Computer Science
1/113
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
What are some advantages and disadvantages of Hard drives?
Advantages:
High capacity(storage)
Reasonable access speed so suitable for everyday storage of data and programs
Cheaper than other storage (E.g. SSD) Disadvantages:
Slower than other types of storage (E.g. SSD)
Get damaged easier
What are some advantages and disadvantages of a USB stick?
Advantages:
Extremely fast
Very Portable
Suitable for transferring files between computers
Disadvantages:
Small capacity(storage)
Why do Embedded systems not require secondary storage?
Because the don’t need to store data while the power is off. Instructions needed to run them are stored in ROM and user data in RAM which is lost when power is turned off
Why are there multiple types of secondary storage with different characteristics?
Because all devices are different and some types of secondary storage are more suited to certain applications than others
How can you reduce the amount of Virtual Memory used?
Increasing the size of RAM which reduces the need for virtual memory
Run less programs/instructions at once
What are some common types of magnetic storage?
Magnetic storage devices:
Hard disk drives
What are some common types of optical storage?
CD
DVD
Blu-ray Discs
Give some examples of solid state storage
Solid state drives (SSDs)
USB memory sticks
What is a General Purpose Computer?
A computer which is designed to carry out may different task. E.g. A PC. A computer which can run multiple tasks/applications
Why is a PC a General Purpose Computer?
It can…
Access the internet
Browse the world wide web
Use word processing software
Play games
Communicate via email and social media
Design and build web pages
Store and retrieve data
Play videos and Music
Give some examples of General Purpose Computers?
Some examples are PCs, Laptops, Tablets, Smartphones, Games consoles and Media systems in cars
What hardware can be found in Computers?
Physical components such as the CPU, hard disk drive, monitor, keyboard and mouse
What is Software?
The programs that run on a computer
What is Hardware?
The Physical Components of computer
What is the General Purpose Computer Model?
It is a model which illustrates the flow of data within a computer.
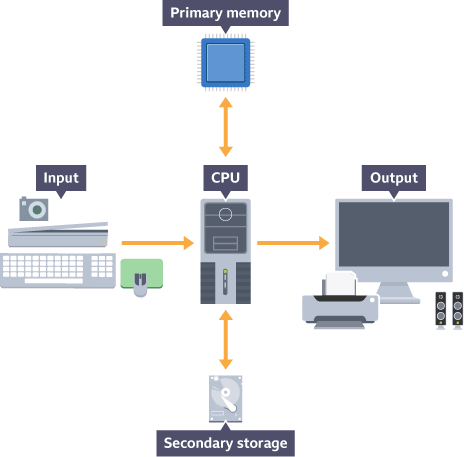
How does the general purpose computer model work?
Data is the input (from an input device), processed in the CPU and held in primary memory while it is being processed. Then the result is either sent to an output (to an output device) or stored in secondary storage (SSD, Hard drive etc.)
What is an input device?
A device (e.g. a keyboard) used to input data/information into a computer
Give some examples of an input device?
Some examples are keyboards, mice, cameras, scanners and microphones
What is an output device
A device (e.g. a monitor) used to output data or information from a computer
Give some examples of output devices?
Some examples are monitors, speakers and printers
What is the purpose of the CPU?
The CPU…
Processes data and instructions
Controls the rest of the computer system - all programs and data processing are run in the CPU and the hardware components are controlled by it
What are the six main components of the CPU?
Control Unit (CU)
Arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
Registers
Cache
Buses
Clock
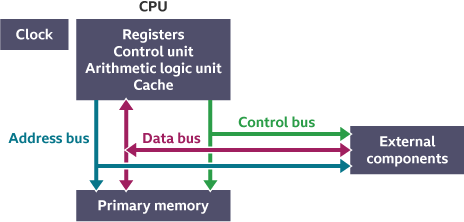
What is the Clock?
A component of the CPU that sends out regular pulses. It synchronises the computer hardware components so everything runs on the pulse
What is the Control Unit (CU)?
The component of the CPU which manages instructions
It Fetches, decodes and executes instructions
It issues control signals which control hardware
It moves data around the computer system
What is the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)?
A component of the CPU that performs arithmetic and logical operations
Where calculations are done and decisions are made
It acts as a gateway between primary memory and secondary storage, data passes through the ALU
What is Secondary Storage?
Non-volatile memory external to the CPU and used for long term storage of programs and data
What is Primary Memory?
The computer’s main memory accessible by the CPU (e.g. RAM and Cache), often faster than secondary storage. It can be accessed quickly by the processor as it is inside the computer. It is limited in size (Normally about 4GB)
What is non-volatile storage
Retains stored memory after power is lost
What is volatile memory?
Memory which requires power to retain data
What is Cache?
