Bio Exam 3 - Animal Diversity
4.8(17)
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Last updated 3:16 AM on 3/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
1
New cards
Animal Characteristics (shared characteristics of all mammals)
heterotrophic - animals derive energy (carbon) from others
Multicellular - extracellular matrix including collagen
Cells are organized into tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function bound together
Multicellular - extracellular matrix including collagen
Cells are organized into tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function bound together
2
New cards
role of zygote in animal development
fertilized egg, has genes from both parents and is first step in development
3
New cards
role of cleavage in animal development
divides eggs
4
New cards
role of blastula in animal development
divides fewer cells until gastrula is formed, hollow ball of cells
5
New cards
role of blastopore in animal development
organizes and defines germ layer, transfers nutrients, start gastrulation
6
New cards
role of gastrula in animal development
begins tissue layer, a ball within a ball
7
New cards
role of gastrulation in animal development
creates three embryonic tissue layers, and creates a digestive tube
8
New cards
role of larvae in animal development
stores food so organism can transfer to adult
9
New cards
role of metamorphosis in animal development
produces larvae into adult with drastic changes
10
New cards
What is a synapomorphy, and which are Synapomorphies in animal development? (3 that we have learned so far)
shared derived characteristics that evolved in a common ancestor and are present in all descendants - blastula, gastrulation, mesoderms
11
New cards
What Animal Milestones happened in the… Edicarian Biota? Include how long ago this was
First fossil evidence of multicellular animals - 565-550 million years ago
12
New cards
What Animal Milestones happened in the… Cambrian Explosion? Include how long ago this was
Diversification of animal types, forerunners of most extant phyla, bizarre body types that have since disappeared - 535 - 525 million years ago
13
New cards
When did multicellular organisms originate according to molecular data?
700-800 million years ago
14
New cards
Burgess Shale significance
contains best records we have of Cambrian fossils
15
New cards
Difference between radial and bilateral?
radial: body arranged around a central axis.
bilateral: body can be divided in near identical halves along a single plane
bilateral: body can be divided in near identical halves along a single plane
16
New cards
What are the terms associated with describing locations with each symmetry?
bilateral: Cephalization, left and right mirror images, dorsal, ventral. anterior, posterior, proximal, distal
radial: oral, aboral, proximal, distal
radial: oral, aboral, proximal, distal
17
New cards
Cephalization
the concentration of sense organs, nervous control, etc., at the __anterior__ end of the body, forming a head and brain, both during evolution and in the course of an embryo's development.
18
New cards
diploblastic vs triploblastic
diploblastic: 2 germ layers (endoderm and ectoderm), cnidaria
triploblastic: 3 germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm), most other animals
triploblastic: 3 germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm), most other animals
19
New cards
three tissue germ layers, and their organs
endoderm: gut, liver, lungs
mesoderm: skeleton, muscle, kidney, heart, blood
ectoderm: skin, nervous system
mesoderm: skeleton, muscle, kidney, heart, blood
ectoderm: skin, nervous system
20
New cards
coelomate example
mollusks, annelids, arthropods, echinoderms, chordates
21
New cards
pseudocoelomate example
roundworms
22
New cards
acoelomate example
flatworms
23
New cards
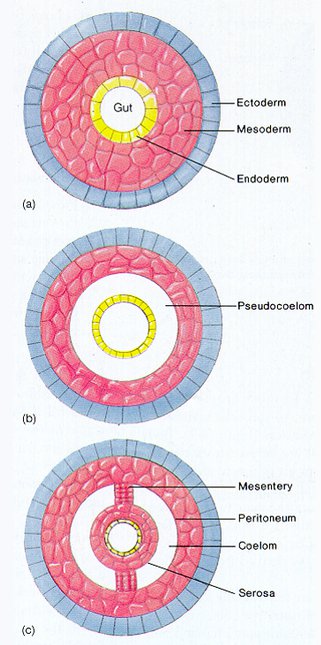
answer A, B, C
a. acoelomate.
