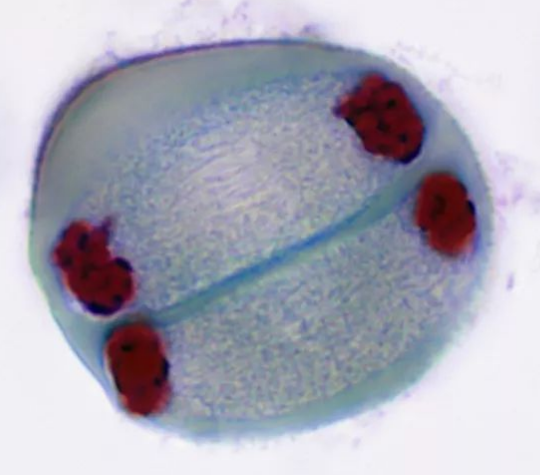
Bio 006 - 10LB: Meiosis*
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Mitosis
Process producing 2 identical diploid daughter cells.
Stages:
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase / Cytokinesis
Meiosis
Process producing 4 non-identical haploid gametes from 1 diploid cell.
Goes through the stages of Mitosis TWICE
Interphase
Phase where cell prepares for division.
G1 Phase
First interphase stage (focuses on Growth)
Cell grows bigger
Copies some organelles
Makes building blocks for chromosomes to form
Build centromeres
Saving up energy for replication
S Phase
DNA synthesis; duplication of centromeres occurs.
Necessary for us to have 2 copies
2 sister chromatids
These chromatids attach to centromeres
Also duplicates centrosomes (important in mitosis AND MEIOSIS)
G2 Phase
Final interphase stage before mitosis
Store more energy
Copies some organelles
Make proteins for chromosome manipulation (i.e. during mitosis)
Cytoskeleton gets dismantled (taken apart).
Prophase 1
Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrosomes start moving to poles
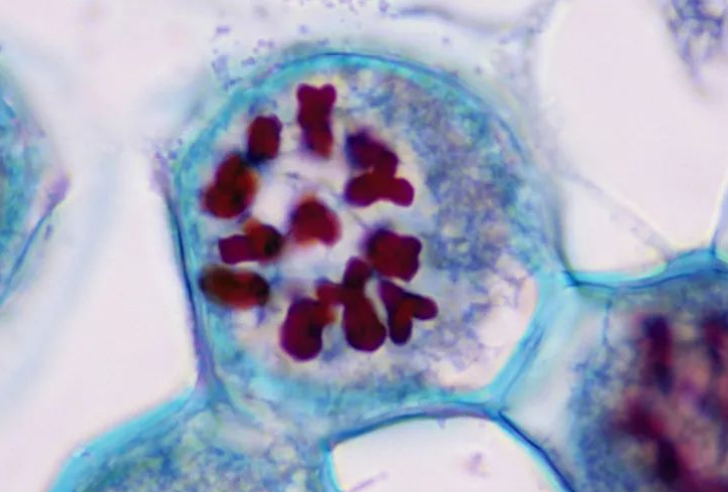
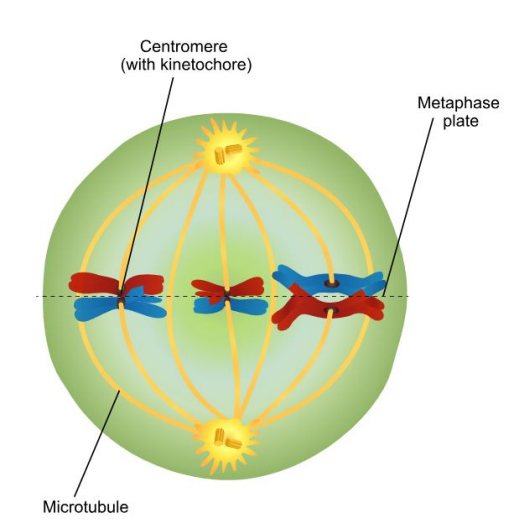
Metaphase I
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate in tetrads in Meiosis. This is where independent assortment takes place
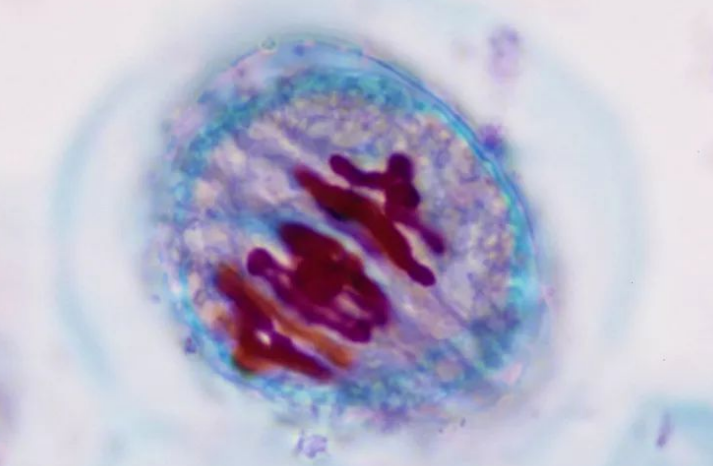
Anaphase 1
Chromatids pulled to opposite poles by spindle fibers.
