LAB PRACTICAL 1 BIO 221
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
337 Terms
What does hemoglobin saturation mean?
The percentage of hemoglobin binding sites that are carrying oxygen.
What 2 things are measured by a pulse oximeter?
Hemoglobin oxygen saturation (SpO₂)
Pulse rate (heart rate in bpm)
What is the normal range of hemoglobin saturation?
96-98 %
Would hemoglobin saturation be higher or lower in arterial blood compared to venous blood?
Higher in arterial blood, because it carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues. Lower in venous blood, because oxygen has been delivered to tissues.
Using a pulse oximeter, record your:
Hb saturation: % (check if within 95-100%) Pulse rate: _ bpm
What is hematocrit (Hct)?
The percentage of whole blood that is red blood cells.
When blood is spun in a centrifuge:
Air: on the top
Plasma: below Air
Red blood cells: on the bottom
Buffy coat: in the middle, thin layer
What is in the buffy coat?
White blood cells (WBCs) and platelets
Normal Hemoglobin (Hb) concentration in women?
12-16 g/dL
Normal Hemoglobin (Hb) concentration in men?
14/18 g/dL
Normal Hematocrit (Hct) in women?
36-48 %
Normal Hematocrit (Hct) in men?
40-54 %
Normal ratio of Hematocrit to Hemoglobin?
3:1
Normal RBC count in women?
3.5-5.5million/mm^3
Normal RBC count in men?
4.3-5.9 million/mm³
What does a spectrophotometer measure?
The amount of light absorbed by a substance.
Wavelength of light absorbed by Hemoglobin?
{\sim}540 nm
Normal Hemoglobin (Hb) concentration in women?
12-16 g/dL
Normal Hemoglobin (Hb) concentration in men?
14-18 g/dL
Normal Hematocrit (Hct) in women?
36-48 %
Normal Hematocrit (Hct) in men?
40-54 %
Normal Hemoglobin saturation (SaO₂)?
96-98 %
Normal ratio of Hematocrit to Hemoglobin?
3 : 1
Normal RBC count in women?
3.5-5.5 million/\operatorname{mm}^3
Normal RBC count in men?
4.3-5.9 million/\operatorname{mm}^3
What does a spectrophotometer measure?
The amount of light absorbed by a substance.
Wavelength of light absorbed by Hemoglobin?
{\sim}540 nm
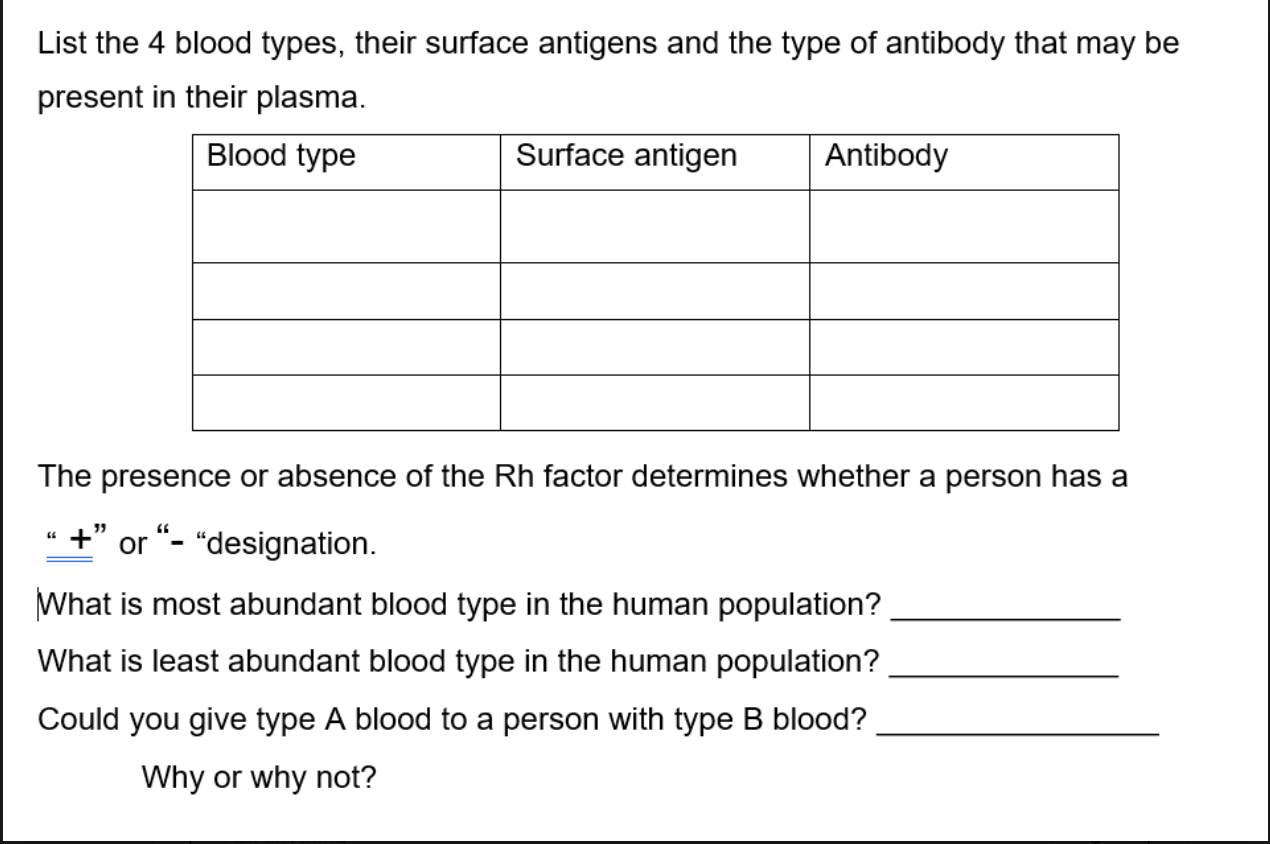
Fill in the Blanks
Most abundant blood type in the human population: O+
Least abundant blood type in the human population: AB−
Could you give type A blood to a person with type B blood? No
Why: The recipient’s plasma contains anti-A antibodies, which would attack the A antigens on the donated blood, causing a transfusion reaction.
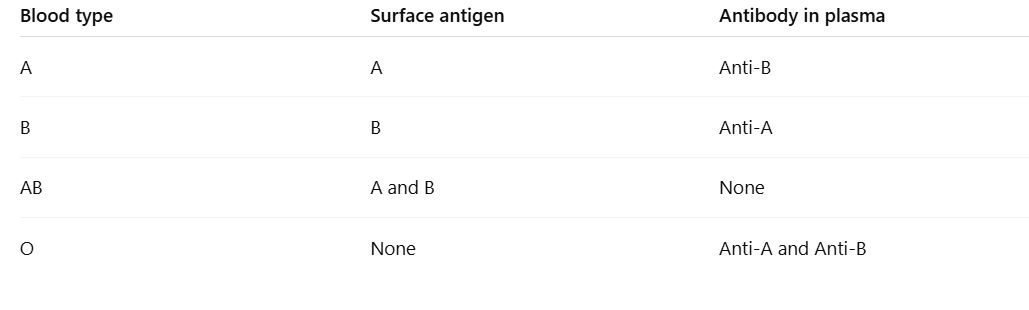
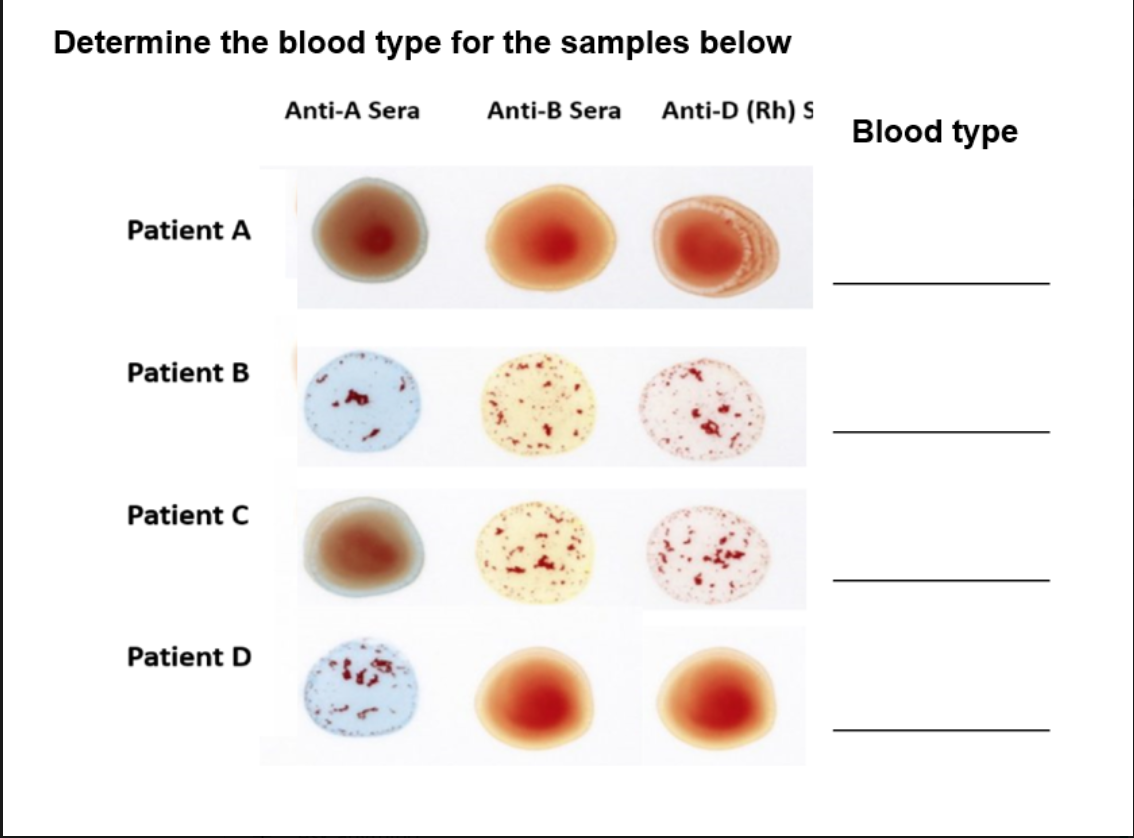
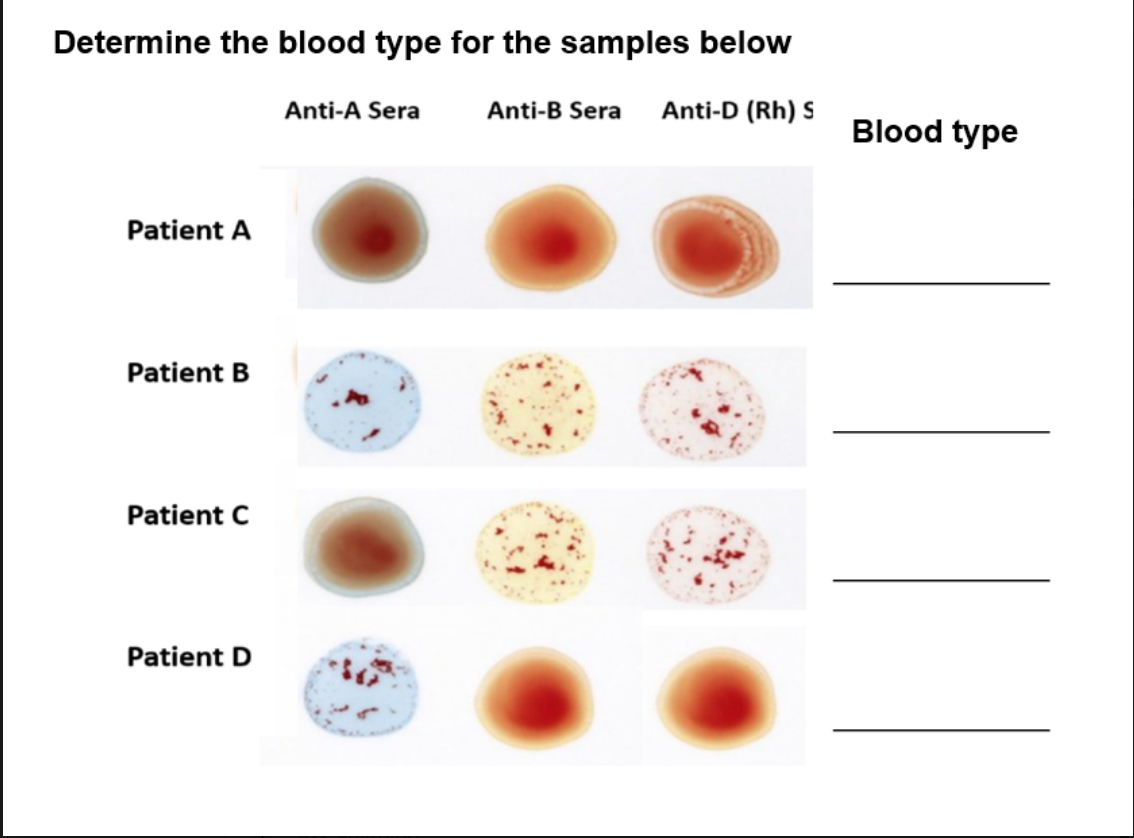
Fill in the blanks.
