Imported and fixed: histology cartilage and bone
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
firm connective tissue is known as
cartilage and bone
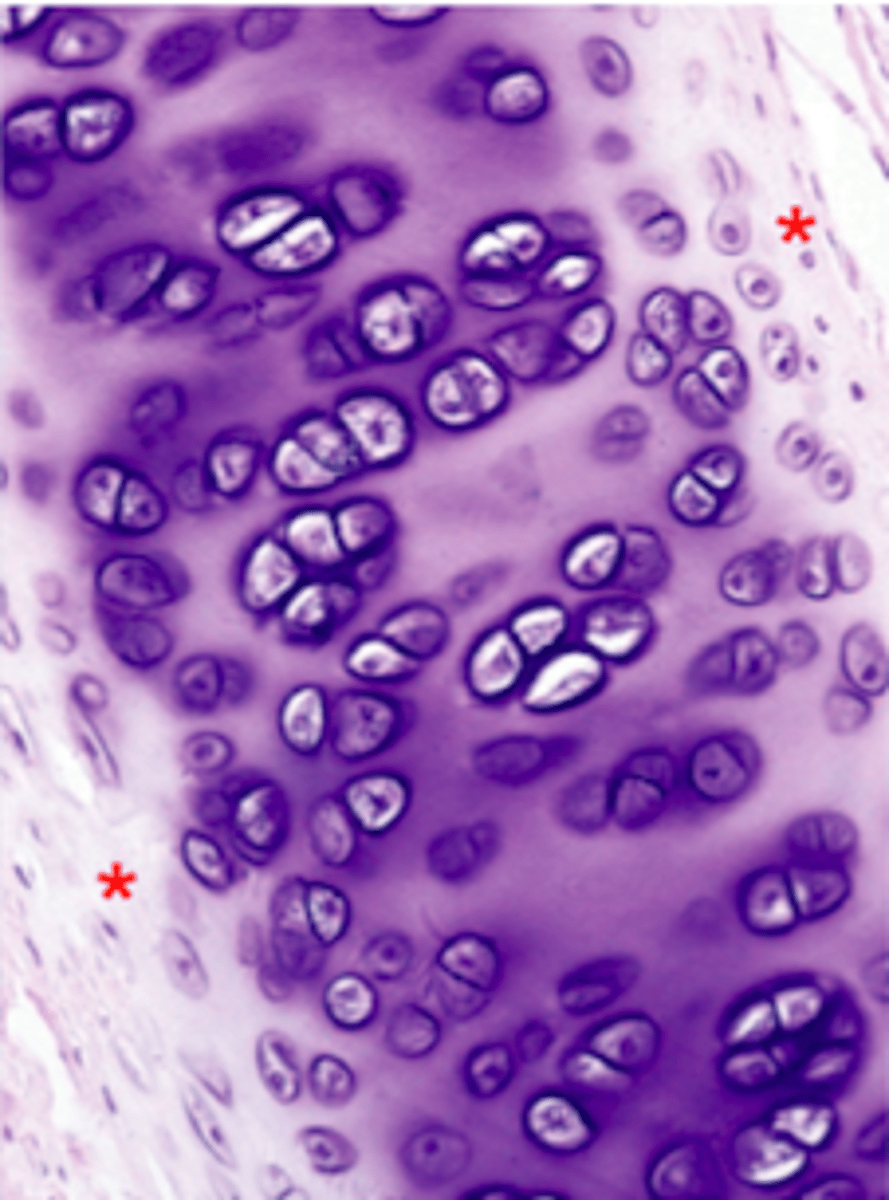
Identify this tissue
Hyaline cartilage
Cartilage is connective tissue that consists of
chondrocytes
but majority is ECM (>95%)
Cartilage is (vascular/avascular)
avascular, receives nutrients by diffusion
Cartilage is firm and pliable, the 3 types are
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
Location:Fetal, Articular, Respiratory, Costal Rib
Hyaline Cartilage
Location: Ear, Larynx, Epiglottis
Elastic Cartilage
Location of Cartilage: IVD, meniscus, TMJ
Fibrocartilage
Function of Cartilage:
Resist compression & cushioning
Hyaline cartilage
Function of Cartilage:
Resist compression & resist shearing forces
fibrocartilage
Function of Cartilage:
Flexible support
Elastic cartilage
Matrix of cartilage:
Collagen II
Aggrecan
Hyaline Cartilage
Matrix of cartilage:
Collagen II
Aggrecan
Elastic Fibers
Elastic Cartilage
Matrix of cartilage:
Collagen II
Collagen I
Versican, Aggrecan
Fibrocartilage
What cartilages have perichondrium?
Hyaline & Elastic cartilage only.