from Mitosis: sister chromatids
from Meiosis: recombined homologous chromosomes
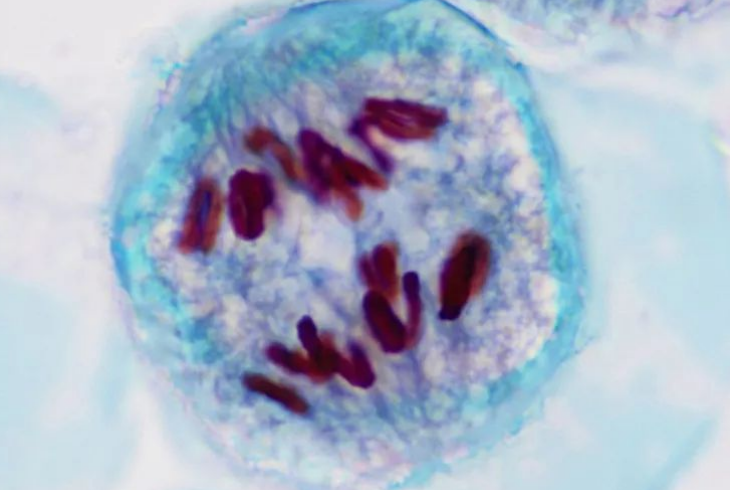
Telophase 1
Nuclei form at poles; cell prepares to divide.
Result: 2 non-identical haploid cells
Now, each of these cells will divide again in M2.
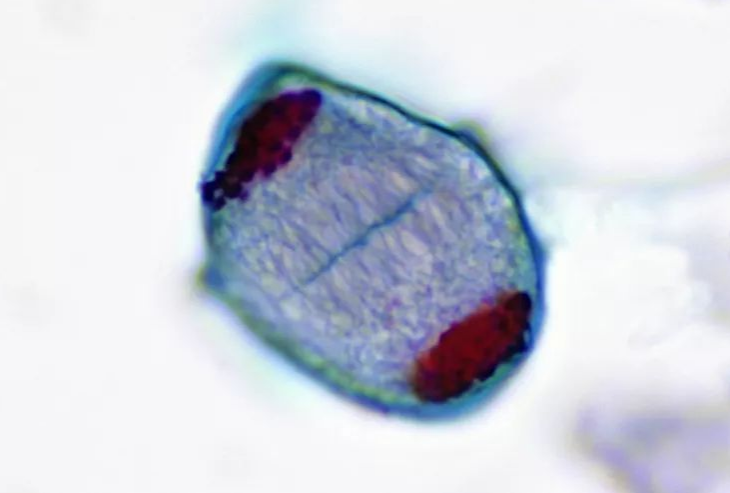
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm following mitosis or meiosis.
Tetrad
Set of 4 chromatids formed during meiosis in Prophase 1.
Synapsis
Homologous chromosomes pairing during Prophase I.
