CIS Hu Phys Ch. 3 - Tissue
1/101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Microvilli
Membrane extensions containing microfilaments; increase surface area to help with absorption
differentiation
The process of gradual specialization (of a daughter cell’s function/structure)
Totipotent cells
Cells that are able to develop into any cell in the body
Four types of tissue
Epithelial; connective; muscle; neural
extracellular fluid
watery medium that surrounds cells
interstitial fluid
watery medium between tissue cells
cytoplasm
gelatinous fluid between nuclear membrane and plasma membrane
cytosol
fluid part of cytoplasm; aka intracellular fluid
organelles
“little organs”, intracellular structures with specific functions
membranous organelles
isolated from the cytosol by phospholipid membranes. examples:
peroxisomes
lysosomes
golgi apparatus
nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
mitochondria
nonmembranous organelles
not completely enclosed by membranes; usually in direct contact with cytosol. examples:
cytoskeleton
microvilli
centrioles
cilia
ribosomes
peroxisome
vesicles containing degradative enzymes; break down acids, compounds, and neutralize toxic compounds
lysosome
vesicles containing digestive enzymes; break down large organic compounds, damaged organelles, and pathogens
golgi apparatus
stacks of cisternae containing chambers; modify and pack proteins
nucleus
nucleoplasm containing enzymes, proteins, etc; surrounded by nuclear envelope (double membrane); controls metabolism, stores/processes genetic info, controls protein synthesis
endoplasmic reticulum
network of membranous sheets and channels extending throughout cytoplasm; synthesize secretory products, store and transport substances inside cell
smooth ER
no attached ribosomes, synthesizes lipids and carbs
rough ER
ribosomes bound to membranes, modifies and packages newly synthesized proteins
ribosomes
RNA and proteins; fixed bound to rough ER, free scattered in cytoplasm; synthesizes proteins
cytoskeleton
proteins organized in microfilaments or tubules; strengthen and supports cell, move cell structures and materials
mitochondrion
double membrane with inner membrane folds enclosing important metabolic enzymes; produces 95% of cell’s ATP
plasma membrane
separates cell contents (cytoplasm) from extracellular fluid; selectively permeable
glycocalyx
formed by superficial membrane carbs; important in cell recognition, binds to extracellular structures, and lubricates cell surface
integral proteins
part of membrane structure and can’t be removed without damaging/destroying membrane. may contain pores.
phospholipid bilayer
aka the plasma membrane. phospholipid molecules form two layers; bind with hydrophilic/phobic parts on surface/inside, respectively. hydrophobic layer in center of membrane isolates cytoplasm from extracellular fluid.
microfilaments
in bundles beneath cell membrane/cytoplasm; found in most cells; provide strength, alter cell-shape, etc
intermediate filaments
found in most cells, specifically the cytoplasm; provide strength, move materials through cytoplasm
microtubules
found in most cells in cytoplasm radiating away from centriole pair; provide strength, move organelles, major components of centrioles/cilia
thick filaments
skeletal/cardiac muscle cells in cytoplasm; interact with actin microfilaments to contract muscles
centrioles (organelles)
nine groups of microtubule triples form a short cylinder, found in pairs near nucleus; organize microtubules to move chromosomes during mitosis
cilia
nine groups of long microtubule doublets form a cylinder around central pair, found at cell surface; beat rhythmically to move fluids or secretions across cell surface
cristae
increases surface area exposed to matrix of mitochondrion
cisternae
flattened sheets/chambers formed by ER
matrix
liquid enclosed by inner membrane within mitochondrion
aerobic metabolism
aka cellular respiration, the process through which ATP is produced. in mitochondria, it produces 95% of the cell’s necessary ATP to live.
membrane renewal vesicles
add to the surface area of the plasma membrane
secretory vesicles
contain secretions (hormones or enzymes) that will be discharged from cell
transport vesicles
deliver some proteins and glycoproteins that were synthesized in RER to golgi apparatus
nucleus
control center for cellular processes
autolysis
destructive process in which digestive enzymes become active and attack cytoplasm
nuclear envelope
surrounds nucleus and keeps it separate from cytoplasm; double layered
nuclear pores
account for ~10% of surface of nucleus; passageways that permit chemical comms between nucleus and cytosol. (proteins and DNA cannot freely cross nuclear envelope.)