Fibrocartilage does NOT have perichondrium
All cells can grow by
intersital expansion
Cell divisions within the matrix, increases in length and girth
Intersitial growth
From perichondrium, form at surface, increases girth
appositional growth
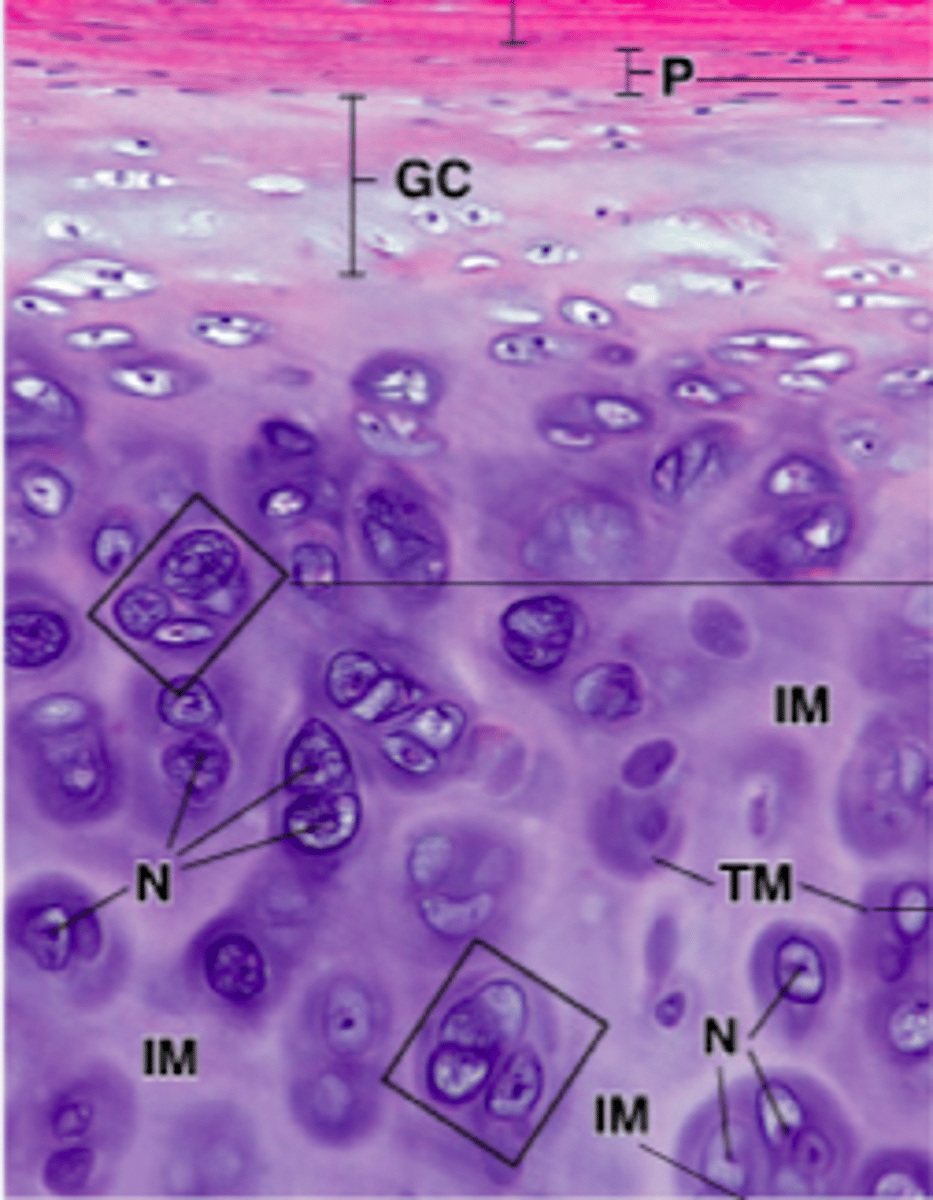
Territorial Matrix (TM) vs. Interterritorial Matrix (IM)
TM: strong basophilic staining
IM: weak basophilic staining
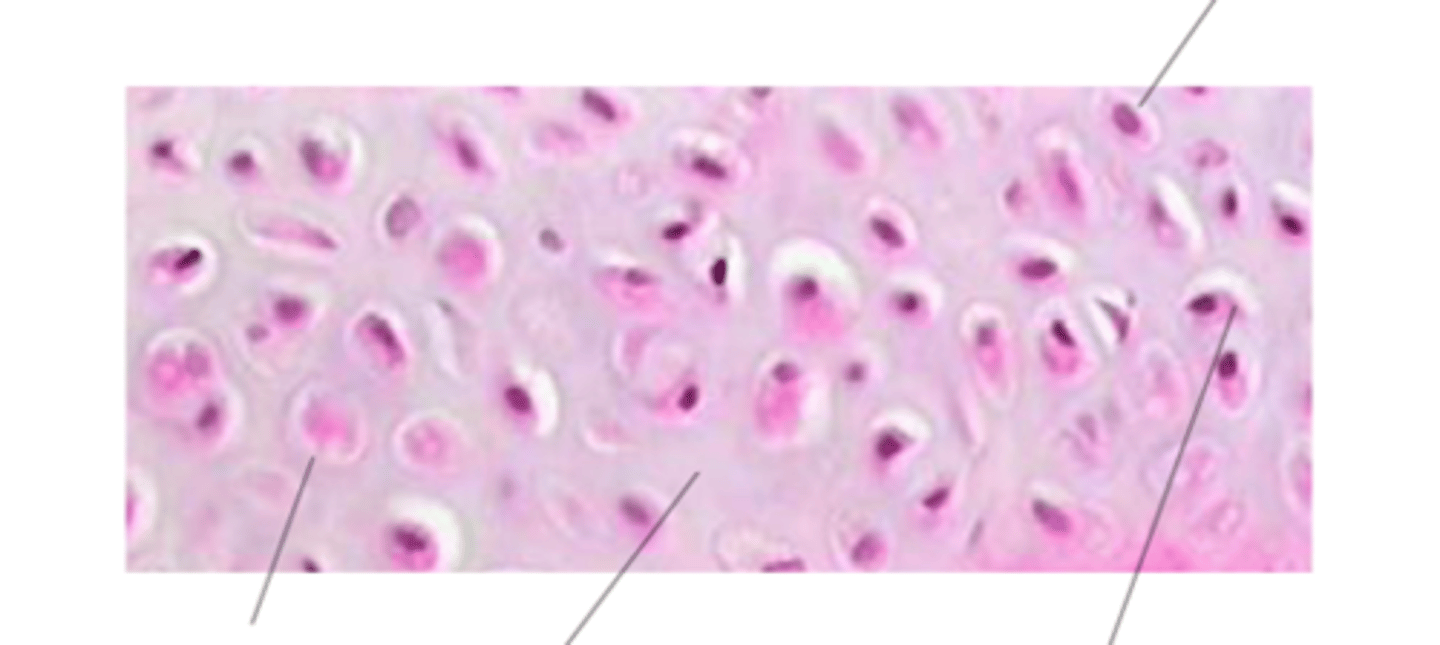
Name what the arrow is pointing to
L to R: chondrocyte, ECM, lacuna
Top: nucleus
isogenous group
cluster of chondrocytes (cartilage cells) that originate from a single progenitor cell
commonly found within the lacunae (small spaces) of the cartilage matrix, particularly in hyaline cartilage
