Unit 2: Global Climate, Vulnerability and resistance
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Natural greenhouse effect:
outgoing longwave radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases leading to an increase in global temperatures that allow for life to survive on earth
Enhanced greenhouse effect:
outgoing longwave radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases that have been released intot he atmosphere by human activity to increase their concentration, leading to extra heat being trapped and global tempertaures to rise abive historic levels
Global energy balance:
the difference between incoming shortwave radiation (insolation) and outgoing longwave radiation that can be chnaged as a result of natural processes or human activities
Inputs:
energy gained from the sun
Outputs:
energy lost to space
Transfers:
convection, conduction and radiation
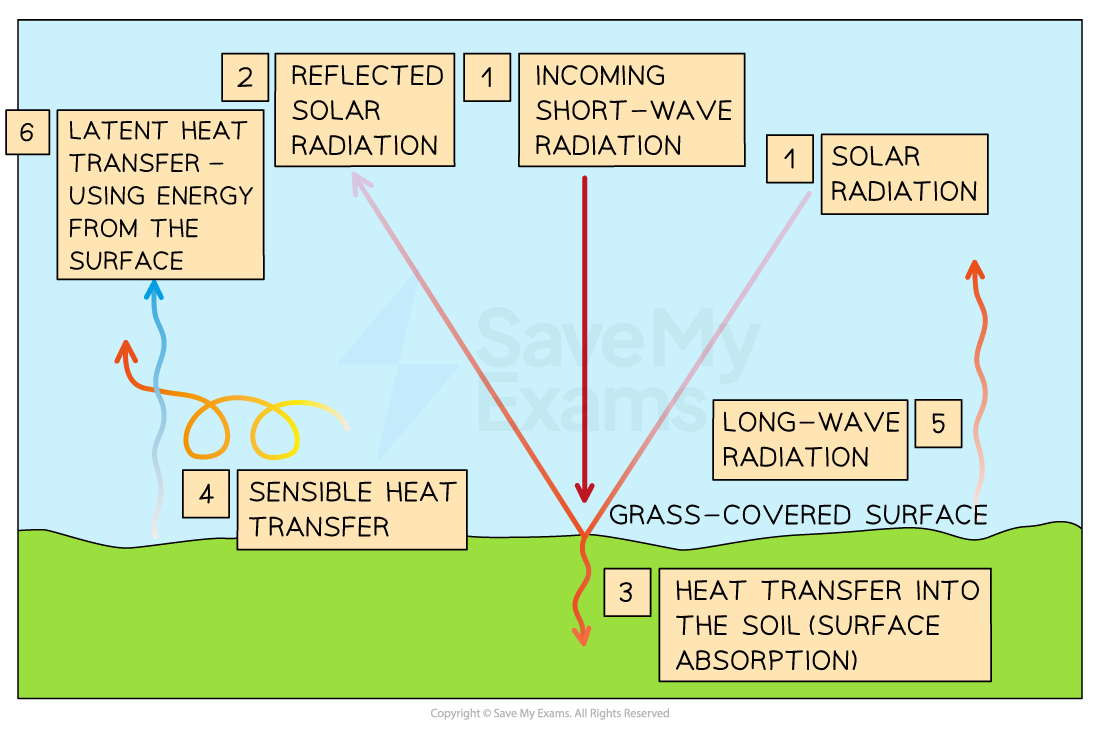
Describe the daytime energy budget:
Incoming Shortwave solar radiation (insolation): influeneced by cloud cover + dust in the atmosphere
Reflecetd solar radiation: Albedo effect = cooling effect
Surface absorbtion: dark surfaces such as soil absorbs heat = warming effect
Sensible heat transfer: loss or gain of energy without a phase chnage (convection + conduction)
Longwave radiation” emitted by the surface and passes into the atmosphere
Latent heat transfer: phase change, evaporation= cooling, condensation=warming effect
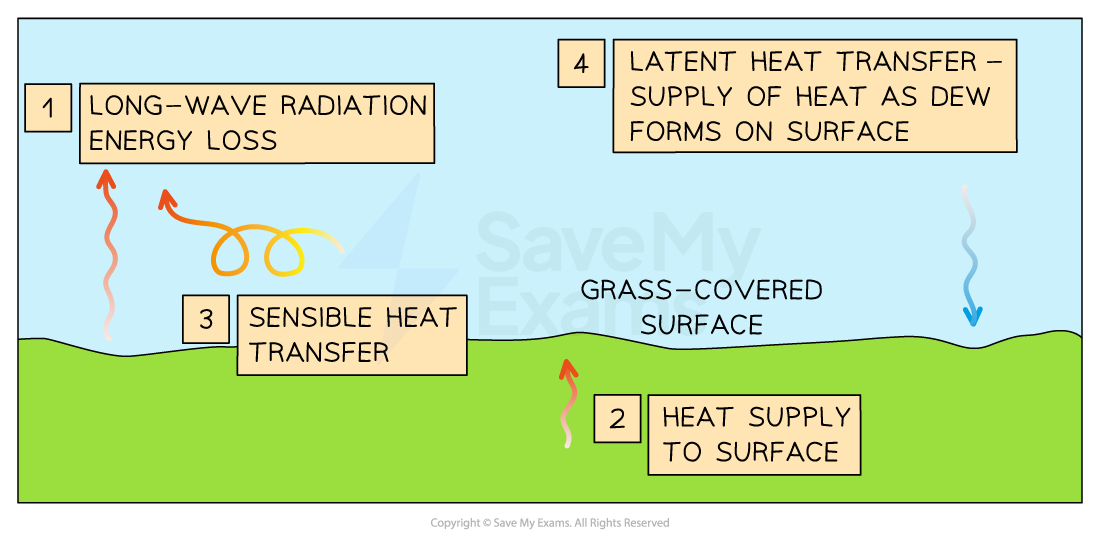