Patient A
Anti-A: No clumping → No A antigen
Anti-B: No clumping → No B antigen
Anti-D: Clumping → Rh present
✅ Blood type = O+
Patient B
Anti-A: Clumping → A antigen present
Anti-B: No clumping → No B antigen
Anti-D: Clumping → Rh present
✅ Blood type = A+
Patient C
Anti-A: Clumping → A antigen present
Anti-B: Clumping → B antigen present
Anti-D: Clumping → Rh present
✅ Blood type = AB+
Patient D
Anti-A: Clumping → A antigen present
Anti-B: No clumping → No B antigen
Anti-D: No clumping → No Rh
✅ Blood type = A-
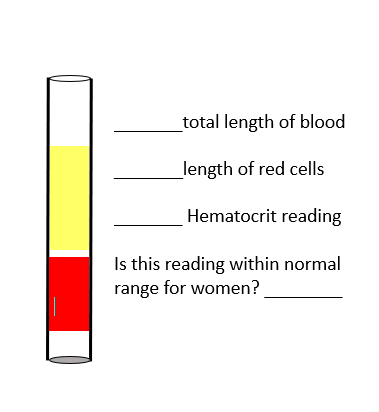
Fill in the blanks
Total length of blood: This is the full length of the column in the tube. From the image, it looks like the entire tube is your reference, so we can call it 100% (or measure in mm if given).
Length of red cells: The red portion at the bottom represents the packed red blood cells. Visually, it looks like about 40% of the total blood length.
Hematocrit reading: Hematocrit is the percentage of red blood cells in total blood. From the image, Hematocrit = 40%.
Is this within normal range for women? Normal hematocrit range for women is roughly 36–48%, so yes, 40% is within normal range.
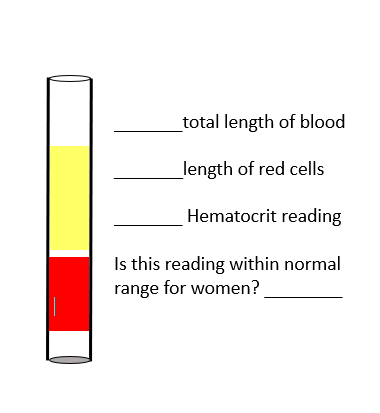
Fill in the blanks
Total length of blood: Entire column of blood in the tube (red + yellow = 100%).
Length of red cells: The red portion at the bottom of the tube (about 30% of the total length).
Hematocrit reading: 30%.
Is this reading within normal range for women? No, the normal hematocrit range for women is approximately 36–48%, so 30% is below normal (indicating possible anemia).
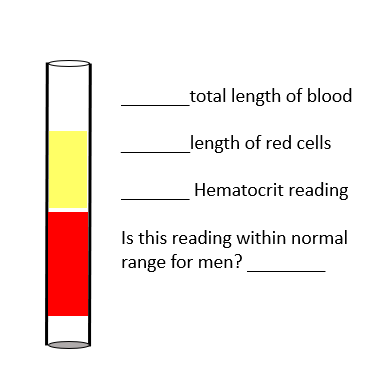
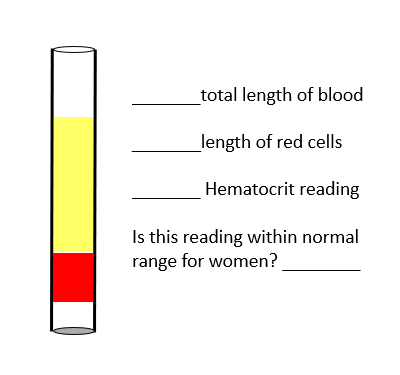
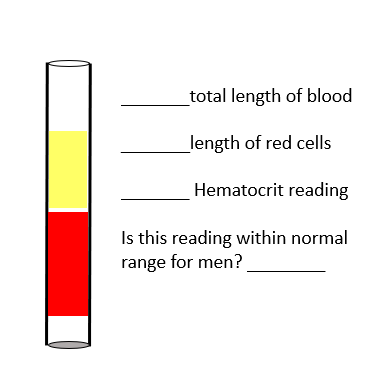
Fill in the blanks
Total length of blood: Entire column of blood in the tube (red + yellow = 100%).
Length of red cells: The red portion at the bottom of the tube, approximately 60% of the total length.
Hematocrit reading: 60%.
Is this reading within normal range for men? ❌ No, the normal hematocrit range for men is about 40–54%, so 60% is above normal (which could indicate polycythemia or dehydration).
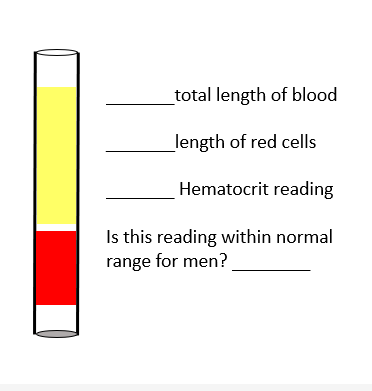
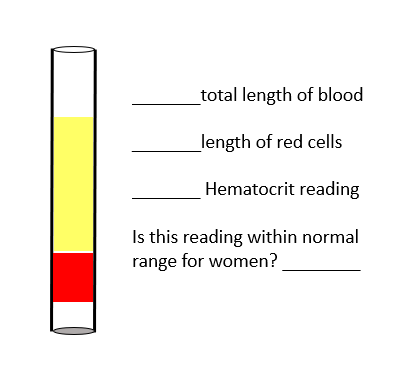
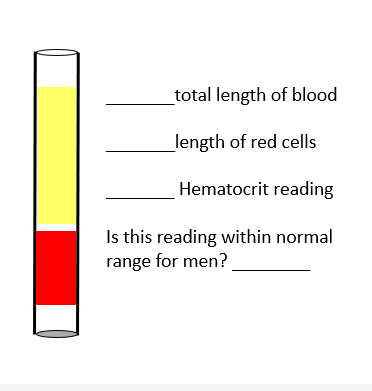
Fill in the blanks
Total length of blood: Entire column of blood in the tube (red + yellow = 100%).
Length of red cells: The red portion at the bottom of the tube, approximately 35–40% of the total length.
Hematocrit reading: About 38%.
Is this reading within normal range for men? ❌ No, the normal hematocrit range for men is approximately 41–53%, so 38% is slightly below normal (could suggest mild anemia or low red blood cell count).
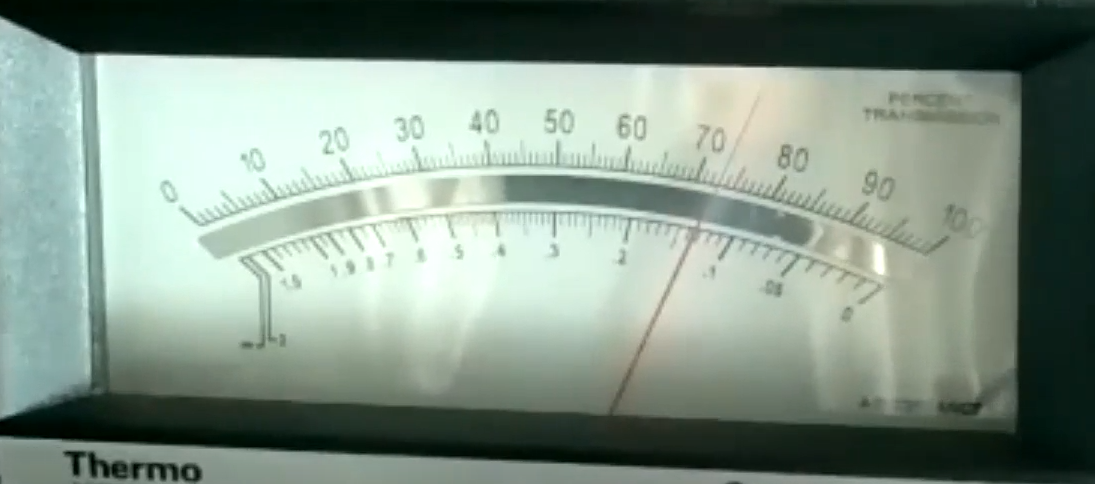

Find the absorbance reading for this 5 gram sample.
