Biology A Level Year 2
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Taxis
Directional response to a stimulus
Kinesis
Non-directional response to intensity of a stimulus (looking at rate of turning)
Positive Phototropism in Shoots
IAA produced at the tips and diffuses to the shaded side, stimulating cell elongation on the shaded side, causing the shoot to bend towards the light; More light contact increases photosynthesis and glucose production
Positive Geotropism in Roots
IAA produced at the tips and diffuses to the lower side of the root, inhibiting cell elongation, causing the root to bend downwards
Community
All the different species living in one area and their interactions
Ecosystem
Biotic (living) organisms and abiotic (non-living) factors in an environment
Species
A similar group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Interspecific Competition
Competition between organisms of different species
Intraspecific Competition
Competition between organisms of the same species
Predator-Prey Relationship
Predator eats prey, decreasing prey population; This leads to less food for the predator, decreasing predator population; Reduced predator population results in increased competition for food, leading to an increase in prey population (cycle repeats)
Random Sampling
Tape measure across area, generate random coordinates, place quadrats at coordinates, and calculate % cover to estimate mean
Systematic Sampling
Tape measure across area, place quadrats at regular intervals, and calculate % cover of species in each quadrat
Mark Release Recapture Method
Capture, mark (harmless method) release, wait sufficient time for even distribution, recapture, and estimate population size using the formula: n1 * n2 / n2m

Succession
Pioneer species colonize hostile environment, die, decompose adding nutrients to the soil, making the environment less hostile; New species outcompete pioneer species, leading to increased plant and animal species diversity, ultimately reaching a stable climax community
Gene
Section of DNA bases on a chromosome coding for one or more polypeptides
Genotype
Genetic constitution of an organism
Epistasis
Interaction between 2 non-linked genes causing one gene to mask the expression of the other gene in the phenotypes
Monohybrid Inheritance
When one phenotypic characteristic is controlled by a single gene
Autosomes
Non-sex chromosomes
Homologous Pairs of Chromosomes
Contains the same genes at the same loci but not necessarily the same alleles
three causes of genetic variation
1. mutation
2. crossing over of homologous chromosomes.
3. Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes.
random fertilisation of gametes.
Phenotype
Characteristic expressed as a result of a combination of alleles, affected by the environment
Codominant Alleles
Both alleles are expressed in the phenotype
Lethal Alleles
Having 2 copies of an allele leads to an unviable embryo which will not develop
Linked Genes
Genes found on the same chromosome
Sex Linkage
Phenotype determined by genes carried on sex chromosomes, mostly carried on X chromosomes
Reasons for Observed Phenotypic Ratios Variation
Random fertilization of gametes and small/large sample size.
Hardy-Weinberg Equations
P^2 + 2PQ + Q^2 = 1 and P + Q = 1
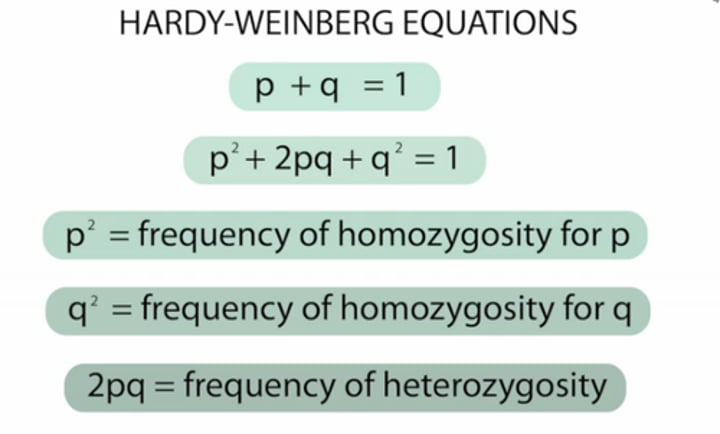
Gene Pool
The complete range of alleles present within a population
Allopatric Speciation
Form of separation where two populations become geographically isolated as a result of a physical barrier to prevent interbreeding
Sympatric Speciation
Occurs when members of 2 different species breed to produce infertile hybrid offspring, reproductively isolating them
geographical isolation
1. separate gene pools no interbreeding no gene flow
2. variation due to mutation
3. different selection pressures
4. different advantageous alleles - those with advantageous alleles more likely to survive reproduce to produce fertile offspring and pass on alleles.