b. pseudocoelomate
c. coelomate
b. pseudocoelomate
c. coelomate
24
New cards
protostome vs deuterostomes
cleavage: protostome is spiral and determinate, deuterostome is radial and indeterminate
coelom formation: protostome is schizoccoelous, deuterostome is enteroccoelous
fate of blastopore: protostome: mouth develops from it, deuterostomes: anus develops from it
coelom formation: protostome is schizoccoelous, deuterostome is enteroccoelous
fate of blastopore: protostome: mouth develops from it, deuterostomes: anus develops from it
25
New cards
determinate vs indeterminate cleavage
spiral/determinate: fate determined early
radial/indeterminate: fate determined late
radial/indeterminate: fate determined late
26
New cards
What are the 5 points of agreement on Animal Phylogeny?
All animals share common ancestor
Sponges (Porifera) are basal
Eumetazoans are a single clade (true tissue layers)
Most animals are bilateral (echinoderms secondarily radial)
Chordates and echinoderms are deuterostomia
Sponges (Porifera) are basal
Eumetazoans are a single clade (true tissue layers)
Most animals are bilateral (echinoderms secondarily radial)
Chordates and echinoderms are deuterostomia
27
New cards
What are important animal milestones that are represented in the following groups, and what is common name: Porifera
parazoans, 1 phylum, sponges, filter feeding
28
New cards
What are important animal milestones that are represented in the following groups, and what is common name: cnidaria
eumetazoans, diploblastic, have forms of polyp and medusa, include medusazoans (jellyfish), and anthozoans (coral and sea anemones)
29
New cards
What are important animal milestones that are represented in the following groups, and what is common name: ctenophora
eumatazoans, comb jellies, diploblastic, plankton species, similar stinging cells to cnidaria
30
New cards
hydrozoans life cycle significance
polyp and medusa, has alternation of generations, can be used for anti aging
31
New cards
anthozoans
corals, anemones, hard/soft corals, coral and zooxanthella symbiosis
32
New cards
bilateria split in animals created these two
protostomia, deuterostomia
33
New cards
protostomia include:
lophotrochozoans, ecdysozoans
34
New cards
lophotrochozoan significance and what is it named for?
most diverse animals, include: mollusks, segmented worms, flatworms, named from lophophore feeding structure, and trochophore larvae stage
35
New cards
ecdysozoans significance
hard exoskeleton, grow by molting, arthropoda, Nematoda (round worms)
36
New cards
lophotrochozoans include
Platyhelminthes: flat worms, triploblastic, coelomate, planaria and parasites
Mollusca: snails, bivalves, cephalopods, diverse body plan, visceral mass, mantle, foot, diverse
Annelida: segmented worms, triploblastic, true coelom, Polychaeta and oligochaetes, repeated segments with specialization
Mollusca: snails, bivalves, cephalopods, diverse body plan, visceral mass, mantle, foot, diverse
Annelida: segmented worms, triploblastic, true coelom, Polychaeta and oligochaetes, repeated segments with specialization
37
New cards
annelida
segmented worms, triploblastic, true coelom, Polychaeta and oligochaetes, repeated segments with specialization
38
New cards
Mollusca
snails, bivalves, cephalopods, diverse body plan, visceral mass, mantle, foot, most diverse in form and habitats: Gastropoda, bivalvia, cephalopoda, and more like chitins
39
New cards
Platyhelminthes
flat worms, triploblastic, coelomate, planaria and parasites
40
New cards
ecdysozoans description and what it is named for
external cuticle or exoskeleton, three major groups: Nematoda, arthropoda, other phyla, most species rich group: crustaceans and insects. Ecdysis named for molting
41
New cards
Nematoda
round worms, triploblastic, pseudocoelomate, soil dwelling & parasitic, microscopic, diverse, trichinella parasite causes parasitic worm disease trichinosis
42
New cards
arthropoda
jointed legs, includes insects, arachnids, crustaceans, myriapods. very diverse - insects on land and freshwater, and crustaceans in salt and freshwater. most species rich phylum
43
New cards
deuterstomia
include echinodermata and chordata
44
New cards
echinodermata
spiny skin, 5 groups: sea stars (starfish), brittle stars, sea urchins/sand dollars, crinoids, sea cucumbers
45
New cards
5 synanyphmorphies/chordate characteristics (great essay)
notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits or clefts, muscular post anal tail, thyroid
46
New cards
vertebrae history
diverged during Cambrian explosion (540 million years ago), contain 52000 species, diverse and successful
47
New cards
how are vertebrates deuterostomes?