Result 1 - Absorbance @ 540 nm: .14 Hb Concentration 5gm/100ml
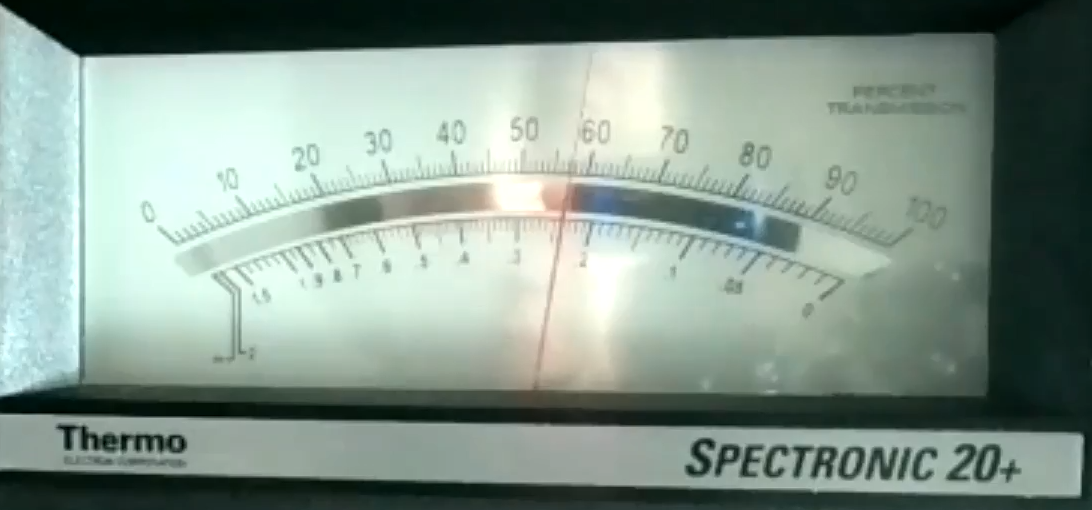

Find the absorbance readings in this 10 gram sample.
Result 2 - Absorbance @ 540 nm: .24 Hb Concentration 10gm/100ml

Find the absorbance reading in this 15 gram sample.
Result 3 - Absorbance @ 540 nm: .33 Hb Concentration 15gm/100ml
How would you graph the 3 samples of absorbance?
You would plot the absorbance values against the corresponding sample weights, creating a line or scatter plot to visualize the relationship between absorbance and Hb concentration.
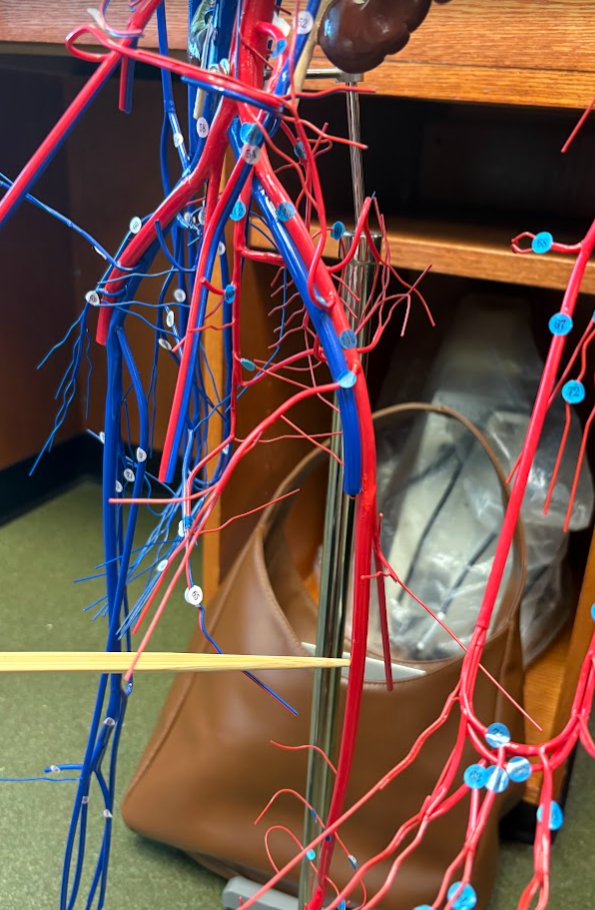
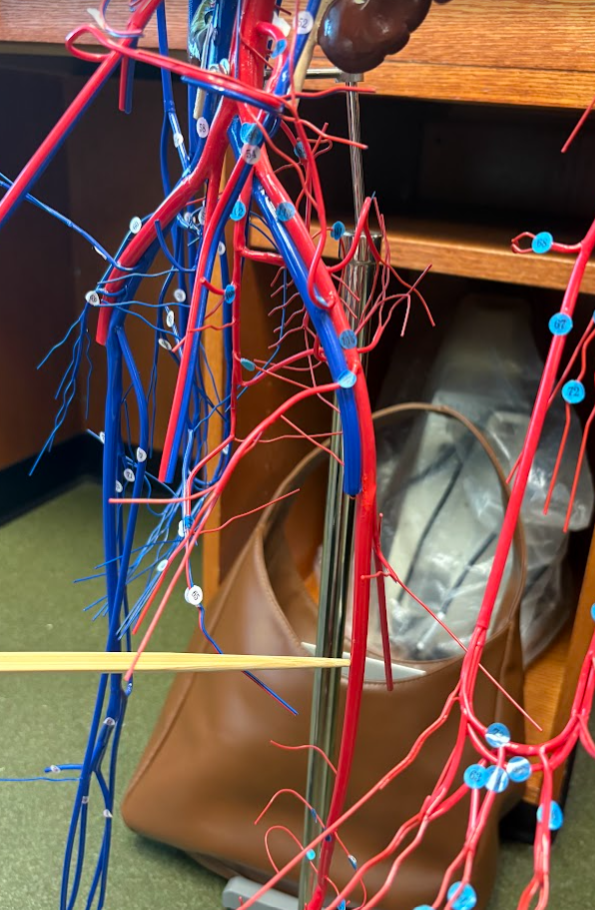
Whole view of model

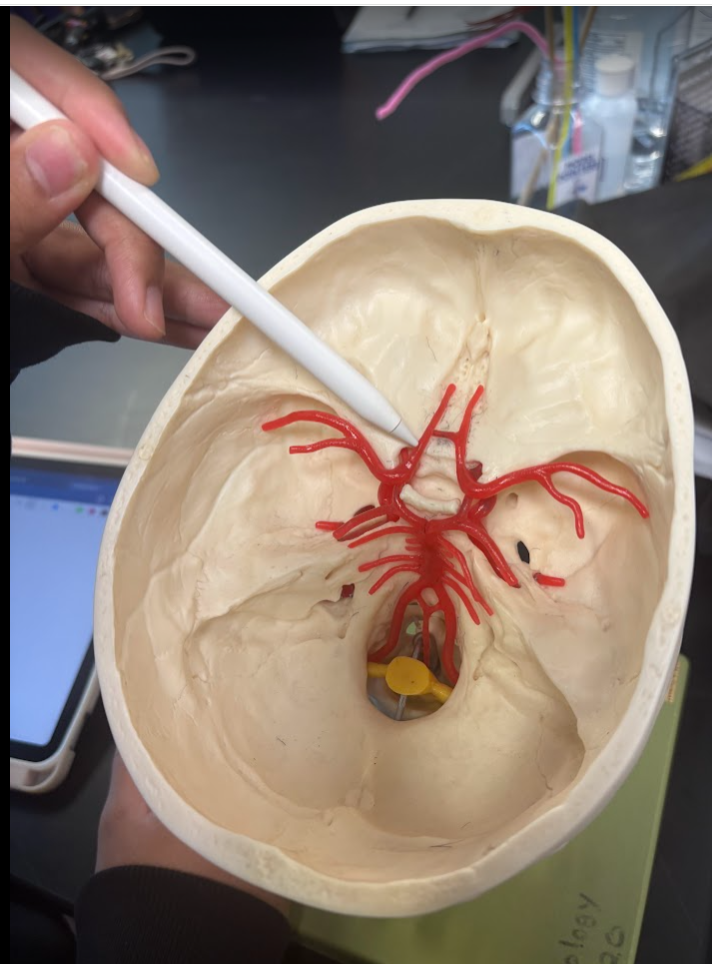
What is this?
