ib econ- 3.2: aggregate demand and aggregate supply
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credit https://www.econinja.net/macroeconomics/3-2-aggregate-demand-aggregate-supply
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is aggregate demand (AD)?
the total amount for all goods and services in the economy, or the value of all goods and services in the economy, in a specified time period.
draw the aggregate demand curve
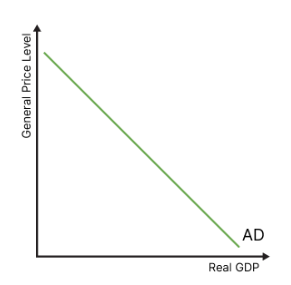
what are the components of ad
measured the same way as gdp using the expenditure method
consumption + investment + gov. expenditure + (exports - imports)
C + I + G + X - M
what are the determinants of consumption?
consumer confidence in the economy: confidence is low during recessions and high during booms - higher confidence = higher consumption
interest rates: higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing money, and make saving seem more attractive, thus decreasing consumption
wealth: having more disposable income increases your marginal propensity to consume
income taxes: higher/more taxes lead to less disposable income which leads to less wealth
level of household debt: more debt reduces marginal propensity to consume, thus lowering consumption
expectations of future price levels: if people believe that things are going to become more expensive in the future, they will consume more now
what are the determinants of investment?
interest rates: higher interest rates make it more expensive to borrow money, and increase the attraction of (and reward for) saving, making businesses less likely to invest when interest rates are high
business confidence in the economy: low during recessions, higher during booms - higher confidence leads to higher levels of investment
technology: firms want to remain up to sate, so the more technological advances that there are, the more investment there is
business taxes: more taxes = less money to invest = less investment
level of corporate debt: more debt = less money to spend = less investment
what are the determinants of government expenditure?
political priorities: elected governments tend to do things that get them re-elected rather than what’s best for the economy
economic priorities: economics is quite subjective so different government officials have different interpretations for how to run the country
what are the determinants of net exports?
income of trading partners: the more other countries earn, the more goods and services they will buy from you - increasing your net exports
exchange rates: if your country’s currency devalues, your goods and services are cheaper to other countries, so they will buy more from you (increasing your net exports). furthermore, foreign goods and services will be more expensive to you, so you will buy less - decreasing imports and increasing net exports.
trade policies: more taxes and quotas on imports will decrease imports, increasing net exports.
what is aggregate supply?
the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing and able to provide in an economy, in a certain time period
what are the two main economic schools of thought regarding as?
neoclassical: sras and lras
keynesian: combined as curve
draw the sras curve
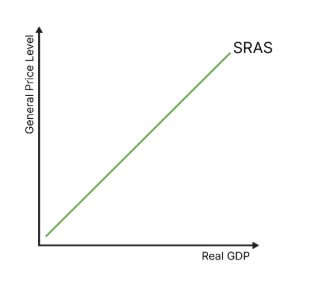
what are the determinants of sras?
cost of factors of production: labour costs (wages), raw material costs, exchange rates, interest rates and bureaucracy
indirect taxes
draw the lras curve
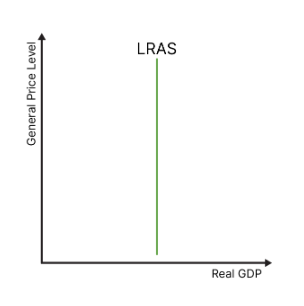
what is lras?
the maximum level of real gdp that the economy is currently hypothetically able to achieve, with full employment in all sectors. it is impossible to produce more than this level, given the current technology and productivity in the economy
independent of price
used by neoclassicalists
draw the keynesian aggregate supply curve
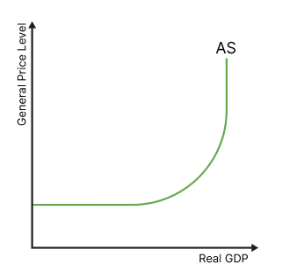
what is the keynesian as curve?