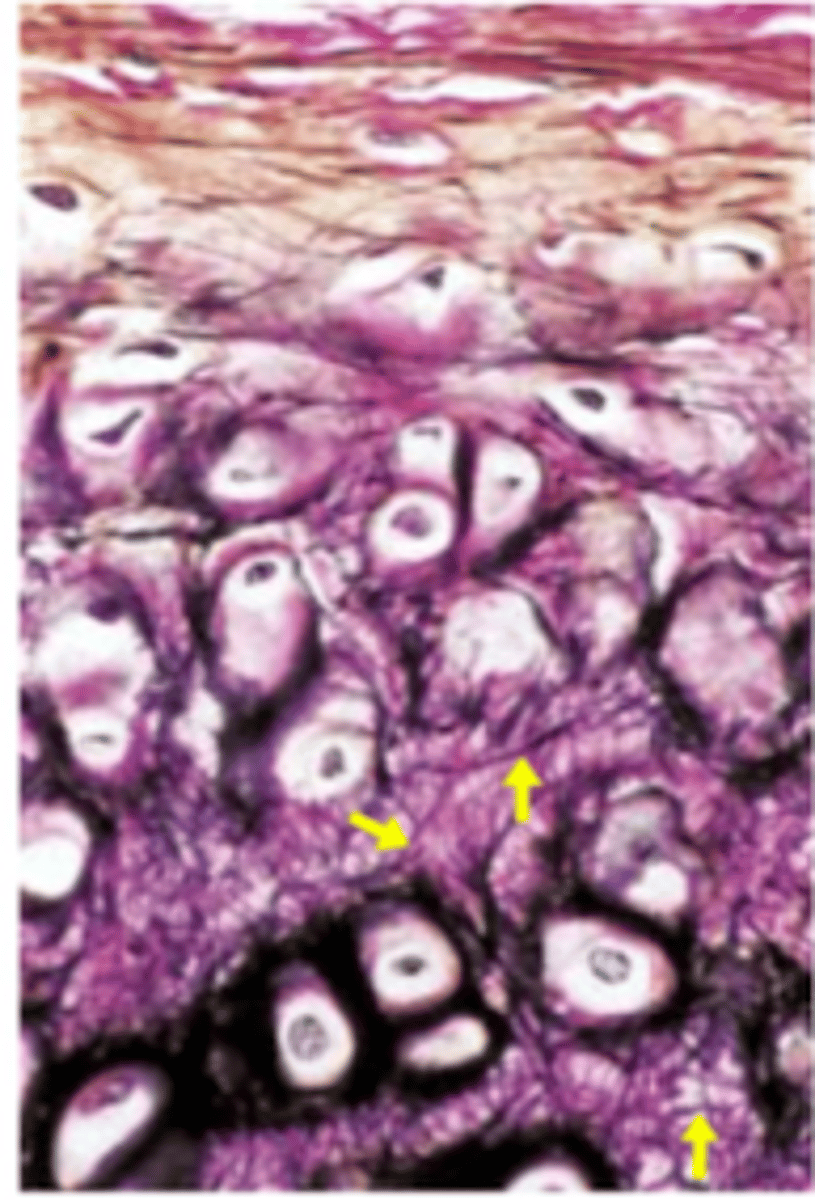
Identify the cartilage
Elastic cartilage is the most pliable cartilage --> it contains interlacing elastic fibers in addition to collagen fibers --> provides both form and flexibility
Fibrocartilage
A combination of dense connective tissue (has col I) and hyaline cartilage (has col II)
Proteglycans are (eosinophilic/basophilic) and have
basophilic, have negative charges
Collagens are (eosinophilic/basophilic) and have
eosinophilic, have positive charges
aggrecan
proteoglycan found in cartilage
ability to bind water is crucial for the cartilage's ability to resist compressive forces. water content allows cartilage to act as a shock absorber, providing cushioning to joints.
