UNIT 2 - TOPIC 4
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Who and when was the two-factor theory of emotions developed?
Schachter and Singer in 1962
What is the two-factor theory emotions?
proposes that emotion results from two components: physiological arousal and the cognitive label we give to that arousal. For example, if a person’s heart is racing, they may interpret it as excitement when on a rollercoaster or as fear if being chased. The same physical response can lead to different emotions depending on how it is labelled.
Step-by-step example of the two-factor theory occurring
- Something happens (e.g. you see a big dog running toward you). 2. Your body reacts — your heart beats faster, your hands shake. 👉 (This is called physiological arousal.) 3. You think about the situation — “That dog looks scary and might bite me!” 👉 (This is called cognitive labelling.) 4. You feel an emotion — fear.
Who and when was the appraisal theory of emotion developed?
Lazarus in the 1960s
Appraisal theory of emotion
argues that cognitive appraisal comes first, before physiological arousal. According to this theory, people evaluate (appraise) a situation as threatening or non-threatening, and this appraisal determines the emotional response. For example, if someone sees a large dog, they may first assess whether it is dangerous, and only then experience fear along with physiological changes.
Key difference between two-factor and appraisal theory
The two-factor theory says that emotion happens when your body reacts first, like your heart racing, and then your mind labels what’s happening based on the situation. The emotion comes from both the physical reaction and the mental label. You need both for the emotion to happen.
The appraisal theory says that emotion starts with your thoughts about the situation. You first judge whether it’s a threat, challenge, or not important. The emotion comes from how you think about it, and the body may react after — but it’s not always needed.
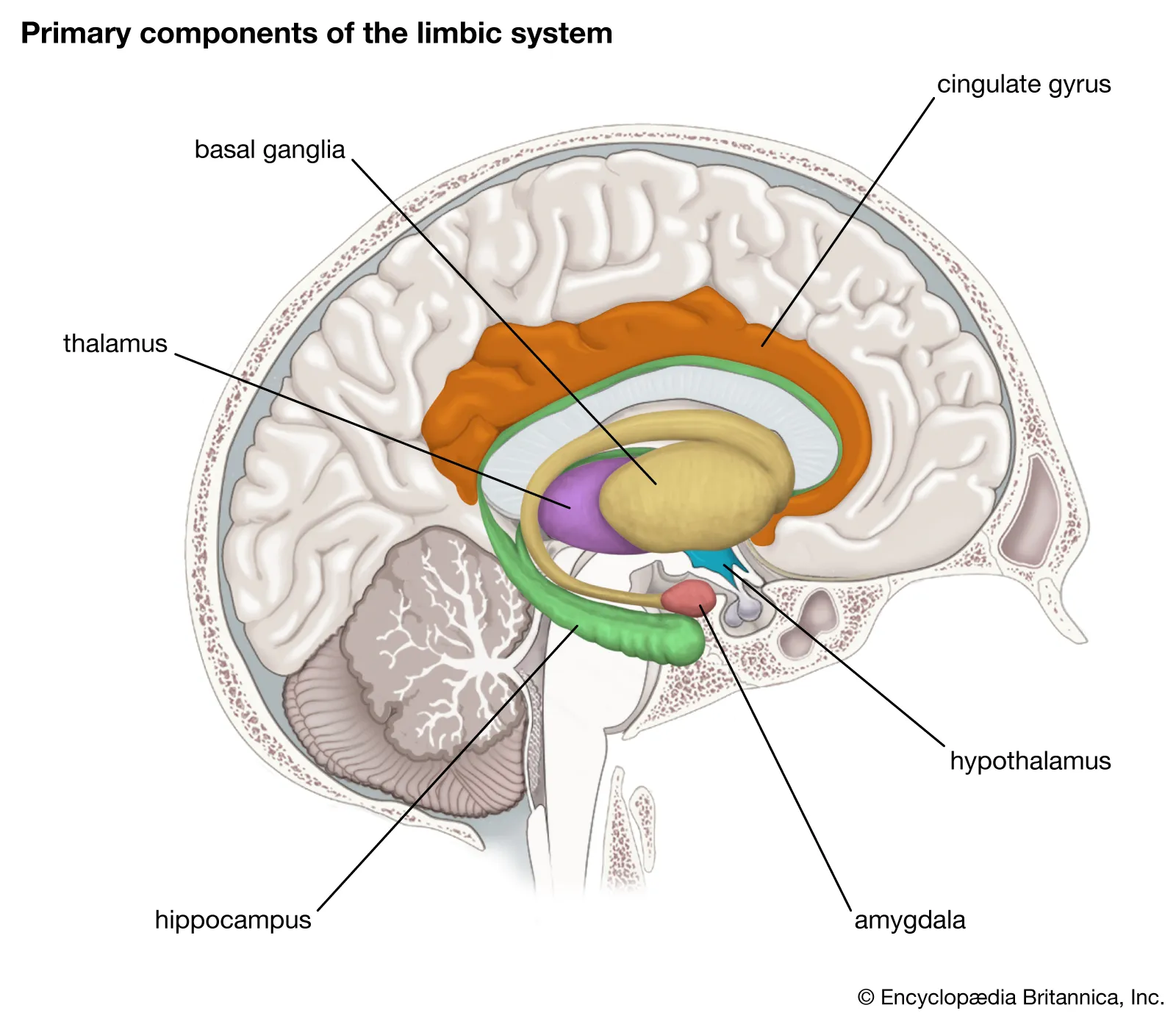
A group of structures in the brain involved in the experience and expression of emotions; includes the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, cingulate gyrus and the basal ganglia
Limbic system diagram
it focuses on how people evaluate their own lives. It focuses on Diener’s model of subjective wellbeing. People with higher SWB generally feel more positive than negative emotions and are satisfied with life. It includes life satisfaction and affective balance.
the practice of maintaining attention on the present moment, while accepting thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations without judgement. It includes attention and acceptance.