The Behavior of Interest Rates (Chapter 5)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Relationship between quantity demanded of an asset and wealth
positive
Relationship between quantity demanded of an asset and expected return
Positive
Relationship between quantity demanded of an asset and risk
Negative
Relationship between quantity demanded of an asset and liquidity
Positive
Shifts in the demand for bonds: wealth
increase in wealth shifts demand for bonds RIGHT
Shifts in the demand for bonds: expected interest rate
increase in expected future interest rate shifts demand for bonds LEFT
Shifts in the demand for bonds: inflation
increase in expected rate of inflation shifts bond demand LEFT
Shifts in the demand for bonds: risk
increase in riskiness of bonds causes bond demand to shift LEFT
Shifts in the demand for bonds: liquidity
increase in liquidity of bonds shifts the demand curve RIGHT
Shifts in the supply of bonds: investment opportunities
higher profitability of investment opportunities shifts supply curve RIGHT
Shifts in the supply of bonds: expected inflation
increase in expected inflation shifts supply curve RIGHT
Shifts in the supply of bonds: government deficit
increased budget deficit shifts the supply curve RIGHT
Fisher Equation
nominal interest = real interest + inflation
Real world application of fisher’s equation
Central bank policy decisions
Inflation-adjusted returns
loan pricing
Forecasting inflation using machine learning
Employ NLP models to extract inflation expectations
Combine with data to improve inflation forecasting
Better inflation prediction → more accurate interest rate setting
Liquidity Preference Theory
All other things being equal, investors prefer cash or other highly liquid holdings
Bs - Bd = Md - Ms
If the bond market is in equilibrium, then the money market must be in equilibrium
Model of Aggregate Money Demand
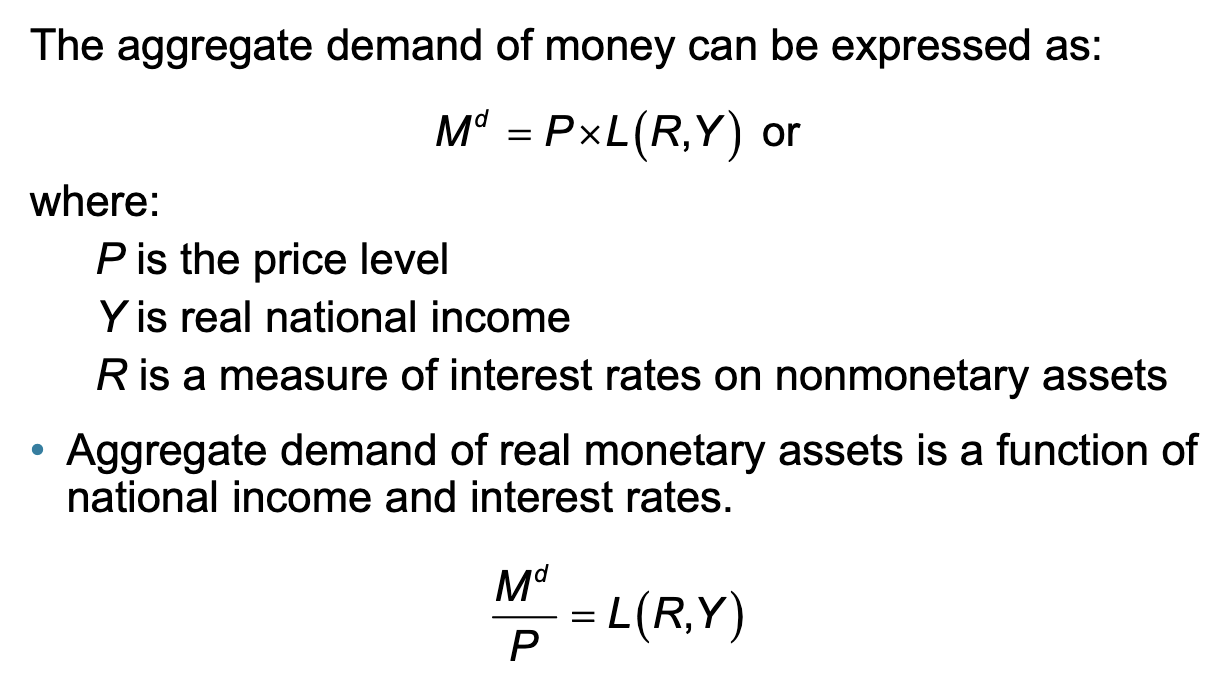
Income Effect on money demand
Increase in income causes the demand curve for money to shift RIGHT
Price level effect on money demand
Rise in the price level causes the demand curve for money to shift RIGHT
Income effect on interest rates
increase in income → increase in money supply → rise in interest rates
Price level effect on interest rates
increase in price level → increase in money supply → increase in interest rates
Expected inflation effect on interest rates
increase in expected inflation → increase in money supply → increase in interest rates
Liquidity effect on interest rates
increase in money supply → lower interest rates