amount in cartilage determines and affects height; intervertebral disc (older=less)
What is a herniated disc in regard to bones?
Portion of the nucelus pulposus protudes into the inrervertebral foramen, pressing on one of the spinal nerves in the process
synovial joint
articular cartilage
no perichondrium
arthritis
caused by degradation of articular cartilage
Osteoarthritis
Caused by overuse and mechanic stress. Treatment via surgery, drugs such as condroitin sulfate, steroid, mild excercises
Connective tissue that is mineralized
Bone
Connective tissue that is not mineralized
Cartilage
ECM contains collagen II, collagen I, proteoglycan
Cartilage
ECM contains organic substances (collagen I fibers, ground substance proteoglycan) and inorganic structures (hydroxyapatite)
Bone
Function of cartilage
cushion, support
Function of bone
support & calcium/phosphate storage
Cartilage blood supply is
avascular
Bone blood supply is
vascular
Cartilage grows via what kind of growth
Intersitial and Appositional Growth
Bone grows via what kind of growth
appositional
Bone organ is made up of
Bone tissue, hemopoietic tissue, fat tissue, blood vessels, nerves
ECM made of:
organic:
collagen fibers, ground substance, proteoglycan
inorganic:
hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2
*need calcium for muscle from workout. get Ca from bone. used too much? not enough Ca for bone remodeling. osteopenia: bone mineral density is lower than normal but not low enough to be classified as osteoporosis
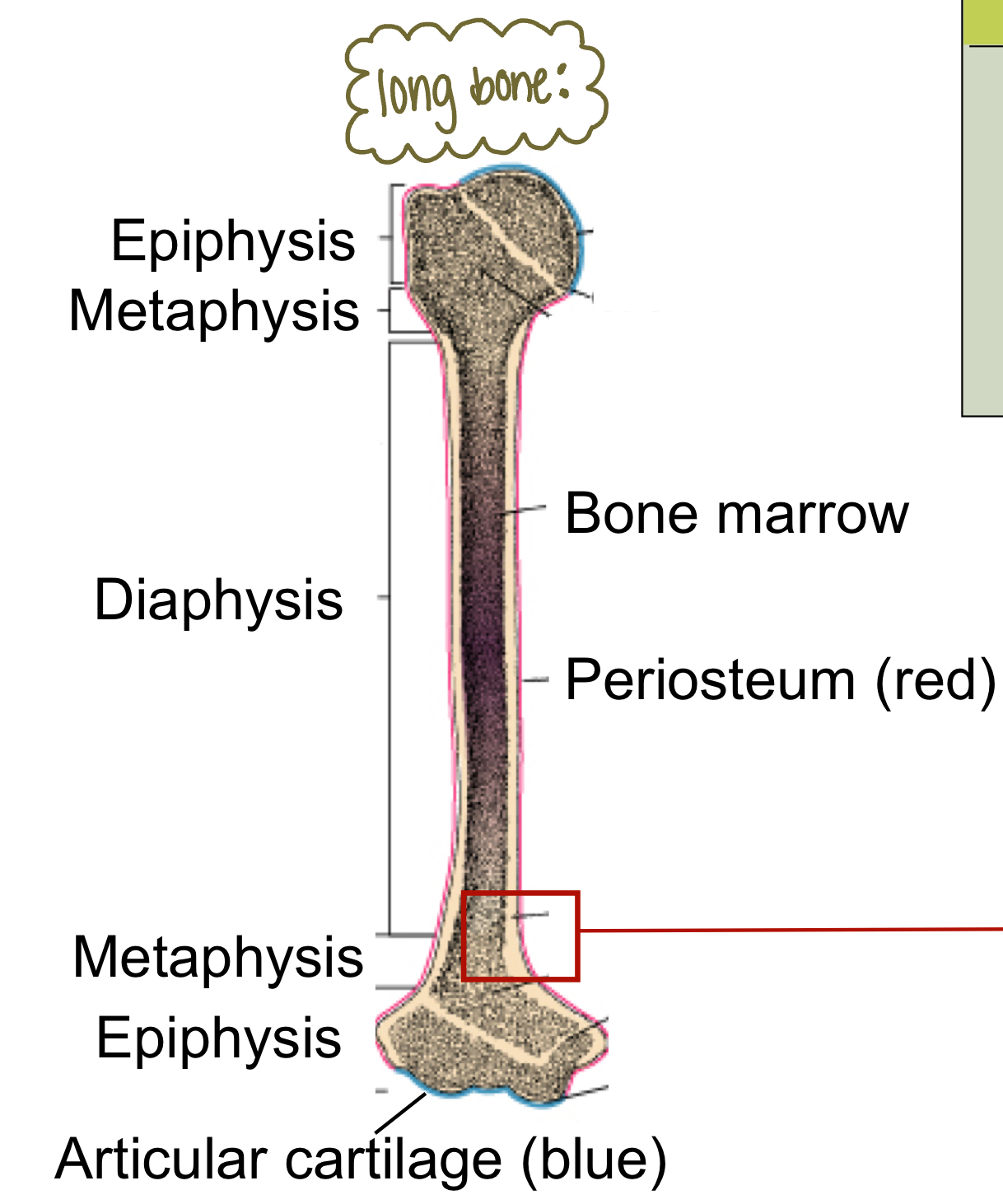
Identify the types of bone in this image
horizontal arrow: compact bone
top arrow: spongy bone
spongy bone VS compact bone:
structure, location, function
compact bone | spongy bone | |
|---|---|---|
structure | organized into structural units called osteons aka Haversian system each osteon has central canal surrounded by concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae |
|
location | outer layer of bone | primarily at the ends (epiphyses) of long bones |
purpose | protection, support, weight-bearing | lightweight, flexible, hematopoiesis, shock absorption |
spongy bone
forms first, covered by white fat, has a lamellated matrix, gets nutrients by diffusion
No: haversian lamellae or interstitial lamellae
Transverse canals are only found in
compact bone
Haversian lamellae & Intersitial lamellae are/not present in spongy bone
NOT
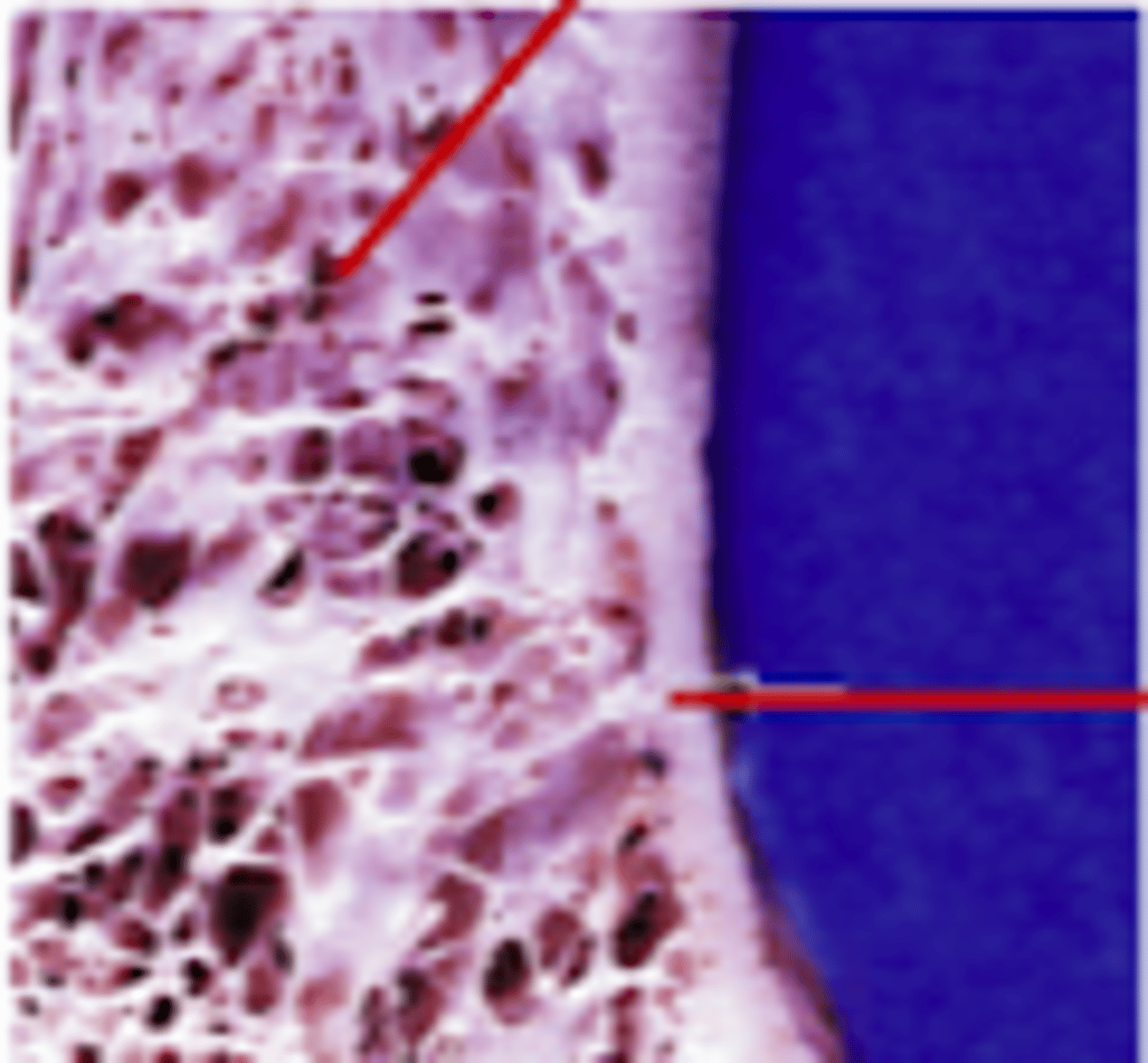
what type of bone is this?