have ‘second mouth’ where blastopore becomes anus, mouth develops secondarily from another opening
48
New cards
synapomorphy
shared derived characters
49
New cards
synplesiomorphy
shared ancestral characters
50
New cards
notochord
basis for endoskeleton, flexible rod
51
New cards
dorsal hollow nerve cord
extends length of the body throughout embryonic development
52
New cards
pharyngeal slits
originally for filter feeding, modified into gill slits for respiration, becomes structures of head and neck for many vertebrates
53
New cards
post anal tail
chordates have tail extending beyond anus, some lose tail during development (like frogs and humans)
54
New cards
craniates
chordates with a skull, includes: myxini (hagfishes), and all vertebrates
55
New cards
vertebrates
craniates with a backbone, includes: Cephalaspidomorphi (jawless fishes)
56
New cards
what is a gnathostome?
vertebrates with jaws, includes: extinct placoderms, Chondrichthyes (sharks and rays with placoid scales), and ourselves
57
New cards
define and differentiate chordates, craniates, and vertebrate
chordates are defined by the 5 characteristics, craniates are a subgroup of chordates characterized by presence of skull and brain, and vertebrates are a subgroup of craniates defined by having a vertebral column or backbone. all vertebrates are craniates and all craniates are chordates, but not all chordates are craniates or vertebrates.
58
New cards
What are the Synapomorphies associated with Chordates, craniates and vertebrates and an example organism of each?
chordates: notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits or clefts, muscular post anal tail, thyroid. EX: lancelet
craniates: head with skull and brain, neural crest, HOX genes. EX: myxini
vertebrates: vertebral column, neural crest cells form bones, cranium
craniates: head with skull and brain, neural crest, HOX genes. EX: myxini
vertebrates: vertebral column, neural crest cells form bones, cranium
59
New cards
What is a Chondrichthyan?
have cartilaginous skeleton, contain spiral valve that increases feeding efficiency in a short intestinal tract. Have a variety of reproductive strategies: oviparous, ovoviviparous, and viviparous
60
New cards
What is an Osteichthyan?
bony fish, but also have a complete mineralization of their skeleton (skeleton made of bone, instead of cartilage).
Synapomorphies: swim bladder, scales, bony opercurlum to protect gills
ex: salmon, tuna, bass, trout
Synapomorphies: swim bladder, scales, bony opercurlum to protect gills
ex: salmon, tuna, bass, trout
61
New cards
What type of Osteichthyan is the sister to tetrapods?
Lobe-finned fishes (coelacanths) are the sister group to tetrapods.
62
New cards
What are the Synapomorphies of Tetrapods?
four limbs with digits (can be altered or lost), lungs (to adapt to land)
63
New cards
what are tetrapods?
Osteichthyes with limbs and feet
64
New cards
amphibia
two part lifecycle (water and land), other variations
Lungless salamanders have direct development
Newts have a 3 part life cycle
Axolotls & tiger salamanders undergo paedomorphosis
Lungless salamanders have direct development
Newts have a 3 part life cycle
Axolotls & tiger salamanders undergo paedomorphosis
65
New cards
amniotes
tetrapods with terrestrial eggs, allow gas exchange for embryos
66
New cards
What group of tetrapods is basal?
lobe-finned fishes and lungfishes
67
New cards
How do Birds and Mammals fit into tetrapod evolution?
two amniote groups diverged early:
reptile (crocodiles, snakes, birds, dinosaur ancestors)
and Mammalia and their ancestors
reptile (crocodiles, snakes, birds, dinosaur ancestors)
and Mammalia and their ancestors
68
New cards
What is the advantage of the synapomorphy of Amniotic eggs?