5. increase in allele frequency
Directional Selection
One group has an advantage while the other has a disadvantage, favoring one type of species
Disruptive Selection
Selection pressure that affects the center of phenotypic distribution, causing the distribution to have two peaks
Stabilizing Selection
Selection pressure is against both extremes
Biomass
mass of dry carbon, as water varies
Gross Primary Production (GPP)
the chemical energy store in plant biomass, in a given area or volume.
Net Primary Production (NPP)
Chemical energy store left after respiratory losses
calculate NPP
NPP = GPP - R
Ammonification
Saprobionts decompose organic waste containing N2, converting it to ammonia (NH3)
Nitrification
Nitrifying bacteria converts ammonia (NH3) to nitrite ions (NO2-) and then to nitrate ions (NO3-)
Denitrification
Anaerobic denitrifying bacteria convert nitrate ions (NO3-) to nitrogen gas (N2) in anaerobic conditions
Nitrogen Fixation
Mutualistic nitrogen-fixing bacteria use enzyme nitrogenase to reduce N2 (g) to ammonia (NH3)
Mycorrhizae
Mutualistic relationship between plant and fungus that increases surface area of the root system, enhancing water and mineral ion uptake
eutrophication
1. fertilisers washed up into ponds/lakes (due to rainfall)
2. causes growth of algae (algal bloom) which blocks sunlight
3. no photosynthesis - plants die
4. saprobionts decompose dead plants (aerobically respire)
5. less oxygen for fish so cant aerobically respire so fish die out.
Positive Feedback
Enhances the original stimulus, amplifying the response
Negative Feedback
Counteracts the original stimulus, regulating the response
low blood glucose
1. detected by alpha cells in the pancreas. alpha cells release the hormone glucagon
2. glucagon binds to specific receptors on liver and skeletal muscle cells.
3. The hormone receptor complex activates the conversion of glucagon → glucose (glycogenolysis).
4. glucose leaves cells via facilitated diffusion into the bloodstream
5. increase in blood glucose concentration
high blood glucose
1. detected by beta cells in the pancreas. beta cells release the hormone insulin
2. insulin binds to specific receptors on liver and skeletal muscle cells.
3. hormone receptor complex activates increases the number of glucose carrier proteins in cell membrane
4. glucose enters the cell via facilitated diffusion from bloodstream
5. decrease in blood glucose concentration conversion of glucose → glycogen in the cell (glycogenesis).
6. glucose used for respiration
Action of Adrenaline
Adrenaline hormone released by adrenal glands binds to specific receptors on liver and skeletal muscle cells forming hormone receptor complex. activates adenylate cyclase converts ATP to CAMP. CAMP activates protein kinase causing enzyme cascade. activating glucose phosphorylase enzyme which converts glycogen into glucose. increasing glucose for respiration
Type I Diabetes Cause
Destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas
Type II Diabetes Cause
Target cells fail to respond to hormone due to receptor abnormalities
Ultrafiltration
1. blood enters wide arteriole and leaves narrow - creating high hydrostatic pressure
2. hydrostatic pressure forces glucose, amino acids, urea, and excess water out from the glomerulus into Bowman's capsule (forming glomerular filtrate)
3. passes through the basement membrane and pores, podocytes
Selective Reabsorption
1. at the proximal convoluted tubule, sodium ions in epithelial cells lining lumen of PCT are actively transported into bloodstream
2. concentration of sodium ions in cell decreases.
