Chapter 9: Oral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Local factors that cause oral manifestations of systemic disease
-mucosa easily injured
-mild/chronic inflammation can cause lesions that would not otherwise show up
-endocrine disorders
-disorders of red and white blood cells
-disorders of platelets, clotting and bleeding
-immunodeficiency disorders
Endocrine disorders
Conditions in which too little or too much hormone is produced
-caused by gland dysfunction affecting hormone control and production
Hyperpituitarism
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Diabetes mellitus
Addison disease
hyperpituitarism
Excess hormone production by the anterior pituitary glan
-caused most often by a benign tumor, a pituitary adenoma, that produces growth hormone
-Gigantism and acromegaly
-Diagnosis involved measurement of growth hormone, amount does not decrease
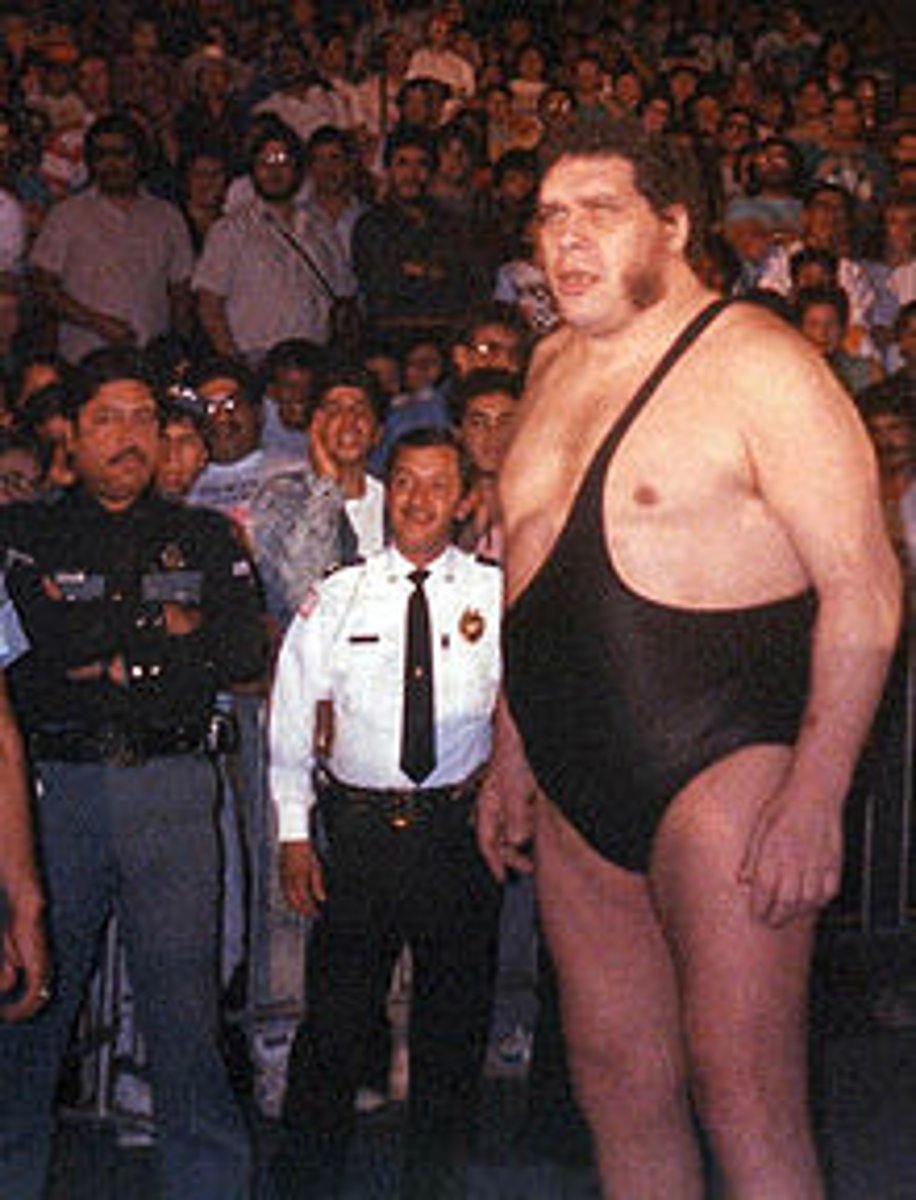

Gigantism
Results if over production of hormone by the anterior pituitary gland occurs before the closure of long bones
-adolescents
-Clinical features: 8+ feet tall, excessive growth of skeleton, weighs several hundred pounds, headaches, chronic fatigue, muscle and joint pain
-Treatment: surgical removal or radiation of pituitary adenoma
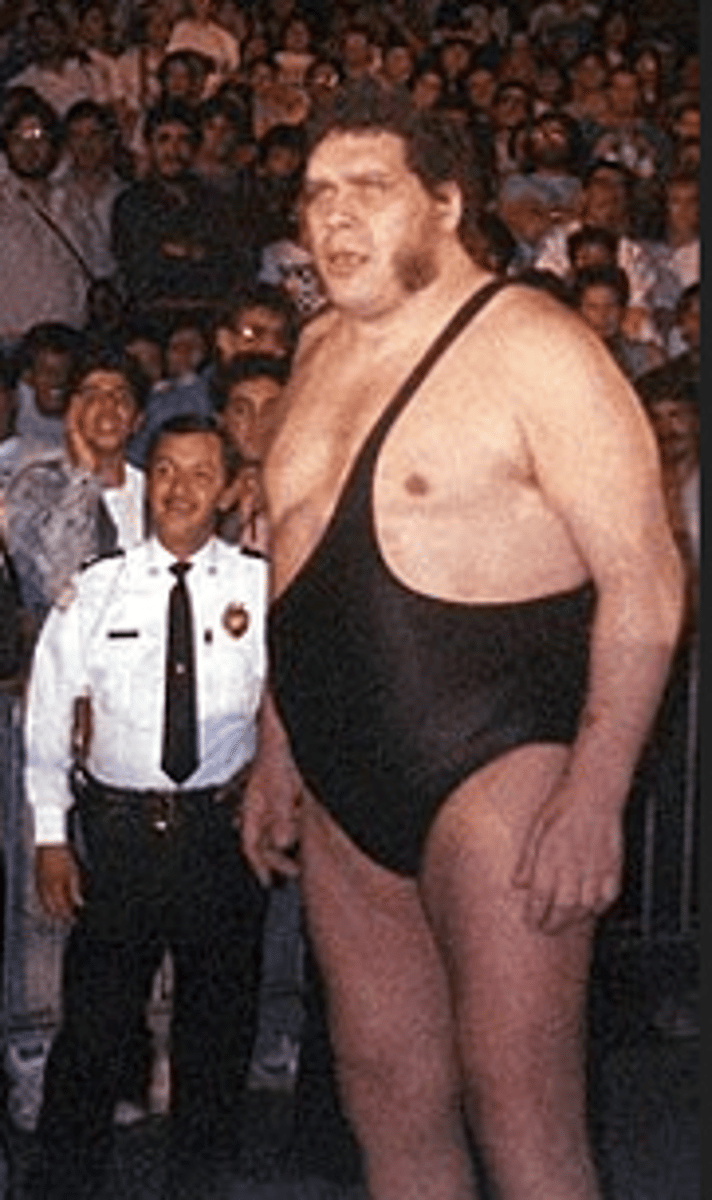

Acromegaly
results from over production of hormones by the anterior pituitary gland during adult life
-affects men and women in their 40s.
-Poor vision, light sensitivity, enlargment of hands and feet, increase in rib size
-Facial changes: enlargement of max. and mand. that can cause separation of teeth and malocclusion, frontal bossing and an enlargement of nasal bones, and enlargement of maxillary sinus that leads to voice deepening
-Thickened lips and macroglossia
-Treatment: pituitary gland surgery or radiation therapy
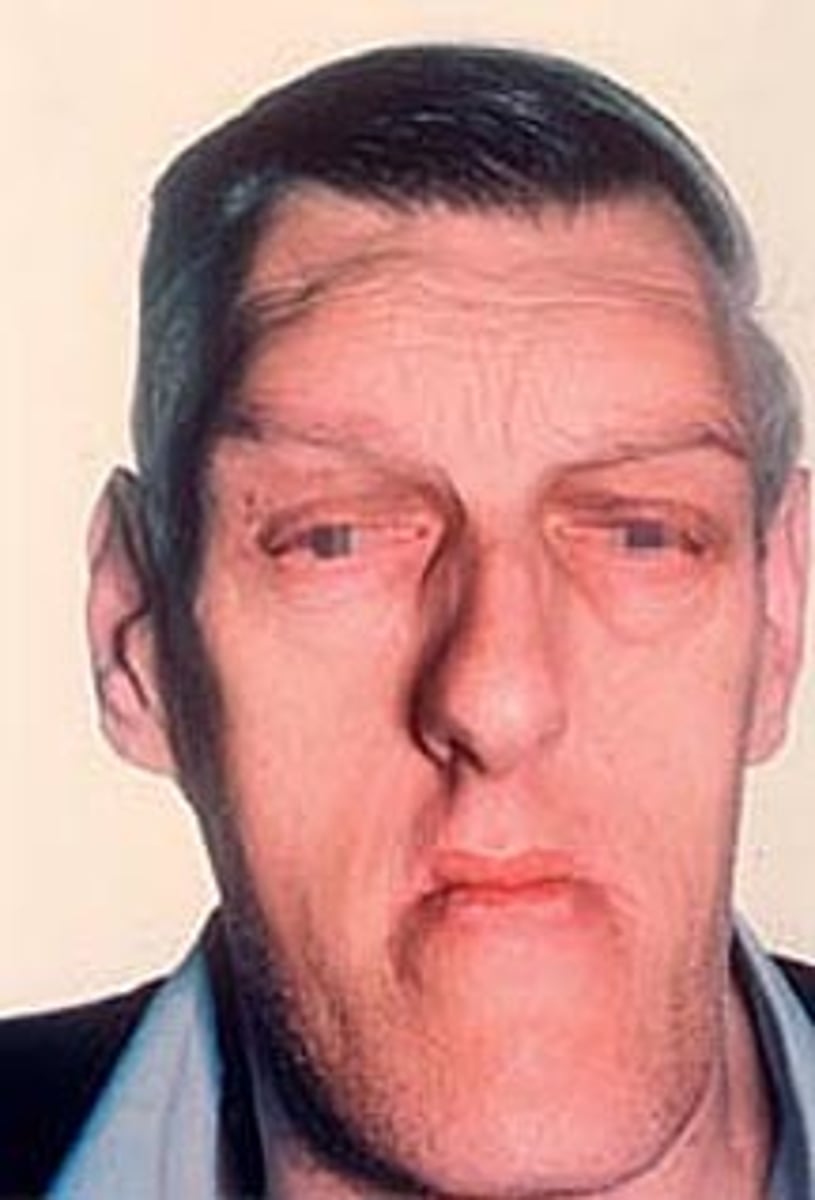
Hyperthyroidism ( Thyrotoxicosis or Graves Disease)
excess production of thyroid hormone
-more common in women than men in their 30s to 40s