mature compact bone
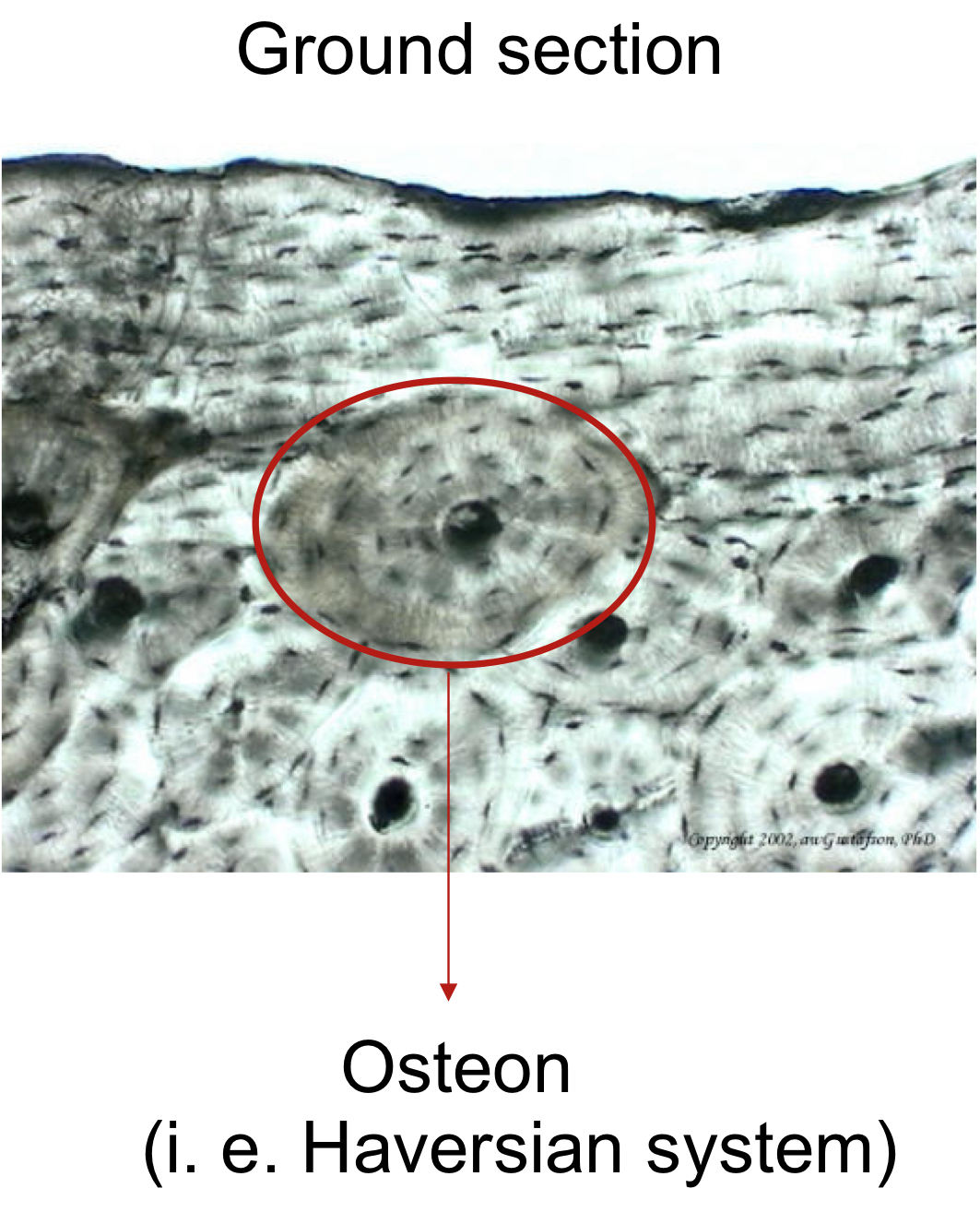
what type of bone is this?