nucleoplasm
fluid contents of nucleus, also contains ions, enzymes, RNA, and DNA
nucleolus
nuclear organelle that synthesizes ribosomal RNA and assembles ribosomes. most prominent in cells that manufacture a lot of proteins (e.g. liver, nerve, muscle)
chromosomes
supercoiled DNA
chromatin
loosely coiled, fine filaments
centromere
holds chromosomes together
genetic code
chemical “language” used
nitrogenous bases
adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
gene
functional unit of heredity, contains all DNA needed to produce certain proteins
messenger RNA
single stranded RNA; contains complementary codons
codon
series of three RNA nucleotides
triplet
sequence of three nitrogenous bases along DNA strand that codes for an amino acid
transcription
takes place in nucleus; dna is copied into mRNA
translation
occurs in cytoplasm on ribosomes. mRNA’s genetic code is followed to build a chain of amino acids into a protein molecule; ribosomes detach at end
tRNA
ferry amino acids to ribosome. each contains nucleotide sequence known as anticodon
cell division
responsible for increase in cell number
apoptosis
cell suicide
(programmed cell death)
mitosis
produces two daughter cells, which each contain 46 chromosomes
meiosis
produces sex cells, which contain only 23 chromosomes
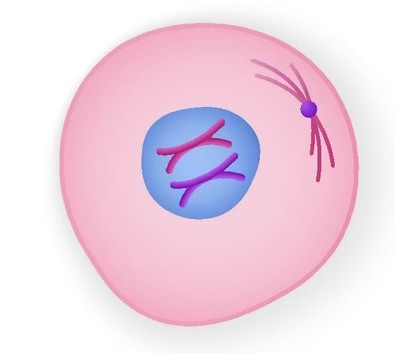
name the phase
interphase. performs normal functions, not actively engaged in division
daughter cells
produced by division of single cell
dna replication
begins when enzymes unwind strands and disrupt H bonds between bases
dna polymerase
bind to exposed nitrogen base; promotes bonding between nitrogenous bases and nucleotides; link nucleotides by covalent bonds
cytokinesis
cell divorce (aw sad)
(process that divides the cytoplasm of two daughter cells)
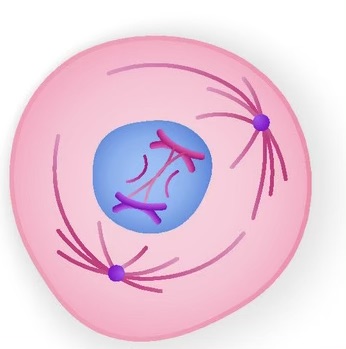
name the phase
prophase. centrioles replicate, spindle fibers connect centriole pairs, chromatid forms
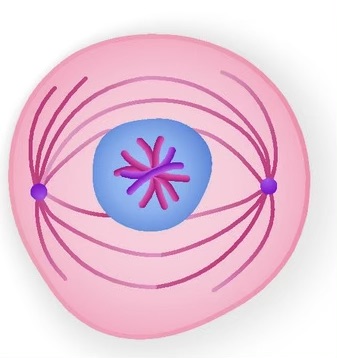
name the phase
metaphase. chromatids move to metaphase plate and align
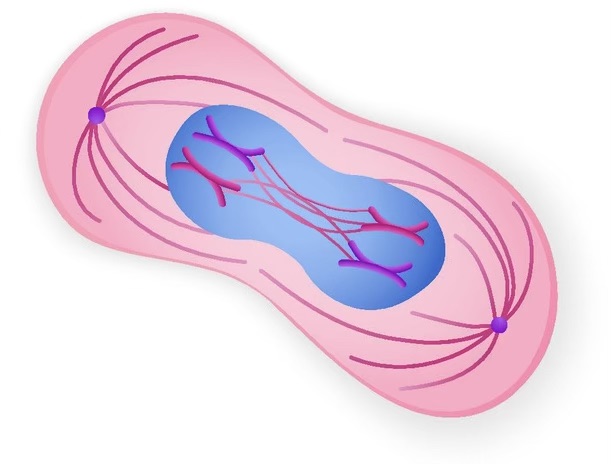
name the phase
anaphase. centromere of each chromatid pair splits and chromatids separate
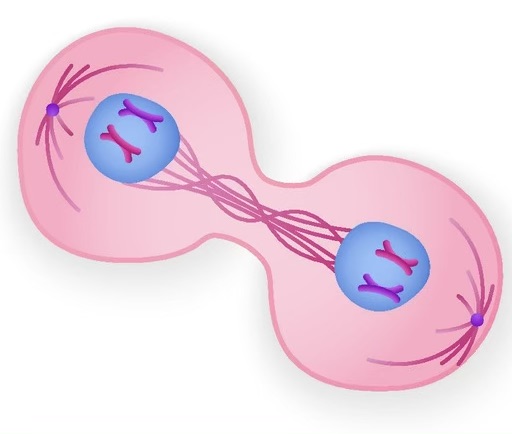
name the phase
telophase. nuclear membranes reform, nuclei enlarge, and chromosomes uncoil from chromatin state
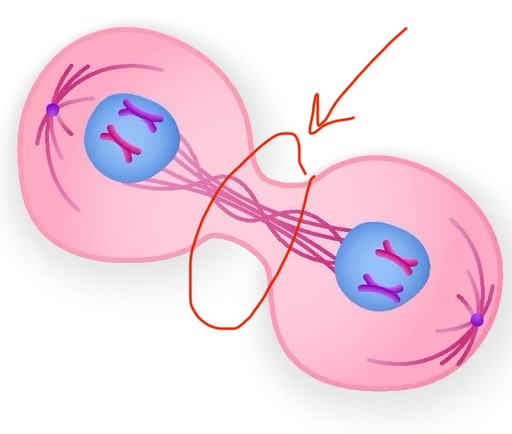
cleavage furrow
gap between two cells in telophase; constricted cytoplasm along metaphase plate
tumor
mass produced by abnormal cell growth/division
benign tumor
not life-threatening, doesn’t metastasize
malignant tumor
bad bad bad. life-threatening, DOES metastasize, divide rapidly and release chemicals that stimulate blood vessel growth. malignant cells may no longer perform original functions (or just perform them in an abnormal way)
invasion
process of when tumor starts spreading outside of isolated mass of cells and migrates to surrounding tissue
metastasis
migration to surrounding tissue
cancer
usually begins with single abnormal cell. cancer cells don’t use energy efficiently, and may cause death when they kill/replace healthy cells, compress vital organs, or deprive normal tissues of essential nutrients
