treatment?
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Play based therapies, eg. Denver Model
- DIR/Floortime
- Relationship Development Intervention (RDI)
- Several others.
are pharmacotherapies for ASD good?
Effective pharmacotherapies lacking. Limited progress in drug development. Importance of continued fundamental research.
what are the 4 main pharmacological targets for neurodevelopmental disorders?
- GABAergic
- glutamatergicergic
- sertonergic
- oxytocin and vasopressin agents
pharmacological targets for neurodevelopmental disorders: what do you know about the GABAergic one? Exs?
targeting GABAA receptors (ganaxolone, alphaxalone, Gaboxadol) - ionotropic
targeting GABAB receptors (baclofen, arbaclofen) - metabotropic
What are ionotropic vs metabotropic receptors?
Ionotropic - openning of channels upon binding of receptor, leading to hyperpolarization
metabotropic - signalling pathway involving second messanger pathway activated upon binding of receptor
pharmacological targets for neurodevelopmental disorders: what do you know about the glutamategicergic ones?
Glutamatergicergic agents targeting metabotropic and ionotropic receptors
- Basimglurant
- Mavoglurant
- d-cycloserine
- N- acetylcysteine (NAC)
- Riluzole
pharmacological targets for neurodevelopmental disorders: what are oxytocin and vasopressin?
- Oxytocin and vasopressin are neuropeptides that contribute to regulation of social behaviour
pharmacological targets for neurodevelopmental disorders: what do you know about the effectiveness of oxytocin and vasopression agents?
- Treatment with intranasal oxytocin has had mixed results in ASD and other NDDs
- Intranasal arginine vasopressin (AVP) found to improve social skills in ASD
- Balovaptan (competitive antagonist of vasopressin1a) improved adaptive behaviour (social behaviour and communication) in children with ASD
what have we learned from single gene disorders?
- Single gene neurodevelopemental disorders have distinct and well-defined behavioural features
- Rare variants with large effect
- High rates of Intellectual Disability
- Features include many autistic traits
- Genetic causes and pathophysiology are clearer.
Therefore single gene disorders are considered useful to aid in mechanism-based identification of targets and development of drugs.
what do you know about Fragile X syndrome?
- Leading cause of Intellectual Disability
- Difficulties in executive function, visuospatial skills, working memory, and attention
- Caused by an increase in the trinucleotide repeat in the 5’ untranslated region of Fmr1 (Fragile X Mental Retardation 1)
- >200 CGG repeats leads to transcriptional silencing of Fmr1 during embryonic development
- Fmr1gene is located on Xq27.3
what are the 4 targets in FXS with reported effects in clinical trials?
Target - mGluR5
Target - Intracellular signalling
Target - proteins regulated by FMRP
Target - GABA modulators
what drug targets mGluR5?
Fenobam - improved Prepulse inhibition (PPI)
what drug targets intracellular signalling?
Lithium - efficacy reported in various signalling pathways
what drug targets proteins regulated by FMRP?
Minocycline - efficacy reported on behaviour
what drug targets GABA modulators?
Arabaclofen - mixed results
Donepezil - efficacy reported on behaviour
When do preclinical studies justify randomized clinical trials?
- Reproducibility
- Meaningful phenotypes and readouts
- Broad phenotyping
- Improved technical design standards
- Dose
- Combination therapy
- Statistical power
- Reporting negative data