compact bone
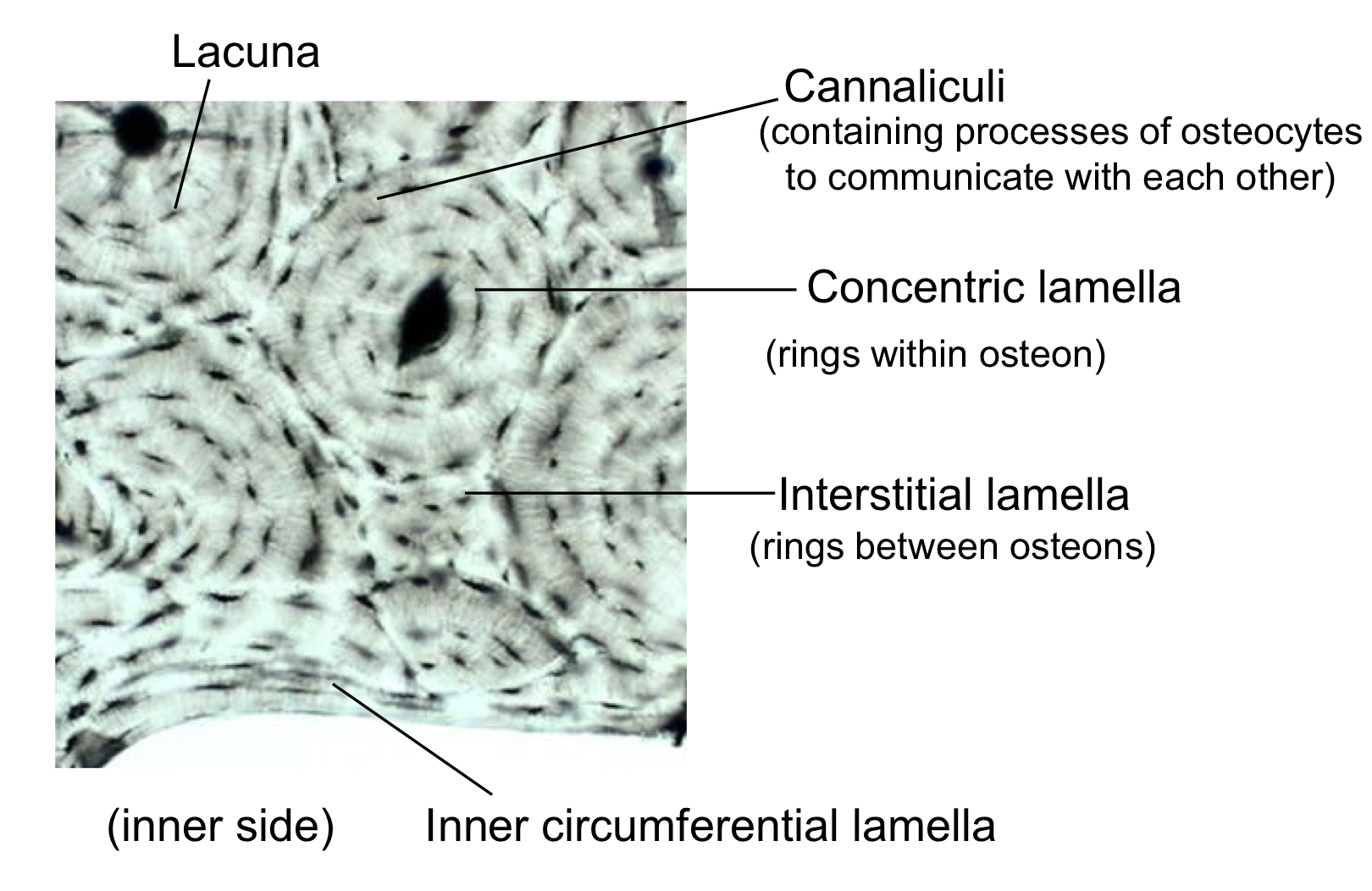
what extends cytoplasmic processes into canaliculi and communicate with each other through GAP junctions?