Clinical features: thyroid enlargement, rosy complexion, erythema of palms, excessive sweating, fine hair, softened nails, exophthalmos, anxiety, weakness, restlessness, and cardiac problems
Oral manifestations in children: premature exfoliation of primary teeth and premature eruption of permanent teeth
Oral manifestations in adults: osteoporosis may affect alveolar bone, rapid caries and periodontal disease, and burning tongue
Treatment: surgical removal of thyroid, medication, and radioactive iodine
MISMANAGEMENT MAY LEAD TO HYPOTHYROIDISM
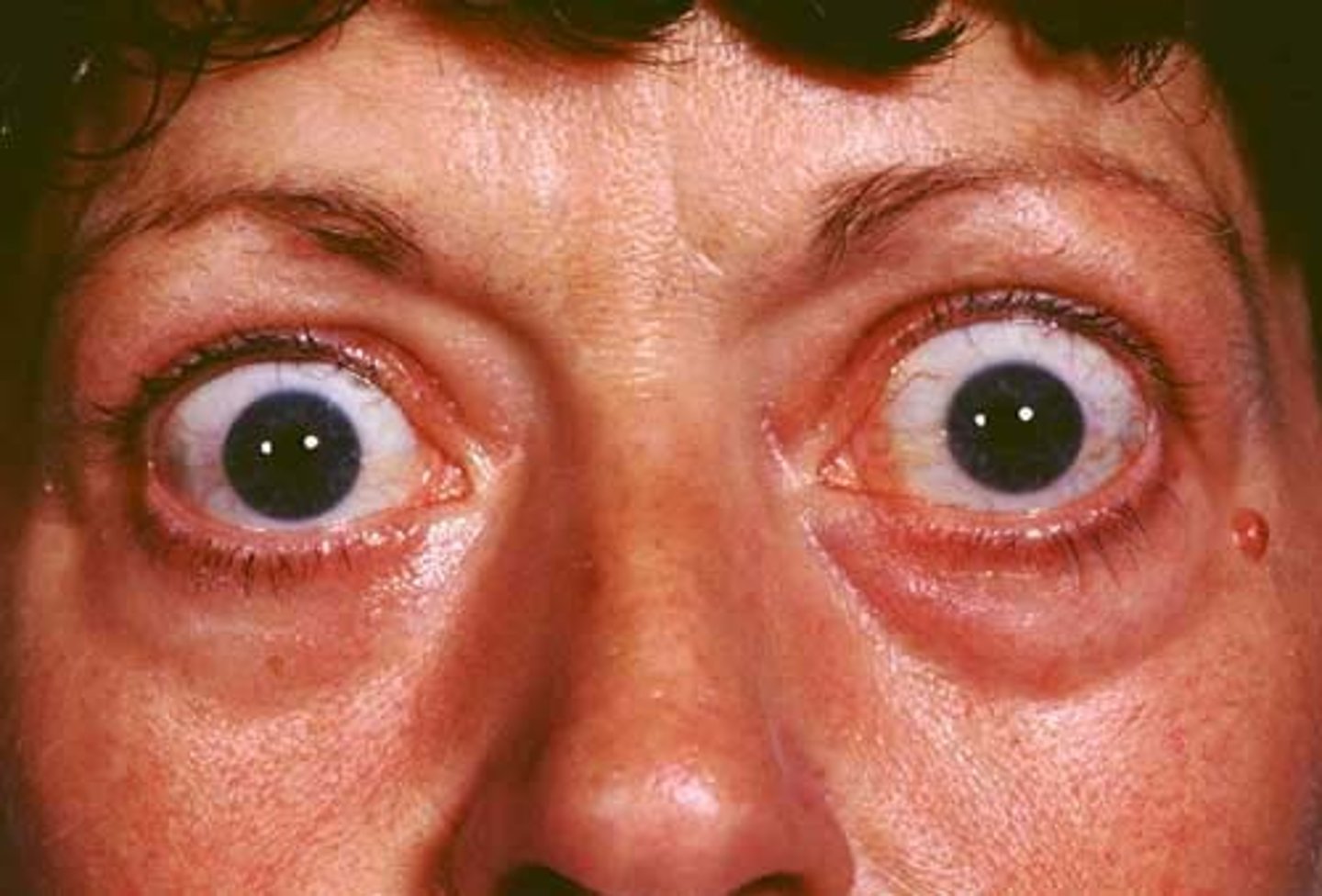
Graves disease
an autoimmune disorder is which antibodies, thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (THIs) stimulate thyroid cells
-thyroid gland enlarges
-too much thyroid hormone is produces
-increased metabolism
hypothyroidism
characterized by a decreased production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland
-Causes: treatment of hyperthyroidism, developmental disturbances, autoimmune destruction of thyroid (Hashimoto thyroiditis), iodine deficiency of mother during pregnancy, drugs
-Treatment: thyroid hormone replacement therapy, levothyroxine
-Cretinism and Myxedema
Cretinism
infancy and childhood hypothyroidism
-thickened lips
-enlarged tongue
-delayed eruption of teeth
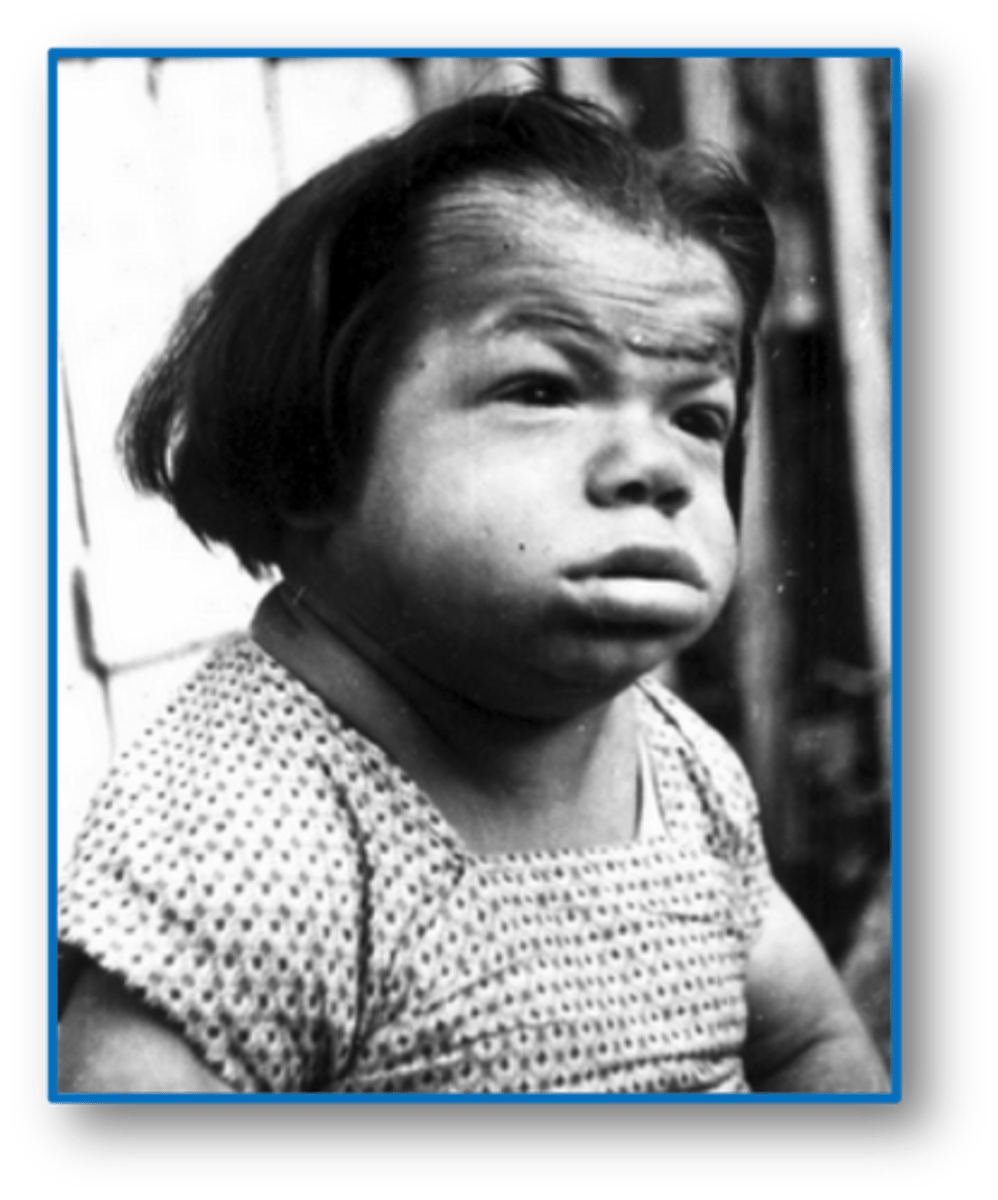

myxedema
hypothyroidism in older children and adults
-macroglossia
hyperparathyroidism
results from the excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands
-plays a role in calcium and phosphorus metabolism
-may be a result of hyperplasia of parathyroid glands, a benign tumor or one or more parathyroid glands, or a malignant parathyroid tumor
-middle aged adults and women
-Treatment: directed at correcting the cause of increased hormone production
symptoms of hyperparathyroidism
-"ground glass" appearance and loss of lamina dura, loosening of teeth
-well-defined unilocular or multilocular radiolucencies
-mild cases are asymptomatic, lethargy and coma with severe cases
-kidney stones, skeletal and gastrointestinal system effects
Diabetes mellitus
a chronic disorder of carbohydrate metabolism characterized by abnormally high blood glucose levels