Anterior cerebral artery
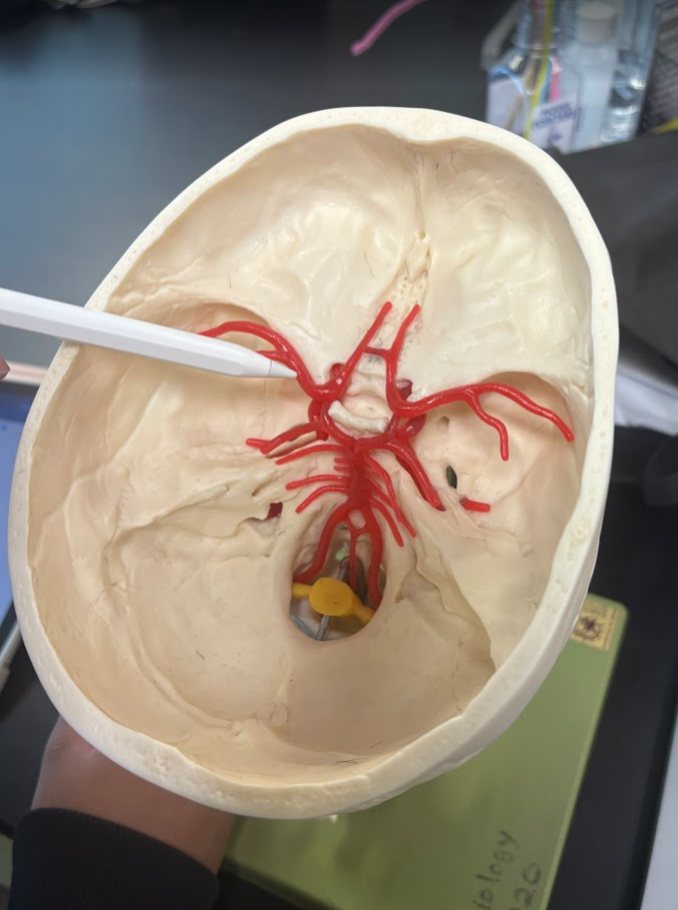
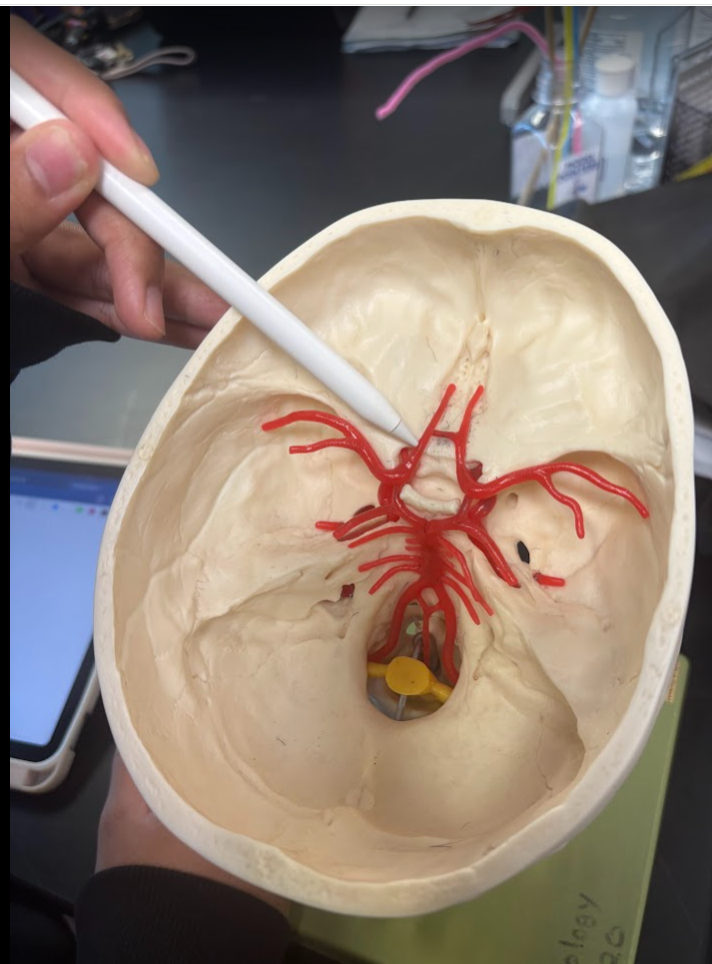

What is this?
Middle cerebral artery
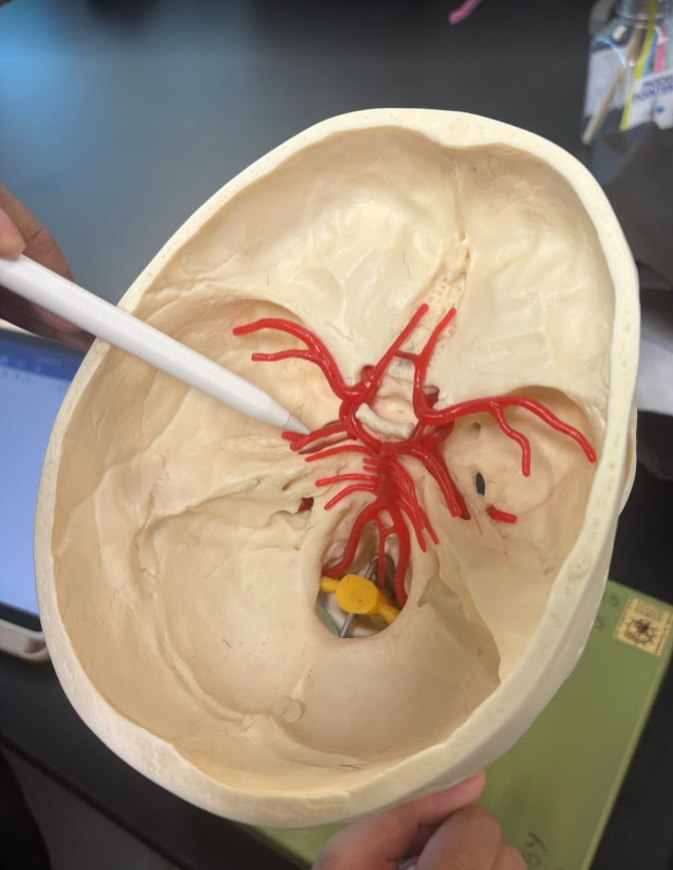
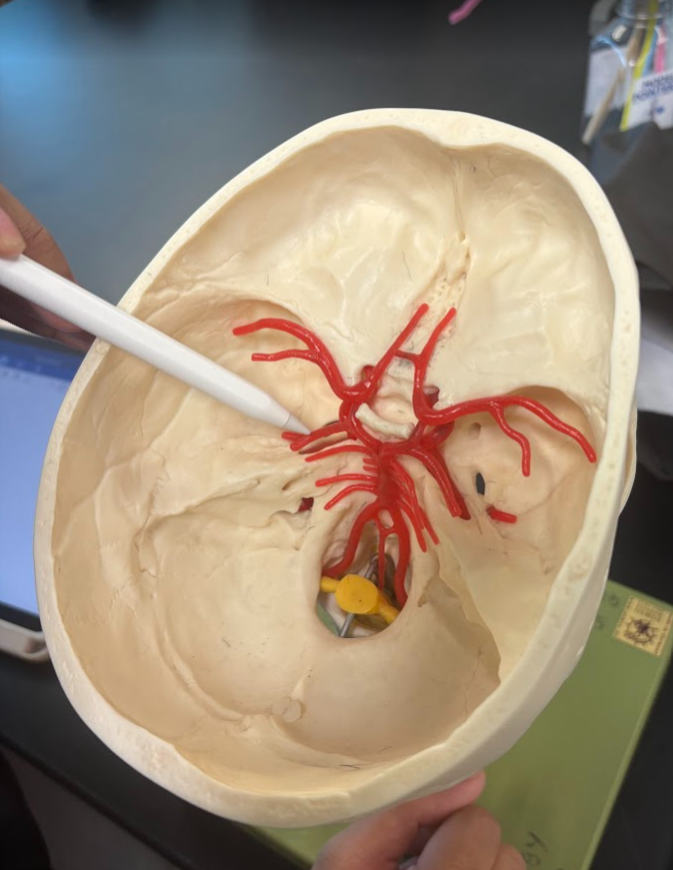
What is this?
Posterior cerebral artery
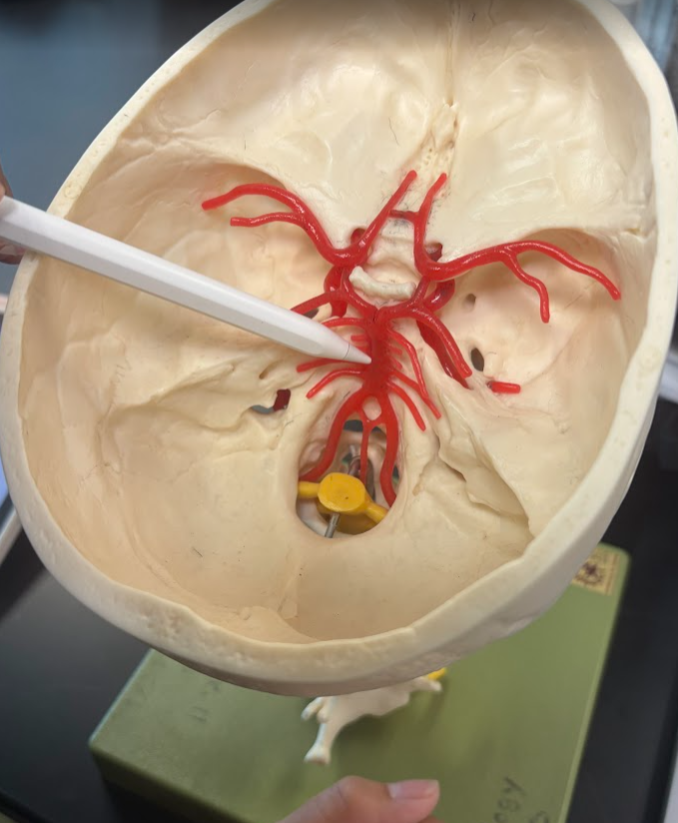
What is this?
Basilar artery
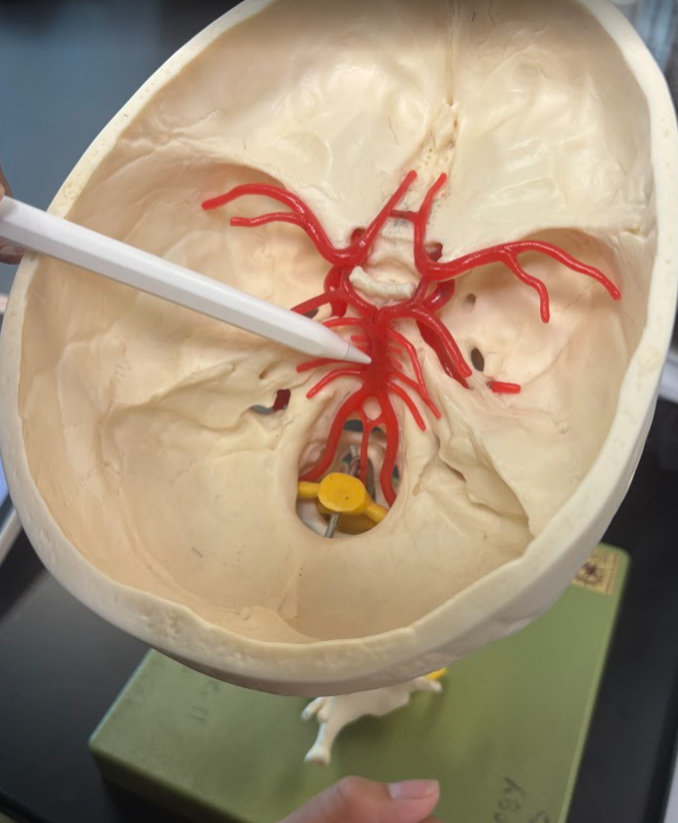
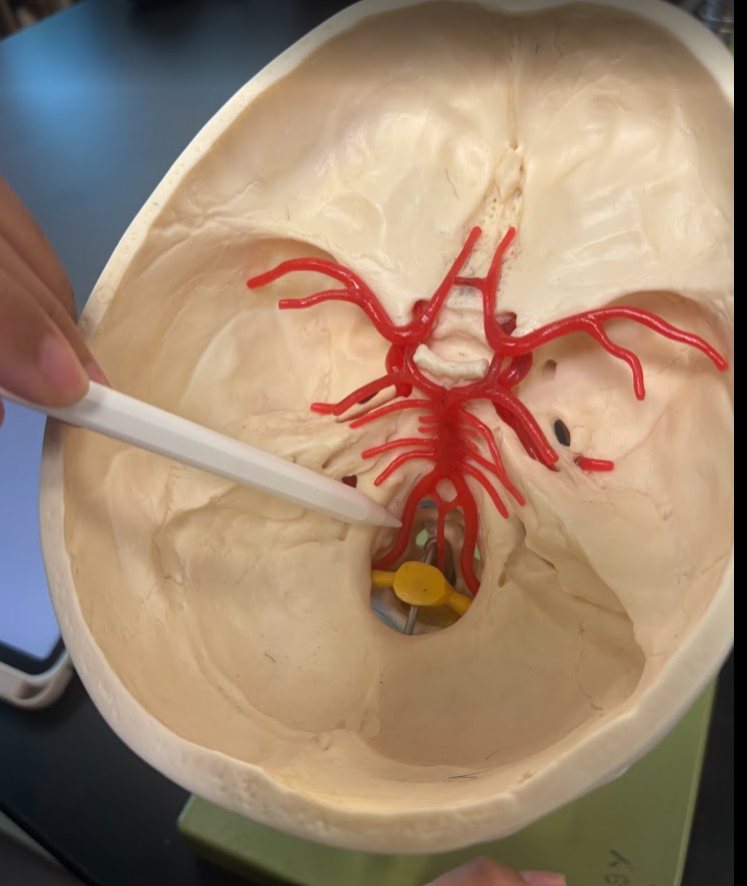
What is this?