3. sodium enters cell from the glomerular filtrate via facilitated diffusion through cotransport protein
4. glucose also enters the cell via cotransport with sodium ions. both glucose and sodium ions enter blood stream via FD
5. decrease water potential of cell so water moves from glomerular filtrate → cell → blood stream via facilitated diffusion
Loop of Henle
1. at the thick ascending limb, Na+ from filtrate are actively transported out of LOH into medulla tissue
2. at thin descending limb water potential of medulla tissue decreases
3. so water moves from filtrate → medulla tissue → bloodstream via osmosis
4. increasing concentration of filtrate at the thin ascending limb 5. sodium ions move out of filtrate via facilitated diffusion
Distal Convoluted Tubule/Collecting Duct - Role of ADH
1. when water potential of blood decreases, detected by osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
2. posterior pituitary gland releases ADH hormone
3. ADH binds to specific receptors on DCT/collecting duct
HRC activates conversion of ATP → CAMP
4. causes vesicles carrying aquaporins to fuse with membrane increasing the number of aquaporins in cell membrane
5. increases membrane permeability to water so more water is reabsorbed back into the blood via osmosis
5. increasing water potential of blood, urine becomes more concentrated
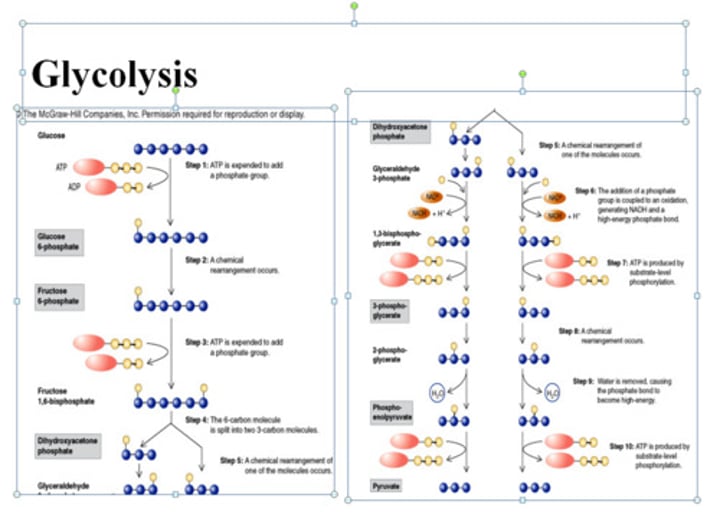
Glycolysis
Anaerobic process in the cytoplasm, converting glucose to pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH
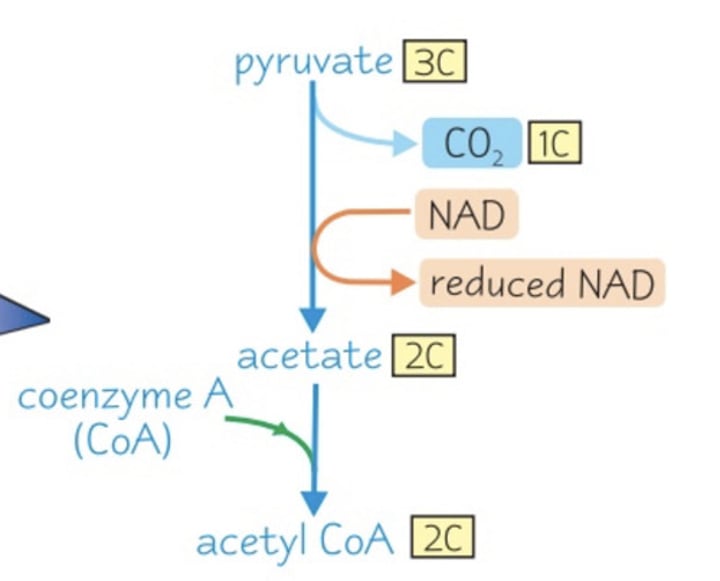
Link Reaction
Pyruvate + Co enzyme A + NAD → acetyl coA + CO2 +NADH
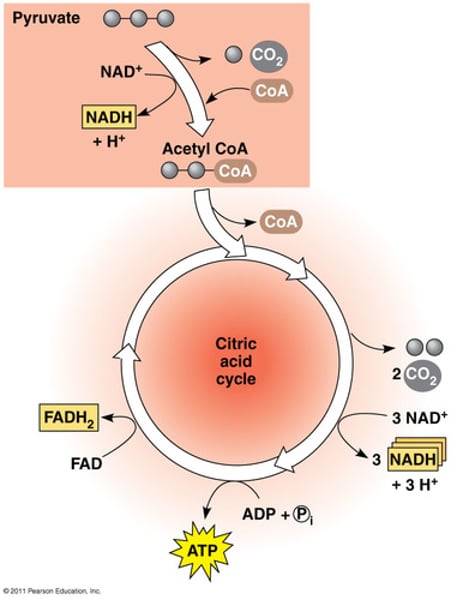
Krebs Cycle
Completes the oxidation of glucose, producing ATP, NADH, and FADH2
Electron Transport Chain + Chemiosmosis
NADH → NAD + H + e-
electrons transferred from coenzyme to coenzyme
series of redox reactions;
energy is made available as electrons are passed on;
H+ passed into intermembrane space
H+ flow back through enzyme;
energy used to synthesise ATP from ADP and phosphate
using ATP synthase
H+ + e- + O2 → H2O
O2 = FINAL ELECTRON ACCEPTOR
Lactate Fermentation (Animals) - Anaerobic Respiration
Pyruvate is converted to lactate/lactic acid, regenerating NAD for glycolysis
Alcoholic Fermentation (Plants) - Anaerobic Respiration
Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and CO2, regenerating NAD for glycolysis
Respiratory Quotient Equation
Volume of CO2 given out/volume of O2 taken in
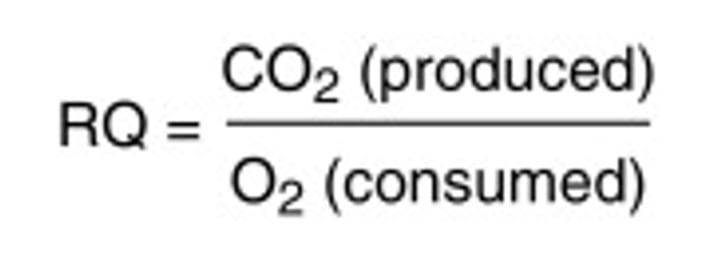
photosynthesis - light dependant reaction
1. light energy absorbed by chlorophyll
2. 2 e- excited leaving chlorophyll. electrons move down ETC via series of redox reactions releasing energy
3. causes H+ to move across thylakoid membrane via FD
4. H+ moves up through ATP synthase
5. energy used to synthesis ATP from ADP + Pi.