-results from a lack of insulin, defective insulin that does not work to lower blood glucose levels, or increased insulin resistance caused by obesity
-Complications: damage to blood vessels, blindness, end-stage kidney failure, paresthesia or numbness, cardiovascular problems
hypercalcemia
elevated blood levels of calcium
hypophosphatemia
low levels of blood phosphorus
hyperglycemia
high blood glucose levels
prediabetes
fasting blood glucose between 100-125 mg/dL
Type 1: Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
Insulin-producing cells of the pancreas are destroyed
-Abrupt onset
-require insulin their entire lives
-3% of all diabetic patients have this type
-thought to be an autoimmune disease-associated with Addison disease, graves disease, and pernicious anemia
-includes the 3 Ps: Polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia
-Management: insulin injections, proper diet, exercise, frequent determination of blood glucose levels
Polydipsia
excessive thirst and intake of fluid
polyuria
excessive urination
polyphagia
excessive appetite
hypoglycemia
low blood sugar
severe hypoglycemia
insulin shock
brittle diabetes
uncontrolled blood glucose levels
Type 2: Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)
Characterized by insulin resistence
-97% of diabetic patients have this tyype
-usually occurs ages 35-40 or older
-gradual onset
-Weight gain
-Clinical features: vascular system, decreased resistance to infection, skin infections, UTIs and tuberculosis, atherosclerosis, diabetic retinopathy that leads to blindness
-acanthosis nigricans, oral candidiasis, mucomycosis, xerosotmia, periodontal disease
adipokines
hormones from fatty tissue
Gestational diabetes (GD)
Occurs during pregnancy
-might disappear after pregnancy (2-10% disappear)
-increase birth weight of child
-mother and child have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life
acanthosis nigricans
pigmented, velvety plaques in the folds and creases of the body
Addison disease (Primary hypoadrenocorticism)
insufficient production of adrenal steroids
