Genetics Unit 1 Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/40
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
Transmission genetics
Hereditary and how traits are passed from generation to generation
2
New cards
Molecular genetics
Chemical nature of the gene
3
New cards
Population genetics
Genetic composition of groups of individuals
4
New cards
Monohybrid cross ratio
3:1
5
New cards
Testcross
A cross between an organism of unknown dominant genotype with an organism of known recessive genotype
6
New cards
Why did Mendel use pea plants?
1. Many varieties
2. Easy to cross
3. They could self fertilize
2. Easy to cross
3. They could self fertilize
7
New cards
Monohybrid cross supports:
Segregation
8
New cards
Dihybrid cross supports:
Independent assortment
9
New cards
Dihybrid cross ratios
9:3:3:1
10
New cards
Trihybrid cross ratios
27:9:9:9:3:3:3:1
11
New cards
Chromosome
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
12
New cards
Interphase
Period of cell cycle for cell growth
13
New cards
S phase
DNA synthesis
14
New cards
Prophase
Condensation of chromosomes. Spindle apparatus forms
15
New cards
Prometaphase
Spindle fibers interact with sister chromatids. They connect to the kinetochore
16
New cards
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
17
New cards
Anaphase
Centromeres divide longitudinally (sister chromatids are then considered chromosomes)
18
New cards
Telophase
Nuclear envelope forms around each group of chromosomes
19
New cards
Meiosis results in
4 haploid daughter cells
20
New cards
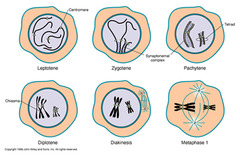
Leptotene
Chromosomes become visible as long, threadlike structure; pairing of chromosomes; double strand breaks (lepto- "thin like") (1)
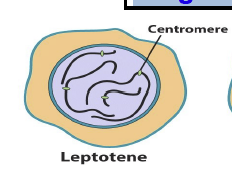
21
New cards
Zygotene
Synapsis of homologous chromosomes begins; synaptonemal complex begins to form (2)
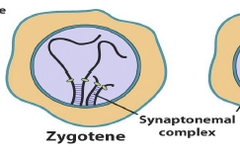
22
New cards
Pachytene
Complete formation of synaptonemal complex and crossing-over begins (pachy- "thick") (3)
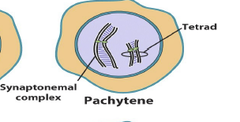
23
New cards
Diplotene
synaptonemal complex disappears, chiasma still present (diplo- "two") (4)
24
New cards
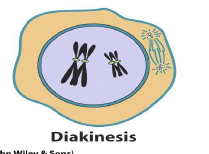
Diakinesis
Maximum chromosome contraction
25
New cards
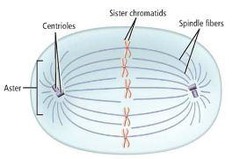
Mitotic spindle
An assemblage of microtubules and associated proteins that is involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis.
26
New cards
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
27
New cards
Incomplete dominance
Intermediate heterozygote phenotype
28
New cards
Codominance
Heterozygote shows phenotype of both parents
29
New cards
Complementation
Phenomenon in which two parents that express the same or similar recessive phenotypes produce offspring with a wild-type phenotype.
30
New cards
Two albino parents have 4 normal offspring. This is an example of:
Complementation
31
New cards
3 ways dominant mutant alleles can affect phenotypes:
Gain of function, dominant-negative mutation, and haploinsufficiency
32
New cards
Germline mosaicism
Specialized type of mosaicism where some gametes carry the mutation and rest are normal
May produce a disease in the offspring that is not carried by parent's somatic cells
AND/OR cause only some offsprings to be affected by autosomal dominant, completely penetrant disease
May produce a disease in the offspring that is not carried by parent's somatic cells
AND/OR cause only some offsprings to be affected by autosomal dominant, completely penetrant disease
33
New cards
One map unit is equivalent to:
1% recombination frequency
34
New cards
Probability of a double crossover:
the product of the probabilities of the single crossovers (times the total to get expected number)
35
New cards
Interference
1 - c where c is observed crossovers/expected number
36
New cards
Dosage compensation
Theory that X chromosome inactivation equalizes gene expression between males and females
37
New cards
Barr body
A dense body formed from a deactivated X chromosome
38
New cards
Sex limited
When expression of a gene depends on the sex of the individual.
39
New cards
Mitochondrial inheritance
Disease occurs in both males and females, inherited through females only
40
New cards
Homoplasmy vs heteroplasmy
Mitochondria within a cell can all have the same mtDNA (homoplasmy) or 2 or more mitochondrial genomes (heteroplasmy)
41
New cards
Mutational load
% of mitochondria that are mutant correlates with the degree of biochemical deficiency