Describe the nightime energy budget:
Long wave radiation: energy loss due to clear skies ↑ output ↑drop in temp BUT if cloud cover then ↓ loss
Sub surface supply: heat stored during the day is transferred to the cool surface during the night (conduction)
sensible heat tranfer: moving warm air adds energy and keeps temp ↑
Latent heat energy transfer: at night vapour to condense to form dew- the process releases latent heat - gain oif energy for surface
State two naturally occurring greenhouse gases other than carbon dioxide. [1]
Methane
Water Vapour
Methane contribution + source?
20% of enhanced green house effect
source: agricutlure , landfills, natural gas leak ( bioa mass decay) and bioamss burning
Nitrous oxide:
6% enhanced grenehouse effect
artificial fertilisers and burning fossil fuels
Fluorinated gases:
high warming potential
aerosols. refrigeration units, air conditoning
Albedo effect:
the amount of insolation reflected h
Negative feed back loop:
reduces and dampens the effect of change stabilising the system
Dynamic equilibrium:
constant short-term adjustments made through negative feedback to maintain balance
Positive feedback loop:
enhances or amplfies the effects of change destablising the system
Feedback loop:
the amplification or reduction of an initial change by natural processes operating within a system. A positive feedback loop amplifies an initial change, while a negative feedback loop reduces it to achieve dynamic equilibrium.
