Science For Life Exam 2022
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:29 PM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
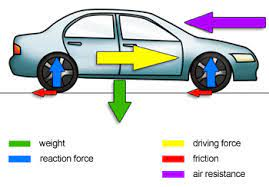
identify the forces acting on a motor vehicle in straight line motion on a horizontal surface
2
New cards
Newton's First Law of Motion
inertia, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it
3
New cards
Newton's Second Law of Motion
f=ma
4
New cards
Newton's Third Law of Motion
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
5
New cards
why do cars have crumple zones?
Purpose: to absorb the force of the crash
Laws of motion: 2nd law - when there is a collision the crumple zone absorbs the force which slows
down the car and there is less force on the passengers.
Laws of motion: 2nd law - when there is a collision the crumple zone absorbs the force which slows
down the car and there is less force on the passengers.
6
New cards
why do cars have seatbelts?
Purpose: protects people when the car is in motion and avoid unnecessary movement.
Laws of motion: 1st - as our bodies move, the seatbelts push back and prevent them from moving
Forward
Laws of motion: 1st - as our bodies move, the seatbelts push back and prevent them from moving
Forward
7
New cards
why do cars have headrests?
Purpose: protect and reduce the motion of the head and the neck
Laws of motion:
3rd - action is the force of the impact, reaction is stopping the neck from breaking.
1st - head is moving and if the head rest isn’t there to stop the head from moving, the damage will
be more severe like neck snapping or spine breaking
Laws of motion:
3rd - action is the force of the impact, reaction is stopping the neck from breaking.
1st - head is moving and if the head rest isn’t there to stop the head from moving, the damage will
be more severe like neck snapping or spine breaking
8
New cards
Know that the weight on Earth is differnt to the weight on the Moon and why?
It is becuase the gravitational attraction on the Moon is much less than it is here on Earth
9
New cards
Atomic Number
Number of Protons
10
New cards
Atomic structure
Size - electron < proton < neutron
11
New cards
atomic mass
Number of protons + number of neutrons. You can work out the number of neutrons by subtracting the number of protons from the mass number.
12
New cards
Electron Configuration – Electron shells
2 in the first shell and 8 in the rest (formula: 2n^2)
13
New cards
Periodic table Groups and Periods
Groups/family (vertical columns)
Periods (Horizontal lines)
Periods (Horizontal lines)
14
New cards
Periods
the period (row) of the periodic table that an element is in correlates to the number of electron shells it has. For example, carbon is in period 2 and thus has 2 electron shell
15
New cards
Groups
The group (column) indicates how many electrons the element has in its outermost shell
Elements in the same group have similar properties. For example, all the elements in Group 1 are highly reactive metals.
Elements in the same group have similar properties. For example, all the elements in Group 1 are highly reactive metals.
16
New cards
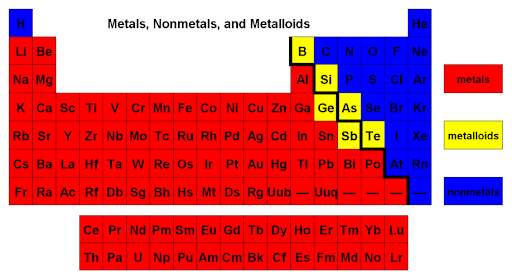
Metals, Non-Metals, and Metalliods
Metals: elements that conduct heat + electricity and are shiny solids that can be made into thin wires and sheets.
Non-metals: elements that do not conduct electricity or heat and usually have a lower boiling and melting point than metals.
Metalloids: elements that have features of both metals and non-metals.
Non-metals: elements that do not conduct electricity or heat and usually have a lower boiling and melting point than metals.
Metalloids: elements that have features of both metals and non-metals.
17
New cards
Cations
- Have Positive charge
- Have lost electrons
- Have lost electrons
18
New cards
Anions
- Have a negative charge
- Have gained electrons
- Have gained electrons
19
New cards
Ionic Bonding
To write the formula of a compound, first, calculate the charge of both elements. Then find the symbols for each element and swap the charges.

20
New cards
Naming Ionic compounds
Metal is named first and its name is not changed.
