Chapter 8 --- transport across membanes, overcoming permeability barrier
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
simple diffusion
small, nonpolar
down concentration gradient
facilitated diffusion
can be channel or carrier
large, polar
down gradient
active transport
large, polar
against gradient
ex: sodium potassium pump
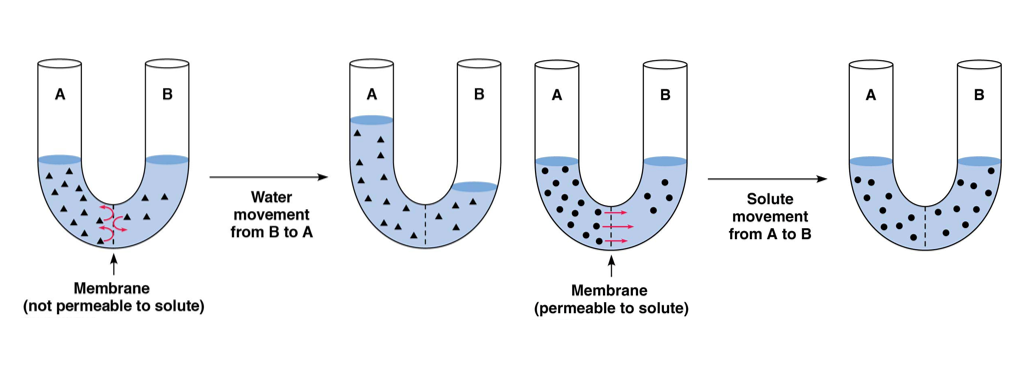
describe simple diffusion vs. osmosis
depends if permeable to solute or not
solute is the thing being dissolved in the solvent
the solvent is usually water
if the solutes cannot move, then the water will move in order to keep the concentration the same
what are the responses of animal cells to changes in osmolarity?
hypertonic solution = shriveled
high extracellular solute, so water moves out of cell
dehydration
isotonic solution = normal
hypotonic solution = lysed
low extracellular solute, so water moves in to cell and explodes
hyponatremia: low blood Na+
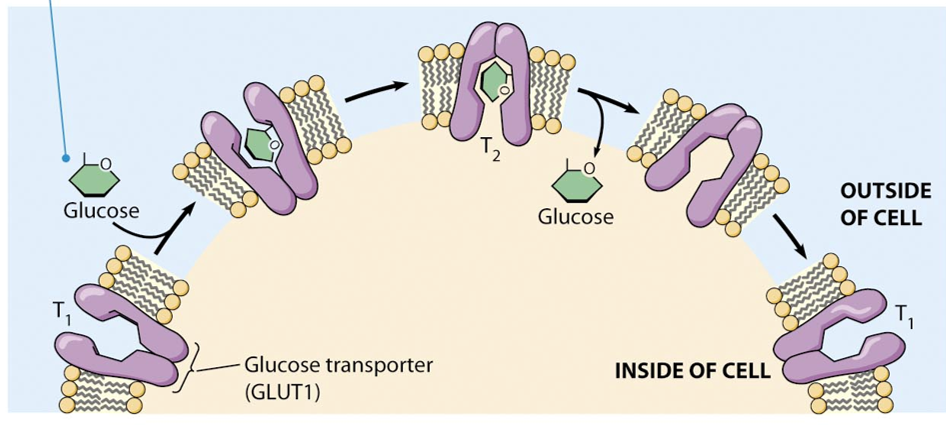
what mechanism does glucose transporter use for movement?
facilitated diffusion
passive transport