-causes of adrenal gland destruction include: malignant tumors, tuberculosis, deep fungal infections, HIV infections, autoimmune disease, unknown
-stimulation of melanocytes: bronzing of skin and melanotic macules on oral mucosa
-Treatment: steroid replacement
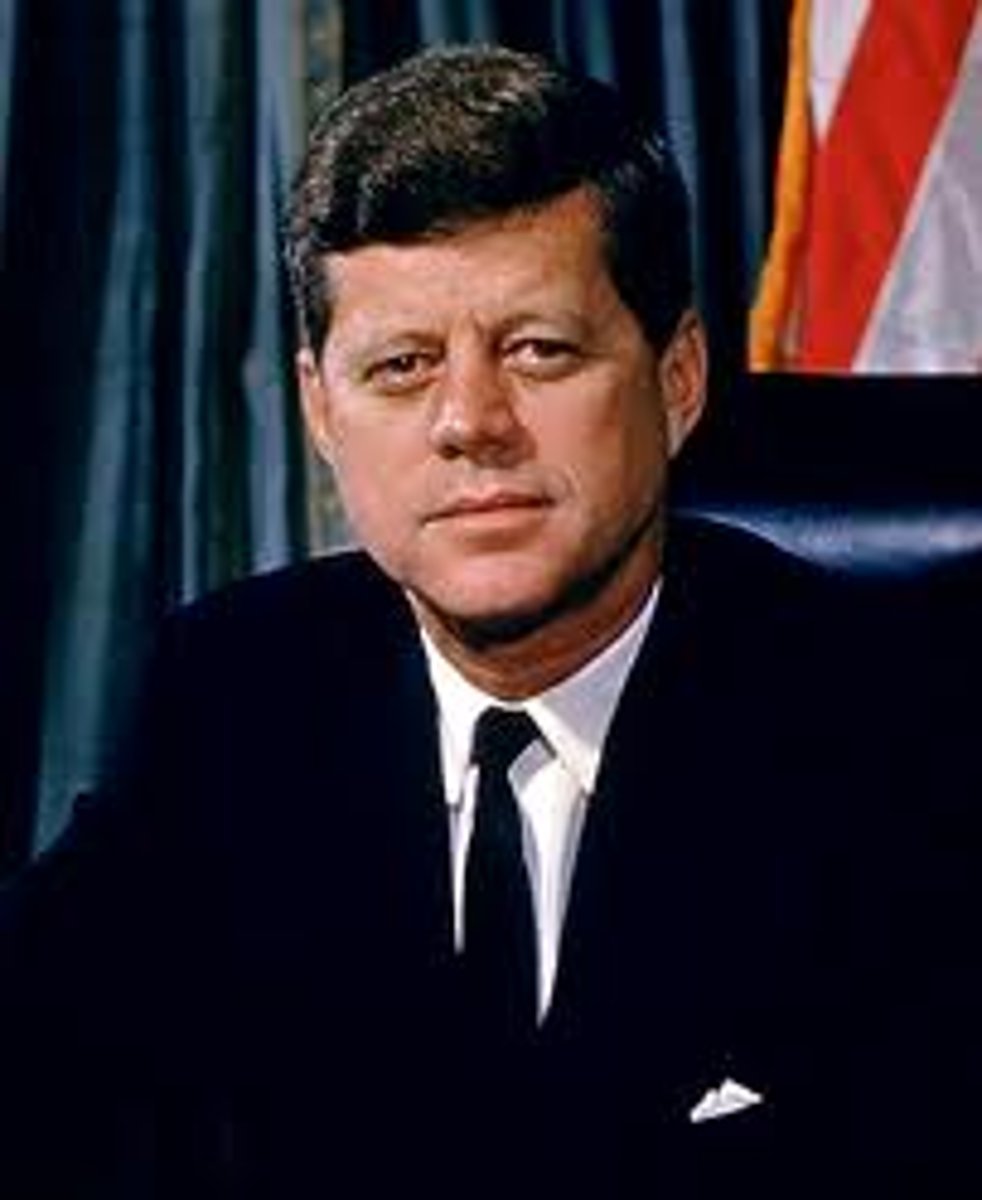

Hypercortisolism (Cushing syndrome)
caused by a sustained increase in glucocorticosteroid levels
-signs develop slowly
-weight gain is the most significant and obvious clinical feature
-signs: hypertension, hyperglycemia, mood alterations, poor healing
Complete blood count (CBC)
important in the diagnosis of blood disorders
-examines red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
-provides info about the number, ratio and appearance of each type of cell
Disorder of Red Blood cells and hemoglobin
anemia
iron deficiency anemia
pernicious anemia
folic acid and vitamin b12 deficiency anemia
sickle cell anemia
aplastic anemia
polycythemia
celiac sprue
Anemia
a reduction in the oxygen carrying capacity of blood
-most often related to a decrease in teh number of circulating RBCs
-Clinical features: pallor of skin and oral mucosa, angular cheilitis, erythema and atrophy of oral mucosa, loss of fungiform and filiform papillae on the dorsum of the tongue
iron deficiency anemia
an insufficient amount of iron is supplied to bone marrow for RBC development
MOST COMMON TYPE OF ANEMIA IN THE UNITED STATES
-often asymptomatic but may experience palpitations or shortness of breath
-Oral manifestations: dysphagia, glossitis, angular cheilitis exacerbated by oral candidiasis, atrophy of papilla and upper alimentary tract, predisposition of esophageal and oral cancer
-Treatment: dietary supplements
Pernicious anemia
Caused by a deficiency in vitamin B12
-probably an autoimmune disorder in most situations
-may be caused by removal of the stomach, gastric cancer, or gastritis
-Clinical features: weakness, pallor, fatigue, nausea, dizziness, diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, weight loss