A small amount of RAM built within the processor. It temporarily stores data/instructions the processor is likely to reuse. Allows faster processing the processor does not have to wait for instruction to be fetched from lower storage (probably RAM)
What are registers?
Highspeed memory within the CPU which stores small amounts of data needed during processing e.g.
The address of the next instruction to be executed
The current instruction being decoded
The results of calculations
What are some examples of a register?
Program Counter
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Current Instruction Register (CIR)
Accumulator (ACC)
Is RAM or Cache faster and what is the downside?
Cache is faster however is more expensive so the cache tends to be very small and RAM is used in larger amounts
Give and Explain the levels of Cache.
The three levels are level 1, level 2 and level 3
L1 - Fastest but very small (64KB) in size as more expensive, holds most frequent instructions and data
L2 - More storage (256-512KB) than L1 but slower, holds data used less frequently than data stored in L1
L3 - Most storage (32MB), but slowest and stores the data used less than the data stored L1 and L2 Cache
What are the key elements of the Von Neuman Architecture?
Data and instructions are stored as binary digits
Data and instructions are stored in primary memory
Instructions fetched one at a time in order
The processor decodes and executes instructions, before fetching the next instruction
The cycle continues until no instructions to fetch
Give and the 5 registers of the Von Neuman Architecture
Program counter
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Current Instruction Register (CIR)
Accumulator (ACC))
What factors affect the CPU performance and how?
Clock speed:
- The more pulses per second, the more fetch-decode-execute cycles that can be performed and the more instructions that can be processed
- Faster the clock speed the faster the CPU can run
- 1Hz = 1 cycle per second
Cache Size:
- The bigger the cache the less time a processor has to wait for instructions to be fetched
- The Bigger the Cache the quicker the CPU can run
Number of Cores:
- Each core can fetch-decode-execute its own instruction
- The more cores the CPU has the more instructions that can be run at once and the faster the CPU can run
- Cores do not always increase performance as not all applications support the use of multiple cores
What are Embedded Systems?
A small computer that forms part of a larger system, device or machine. Its purpose is to control the device and to allow a user to interact with it. Only have one or limited tasks.
Give some examples of Embedded systems?
Central Heating Systems
Engine management systems in vehicles
Domestic appliances (e.g. Dishwashers, TVs and Digital phones)
Digital Watches
Electronic Calculators
GPS systems
Fitness trackers
What are some disadvantages of Embedded Devices?
They are not programmable by the user (it is done by the manufacturer)
Has to be connected to another device to be upgraded
They have limited functions
What are some advantages of Embedded Devices?
They are cheaper to design and build as they have limited functions
They tend to require less energy (useful for when they run of batteries)
Can be built using cheaper and less powerful processors as they don’t need much processing power,
What is Memory?
A component of the computer that holds data, programs and instructions currently in use
What is ROM?
Read Only Memory
It is non-volatile, primary memory containing unmodifiable data usually added when manufactured
It can be read from but not written to.
This is where the BIOS (Basic Input Output System) program is found
What is RAM and what is it used for?
Random Access memory
It’s volatile memory that is constantly being written to and read from
The Data can be accessed from anywhere within the memory (Why it’s called ‘Random Access’ memory)
RAM is used to hold data and instructions
In modern PCs, RAM holds the OS and any open documents and programs
It is easier to upgrade than other types of primary memory
What is BIOS and what does it do?
Basic Input Output System found in ROM
Runs when computer is switched on checking the device in functioning correctly
It then runs the bootup/bootstrap program which loads the computer’s operating system (OS) from the hard drive into the RAM
It is always needed so stored in ROM
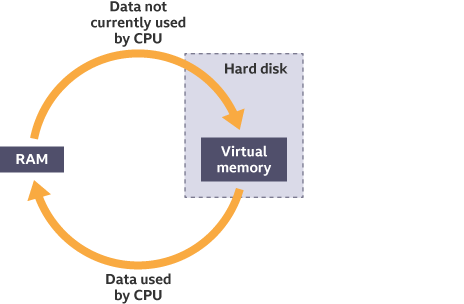
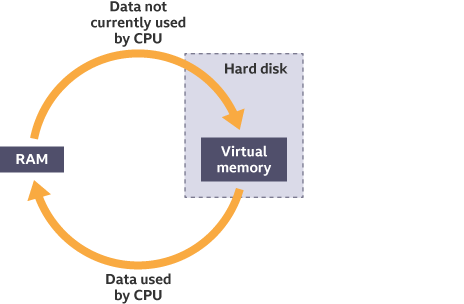
What is Virtual Memory?