Vertebral artery
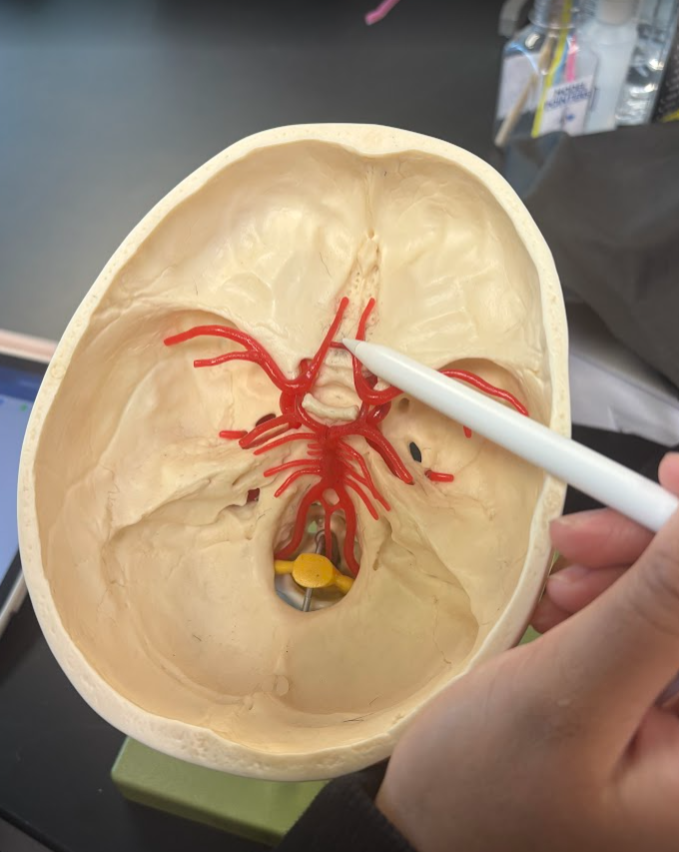
What is this?
Anterior communicating artery
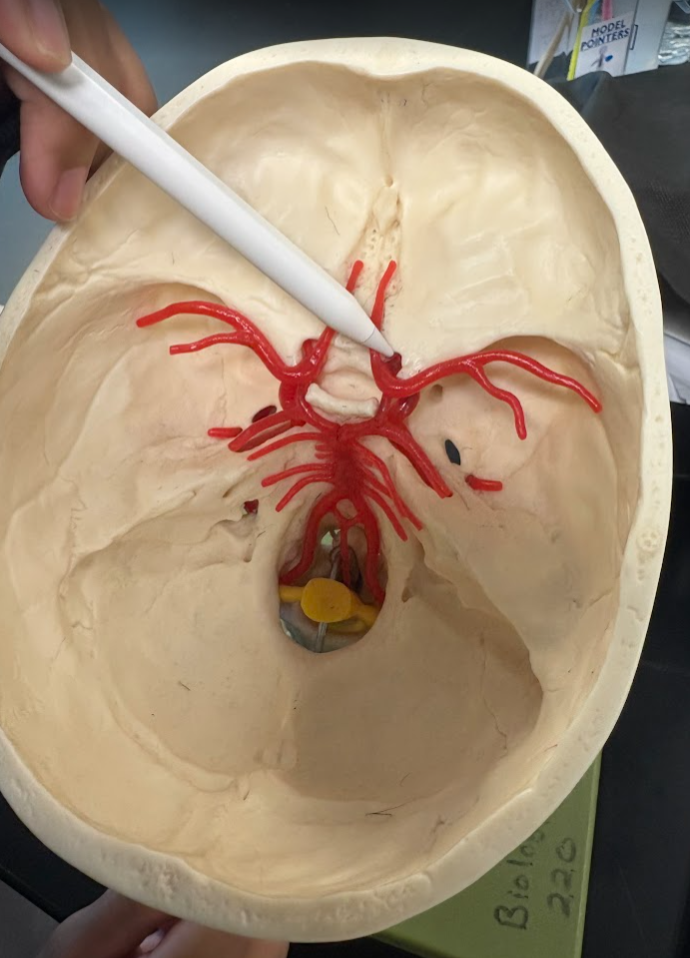
What is this?
Internal carotid artery
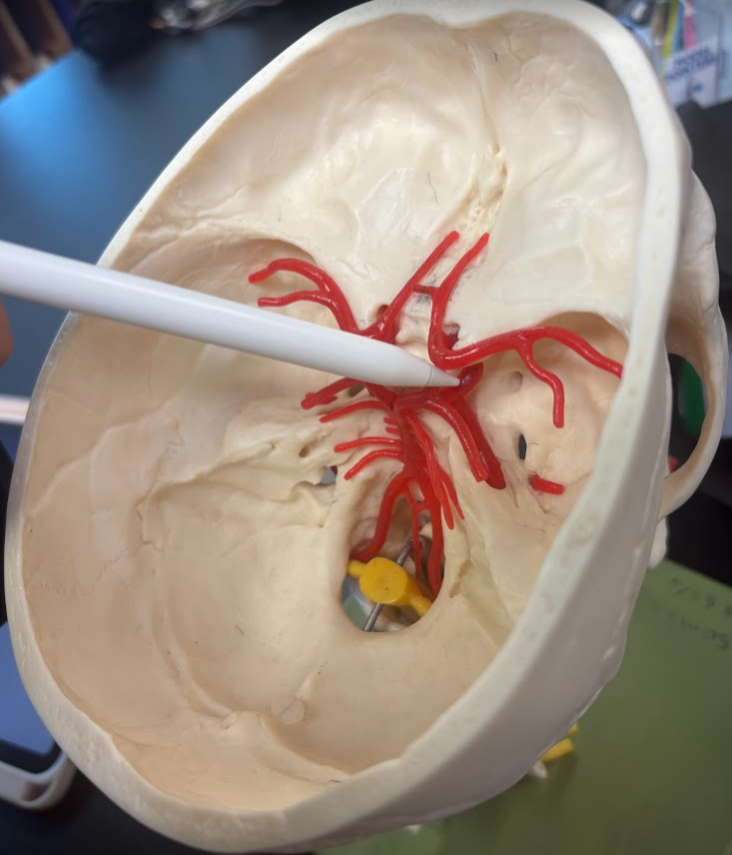
What is this?
Posterior communicating artery
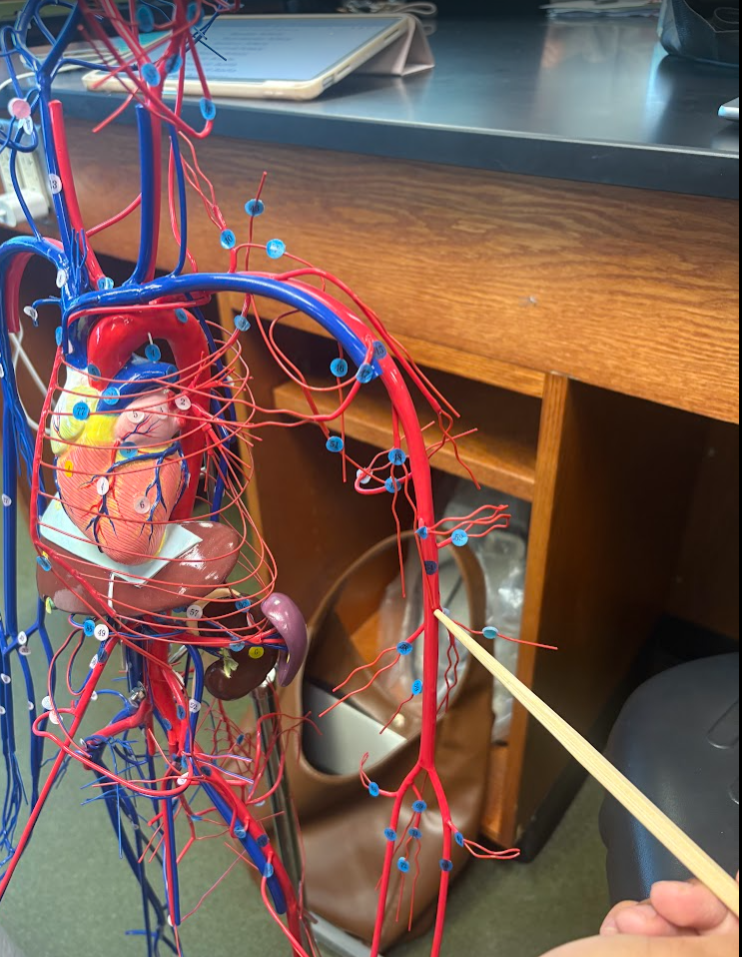
What is this?