allows eggs to be placed on land, allows gas exchange for embryos while preventing dessication
69
New cards
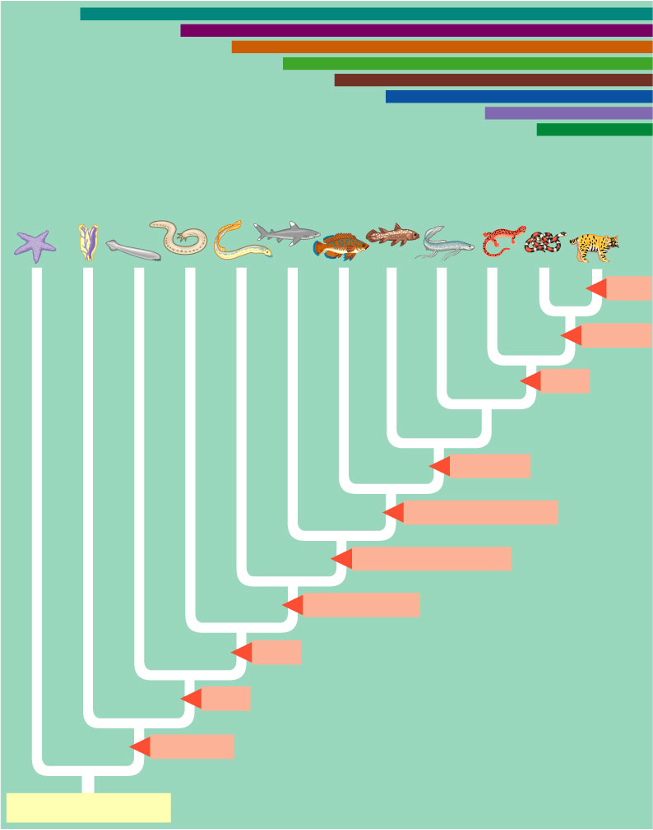
Fill in from bottom left to top right, then name species left to right
ancestral deuterostome, notochord, brain, head, vertebral column, jaws/mineralized skeleton, lung & lung derivatives, lobed fins, legs, amniotic egg, milk.
organisms: echinodermata, Urochordata, lancelets, hagfishes, lampreys, chondrichytes, ray-finned fishes, coelacanth, lungfishes, amphibians, reptiles, mammals
organisms: echinodermata, Urochordata, lancelets, hagfishes, lampreys, chondrichytes, ray-finned fishes, coelacanth, lungfishes, amphibians, reptiles, mammals
70
New cards
mammal synapomorphies
mammary glands, hair, three bones in ear, warm blooded
71
New cards
What are the five major Eiutherian Groups and which common mammals fit in each?
rodentia: mice, rats, squirrels
Chiroptera: bats
primates: humans, apes, monkeys
Carnivora: cats, dogs, bears
Cetacea: whales, dolphins, porpoises
Chiroptera: bats
primates: humans, apes, monkeys
Carnivora: cats, dogs, bears
Cetacea: whales, dolphins, porpoises
72
New cards
synapsid
A synapsid is a type of vertebrate characterized by having a single temporal opening on each side of the skull.
73
New cards
Define Monotreme, Marsupial and Eutherian?
monotremes: lay eggs
marsupials: give birth to undeveloped young, raise in pouches
Eutherian: placental mammal give birth to fully developed young
marsupials: give birth to undeveloped young, raise in pouches
Eutherian: placental mammal give birth to fully developed young
74
New cards
Where do humans fit within Primate Phylogeny? What are the Other great apes?
Humans are great apes/apes, and share a common ancestor with chimpanzees 6-8 million years ago. Other great apes: orangutans, gorillas, and chimpanzees/bonobos
75
New cards
How do modern humans fit with fossil homonids?
homo genus, these species have similar body plans to modern humans, including a larger brain size, bipedalism, and adaptations for tool use.
76
New cards
what are the synapomorphies of humans?
bipedalism, human traits (large brain, reduced teeth and jaw)
77
New cards
What are the Biological challenges to multicellular animals?
cell coordination, resource allocation, waste removal, reproduction, homeostasis
78
New cards
Define the hierarchy of tissues, organs and organ systems?