permeability
property that determines which substances can enter/leave cytoplasm
freely permeable membranes
allow any substance to pass without difficulty
selectively permeable membranes
e.g. the plasma membrane; allow passage of some materials and restrict others
impermeable membranes
you shall not pass
(nothing can pass through. sorry, had to sneak in a LoTR reference.)
diffusion
movement driven by concentration differences; passive
facilitated diffusion (carrier-mediated transport)
may be active or passive; integral carrier proteins assist passage of specific substances
vesicular transport
intracellular vesicles form to transport substances. always active.
osmosis
diffusion of water across membrane
pinocytosis
vesicles form and bring fluids/small molecules into cell; often called “cell drinking”
receptor-mediated endocytosis
target molecules bind to receptor proteins and trigger vesicle formation
phagocytosis
large particles brought into cell by cytoplasmic extensions called pseudopodia; only phagocytes or macrophages perform phagocytosis
exocytosis
intracellular vesicles fuse with plasma membrane to release fluids/solids
epithelial tissue
layer of cells that forms a barrier w specific properties; covers every exposed body surface, lines organs/blood vessels, and surrounds internal cavities; produces glandular secretions (?)
connective tissue
contain specialized cells and extracellular matrix (which contains protein fibers and a liquid known as ground substance); fills internal spaces, provides structural support, stores energy
muscle tissue
have ability to contract forcefully. three types:
skeletal muscle tissue, which is attached to skeleton and moves/stabilizes position of internal organs/bones w contractions
cardiac muscle tissue, which is only found in the heart. contractions propel blood through vessels.
smooth muscle tissue, which is found in walls of blood vessels, glands, and along all tracts
neural tissue
specialized to carry info from one place to another. two basic types:
nerve cells (neurons), which transmit info through electric impulses
supporting cells (neuroglia, or just glia) which protect neurons
can be divided into central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (all other nerves not in brain/spinal cord)
histology
study of tissue
circadian rhythm
repeats roughly every 24 hours; dictates certain physiological functions (cortisol release before waking up, high temperature before bed); influenced by period gene and PER protein
PER protein
builds up during the day and degrades at night, induces sleepiness (?); when it’s bound with TIM, it can enter the nucleus; DBT protein delays accumulation; negative feedback loop
risks of disrupted circadian rhythm?
cancer, disrupted metabolic pathways, other diseases = increased rates
anaerobic respiration
atp creation without oxygen. results in buildup of lactic acid + fermentation
endogenous
occurs inside a cell
exogenous
occurs outside a cell
glycolysis
metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate; does not produce the most ATP