Solutions Part 5
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
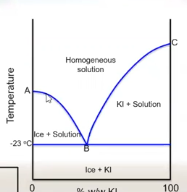
what is the point where the 2 curves meet at B called
eutectic point
what does the eutectic point represent
the lowest temprature at which the liquid solution can exist
what do solid dispersions do
enhance the dissolution of poorly soluble drugs
how does the enhanced dissolution effect work in drugs
the drug is mixed with a freely soluble carrier
what happens if the eutectic temprature is below room temperature
the mixing of two solids can result in the formation of a liquid
what are the two main types of a solid in a solid
intimate crystalline mixture
mixed crystal
how do you form intimate crystalline mixtures
below the eutectic point
what is the eutetic point
where liquid and solid phases have the same composition
whats the difference between raoults law and henry’s law
raoults law applies to the solvent in a solution
while
henrys law applies to the solute in a solution
raoults law (data book)

what are ideal solutions
solutions that obey raoults law
what is raoult’s law
the relative lowering of the vapour pressure is equal to the mole fraction of the solute in solution
binary solutions that do not obey raoult’s law are called…
non ideal solutions
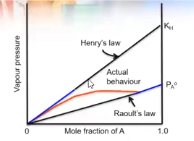
describe the differences in henry’s law and raoult’s law in the table
henry’s law is obeyed by the solute when only a small amount is present
raoults law is obeyed by the solvent when a large amount of it is present
how to calculate total vapour pressure
pA + p0
whats the eutetic point used for
increasing the solubility of drugs