Brachial artery (54)
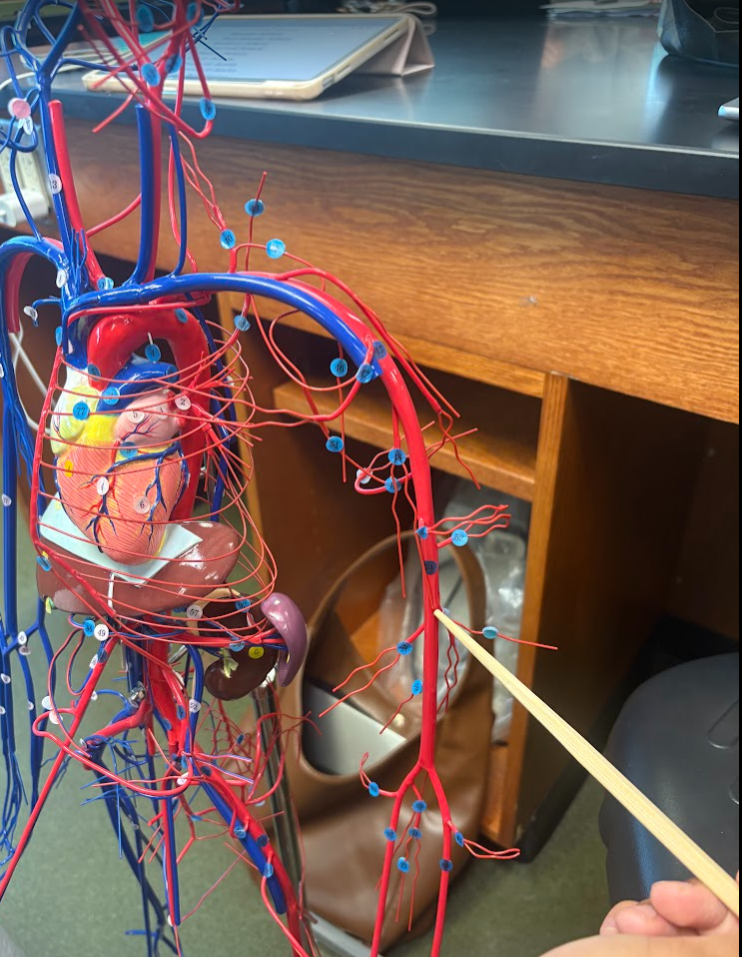
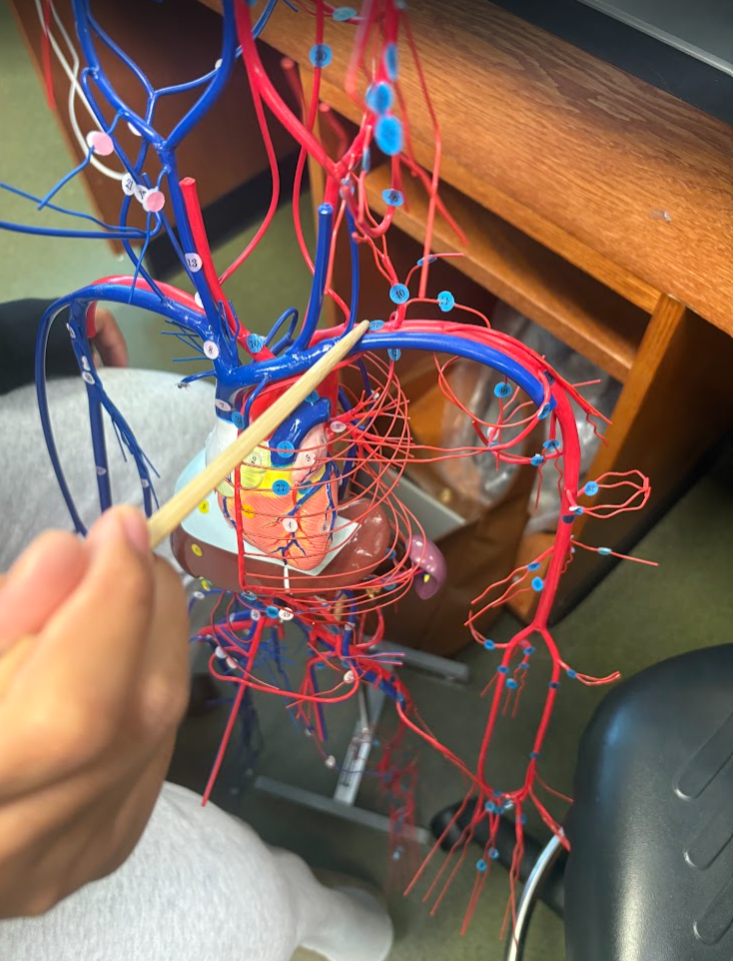
What is this?
Left subclavian artery (37)
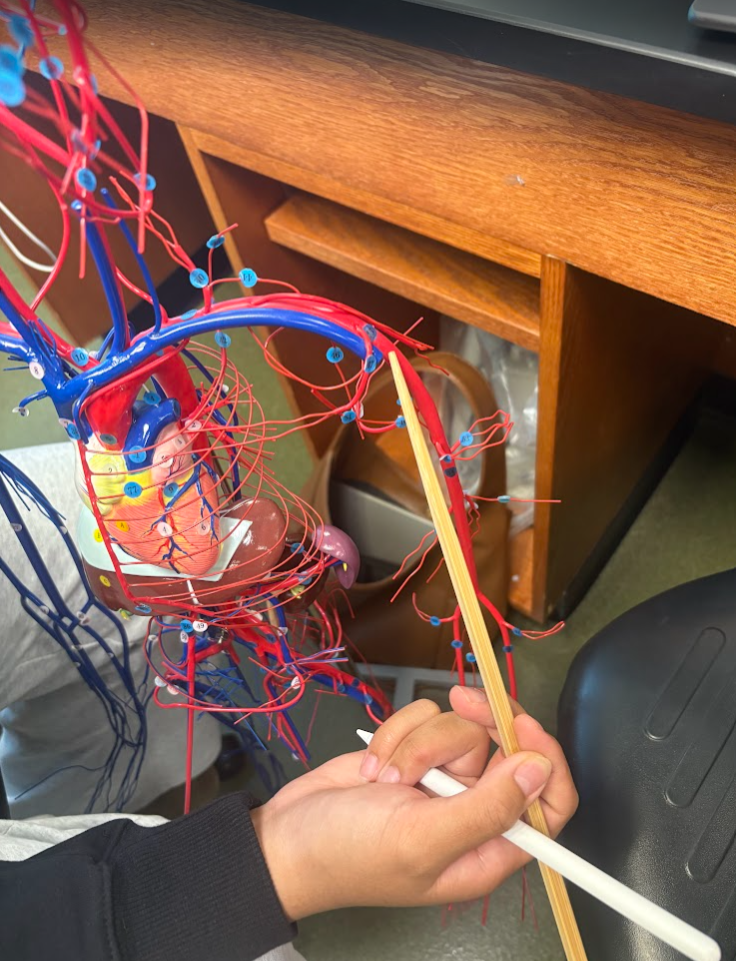
What is this?
Axillary artery (45)
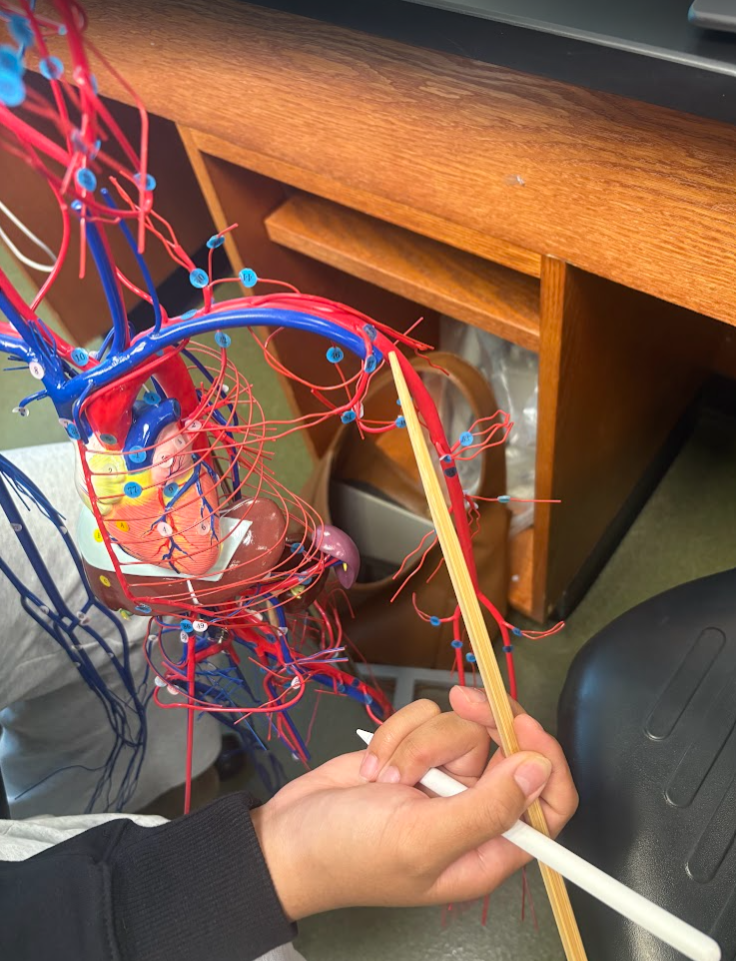
What is this?
