Patho Ch 1 & Pharm Ch 1-2 Notes Exam #1
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from lecture notes on General Aspects of Pathophysiology & Pharmacology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment regardless of external changes
Health
Physical, mental, and social well-being
Disease
Deviation from the normal state of homeostasis
Pathophysiology
Functional (physiologic) changes in the body as a result from disease
Idiopathic
Cause of disease is unknown
Iatrogenic
Error/treatment/procedure that may cause the disease
Prophylaxis
Preserve health; prevent spread of disease
Pathogenesis
Development of the disease, step by step processes causing problems (cause & effect)
Acute Disease
Sudden/acute onset of disease, short-term, develops quickly
Insidious Disease
Gradual, vague, or mild signs of a disease (gradual)
Chronic disease
Develops gradually with milder symptoms
Subclinical state
Pathologic changes, no obvious manifestations
Latent state
No symptoms or clinical signs evident
Prodromal period
Early development of the disease; signs are nonspecific or absent (malaise - gradual buildup)
Local Manifestation
Clinical evidence with signs and symptoms at the site of the problem
Systemic Manifestation
General indicators of illness, i.e. fever
Signs
Objective indicators of disease
Symptoms
Subjective feelings
Lesions
Specific local change in the tissue (scratch all the way to tumor)
Syndrome
Collection of signs and symptoms
Remission
Period which manifestations subside
Exacerbation
A worsening of severity (“flare- up” - e.g., MS)
Precipitating factor
Condition that triggers an acute episode
Complications
New secondary or additional problems
Therapy
Measures to promote recovery/slow progress
Sequelae
Potential unwanted outcomes
Convalescence or rehabilitation
Period of recovery and return to healthy state
Morbidity
Disease rates within a group
Mortality
Relative number of deaths resulting from the disease
Epidemiology
Tracking the pattern or occurrence of disease
Incidence
Number of new cases in a given population within a given time period
Prevalence
Number of new, old, or existing cases within a given population and time period (all cases)
Epidemics
A higher number of expected cases of an infectious disease occur within an area
Pandemic
Involve a higher number of infectious diseases in many regions of the globe
Infarction
Area of dead cells as a result of oxygen deprivation, implies loss of function with enough loss of tissue/cellular death
Gangrene
Area of necrotic tissue that has been invaded by bacteria, linked with Diabetes and feet infections leading to amputation
Atrophy
Decrease in the size of cells; results in reduced tissue mass (abnormal can be due to excessive muscle non-use e.g., bed rest)
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell size; results in enlarged tissue mass (abnormal can be due to hormonal imbalance)
Hyperplasia
Increased number of cells; results in enlarged tissue mass (skeletal muscle cannot do hyperplasia, abnormal can be due to hormonal imbalance)
Metaplasia
Mature cell type is replaced by a different mature cell type (differentiation - less functional/specialized), ciliated cells, respiratory epithelium, and goblet cells can be replaced with stratified squamous tissue
Dysplasia
Cells vary in size and shape within a tissue (“Pre-cancer”)
Anaplasia
Undifferentiated cells, with variable nuclear and cell structures, cancer malignancies, cells found in a different area
Neoplasia
New growth commonly called tumor, can be benign or malignant
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death, injured cell releases enzymes that engulf and destroy itself, *usually physiologic*, affects single cells
Necrosis
results from irreversible cell injury, dying cells cause further cell damage due to cellular disintegration (abnormal, not programmed), injured cell has ruptured plasma membrane, *always pathologic*, affects other cells through inflammation
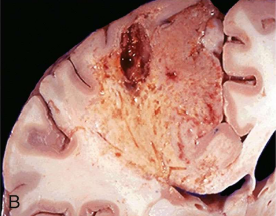
Liquefaction necrosis
Dead cells liquefy because of release of cell enzymes (brain)
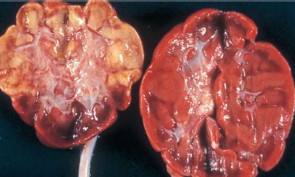
Coagulative necrosis
Cell proteins are altered or denatured coagulation
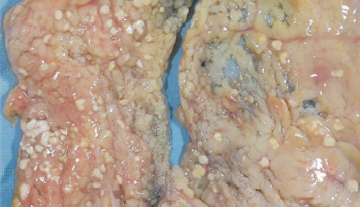
Fat necrosis
Fatty tissue broken down into fatty acids
Caseous necrosis
Form of coagulation necrosis with a thick, yellowish cheesy substance, specifically tuberculosis, creates a Ghon complex - where an area is walled off with Caseous necrosis
Hypoxia
Reduced oxygen in tissues, most common cause of cellular injury due to it causing Ischemia
Ischemia
Most common, lack of Oxygen delivered through blood flow
Pharmacology
Study of drugs and their origin, nature, properties, and effects on living organisms
Generic Name
