Econ 102 - CHAPTER 10: Externalities and Public Goods
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Externality
Side effect on bystanders not reflected in market prices.
A price change is not an externality
Negative Externality
A side effect that harms bystanders.
Choices that impose costs on others
overproduction.
Marginal Social Cost = MPC + MEC
Market failure: There is too much of this activity taking place
Positive Externality
A side effect that benefits bystanders.
Choices that generate benefits for others
underproduction
Marginal Social Benefit = MPB + MEB
Market failure: There is too little of this activity taking place
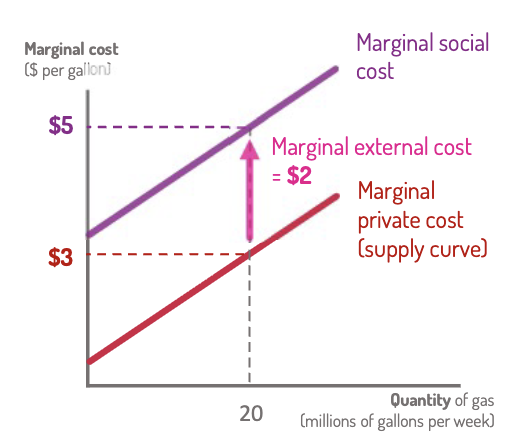
Marginal Private Cost (MPC)
extra costs paid by the seller from producing one extra unit.
Gas Example: Money spent on extra labor, electricity, etc., to produce another gallon of gas.
This is the firm’s supply curve
Marginal External Cost (MEC)
extra cost imposed on bystanders from producing one extra unit.
Gas Example: The additional pollution from this extra gallon of gas
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
All marginal costs, no matter who pays them.
MSC = marginal private cost + marginal external costs
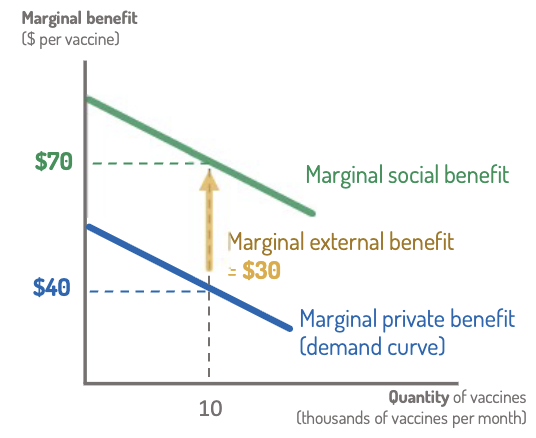
Marginal Private Benefit (MPB)
The extra enjoyment by the buyer from purchasing one extra unit.
Vaccine Example: The value of protecting your own health, plus the value of being able to do activities that require a vaccination.
This is the buyer’s demand curve!
Marginal External Benefit (MEB)
The extra benefit accruing to bystanders from one extra unit.
Vaccine Example: The additional vaccine further reduces the risk that the virus is passed on to other members of society
Marginal Social Benefit
All marginal benefits, no matter who gets them.
MSB = Marginal Private Benefit + Marginal External Benefit
Socially optimal quantity
The quantity that is most efficient for society as a whole, including the interests of buyers, sellers, and bystanders.
when marginal social benefit = marginal social cost
Four-Step Recipe for Analyzing Externalities
Find equilibrium quantity (where supply = demand)
Identify the externality (positive or negative).
Find socially optimal quantity (where MSB = MSC).
Compare the two:
If equilibrium > optimal → overproduction (negative externality).
If equilibrium < optimal → underproduction (positive externality).