6. Photolysis of water produces protons, electrons and
oxygen
7. NADP reduced by electrons to form NADPH. (final electron acceptor)
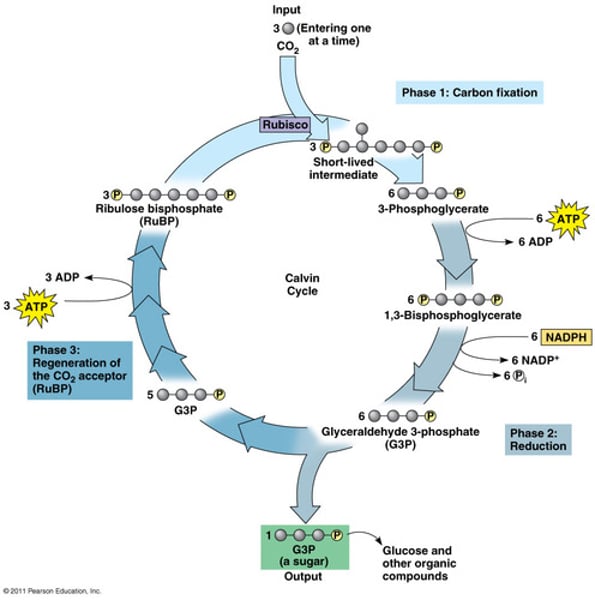
photosynthesis - light independent reaction calvin cycle
1. RUBP combines with CO2 to form 2x GP using enzyme rubisco
2. 2x GP converted into 2x triose phosphate using energy released by hydrolysis of ATP into ADP + pi and conversion of NADPH into NADP
3. 1/6 triose phosphate used to synthesize sugars (glucose)
4. 5/6 triose phosphate used to regenerate RUBP.
photosynthesis - the hill reaction
oxidised DCPIP - BLUE
reduced DCPIP - clear
why would DCPIP take longer to decolourise in the presence of ammonium hydroxide.
less electrons for DCPIP to accept as ammonium hydroxide accepts electrons.
ammonium hydroxide inhibits enzymes that are used in the light dependant reaction. takes longer for electrons to pass down the ETC
limiting factors of photosynthesis
1. light intensity
2. CO2
3. temperature.
sequence of events in reflex arc
1. stimulus
2. receptor
3. sensory neurone - relay neurone
4. central nervous system
5. motor neurone
6. effector
7. response
two advantages of simple reflexes
1. prevents damage to tissues
2. fast involuntary response rapid action requires no decision making
explain how a resting potential is maintained across the axon membrane in a neurone
axon membrane more permeable to potassium ions than sodium ions.
3 sodium ions actively transported out of the axon and 2 potassium in.
facilitated diffusion of potassium ions out of the axon via permanently open potassium ion channel
explain the all or nothing principle
once the threshold has reached membrane potential immediately increases to +55mv (action potential)
time when another action potential cannot be generated
the refractory period
The structure of a myelinated motor neurone.
cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. Dendrons are short extensions of the cell body. Dendrites are small extensions of the dendrons. The axon is a single extension of the cell body. myelin sheath made up of schwann cells. nodes of ranvier.