Assigned by United States Adopted Name (USAN) Council, initial lowercase letter; never capitalized always
Trade Name
Assigned by the Pharmaceutical Company (Patent), capitalized first letter - always for trade name, might have Tall Man Lettering (e.g., CeleXA vs CeleBREX)
Chemical Name
Complete molecular formula
Official Name
Listed name in USP/NF reference, usually the same as generic and is when the drug is developed
Over-the-counter (OTC)
No purchasing restrictions by the FDA
Legend drug
Prescription drug: determined unsafe for over-the-counter purchase because of possible harmful side effects if taken indiscriminately, includes birth control pills, antibiotics, cardiac drugs, and hormones
Controlled substance
Drug controlled by prescription requirement because of the danger of addiction or abuse
Off-label medication
Drug used in a way not indicated on the FDA label (e.g., Viagra)
Indications
List of medical conditions or diseases for which the drug is meant to be used
Actions
Description of the cellular changes that occur as a result of the drug
Contraindications
List of conditions for which the drug should not be given
Cautions
List of conditions or types of patients that warrant closer observation for specific side effects when given the drug
Side effects and adverse reactions
List of possible unpleasant or dangerous secondary effects, other than the desired effect
Interactions
List of other drugs or foods that may alter the effect of the drug and usually should not be given during the same course of therapy
Primary prevention
Protect healthy people from developing a disease or experiencing an injury in the first place
Secondary prevention
Happens after an illness or serious risk factors have already been diagnosed, goal to halt or slow progress, limit long-term disability, prevent re-injury (hypertension, bad lipid levels)
Tertiary prevention
Helping people manage complicated chronic health problems, preventing further physical deterioration and maximizing quality of life (major complicated diagnosis e.g, cancer or AIDS)
Stage 1 Research Process
No human subjects, “basic science”, identify tech to be used, lab work.
Stage 2 Research Process
Small number of human subjects
Stage 3 Research Process
Clinical trials begin, can take a number of years to be deemed safe and reach the market, and can also be removed and pulled from the market, “double blind studies”, large number of patients with the disease or risk of the disease
Gross level
Organ or system level
Microscopic level
Cellular level
Biopsy
Excision of small amounts of living tissue
Autopsy
Non-living, examination of body and organs after death
Diagnosis
Identification of a basic disease including evaluation of signs and symptoms as well as lab tests
Differential diagnosis
3-5 things that are likely to be the disease
Working diagnosis
Treating as a diagnosis but don’t truly know (best guess)
Etiology
Causative factors in a particular disease, correlations (multifactorial - not just 1 cause)
1906 Pure Food and Drug Act
1st federal law enacted, 1st attempt to protect consumers, label container if dangerous ingredients, established 2 references (USP - United States Pharmacopeia and NF - National Formulary)
How many schedules of controlled substances are there?
5
Schedule I (C-I)
Illegal - not approved for medical use in the United States; high abuse potential
Schedule II (C-II)
High abuse potential; written prescription only; no refills without new prescription
Schedule III (C-III)
May lead to moderate dependence; written, faxed, or phoned prescription by physician; may be refilled up to 5 times in 6 months
Schedule IV (C-IV)
Lower abuse potential; prescription may be written by health care professional and signed by physician; phoned in by health care professional; may be refilled up to 5 times in 6 months
Schedule V (C-V)
Lowest abuse potential; may be refilled up to 5 times in 6 months
FDA
Oversees drug testing before release
Inspects plants where foods, drugs, medical devices or cosmetics are made
Reviews new drug applications for food additives
Investigates/removes unsafe drugs from the market
Ensures labeling of foods, cosmetics, and drugs
Concerned with general safety standards in the production of drugs, foods, and
cosmetics
Responsible for the approval and removal of products on the market
DEA
Concerned only with controlled substances
Enforces laws against drug activities (illegal drug use, dealing, and manufacturing)
Monitors need for changing the schedules of abused drugs
Created as the need for better control of addictive drugs became urgent
Handles all the needs and safety controls for the more dangerous drugs
What are the top 8 Drug Classifications
1. Lipid-lowering agents
2. Antidepressants
3. Narcotic analgesics
4. Antihypertensive
5. Diuretics
6. Antidiabetics
7. Antibiotics
8. Anticoagulants