Radial artery (60)
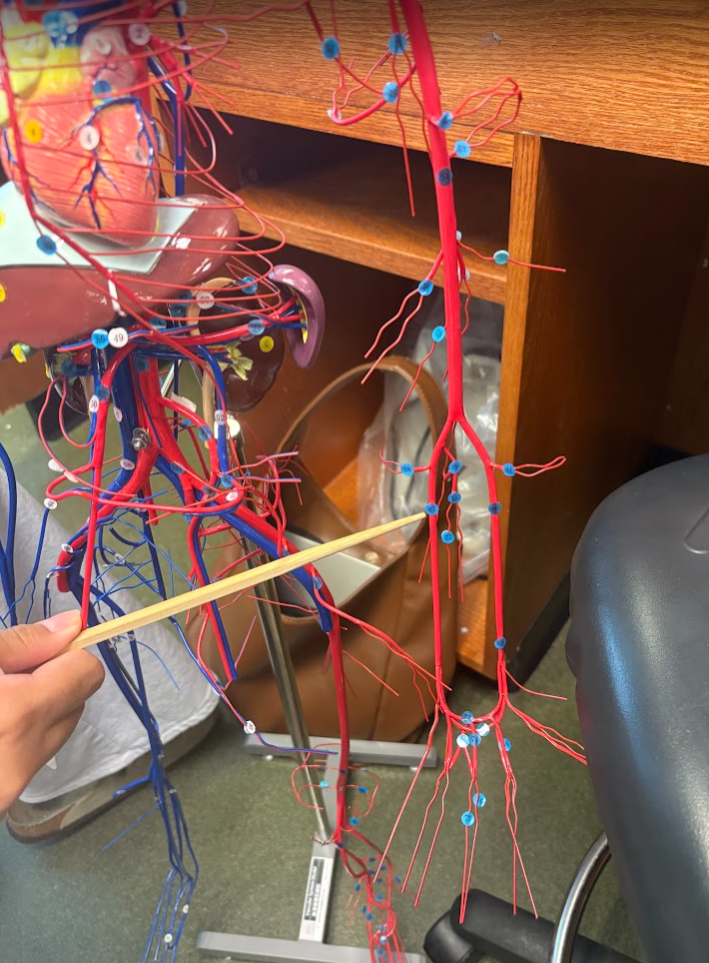
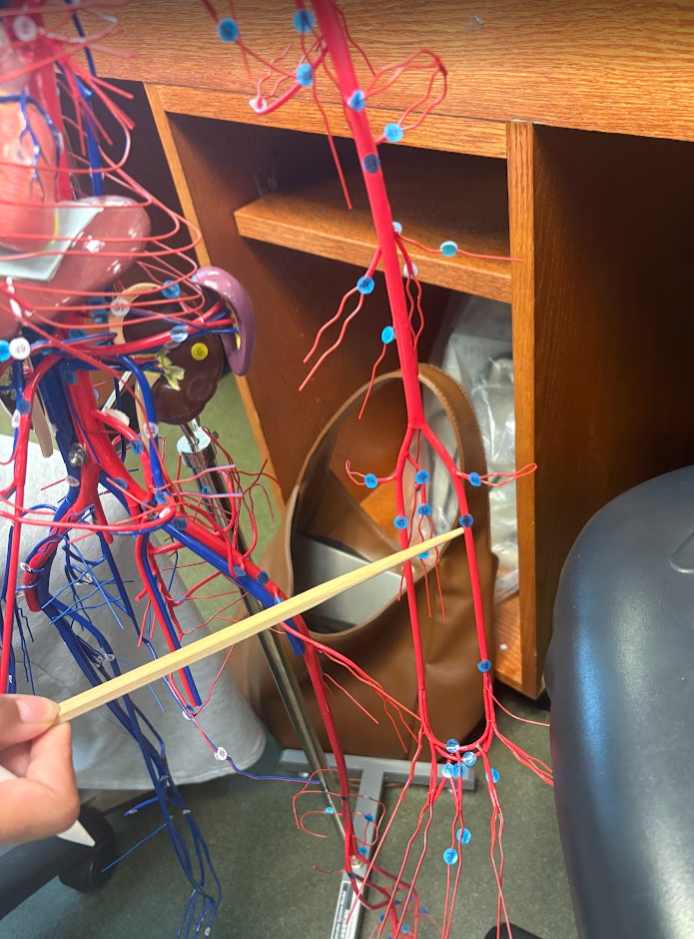

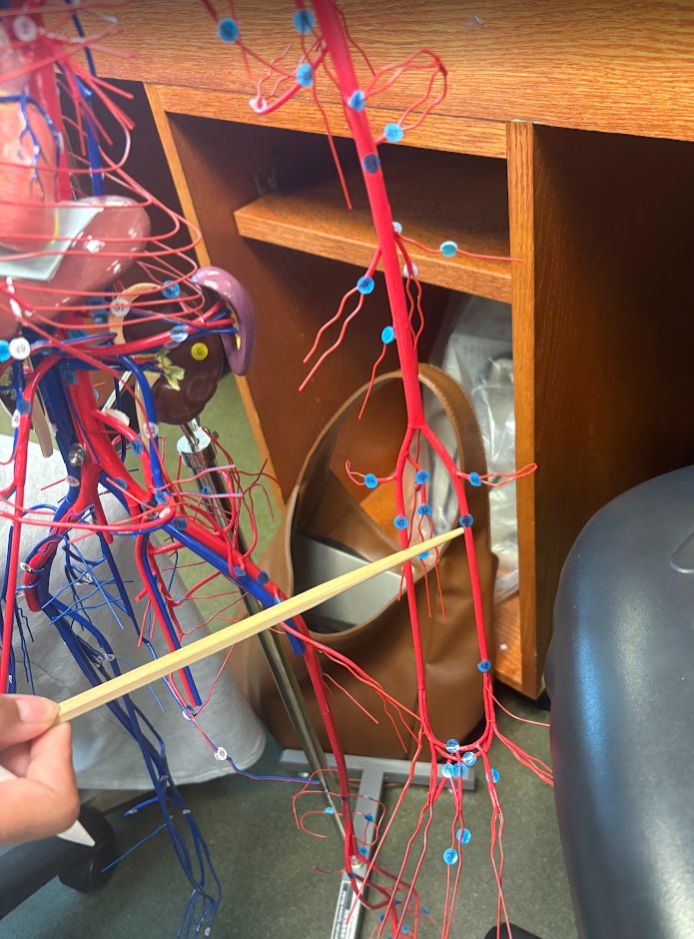
What is this?
Ulnar artery (67)
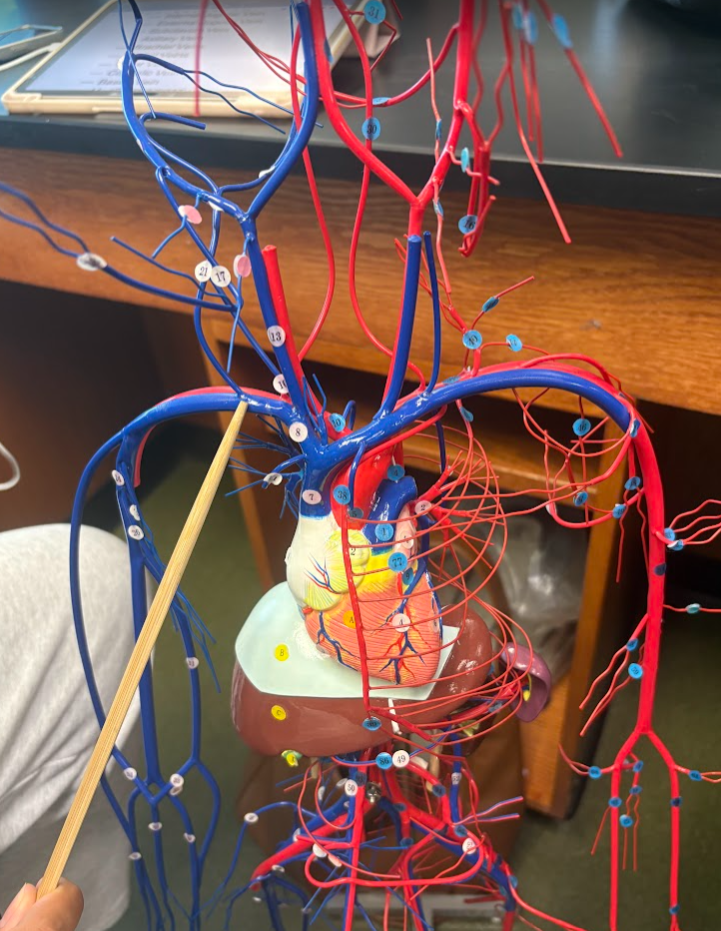

What is this?
Subclavian vein (23)
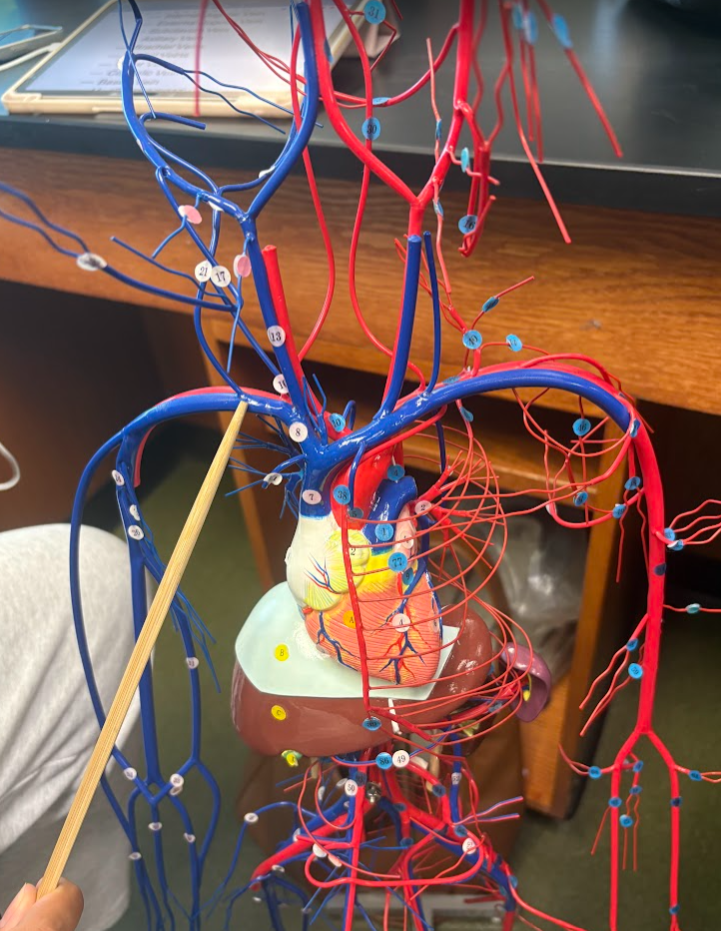

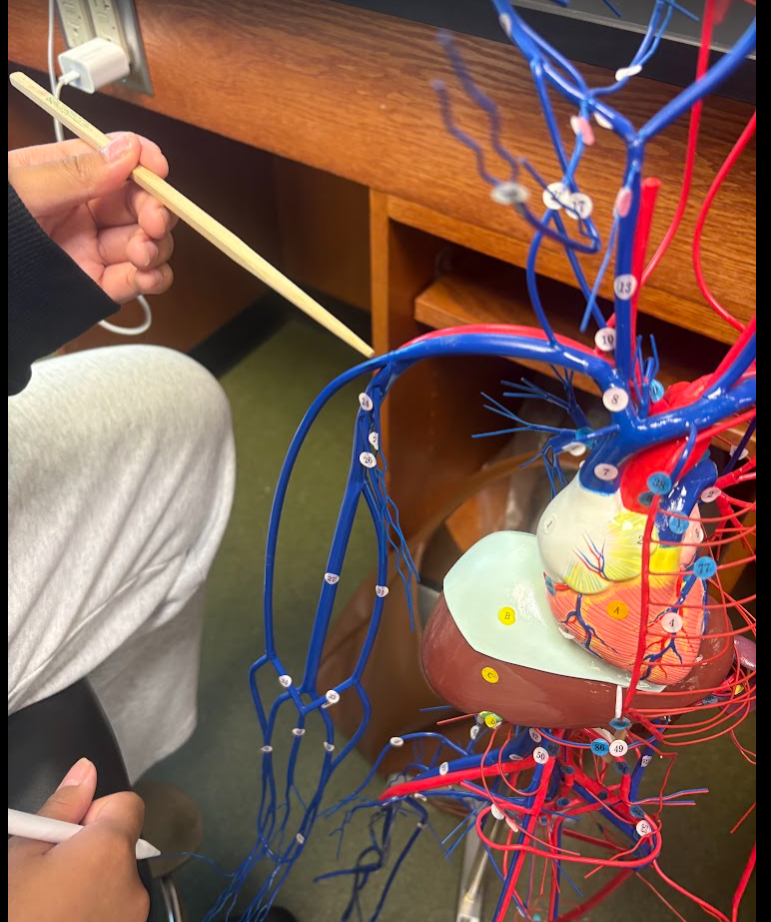
What is this?