Factors affecting the speed of conductance
myelination and saltatory conduction
axon diameter
temperature.
why is there faster response with myelinated neurone
saltatory conduction - depolarisation only occurs at the nodes of ranvier as this is where membrane is exposed and permeable to ions.
why is there slower response with unmyelinated neurone
no saltatory conduction so depolarisation occurs along the whole length of the axon
sequence of events allowing information to pass from one neurone to the next across a cholinergic synapse
1. impulse causes Ca2+ channels to open and Ca2+ to enter axon via facilitated diffusion
2. this causes vesicles move to and fuse with (presynaptic) membrane;
3. acetylcholine diffuses across synaptic cleft
5. binds with receptors on postsynaptic membrane;
6. Na+ enter (postsynaptic) neurone;
7. depolarisation of (postsynaptic) membrane;
8. if above threshold nerve impulse/action potential produced
two types of summation
1. spatial
2. temporal
explain spatial summation
simultaneous release of neurotransmitter from several (more than one) synaptic knobs so sufficient neurotransmitter is released to reach threshold and generate action potential.
explain temporal summation
series of impulse arriving from the same neurone in rapid succession. impulses added together. so sufficient neurotransmitter is released to reach threshold and generate action potential
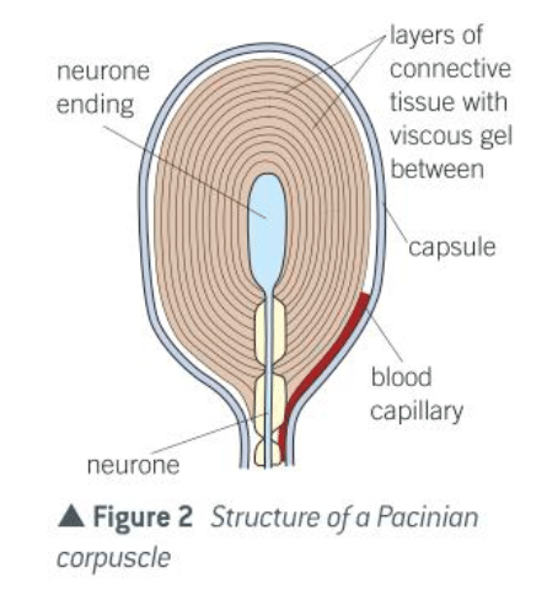
How applying pressure to pacinian corpuscle produces changes in membrane potential
1. stimulus causes stretch-mediated Na+ channels to open
2. Na+ moves into the axon via facilitated diffusion
3. membrane potential becomes more +ive
increasing pressure - more stretch-mediated Na+ channels open. More Na+ enters. membrane potential becomes more +ive
4. causes depolarisation of axon membrane so increased magnitude of generator potential and more frequent action potentials
pigment in rod cells and cone cells
rod - rhodopsin
cones - iodopsin
three types of cone cells
red sensitive, green sensitive, blue sensitive.
why cone cells have high visual acuity
cone cells DO NOT show convergence as they show a 1:1 raio with a bipolar neuron. (no summation).
why rod cells have high sensitivity to low light intensity
rod cells show convergence. more than one rod cell shares a bipolar nerone. spatial summation.
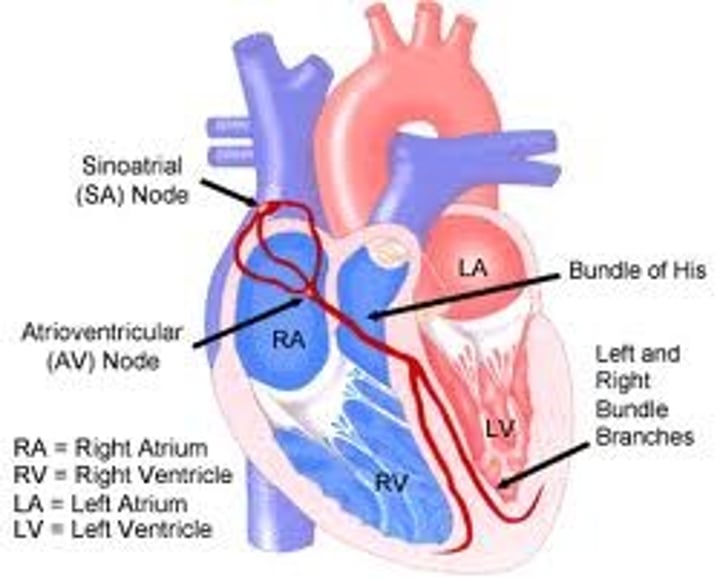
how heartbeat is initiated and coordinated
1. SAN sends a cardiac impulse which travels through atria walls causing atria to contract simultaneously (atrial systole)
2. non-conductive tissue prevents impulses from reaching the ventricles
3. delay allows ventricles to fully fill with blood before they contract and allows atria to empty blood.