Cells, Tissue, Organs, Organ System, Organism
Tissues: Groups of cells of similar function and Appearance
(only organization in sponges)
Organs: Functional Groups of Tissues that perform a specific Function
Organ Systems: Groups of organs that accomplish a major function of regulation
Tissues: Groups of cells of similar function and Appearance
(only organization in sponges)
Organs: Functional Groups of Tissues that perform a specific Function
Organ Systems: Groups of organs that accomplish a major function of regulation
79
New cards
What are the four major tissue types in animals?
epithelial tissue: surface of body
connective tissue: supports and connects tissues and organs in body (bone, cartilage, blood)
Muscular Tissue: movement and mechanical work
nervous tissue: communication and coordination in body
connective tissue: supports and connects tissues and organs in body (bone, cartilage, blood)
Muscular Tissue: movement and mechanical work
nervous tissue: communication and coordination in body
80
New cards
Define Homeostasis
ability for organism to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external environment - regulation
81
New cards
What is the difference between a regulator and a conformer, what is the advantage of each?
regulators control and maintain a constant internal temperature regardless of changing environment, while conformers allow internal body temperature to change in response to changing environment
82
New cards
What is the difference between Negative and Positive Feedback?
negative feedback reduces stimulus to keep system stable (ex: heat-sweat-evaporative cooling) while positive feedback amplifies stimuli, which does not help homeostasis (ex: population growth, childbirth)
83
New cards
How does Thermoregulation demonstrate the principles of Homeostasis, feedback, and how form function and behavior can contribute to homeostasis?
homeostasis because despite a changing environment, these organisms need to maintain an internal temperature to survive. feedback systems are crucial in helping thermoregulation, for example: shivering and sweating. Form function and behavior can help thermoregulation: thick fur, blubber, larger animals lose heat slower, and physical grouping of animals
84
New cards
How does Metabolic rate and Energy Use relate to thermoregulation?
metabolic processes produces heat, body uses energy for thermoregulation through processes like shivering, sweating, panting, and movements
85
New cards
Define Basal metabolic rate and standard metabolic rate ( I did a lot of research on this, and they are interchangeable terms. I am not sure why we are supposed to know the difference between these two.)
basal metabolic rate - like SMR, but under more strict conditions like after sleeping, no exercise, etc
standard metabolic rate - rate of energy consumption of an organism under standardized/variable conditions (rested, fasting, thermoneutral)
\
\
standard metabolic rate - rate of energy consumption of an organism under standardized/variable conditions (rested, fasting, thermoneutral)
\
\
86
New cards
Define Endotherm/Ectotherm. Homeotherm/Poikilotherm
Endotherm - body heat derived from metabolism
Ectotherm - body heat derived from environment
Homeotherm - body temperature remains constant
Poiklotherm - body temperature fluctuates with environment
Ectotherm - body heat derived from environment
Homeotherm - body temperature remains constant
Poiklotherm - body temperature fluctuates with environment
87
New cards
Distinguish between hibernation and torpor and their role in Energy Management.
Hibernation is a long-term state of reduced metabolism and lowered body temperature that some animals enter during the winter months when food is scarce. Torpor, on the other hand, is a short-term state of reduced metabolism and body temperature that some animals enter during times when food is temporarily scarce, such as during the night.
88
New cards
What do heterotrophs need for survival?
external energy, essential nutrients (6): water, carbs, fats, proteins, minerals, vitamins
89
New cards
Define : Carnivore, Herbivore and Omnivore
carnivores - commonly predators, eat other animals
Herbivores - eat plants
omnivores - eat both
Herbivores - eat plants
omnivores - eat both
90
New cards
Beyond Calories what 4 classes things are essential nutrients, what are they and what are they needed for?
