Mitosis IGCSE
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Think again about those two ——— fusing together in the very first moments of your life. Soon after the zygote was formed, it began to ——— over and over again, producing a ball of ——— that eventually grew into ———. Each time a cell ———, the two new cells were provided with a perfect copy of the two sets of chromosomes in the original ———. The new cells produced were all genetically ———.
Think again about those two gametes fusing together in the very first moments of your life. Soon after the zygote was formed, it began to divide over and over again, producing a ball of cells that eventually grew into you. Each time a cell divided, the two new cells were provided with a perfect copy of the two sets of chromosomes in the original zygote. The new cells produced were all genetically identical.
This type of cell division, which produces genetically ——— cells, is called mitosis. ——— is the way in which any plant or animal cell divides when an organism is growing or repairing a ——— part of its body. Mitosis produces new cells to make the body grow larger, or to replace damaged cells. For example, if you ——— yourself, new skin cells will be made by mitosis to help to heal the wound.
This type of cell division, which produces genetically identical cells, is called mitosis. Mitosis is the way in which any plant or animal cell divides when an organism is growing or repairing a damaged part of its body. Mitosis produces new cells to make the body grow larger, or to replace damaged cells. For example, if you cut yourself, new skin cells will be made by mitosis to help to heal the wound.
Mitosis is also used in ——— reproduction. You have seen, for example, how a potato plant can ——— by growing stem tubers which eventually produce new plants. All the cells in the new ——— are produced by ———, so they are all genetically identical.
Mitosis is also used in asexual reproduction. You have seen, for example, how a potato plant can reproduce by growing stem tubers which eventually produce new plants. All the cells in the new tubers are produced by mitosis, so they are all genetically identical.
Just before mitosis takes place, each of the ——— in the parent cell are copied. This must happen so that there are enough chromosomes to be shared out into the ——— ——— – for example, in a human, each cell needs to get ——— chromosomes of its own. Each copy remains attached to the original one, so each chromosome is made up of two ——— threads joined together. The two identical threads are called ———, and the point where they are held together is called the ———.
Just before mitosis takes place, each of the chromosomes in the parent cell are copied. This must happen so that there are enough chromosomes to be shared out into the new cells – for example, in a human, each cell needs to get 46 chromosomes of its own. Each copy remains attached to the original one, so each chromosome is made up of two identical threads joined together . The two identical threads are called chromatids, and the point where they are held together is called the centromere.
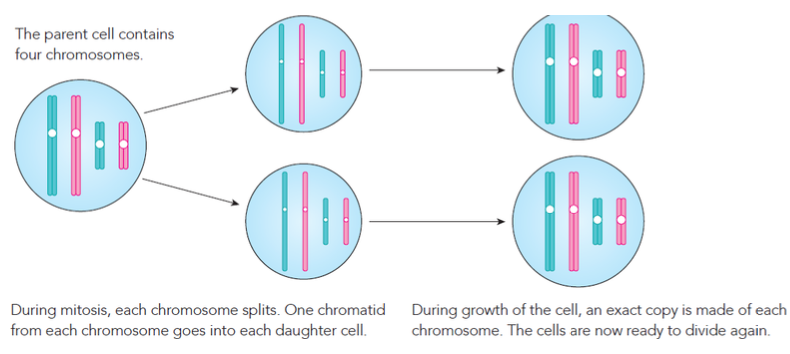
In the image, you can see a diagram of a cell with four ———. There are two sets of two ——— – the blue ones belong to one set, and the pink ones belong to the other set. The rest of the diagram shows what happens when this cell divides by ———.
In the image, you can see a diagram of a cell with four chromosomes. There are two sets of two chromosomes – the blue ones belong to one set, and the pink ones belong to the other set. The rest of the diagram shows what happens when this cell divides by mitosis.
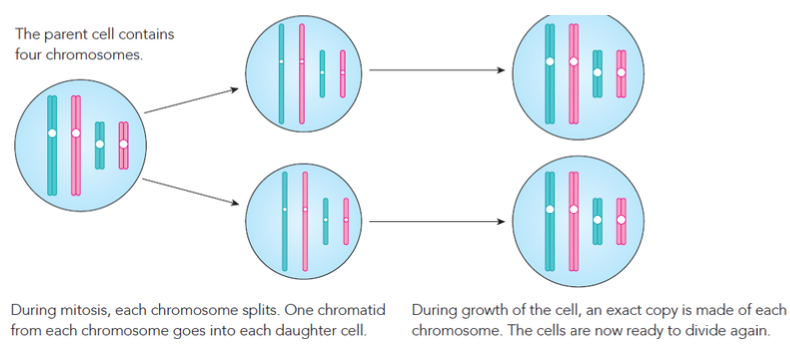
At the end of ———, two new cells have been formed from one ——— cell. The new cells are sometimes called ——— cells. Each daughter cell has one copy of each of the ——— chromosomes. As the new cells grow, they make new ——— of each chromosome, ready to ——— again.
At the end of mitosis, two new cells have been formed from one parent cell. The new cells are sometimes called daughter cells. Each daughter cell has one copy of each of the four chromosomes. As the new cells grow, they make new copies of each chromosome, ready to divide again.
Strictly speaking, we should think of mitosis as being a division of the ——— of a cell, not of the ——— itself.
This is because sometimes a nucleus divides to form two ———, which both stay inside the ——— cell. This happens, for example, when pollen grains develop. But normally the ——— cell divides, not just the ———. So, we end up with new cells each with a nucleus containing perfect copies of the ——— that were present in the ——— cell.
Strictly speaking, we should think of mitosis as being a division of the nucleus of a cell, not of the cell itself.
This is because sometimes a nucleus divides to form two nuclei, which both stay inside the same cell. This happens, for example, when pollen grains develop. But normally the whole cell divides, not just the nucleus. So, we end up with new cells each with a nucleus containing perfect copies of the chromosomes that were present in the original cell.