4. AVN sends impulse down towards bundle of his in the septum un through the Purkinje fibres.
5. this allows the ventricles to contract from the bottom upwards.
atrial systole
pressure in atria greater than in the ventricles. (due to atrial contraction). AVV open. blood moves from atria into ventricles
diastole
pressure in arteries greater than pressure in ventricles. SLV close. blood moves out of arteries.
ventricular systole
1. pressure in ventricles greater than in atria. forcing AVV close to prevent backflow.
2. pressure in ventricles greater than pressure in arteries. SLV open. blood moves from ventricles up to arteries
increase in heart rate - nervous system response
1. increase in CO2 detected by chemoreceptors in carotid artery/aorta.
2. sends impulses to medulla oblongata.
3. increases frequency of impulses by the sympathetic nervous system to the sinoatrial node
4. increase in heart rate
decrease in heart rate - nervous system response
1. decrease in CO2 detected by chemoreceptors in carotid artery/aorta.
2. sends impulses to medulla oblongata.
3. increases frequency of impulses by the parasympathetic nervous system to the sinoatrial node
4. decrease in heart rate
increase blood pressure - nervous system response
1. detected by pressure receptors in carotid artery/aorta.
2. sends impulses to medulla oblongata.
3. increases frequency of impulses by the parasympathetic nervous system to the sinoatrial node
4. Decreases impulse from SAN
5. Decreased impulses from AVN
5. normal blood pressure decreased heart rate
decrease blood pressure - nervous system response
1. detected by pressure receptors in carotid artery/aorta.
2. sends impulses to medulla oblongata.
3. increases frequency of impulses by the sympathetic nervous system to the sinoatrial node
4. Increased impulse from SAN
5. Increased impulses from AVN
6. increase in heart rate
7. normal blood pressure
structure of myofibril sarcomere.
I band - only actin
A band - myosin and actin
H zone - only myosin (no myosin heads)
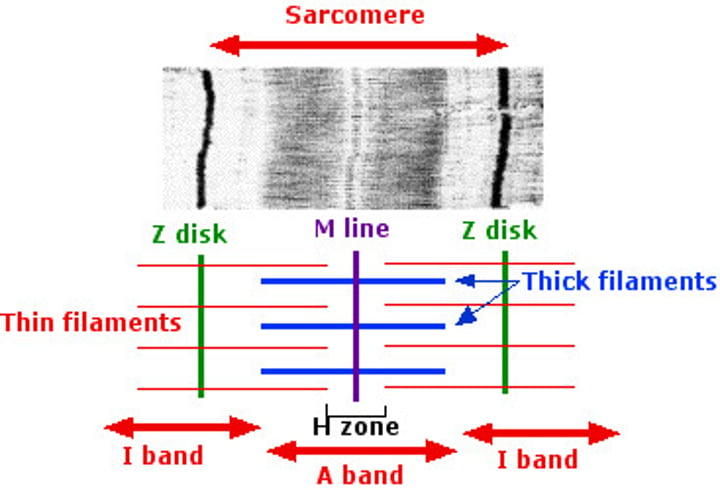
stages in muscle contraction
1. Ca2+ diffuse into myofibrils from (sarcoplasmic) reticulum
2. ca2+ binds to troponin
3. this removes tropomyosin exposing actin binding sites
4. myosin heads contain ATPase - hydrolyses ATP into ADP + Pi
5. energy released used to move myosin heads up towards binding sites on actin.
6. energy uses to move myosin heads forward pushing actin forwards (powerstroke)
7. another ATP binds to myosin head so myosin head detaches from actin
slow muscle fibres
aerobically respire - slow longer lasting exercise.
fast muscle fibres
anaerobically respire - fasts bursts of exercise white in colour
Describe how the PCR is carried out
1. DNA heated to 95°C to separate strands by breaking hydrogen bonds
2. Cool to 55 °C to allow primers bind and nucleotides to attach by complementary base pairing
3. Increase temperature 72°C for DNA polymerase to join nucleotides together with phosphodiester bonds on the new strands
4. Repeat cycle many times
How bacteria with resistance gene in their plasmids are produced
1. Cut desired gene at specific palindromic sequence using restriction enzymes/endonucleases to create sticky ends
2. Cut the plasmid open using SAME restriction enzymes to create sticky ends complementary to sticky ends on the desired gene
3. Use DNA ligase to join sticky ends together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.
4. Return plasmid to bacteria cells using electric shock and calcium salts