-Oral features: angular cheilitis, mucosal pallor, painful, atrophic, and erythematous mucosa, mucosal ulceration, loss of papillae on the dorsum of the tongue, and burning and painful tongue
-oral manifestations are indistinguishable from those of pernicious anemia
-Treatment: Injections of vitamin B 12
Sickle cell anemia
an inherited blood disorder
-African American, mediterranean or asian individuals
-occurs before the age of 30
-more common in women
-RBCs develop a sickle shape when there is decreased oxygen
-Clinical features: weakness, shortness of breath, fatigue, joint pain, nausea, crisis, acute chest syndrome, abnormal kidney function, heart enlargement and cardiac function
-loss of trabeculation and large, irregular marrow spaces appear
-Diagnosis: shape may be seen on blood smear, low RBC count, low hemoglobin
-Treatment: administration of oxygen, |V fluid, oral fluids
Sickle cell crisis
severe sickling of erythrocytes
acute chest syndrome
pulmonary involvement
aplastic anemia
Clinical manifestations: fatigue, weakness, tachycardia, low platelets, ecchymosis, retinal and cerebral hemorrhages, predisposed to infections
Oral manifestations: infections, spontaneous bleeding, petechiae, purpuric spots
-diagnosis: based on laboratory test results, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia
purpuric spots
purplish or brownish-red discolorations caused by bleeding into tissues
leukopenia
abnormally low white blood cells
thrombocytopenia
decrease in platelets
polycythemia
characterized by an increase in the number of circulating RBCs
-3 forms: polycythemia vera (primary), secondary and relative
-oral manifestations: deep red to purple, edematous and bleeding easily oral mucosa, submucosal petechiae, ecchymosis, hematoma formation
-Diagnosis: laboratory testing and measurement of hemoglobin and hematocrit
-Treatment: removal of causative factors, chemotherapy, phlebotomy (removal of up to 500 mL of blood each day)
Agranulocytosis
a significant reduction in circulating granulocytes, particularly neutrophils
-can result from a problem in development of neutrophils or accelerated destruction of neutrophils