Solving Externality Problems
Private Bargaining (Coase Theorem)
Corrective Taxes & Subsidies
Cap and Trade
Laws, Rules, and Regulations
Coase Theorem
If bargaining is costless and property rights are clearly established and enforced, then externality problems can be solved by private bargains
Two examples of private bargaining:
1. Neighbor’s loud music (negative externality issue)
2. Humana Health Insurance (positive externality issue)
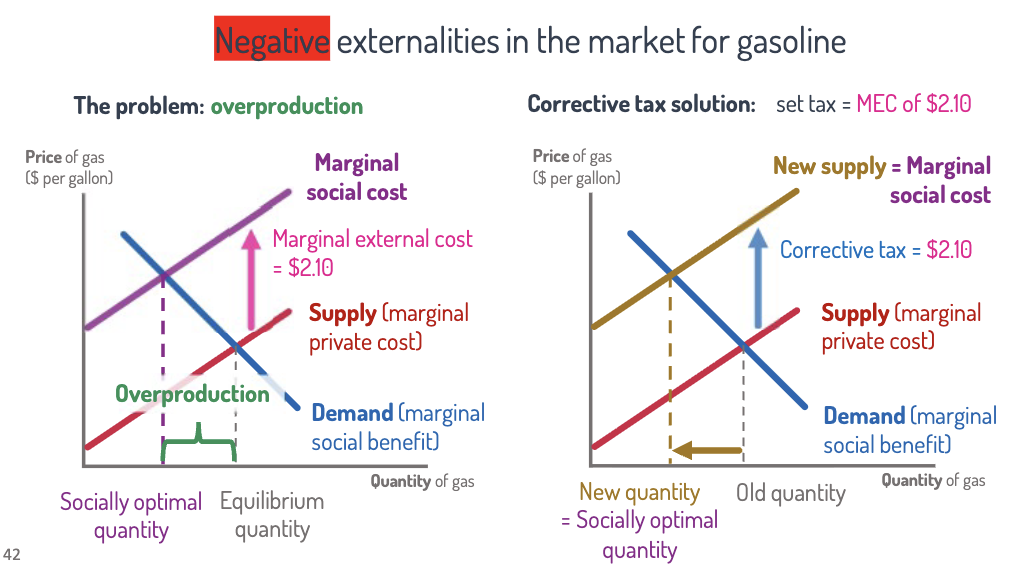
Corrective Tax/Subsidy
Problem: People ignore the external costs (or benefits) of their choices.
Solution: Introduce something these people cannot ignore.
Corrective Tax
Negative externality solution:
Set the corrective tax = marginal external cost.
Corrective tax: This tax incentivizes people to do less of the activity.
Corrective Subsidy
Positive externality solution:
Set the corrective subsidy = marginal external benefit.
Corrective subsidy:
This subsidy incentivizes people to do more of the activity.
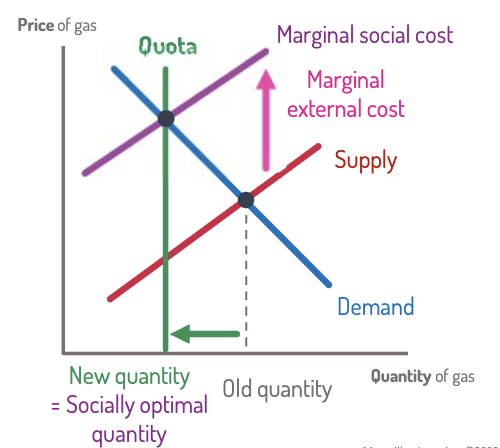
Cap and trade
A quantity regulation implemented by allocating a fixed number of permits, which can then be traded.
Private goods
Rival and Excludable
Ex:
Cars
Cupcakes
A can of coke
Airline seat
Solution:
Government provides or funds public goods using tax revenue.
Common Resources
Rival and Non-Excludable
Ex:
Fish in Ocean
National Parks (to some extent)
Highways (to some extent)
Private gains but shared costs.
Tragedy of the commons:
The tendency to over consume a common resource.
Overuse of goods
Solutions
Assign ownership rights (privatize the resource).
Set quotas or limits (like fishing permits).
Government management (parks, conservation laws).
Club Goods
Non-Rival and Excludable
Ex:
Email
Cable TV (HBO)
Satellite Radio (SiriusXM)
Public goods
Non-Rival and Non-Excludable
Ex:
National Defense
Public Broadcasting (NPR)
Public Education
Free Rider problem:
When someone can enjoy the benefits of a good without bearing the costs
market is underproduction