Explain two positive feedback loops that contribute to climate change. [6]
Increased temperatures - cold permafrost melts and ice no longer preserves animals - decomposition of dead plants + animals occurs- CO2 and methane released in the atmosphere- enhanced greenhouse effect
Increased global temperature- increased sea ice + glacial melt - newly exposed land and water have low albedo- more insolation absorbed - ↓ longwave radiation emitted = warming effect
Factors affecting solar radiation:
Milankovitch cycles:
Eccentricity
Obliquity
precission
Sunspot activity
Global dimming
Eccentricity:
the change in earth’s orbot every 100,000 years
Ellipictical: extreme seasons, circular: not extreme
Obliquity:
the chnage in earths axis (tilt) every 40,000 years
longer tilt- larger differnce in seasons
Precission:
the wobble (direction) in earth’s axis every 26,000 years
decides the position of the north star
Sunspot activity:
heating of ccolspots of the sun and increased solar flares lead to increased avergae temperatures
11 year cycle
Global dimming:
reduction in the amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface because volcanic activity or industrial activity has put dust in the atmosphere that reflects shortwave radiation away leading to a decrease in global temperatures
Tipping point:
the point at which the accumulation of small and gradual changes may sometimes cause a dramatic transformation
Explain two reasons for international variations in greenhouse gas emissions in relation to globalization. [4]
Increased trade - cargo ships produce 3% of carbon emissions- increased GHGs
Increased tourism- increased aerosols and GHGs from aeroplanes
Explain two reasons why carbon emissions are higher in countries which have a higher GDP. [4]
high GDP - high purchasing power - higher consumption of goods- high trades (GHG’s from transport) and high production of goods (GHGs from factories)
high GDP- likey more working population- increased use of transport to go to jobs
Explain two reasons why increased trade by emerging economies has led to increased greenhouse gas emissions. [4]
Increased trade - increased transports thus fossil fuels (cheaps)- cargo ships produce 3% of carbon emissions- increased GHGs
High demand- high production - industrialisation in emerging economies- production of goods from factories - increased GHGs
Explain how the global energy balance can be changed by: solar radiation variations [2]
Sunspot actvity and solar flares can leading to increased radiation being emitted from the sun on 11 year cycles- this would mean input is higher than output- warming
Eccentricity every 100, 000 years- if orbit is elliptical, earth will be closer to sun during certain seasons- increased radiation- increased input
Explain how the global energy balance can be changed by: global dimming due to volcanic eruptions. [2]
Volcanic activity releases atmospheric dust and aerosols- insolation in reflected back- cooling effect as increased output
Outline how extreme warming can affect the albedo of a region. [2]
high warming- icemelt- decreased albedo since water/ land
Outline how extreme warming can affect the operation of a feedback loop. [2]
temepratures above 45 degrees decrease the rate of photosynthesis- decreased carbon stored in soil/ roots- increased carbon in the atmopshere- global warming (positive loop)
Outline what is meant by terrestrial albedo. [2]
the amount of insolation reflected from Earth’s surfaces where lighter surfaces reflcet a higher percentage of incoming shortwave radiation (not atmosphere, etc)
Global dimming case study:
Mount Pinatubo- Phillippines 1991
released 17 megatons SO2
ash cloud (35km)
1992: 1C decrease in global temp
natural, national, global
Eccentricity + obliquity case study:
current tilt is 23.5
beacuse of this Southern and Northern hemisphere have opposite seasons
during southern summer, sun is 5 million km closer to the Sun at perihelion (due to elliptical orbit)
thus S.H recieves 7% more radiation than N.H
if obliquity and eccentrity are more ellipctal and higher, seasons will be mpre extreme
Renewable energy case study:
GERMANY: 46% of energy mix is renewable energy
led to a decrease carbon emissions from 12.03 (1990) to 7.26 (2020) megatons per capita
Human, developed
Developing country/ industrialisation case study:
China + 30% of global CO2 emission
60% from manufacturing of steel and concrete (infrastructure AND trades)
human, developing
State and explain one change to agriculture caused by global climate change. [3]
Decreased agriculture due to soil infertility- desrtification- high temps so high evaporation + drought
“Climate change will kill people.” To what extent do you agree with this statement? [10]
Explain two reasons why sea-level change may result from global warming. [4]
high temperatures- increased glacial melt
high temperatures- thermal expansion
Suggest two health hazards that may result from climate change. [2+2] [4]
high temps- heat waves- heatstrokes
high temp- favourable temps for pathogenic bacteria to grow- Lyme disease
Explain two ways in which climate change impacts upon ocean transport routes. [2+2] [4]
high temps- increased glacial melt- new transport routes- example: Arctic Ice pack- now passage is 40% shorter
High temps-high sea water temp- higher risk of tropical typhoons, etc- disrupting ocean routes
Suggest how climate change may cause spatial changes in biomes. [2]
The artic tundra and boreal forests are moving pole-ward to cooler more suitable regions
Suggest how climate change may cause spatial changes in animal migration patterns. [2]
As biomes are moving to cooler climates- so are the animals that has them as their habitat- humpback wales are moving poleward
Flooding case study:
1/3 of Pakistan flooded: 2022
1700 deaths, 12, 800 injuries
2 million homes destroyed
7.9 million displaced
Desertification case study:
80% of Sahel region Africa desertified
decreases in Baobab trees and Dama gazelle
restoration created 350,000 jobs
Permafrost case study:
Siberia, Russia
1.5 million hectares of permafrist thaw lead to
13% increase in agriculture
HEP case study:
India
40-60% increase in discharge of himalayan fed river
Increased energy for
Tehri dam that supplies energy to 10 million people
Carbon offsetting:
reducing, avoidingor removing CO2 emissions in one part of the world to compensate for emissions in another
Carbon capture and storage:
the use of technology to capture, remove and store CO2 from industrial facilities and powerplants
Carbon tax:
a tax paid by organisations that produce extensive greenhouse emissions
Carbon trading:
the buying of credits to allow the organisation to emit more greenhouse emissions than their permit
Carbon credit:
a permit indicating the amount of greenhouse gas emissions an organisation is allowed to emit
How is Bangladesh vulnerable to climate change?