-Clinical manifestations: sudden onset of fever, chills, jaundice, weakness, sore throat, oral infection, oral necrotizing ulceration, excessive oral bleeding, rapid destruction of tooth-supporting structures, lymphadenopathy
-Diagnosis: Laboratory testing WBC count is reduced to less than 1000 cells/microliter (normally 4500-10,000)
-Treatment: transfusions, antibiotics, removal of cause
ALL SURGICAL PROCEDURES INCLUDING DENTAL HYGIENE PROCEDURES ARE CONTRAINDICATED
neutropenia
a reduction in the number of circulating neutrophils
Cyclic neutropenia
a cyclic decrease in the number of circulating neutrophilic leukocytes
-every 21-27 days, lasting 2-3 days
-Oral manifestations: gingival inflammation, ulceration of the tongue, ulceration of mucosal tissues, VERY PAINFUL
Leukemia
malignant neoplasms of hematopoietic (blood forming) stem cells
-characterized by an excessive number of abnormal WBCs in circulating blood
-unknown cause
-Acute and Chronic
-Oral manifestations: gingival enlargement, oral infections, bleeding gums, petechiae, ecchymoses, toothache caused by pulp infection, acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Acute leukemia
characterized by very immature cells and a rapidly fatal course if not treated
-Clinical features: sudden dramatic onset, weakness/fatigue caused by anemia, fever caused by infection, enlargement of lymph nodes, bleeding caused by thrombocytopenia
-Diagnosis: laboratory tests find elevated WBC with the presence of immature cells, anemia, and low platelet count
-Treatment: bone marrow transplant and supportive care such as antibiotics
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
involves immature lymphocytes
-primarily affects children and young adults
-good prognosis
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)
involves immature granulocytes
-primary affects adolescents and young adults
-poor prognosis
Chronic leukemia
-Features: slow onset, easy fatigability, weakness, weight loss, anorexia, pallor of lips and gingiva, gingival enlargement, petechiae and ecchymosis, gingival bleeding, cervical lymphadenopathy
-Diagnosis: high WBC count, up to 500,000