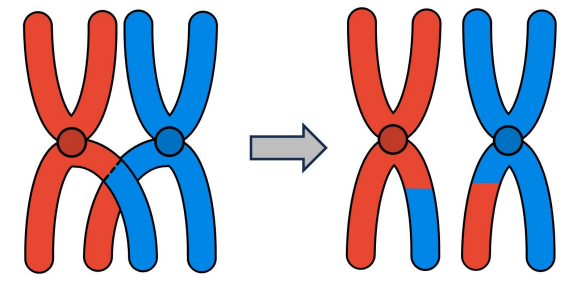
Crossing Over
Genetic recombination between homologous chromosomes in Prophase 1.
Independent Assortment
Random distribution of alleles during gamete formation in Metaphase 1 during Meiosis
Diploid
Cell with two sets of chromosomes (2n).
Haploid
Cell with one set of chromosomes (n).
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
Kinetochore
Protein structure where spindle fibers attach.
Spindle Fibers
Microtubules that pull chromosomes apart.
Gametes
Reproductive cells formed through meiosis.
Zygote
Fertilized egg formed from gametes.
Lab Practical
Hands-on assessment of knowledge and skills.
PMAT
Abbreviation of the 4 Stages in Mitosis/Meiosis
Prophase 2
Nuclear envelope breaks down (again)
New spindle fibers form
Centrosomes move to poles
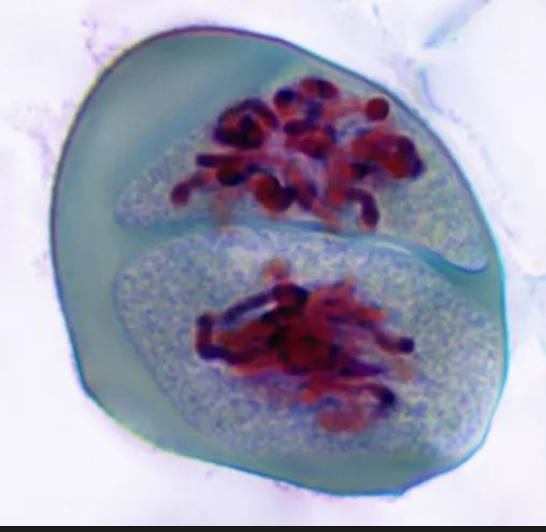
Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
Spindle fibers from centrioles attach at kinetochore
Chromosomes single file, same as in mitosis (except now, recombined)
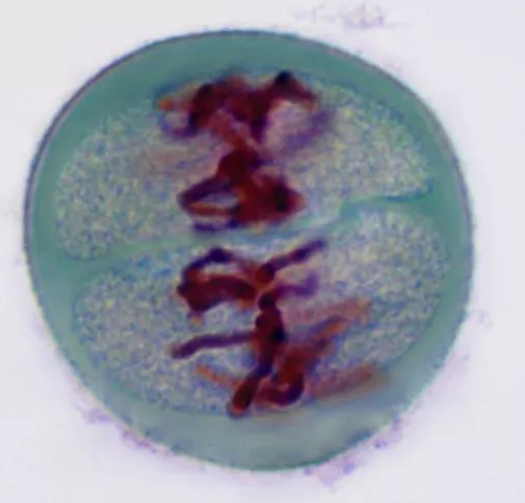
Anaphase 2
Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids to opposite poles
Similar to mitosis
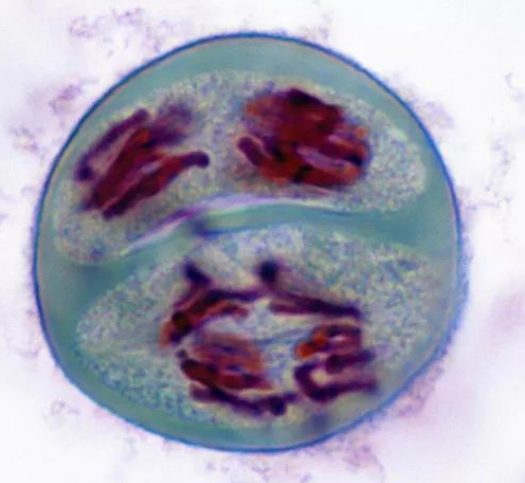
Telophase 2
Distinct nuclei (i.e. new nucleuses) form at opposite poles
Cell ready to divide
At the end we have: 4 haploid non-identical cells (gametes)