low-lying , flat, 75% of country above sea level and 80% on floodplains of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna delta
prone to flooding- The monsoon rainfall is predicted to rise by 40% by 2030
High population density- inadequate housing
in 1998 (75% of Bangladesh was flooded) - 30 million homeless
42 milion illiterate
How is Ghana vulnerable to climate change?
vulnerable to drought and reduced rainfall- Rainfall is expected to decrease 4% by 2040
Projected to increase by a further 1-3°C by the 2060s
45% or workforce still in agriculture
Explain two reason why wealthy people are less vulnerable to climate change? (2+2)
Are able to afford extreme weather events resistent infratsructure- safe from hazards/ or can relocate
access to aducation- are aware on how to stay protected from extreme weather events
can afford high food prices caused by decrased agriculture due to desertification
Mitigation:
actions that reduce emissions that contribute to global warming and climate change
Adaptation
actions which minimise or prevent the negative impacts of global warming and climate change
State and explain one geopolitical attempt to reduce the challenges posed by global climate change. [1+2] [3]
Nile Basin initiative between 11 countries including Egyot and ethiopia
air and equitable access to the river’s water for drinking, agriculture, energy production (promotes HEP)
High temps- droughts + low rainfall in northafrican arid countries- agreement provides stable supply of water
Egypt 90% of water from this- 85% for agriculture
State and explain one global geopolitical attempt to mitigate the causes of global climate change. [3]
The paris agreement
international treaty with 196 countries
limit warming to 1.5 C
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): what is being done to reduce emission
Explain two geopolitical strategies used to reduce the effects of climate change? (2+2)
Nile Basin initiative - equitable water supply
African Union’s Great Green Wall Initiative: Afforrestation (30 million hectares so far)
State and explain two mitigation strategies that attempt to reduce the rate of global climate change. [6]
Carbon trading: EU emission trading system: countries are give carbon permits/ allowances- cant exceed quota- decreased total emissions by 29%
Renewable energy: 46% of germany’s energy mix, decrease from 12.03 to 7.96 megatons (1990-2020) as fossil fuels are not used
Explain how carbon offset schemes and carbon trading might lead to a global reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. [4]
Afforestation projects remove CO2 from the atmosphere by photosynthesis - this would offset CO2 emissions produced by businesses
Carbon trading would limit the number of CO2 emitted by creating a market in which emission permits issued by governments can be traded- companies that exceed their limit will have to buy from others
Geoengineering:
large scale intervention in Earth’s natural systems to counteract climate change
Enhanced weathering:
adaptation strategy
Spreading large amounts of crushed rockss in the sea to fix atmospheric CO2
Carb Fix - ICELAND
basalt tracks, grinded in fine power
+ve: large scale carbon removal via naturally abundany materials
-ve: increased land use for mining + distribution of the minberals= habitat destruction
slow carbon removal rate
Ocean fertlisation:
adaptation
sumping iron sulphate in the ocean to stimulate phytoplankton growth - increased photosynthesis- decreased carbon
Iron fertilisation experiment 2007: Antartctic ocean
absorbed 1.5 megatons of CO2
+ve: low cost + high potential as carbon sinks
-ve: uncertainty about the ecological consequences- eutrophication
short lived effects
BioChar:
adaptation
pyrolysis(biomass combustion with low oxygen) - carbon rich substance stored in soil
Kenya: 2-3 tonnes of CO2/ per hectare every year in agricultural regions
+ve: increased soil quality- decreased fertilisers
-ve: land needed for large scale use
expensive as high energy
Direct air capture:
adaptation
CO2 and other GHGs extracted from atmosphere using a chemical sorbent- large fans move air through filter