-Treatment: Chemotherapy, cryotherapy, bone marrow transplant
Celiac disease
a chronic disease
-associated with sensitivity to dietary gluten
-Oral manifestation: painful burning tongue, atrophy of papillae of tongue, ulceration of oral mucosa, diarrhea, nervousness, and paresthesia of extremities
hemostasis
cessation of bleeding
-defects caused by abnormalities of either platelets or coagulation factors
Platelets (thrombocytes)
aggregated to forms a temporary clots
fibrin
an insoluble protein essential to blood clotting
clotting factors (coagulation factors)
convert fibrinogen to fibrin
Normal platelet count
200,000-400,000/mm3
< 20,000 mm3 platelet count
spontaneous gingival bleeding occurs at this count
Thrombocytopenia
platelet count less than 100,000/mm3
bleeding time
used to provide an assessment of the adequacy of platelet function, not platelet number
normal bleeding time
between 1 and 6 minutes
prolonged bleeding time
in patients with platelet abnormalities
-greater than 5 to 10 minutes
Prothrombin Time (PT)
the ability to form a clot
normal prothrombin time
between 11 and 16 seconds
International Normalized Ratio (INR)
The ratio of PT to thromboplastin activity
-0.8 to 1.1 are normal for patients not on Warfarin
-2-3 for patients on Warfarin
Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT)
measures the other way by which clot formation occurs
-used to monitor heparin therapy
-Normal: 25-40 seconds
-Prolonged: 45-50 seconds (mild bleeding) 50+ seconds (severe bleeding)
Purpura
A reddish-blue or purplish discoloration of skin or mucosa from spontaneous extravasation of blood
-may be due to a defect or deficiency in blood platelets
-blood may ooze from gingival margins, without the presecnce of gingivitis or inflammation
Thrombocytopenic purpura
a bleeding disorder that results from a severe reduction in circulating platelets
-unknown cause, autoimmune or associated with drugs
-Features: spontaneous purpuric or hemorrhagic lesions, bruise easily, blood in urine, frequent nosebleeds, spontaneous gingival bleeding, petechiae, ecchymosis