osteocytes
Osteons are found in
compact bone only
Surface cells such as periosteal cells and endosteal cells that eventually give rise to osteoblasts
Osteoprogenitor
osteoclast vs osteoblast vs osteocyte
osteocyte (3) | osteoblast (2) | osteoclast (4) | osteoprogenitor cells (1) | |
location | Embedded in bone matrix | Bone surface | Bone surface, near sites of bone resorption | Inner layer of periosteum, endosteum |
function | Maintain bone matrix, sense mechanical stress surrounded by matrix | Build new bone, secrete bone matrix not yet surrounded by matrix secretes bne matrix | Break down bone, resorb bone tissue large multinuc cell derived from mononuclear hemopoietic cells phagocytotic | Differentiate into osteoblasts, bone repair |
disease | osteopetrosis paget disease | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
disease synopsis | increased bone mass due to defect osteoclast, fragile bones, unerrupted teeth overactive osteoclast too much remodeling and not enough building; softer bones |
what is the bone matrix comprised of:
col 1, osteocalcin, osteopontin, alkaline phosphatase, BSP
Secretes bone matrix but not yet surrounded by matrix
Osteoblasts
Responsible for matrix deposition, maintains bone matrix. Osteoblasts that are surrounded by matrix are now called
Osteocyte
Characteristics of Osteoclasts (4)
-Large multinucleated cells
-Derived from mononuclear hemopoietic cells
-Phagocytotic
-Responsible for bone resorption
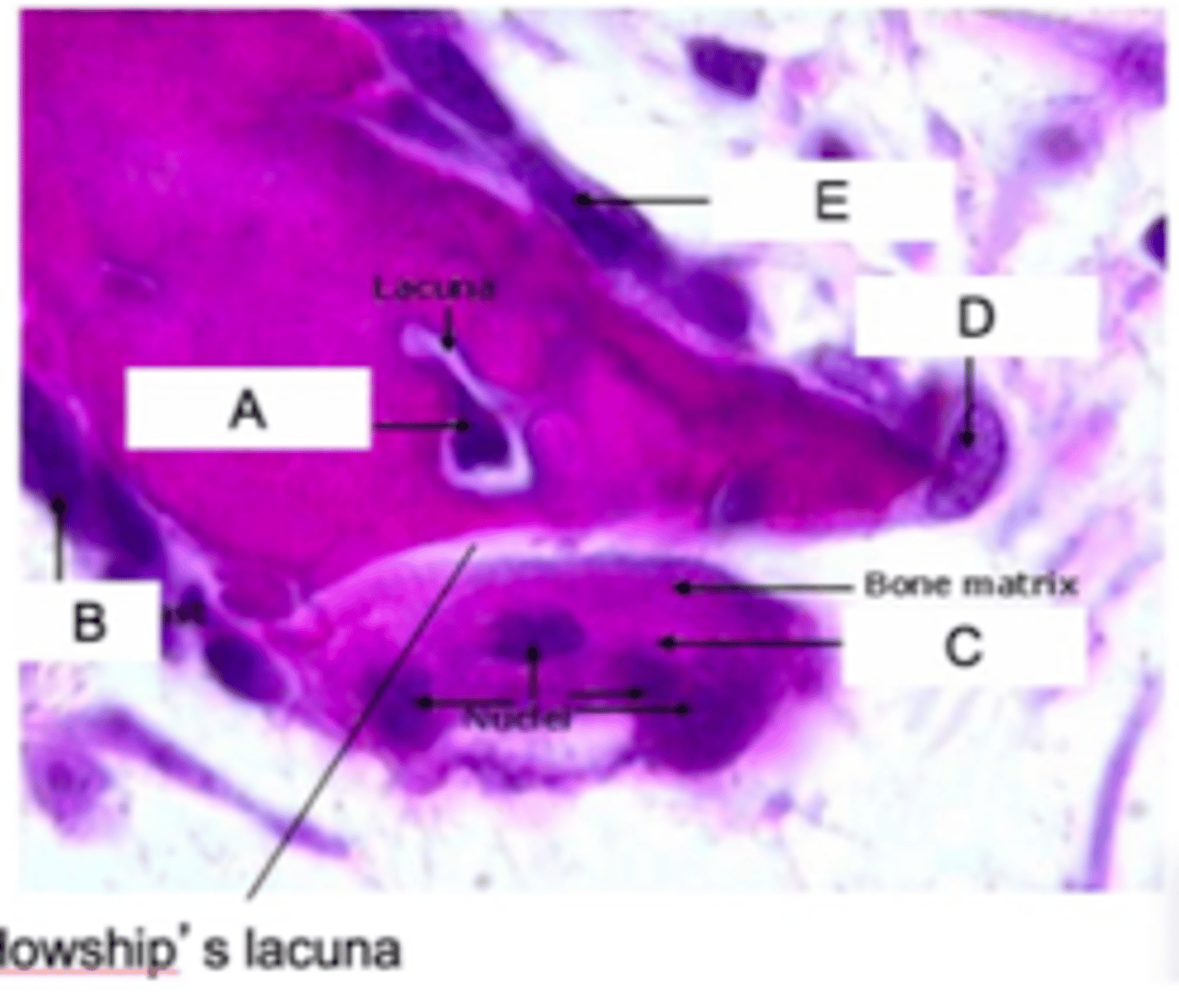
Identify all the letters in this image A-E
A: osteocyte
B: osteoblasts
E: osteoblasts
D: osteoclasts
C: osteoclasts
Space created by osteoclast resorption
Howship's Lacuna
Collagen II is produced only by
chondrocytes
What is the difference between osteoblast and osteocyte?
osteoblast: not surrounded by matrix
osteocyte: immersed in matrix
Macrophages and osteoclasts are derived from
monocytes
Macrophages can be found in
connective tissue
Osteoclasts can be found in
bone
Osteoclasts-mediated bone resporption occurs in 3 ways
Decalcify through acidification
Degradation of bone matrix
Clean up
What happens in Decalcify through acidification ?
pumping out H+ protons, cytoplasmic infolding
What happens during degradation of bone matrix
digestion by enzymes released by lysosomes
What happens during the "clean up"?
endocytosis
Low bone mass, structure deterioration of bone tissue Bone fragility, and more susceptible to fracture
Osteoporosis
Increased bone mass, due to defect osteoclast function
Bone fragility, and more susceptible to fracture; Unerrupted teeth
Osteopetrosis
Increased bone remodeling, overactive osteoclast Softer bone, more susceptible to fracture
Paget disease