Non-metal is named second and the end of its name is changed from -ine to -ide
Non-metal is named second and the end of its name is changed from -ine to -ide
21
New cards
Naming Covelant compounds
1. Write the name of the FIRST element
2. write the name of the SECOND element -ide ending
3. Use prefixes to tell the number of atoms of each element
2. write the name of the SECOND element -ide ending
3. Use prefixes to tell the number of atoms of each element
22
New cards
Covelant bonding
A covalent bond consists of the mutual sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms.
23
New cards
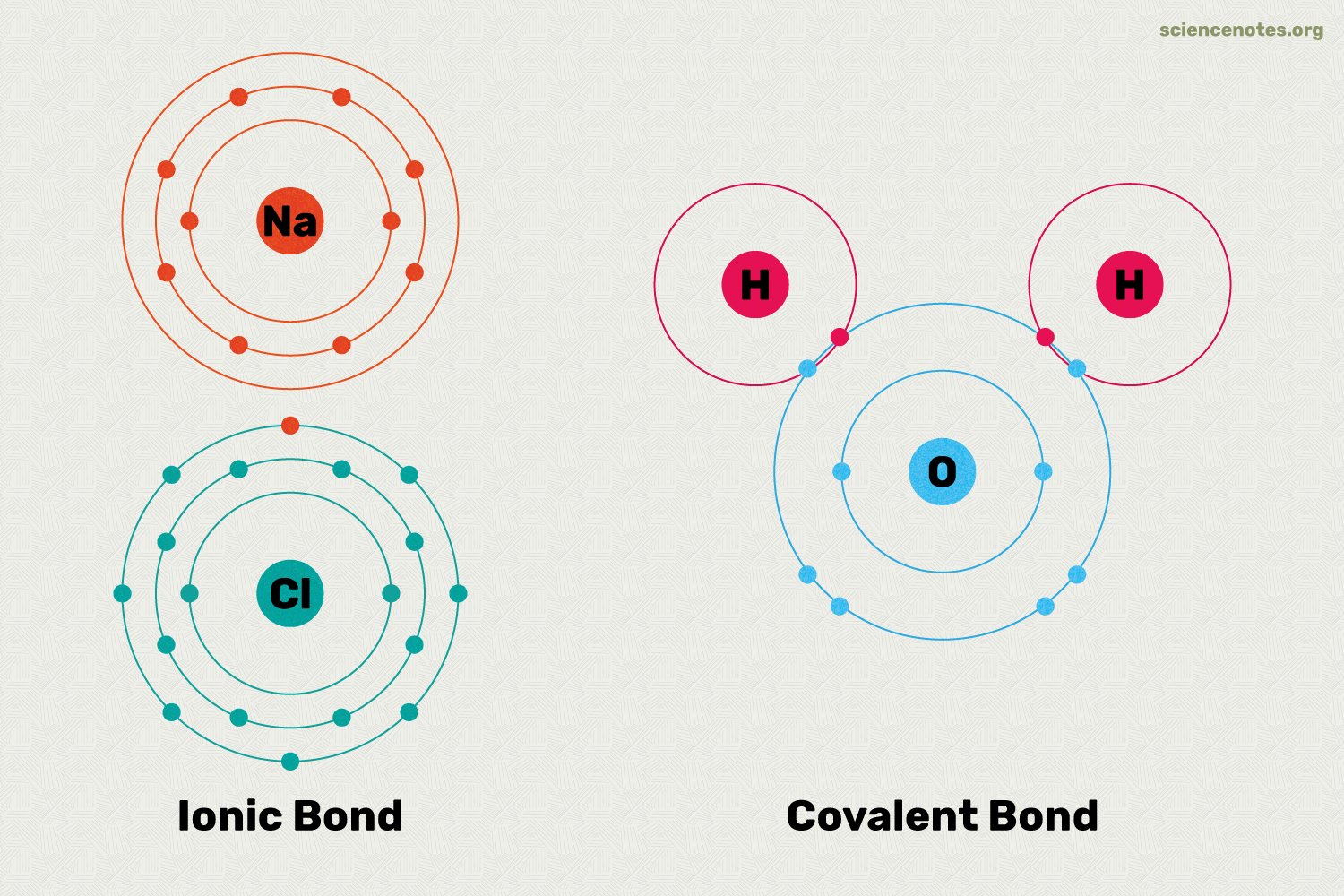
IONIC VS COVELENT STRUCTURE
24
New cards
Combustion ( type of reaction )
Combustion is when oxygen reacts with any other substance. It usually produces heat and carbon dioxide.