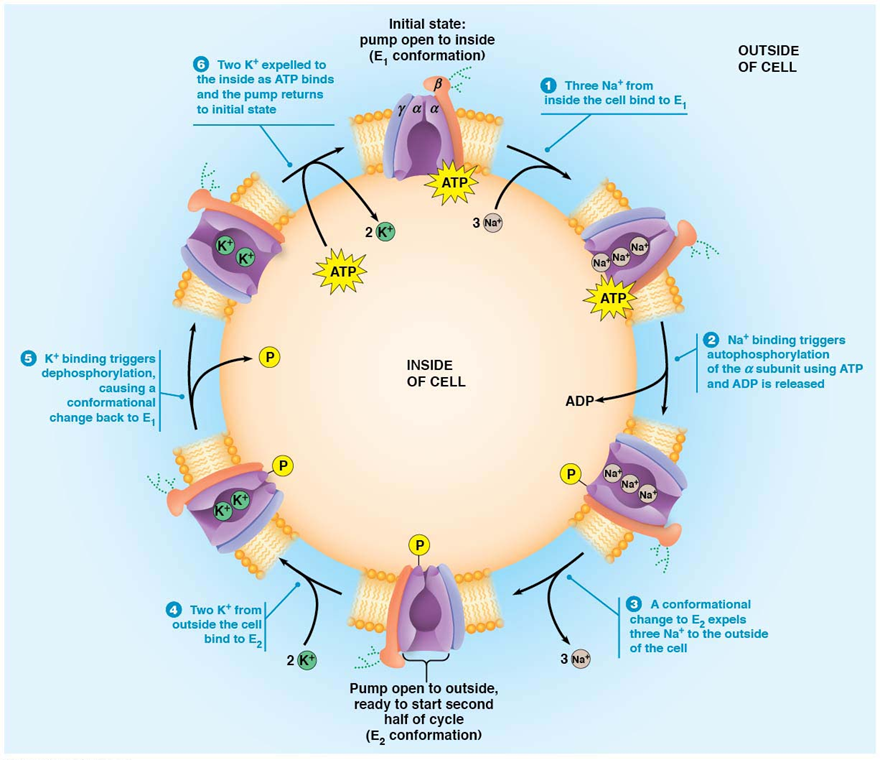
sodium-potassium pump - initial state and 6 steps
pump open to inside (E1 conformation)
3 Na+ from inside the cell bind to E1
Na+ binding triggers autophosphorylation of the alpha subunit using ATP and ADP is released
a conformational change to E2 expels three Na+ to the outside of cell
pump open to outside, ready to start second half of cycle (E2 conformation)
2 K+ from outside the cell bind to E2
K+ binding triggers dephosphorylation, causing a conformational change back to E1
two K+ expelled to inside as ATP binds and the pump returns to initial state
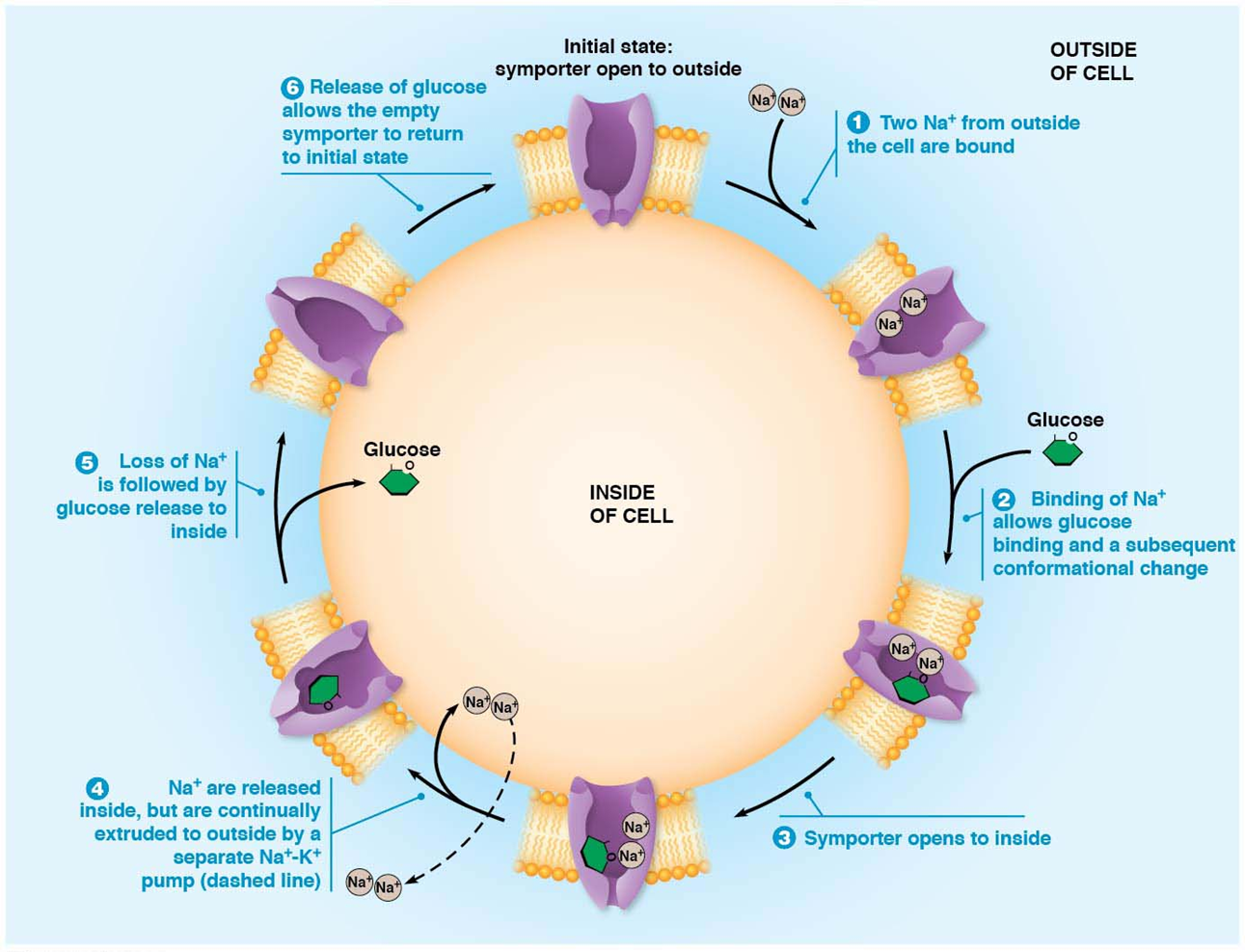
initial state and 6steps of the Na+-Glucose symporter
active transport of glucose
symporter open to outside
two Na+ from outside of cell are bound
binding of Na+ allows glucose binding and a subsequent conformational change
symporter opens to inside
Na+ are released inside, but are continually extruded to outside by a separate Na-K pump
loss of Na+ is followed by glucose release to inside
release of glucose allows empty symporter to return to initial state