It’s the use of secondary storage as additional primary storage
It’s used when there is no more RAM
It enables data that is not in use in RAM to be transferred to the hard disk. Freeing up room in RAM for other programs and data
What is Swapping (In terms of Virtual Memory)
When RAM is full, data not currently being used is transferred to the hard disk, freeing room for other programs/data
When the data on the hard disk is needed again, any other unused data is transferred to the hard disk
Then the original data is transferred back to RAM
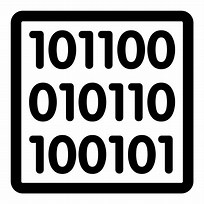
What form is data stored on secondary storage devices?
Binary
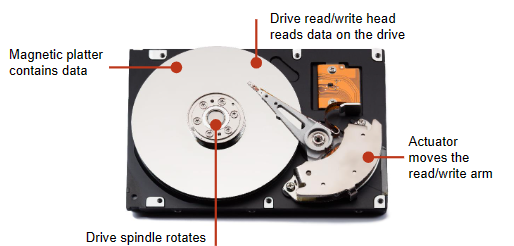
How do magnetic storage devices work?
They use magnetic fields to magnetise tiny individual sections of a metal spinning disk
Each tiny section represents one bit
A magnetised section represents a binary ‘1’ and demagnetised section represents ‘0’
As a disk is spinning a read/write head moves across its surface, to write data, the head magnetises/demagnetises the section of the disk spinning under the head
To read data the head makes a note of weather a section is magnetised or not
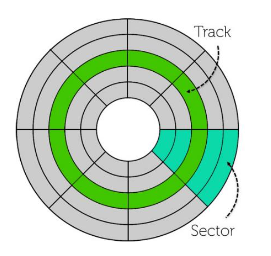
What do magnetic disks contain?
Concentric circles called tracks
Each track is divided into sectors
Disk heads on the mechanical arm which reads and writes data
What are the advantages of magnetic storage?
They have very large storage capacity, 6TB+, as the sections that store data are very small
Very cheap compared to SSDs
Relatively fast write speed
What are some disadvantages of magnetic storage?
Not very durable
Lots of mechanical parts
Platter precision and disk head not very portable so have to be sealed
Vulnerable to magnetic fields, strong magnet may erase data the device holds
What are hard drives used for?
For backing up data
For transporting data
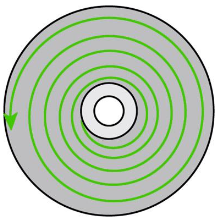
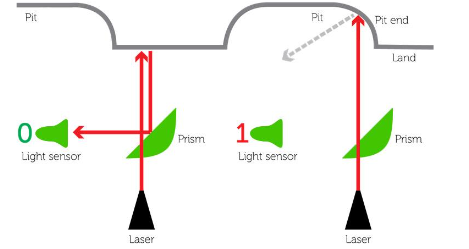
How does optical storage work?
Data is stored as pits and lands, burnt/pressed into a spiral track, from the inside and out
A laser beam passes over the pits and lands where reflected light (lands) represent ‘1’ and no reflections (pits) represent ‘0’
What are some advantages of Optical storage?
Cheap
Very easily portable
Take up little space
What are some disadvantages of Optical Storage?
Have a smaller storage capacity than other storage types
Easily damaged/scratched
Requires a CD reader
Slow write speeds
What is optical storage used for?
Songs, videos + other multi-media storage
Backups
Archiving data
Why do different forms of optical storage have the same capacity?
A CD has bigger pits as red light has a larger wavelength than blue light used with Blu-ray
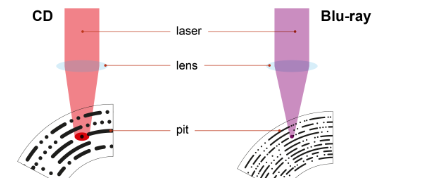
What are the storage capacities of CD-ROM, DVD and Blu-Ray?
CD-ROM - up to 720 MB
DVD - up to 8.4 GB (dual layered disk)
Blu-ray - up to 50 GB (Dual layered disk)
Give and explain the three types of Optical media?
ROM media - data is pre-written and can’t be overwritten, Music,films, software and games etc.
R media - Optical device writes data to them by shining a laser onto the disc, burns pits, written once nut read multiple times e.g. Copies of data
RW media - Similar to R but can be written to multiple times
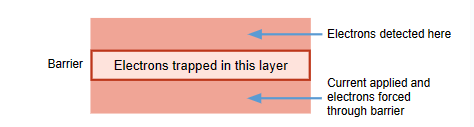
How does flash memory work?
A large electric current is used to force electrons through a barrier and trap them on the other side
They stay on the other side until flashed with a new current
Trapped (charged) electrons are ‘0’ and not trapped is ‘1’
What are SSDs
They use non-volatile flash memory to store information
What are some advantages of SSDs?