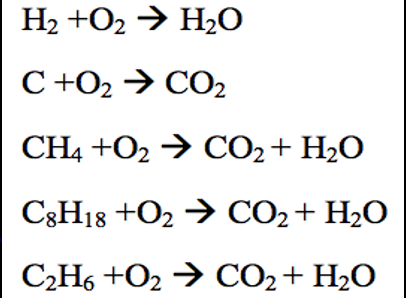
25
New cards
Neutralization
is when an acid reacts with a base producing salt and water.
- Sulfuric acid always forms sulfates
- Hydrochloric acids forms chlorides
- Nitric acid forms nitrates
when writing a salt the first name is from the metal and the second is from the acid.
- Sulfuric acid always forms sulfates
- Hydrochloric acids forms chlorides
- Nitric acid forms nitrates
when writing a salt the first name is from the metal and the second is from the acid.
26
New cards
Synthesis
Synthesis reactions occur when two substances
(generally elements) combine and form a compound
Reactant 1 + Reactant 2 → Product
Eg. C + O2 → CO2
(generally elements) combine and form a compound
Reactant 1 + Reactant 2 → Product
Eg. C + O2 → CO2
27
New cards
Decompostion
Decomposition is when a compound breaks down into elements
1 Reactant → Product + Product
Eg. 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
1 Reactant → Product + Product
Eg. 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
28
New cards
Single displacement
One metal deposits on another. A metal solution reacts to become a pure solid metal.
Eg. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
A + BC → B + AC
For A to kick out B, A has to be more reactive. If B is more reactive, it keeps its position and stays the same.
Eg. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
A + BC → B + AC
For A to kick out B, A has to be more reactive. If B is more reactive, it keeps its position and stays the same.
29
New cards
Double Replacement
A metal replaces a metal in a compound and a non-metal replaces a non-metal compound
( Ions switch partners )
AB+ CD-> AD + CB
( Ions switch partners )
AB+ CD-> AD + CB
30
New cards
DNA
A molecule containing genetic information is in charge of construction and development.
31
New cards
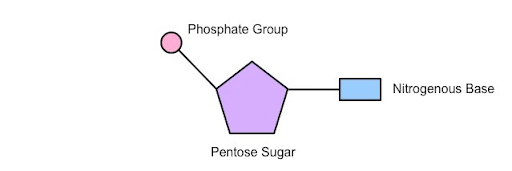
Basic structure NUCLEOTIDES
- Phospahte group
- Nitrogenous Base
- Pentose Sugar
- Nitrogenous Base
- Pentose Sugar
32
New cards
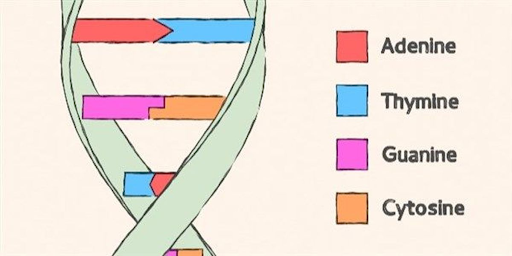
BASIC CODES -
ADENINE, THYMINE, GUANINE, CYTOSINE
Car in a garage ( Cytosine + Guanine)
Apples in a tree (Adenine + Thymine)
Car in a garage ( Cytosine + Guanine)
Apples in a tree (Adenine + Thymine)
33
New cards
CHROMOSOMES
A structure found inside the nucleus of a cell.
A chromosome is made up of proteins and DNA organized into genes.
Each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
A chromosome is made up of proteins and DNA organized into genes.