-Treatment: transfusions, corticosteroids, and splenectomy
-DENTAL SURGERY AND SCALING ARE CONTRAINDICATED until laboratory tests confirm improvement
nonthrombocytopenic purpura
bleeding disorders that can result from either a defect in capillary walls or disorders of platelet function
-vitamin C deficiency, infections, chemicals, or allergies may cause alterations in vascular walls
-Von Willebrand disease
-Features: spontaneous gingival bleeding, petechiae, ecchymosis, and hemorrhagic blisters
-Treatment: systemic corticosteroids, splenectomy, permanent/temporary discontinuation of causative agent
Hemophilia
a disorder of blood coagulation
-results in severely prolonged clotting time
-caused by a deficiency in plasma proteins involved with coagulation
-oral manifestations: spontaneous gingival bleeding, petechiae and ecchymosis
-risk of hemorrhage after oral surgery and scaling
Type A hemophilia
Caused by a deficiency of plasma thromboplastinogen or factor VIII
Type B hemophilia
less common
-the clotting defect is plasma thromboplastin or factor IX
Mucositis
Caused from radiation therapy
-begins second week of therapy and ends a few weeks after the completion
-Painful
-Erythematous and ulcerated mucosa
-difficulty eating, pain on swallowing and loss of taste
Radiation therapy
destroys major salivary glands which may result in xerostomia
-prone to rampant caries and oral candidiasis
-prone to osteonecrosis
-should have oral evaluation before therapy
-potential sources for infection and questionable teeth should be removed
Chemotherapy
these drugs affect basal cells of the epithelium
-mucositis and oral ulceration are common
-decrease in all blood cells may occur leading to anemia, infection and bleeding problems
Xerostomia
blood pressure drugs, anti anxiety medications, antipsychotic medications and antihistamines can cause?
Prednisone
suppresses the immune system and can lead to candidiasis and oral infections
gingival enlargement
Phenytoin (Dilantin), nifedipine (Procardia) and cyclosporine can cause?
medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ)
Associated with bisphosphonate therapy