Clime Works: Swiss company- in Iceland captured 4000 tonnes of CO2
+ve: can be deployed anywhere, potentual for large scale
-ve: expensive, adaptation, low incentive as impact global not localised
Civil society:
society considered as a community of citizens linked by common interests and collective activity
Corporate strategy case study Ikea:
Ikea: commitment to being climate positive by 2030
invested 2.5 million euros in renewabele energy projects : purchased 547 wind turbines and 935,000 solar panels
60% of Ikeas product are made from recycled substances
anual reduction of 1.5 megatons
Civil strategy case study:
Kigali Cooling Efficiency Program : Rwanda
promotes efficient air conditioning and refrigeration in hot climates and traditional cooling methods
Collaborating with the International Energy Agency (IEA), K-CEP's activities are estimated to prevent the emission of 4.2 gigatons of CO₂ by 2050,
Explain two corporate strategies used to address global climate change. [4]
Unilever if focused on having a carbon-neutral supply chain by having agrculturally sustainable raw material suppliers- 52% decrease in in CO2 per ton of a product
Ikea encourages a circular economy by using recycled materials for 60% of its products and having felxible return policies
Explain how two methods of geo-engineering could mitigate climate change. [2+2] [4]
Direct air capture: removing CO2 and other greenhouse gases from the air by using a chemical sorbent and moving the air through filters via fans
Biochar: cyrolysis- low oxygen combustion of biomass to produce a carbon rich substance from pulling atmospheric carbon
Suggest two human factors that can increase vulnerability to extreme weather events. [2+2] [4]
Wealth - if low wages, likely not able to afford strong and resistent housing- less safe
Age - elderly have more chronic health problems- less likely to flee from potential harm- weaker bodies
Gender- in developing countries - have decreased acess to education - unaware of how to survive extreme weather events
Explain two government-led strategies to reduce the causes of global climate change. [2+2] [4]
EU emission trading system- carbon trading and credit- CO2 quotas
India- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPPC) - energy effciency- renenwable energy 170 GW- 20% decrease in CO2 per unit gdp (2005-2020)
Suggest two ways in which economic development leads to international variations in greenhouse gas emissions. [2 + 2] [4]
can afford renewable energy
can invest in energy preserving infrastructure
Explain two reasons why wealthy people are less vulnerable to climate change. [2 + 2] [4]
can afford to invest in airconditioning, etc →dont have to deal with warm temps
often have tertiary sector jobs- not impacted by climate chang directly unlike agriculture
Outline one way in which patterns of animal migration are affected by climate change [2]
birds migrate earlier→issues as not in spring when insects pollinate flowers so ↓ food source
Suggest two ways in which social differences may lead to increased vulnerability to climate change [4]
LIC households won’t be able to adapt to climate change →↓ flood insurance
↑ frwshwater temp- ↑ bacteria →wont be able to afford sanitisation systems
“Climate change will amplify disparities.” To what extent do you agree with this statement? [10]
Climate change will amplify social disparities in developing countries- extreme weather events- Bangladesh low lying- vulnerable to flood as 80% in Delta of 3 converging rivers- In 1998 flood, 30 million homeless- already 40% lives below poverty line
Climate change will amplify
Climate change will amplify economic disparities on a global scale- many developing countries that haven’t industrialised yet- primary sector- desertification-Sahel region 80% desertified- whereas developed countries- russia- permadrost melt- 13% increase in agriculture
Climate change will amplify
‘The power to effect change is in the hands of the masses not the few.’ To what extent do you agree with this statement? [10]
“Responding to climate change is more important than working towards the UN Sustainable Development Goals.” To what extent do you agree with this statement? [10]