Each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
34
New cards
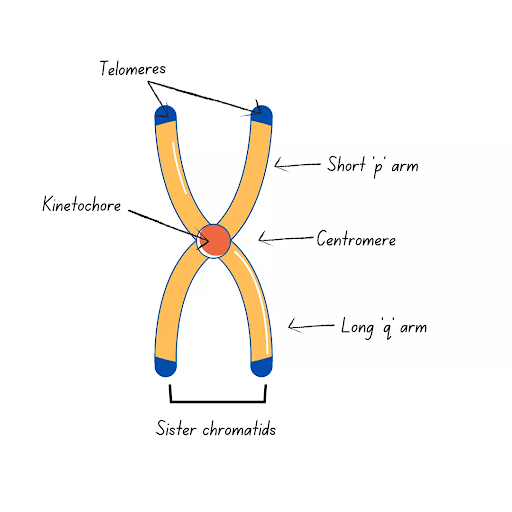
Chromosomes structure
35
New cards
Autosomes
control the inheritance of all an organism's characteristics except the sex-linked ones. Humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 23 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total).
36
New cards
sex chromosomes
A type of chromosome involved in sex determination. Humans and most other mammals have two sex chromosomes, X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes in their cells, while males have one X and one Y.
37
New cards
SEX DETERMINATION AND PREDICTIONS
A child's biological sex (male or female) is determined by the chromosome that the male parent contributes. Males have XY sex chromosomes while females have XX sex chromosomes; the male can contribute the X or Y chromosome, while the female must contribute one of their X chromosomes.
38
New cards
Gene
The basic unit of heredity is passed from parent to child.
39
New cards
Homozygous
having two identical alleles of a particular gene or genes.
40
New cards
Heterozygous
having two different alleles of a particular gene or genes.
41
New cards
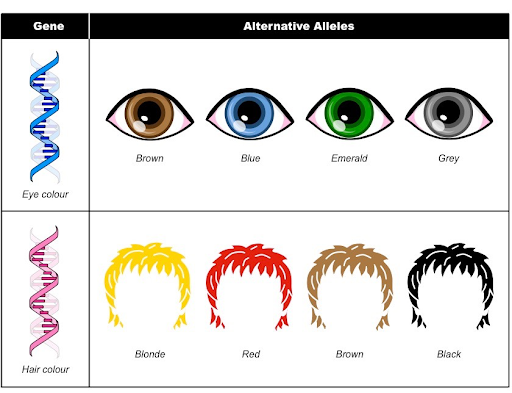
Alleles
An allele is one of two or more versions of a DNA sequence (a single base or a segment of bases) at a given genomic location.
42
New cards
Dominant/recessieve
Relating to or denoting heritable characteristics controlled by genes that are expressed in offspring only when inherited from both parents.
Dominant- An allele of a gene is said to be dominant when it effectively overrules the other (recessive) allele.
Recessive - A recessive gene is a gene that can be masked by a dominant gene.
Dominant- An allele of a gene is said to be dominant when it effectively overrules the other (recessive) allele.
Recessive - A recessive gene is a gene that can be masked by a dominant gene.
43
New cards
Genotypes
A person's genotype is their unique sequence of DNA
44
New cards
Phenotypes
Phenotype refers to an individual's observable traits, such as height, eye colour and blood type (Characteristics)
45
New cards
Mitosis
Cell division for growth and repair
46
New cards
meiosis
Cell division for the production of sex cells
47
New cards
Negitaves of genetic technology
Potential Harms to Health. New Allergens in the Food Supply. Antibiotic Resistance. Production of New Toxins. Concentration of Toxic Metals. ...
Potential Environmental Harms. Cross Contamination.
Increased Weediness. Gene Transfer to Wild or Weedy Relatives. ...
Unknown Harms to the Environment.
Potential Environmental Harms. Cross Contamination.
Increased Weediness. Gene Transfer to Wild or Weedy Relatives. ...
Unknown Harms to the Environment.
48
New cards
positives of genetic technology
Genetic technologies are changing the way we produce food, improving crop yield and preventing catastrophic losses from droughts, floods and pests.
49
New cards
Climate change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns.
50
New cards
Consequences of global warming
melting ice caps, rising sea levels, extreme weather, drought, increased extinction rates, tropical diseases
51
New cards
Natural greenhouse effect
Heat buildup in the atmosphere due to the presence of 'greenhouse' gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor.
52
New cards
enhanced greenhouse effect
the increased capacity of the atmosphere to trap thermal energy because of an increase in greenhouse gases due to human activity
53
New cards
Carbon cycle
Describes how carbon moves between the atmosphere, soils, living creatures, the ocean, and human sources.