Highly durable as no moving parts
Very fast read/write speeds
No noisy fan/drive arm
Faster start up times than other storage types (HDD etc.)
High capacity (100GB - 16TB)
What are some disadvantages of SSDs?
More expensive then magnetic hard disks (HHDs)
Similar storage capacity as magnetic discs (HDDs)
Advantages of Flash memory?
Portable
Durable as they have no moving parts
What devices are flash memory used in?
Flash memory is commonly used in smartphones, tablets, USB drives, digital cameras, and solid-state drives (SSDs) due to its fast access speeds and durability.
What are some factors a user should consider when deciding which storage media to use?
Cost - Cost per Gigabyte
Capacity - How much data the medium can hold
Speed of access - how quickly data can be transferred to and from the medium
Portability - how portable the medium is/does it need to be portable?
Durability - how robust the medium is/how robust it needs be?
Reliability - How resilient and long-lasting the medium is?
Why is densely base 10
It has 10 units (0-9)
Why is binary base 2?
It has two units (0-1)
What is hexadecimal (hex)?
A number system using 16 symbols (0-9 and A-F), it is base 16 as it has 16 units
Give some examples of things typically stored in hex
Colour values and Mac addresses
Why do programmers use hex instead of binary?
They are easier to write and check than using binary
What is the difference between ASCII and Extended ASCII?
Extended ASCII is 8 bits and stores 256 characters while ASCII is only 7 bits and stores 128 characters
How to calculate the number of different combinations with a certain number of bits?
2^n
Where n is the number of bits
E.g. 4 bits has 2^4 combinations = 16
What is B6 hex in denary?
B=11 11x16=176 176 + 6 = 182 Answer = 182
What is 10111 in hex?
1 0 1 1 1 16+4+2+1 = 23 23/16 = 1 remainder 7 So 1=1 7=7 Answer = 17
How does multiplication in binary work?
You must shift the number to the left so… 2 in binary is one places 4 in binary is two places E.g. 10111 x 8 = 10111 = 10111 x 3 places so = 10111000
What is 15 in hexadecimal?
15 = F
What is 10111 x 100?
100 = 4 4 = two places 10111x100 = 1011100 Answer = 1011100
What is 10111/100? 100 = 4 4 = 2 places 10111/100 = 101 as in this binary there aren’t any decimals
What are character sets?
Letters, Punctuation and digits stored as binary numbers
Give some examples of character sets?
American Standard for Information Interchange (ASCII)
Unicode
What is the difference between ASCII, Extended ASCII and Unicode?
ASCII is 7 bits and can store 128 characters
Extended ASCII is 8 bits and can store 256 characters
Unicode is 16 bits and can store over 65,000 characters
Why is Unicode better than ASCII?
It can be used for multiple languages
Can be used for emojis
Can have more characters
What does more pixels and colours mean?
It means that there will be more bits per pixel and the larger colour depth, the larger the file will be?
What is colour depth?
The range of colours available
What is image size?
The number of pixels that an image contains. Expressed as height and width e.g. 640 × 480
What three factors can be used to estimate the size of the file?
Image height (number of pixels)
Image width (number of pixels)
The colour depth per pixel
How to calculate the file size for an image?
File size of image = height (pixels) x width (pixels) x colour depth (bits)
Calculate the size of an image when the height is 200, width is 400 and colour depth is 16. Give your answer in kilobytes (KB).
200 × 400 × 16 = 1,280,000 bits
1,280,000 / 8 = 160,000 bytes
160,000 / 1000 = 160 kilobytes (KB)
What affects the image quality
The resolution of the image
Explain the resolution of an image?
How many pixels there are in any area, how many pixels there are in a inch (PPI), images with larger pixels have less information to fill the area so are more blocky/pixelated than higher resolution images. The higher the resolution the larger the file size

What is data?
Units of information, often acted on by instructions
What is metadata?
Data about the file/image (data about data) without it the image data wouldn’t be correctly interpreted so the image wouldn’t be correctly displayed
Give some examples of metadata
File type
Date created
Author
Height/width of image -defines number of rows/columns the pixels should be arranged in
The resolution
The colour depth
How does a microphone capture sound?
The sound is captured and regular intervals (sample)and converted into a digital signal with an analogue to digital converter (ADC)
What is a sample in sound?
A digitally recorded fragment of sound, taken from an existing sound/track. Happens at regular intervals
What is the sample rate in terms of sound?
The number of samples recorded in a given period of time. Higher the sample rate the closer the recorded signal is to the original (Hertz - number of samples a seconds), although it will be larger
How many kilohertz are audio files usually recorded at?
44.1 kilohertz - good sound quality while keeping file size down
What is bit depth?
The number of bits used to record each sample. The higher the bit depth the more accurate the sound can be recorded but larger the file size. Typically 16 and 24 bits