proteins: growth, tissue repair, enzyme and hormone production
Carbohydrates: primary source of energy
Lipids: fats help absorb vitamins, produces hormones, maintains healthy cell membranes
Vitamins and minerals: supports immune system, maintains healthy bones, convert food to energy
Carbohydrates: primary source of energy
Lipids: fats help absorb vitamins, produces hormones, maintains healthy cell membranes
Vitamins and minerals: supports immune system, maintains healthy bones, convert food to energy
91
New cards
Describe the 4 stages of food processing and the Physiological challenges associated with each stage + alternatives to each stage. (GREAT ESSAY HAHAHHAHAHAHAHAHAHA WOOHOOO)
ingestion: getting food into alimentary canal, alternative: filter feeding in whales and some fish, filter food particles from water
digestion: breaking down food into small enough molecules, alternative: extracellular digestion where enzymes are secreted outside organism’s cells to break down food used by insects, spiders, and some invertebrates
absorption: cells take up molecules, alternative: direct absorption, nutrients absorbed through skin in some amphibians
elimination: spelling undigested material, alternative: storage, waste products stored in body until ready to be eliminated in some insects and reptiles
digestion: breaking down food into small enough molecules, alternative: extracellular digestion where enzymes are secreted outside organism’s cells to break down food used by insects, spiders, and some invertebrates
absorption: cells take up molecules, alternative: direct absorption, nutrients absorbed through skin in some amphibians
elimination: spelling undigested material, alternative: storage, waste products stored in body until ready to be eliminated in some insects and reptiles
92
New cards
What are the four main modes of feeding found in animals?
filter feeding: take small particles out of water or air, mainly whales, clams, flamingos
substrate feeding: feeds on material it is in contact with, mainly earthworms, termites, leafcutter ants
fluid feeding: feed on liquids, like blood or nectar, mainly mosquitos, ticks, hummingbirds
bulk feeding: ingest large amounts of food, mainly humans, lions, Venus flytraps
substrate feeding: feeds on material it is in contact with, mainly earthworms, termites, leafcutter ants
fluid feeding: feed on liquids, like blood or nectar, mainly mosquitos, ticks, hummingbirds
bulk feeding: ingest large amounts of food, mainly humans, lions, Venus flytraps
93
New cards
Describe process of digestion, including the following structures and their contributions.
Mouth
Salivary gland
Esophagus
Stomach
Pancreas
Liver
Gall Bladder
Small intestine
Rectum
Mouth
Salivary gland
Esophagus
Stomach
Pancreas
Liver
Gall Bladder
Small intestine
Rectum
Mouth: saliva helps break down food in mouth
Salivary gland: produces saliva
esophagus: muscular tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach
stomach: mixes and grinds food, also secretes digestive enzyme pepsin
pancreas: produces digestive enzymes like amylase, lipase, etc that go to small intestine
liver: produces bile, helps breakdown fats and aids in absorption of fat soluble vitamins
gall bladder: stores and releases bile into the small intestine when needed to aid in the digestion of fats
small intestine: primary site of nutrient absorption, also absorbs nutrients and water
large intestine: absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food material and forms feces
Rectum: stores feces until they can be eliminated through the anus during a bowel movement
Salivary gland: produces saliva
esophagus: muscular tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach
stomach: mixes and grinds food, also secretes digestive enzyme pepsin
pancreas: produces digestive enzymes like amylase, lipase, etc that go to small intestine
liver: produces bile, helps breakdown fats and aids in absorption of fat soluble vitamins
gall bladder: stores and releases bile into the small intestine when needed to aid in the digestion of fats
small intestine: primary site of nutrient absorption, also absorbs nutrients and water
large intestine: absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food material and forms feces
Rectum: stores feces until they can be eliminated through the anus during a bowel movement
94
New cards
What adaptations are seen in the stomach and intestine to deal with different types of food? (3)
stomach acid secretion, enzyme secretion, instestinal surface area
95
New cards
Define:
Peristalsis
Sphincter
Peristalsis
Sphincter
peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of the smooth muscle in the walls of the digestive tract, help move food along
Spinchter: ring of muscle that surrounds an opening or passage in the body that controls its opening and closing
Spinchter: ring of muscle that surrounds an opening or passage in the body that controls its opening and closing
96
New cards
What hormones and feedback systems are involved in regulation of the digestive process? (name 3 example enzymes)
gastrin is released by cells to help break down food, secretin released by small intestine in response to partially digested food, insulin released by pancreas in response to presence of glucose in blood