keynes believed in one unified aggregate supply “in the long run, we are all dead”
at low economic output, there is plenty of spare capacity in the economy, and extra output can be insured without any strain on price
once this spare capacity diminishes, there is pressure on scarce resources, increasing the general price level
at some point, everything will be fully employed, and it will be impossible to produce more output regardless of price level
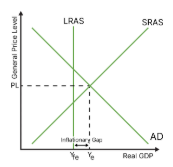
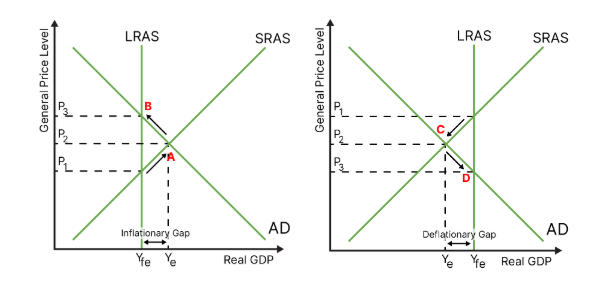
draw an inflationary gap
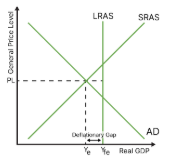
draw a deflationary gap
what is an inflationary gap?
occurs when the economy has a higher output than its potential, in other words, employment is beyond full (could be due to long and unfair working conditions, child labour etc). this is not ideal because it is unsustainable and leads to higher prices
what is a deflationary gap?
occur when the economy has a lower output than its potential, in other words, it has unemployment of at least one factor of production. this is not ideal because it leads to inefficient.
what causes shifts in lras or keynesian as?
changes in quantity or quality of factors of production
improvements in technology
increases in efficiency
changes in institutions
what are the assumptions/implications of the neoclassical model?
believe markets are self-regulating and gov. intervention is not necessary
prefer policies that free up markets such as market-based supply side policy
originated in post ww1 Austria where inflation was rampant, so inflation is very important
what are the assumptions/implications of the keynesian model?
believe gov. intervention is necessary to ensure full employment and economic growth
prefer policies that regulate/intervene in markets such as fiscal policy
originated in the great depression where unemployment was rampant, therefore - unemployment, wellbeing, and economic growth are more important than inflation
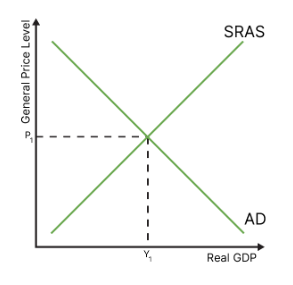
draw the diagram for short run equilibrium
draw the diagram for neoclassical equilibrium
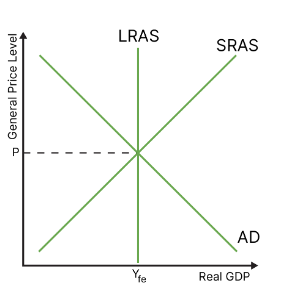
what does it mean when the eocnomy is in neoclassical equilibrium
all lines (lras, sras and ad) intersect
this does not mean everyone is working, but rather that the economy is at its natural rate of unemplyment (everyone willing and able to work has a job)
because everything is at full employment, any increase in ad will just result in price increases
what do neoclassicalists believe about inflationary or deflationary gaps?
should an inflationary gap exist, production prices will increase as there is more demand for products than can be produced
this increases the costs of goods and services, raising the price level further, which decreases aggregate demand. equilibrium is restores, albeit at a higher general price level.
should a deflationary gap exist, production costs will decrease as there is more spare capacity in the economy
this decreases the cost of goods and services, decreasing price level further, which increases aggregate demand. equilibrium is restored, albeit at a lower general price level.
draw the diagram for keynesian equilibrium
equilibrium can be at any point along as - keynesians do not believe in the neoclassical belief of equilibrium automatically adjusting itself to a specific location
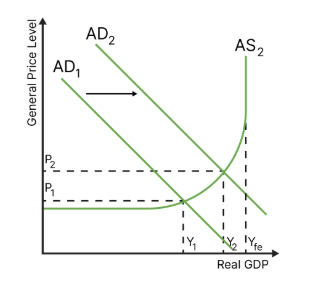
why do keynesians believe strongly in government intervention to correct equilibrium
production costs (especially labour) are downward sticky (rarely tend to decrease): this means that workers rarely accept lower salaries, and if they do then productivity is weakened
in this case, production costs will not go down if there is an inflationary gap, and the equilibrium will not correct itself