Axillary vein (24)
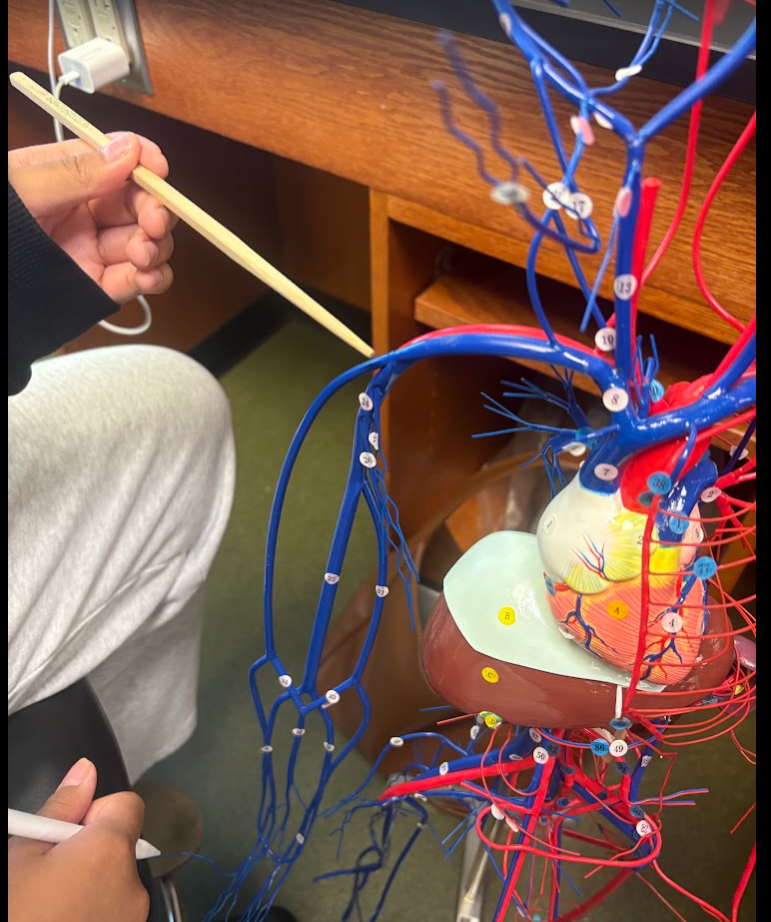
What is this?
Brachial vein (27)
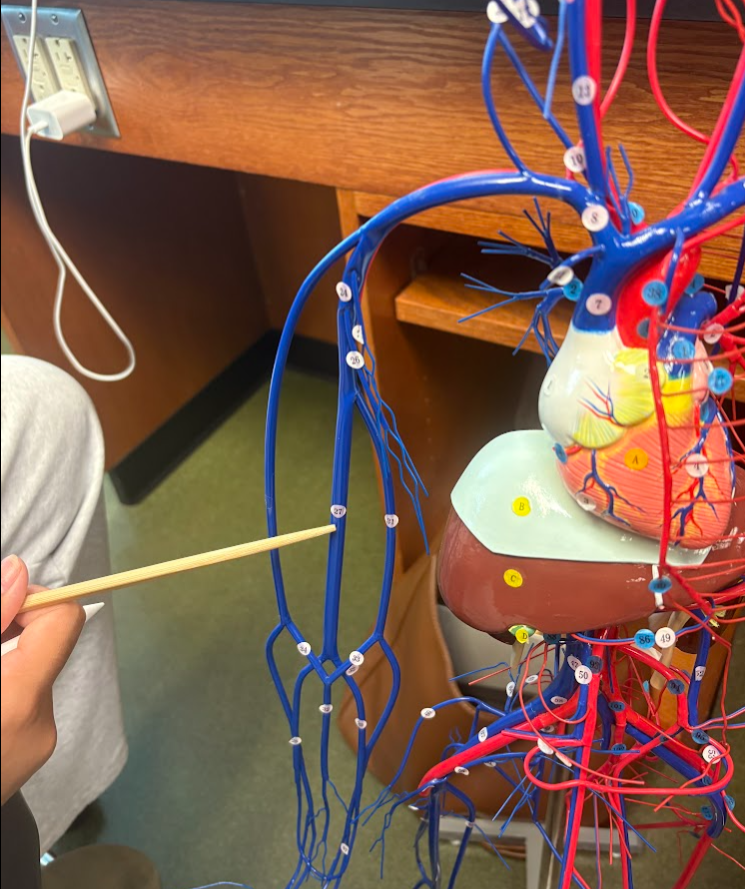
What is this?
Cephalic vein (30)
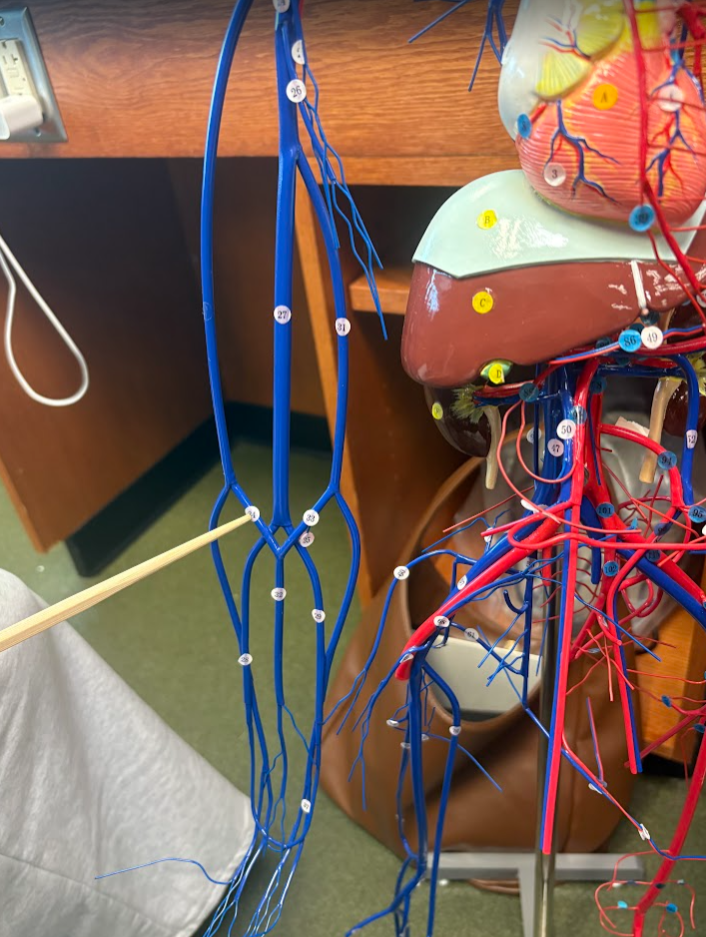
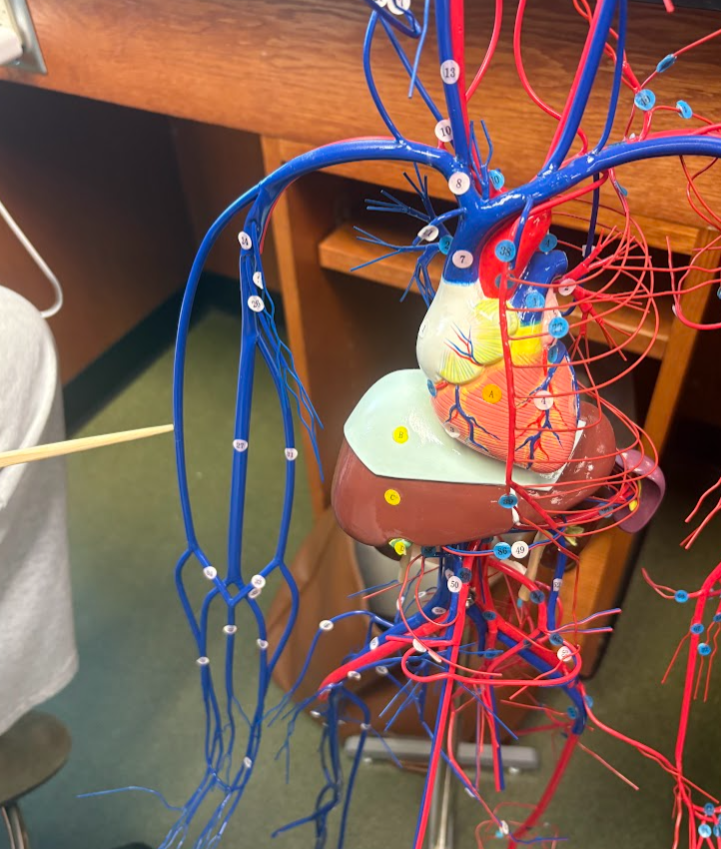

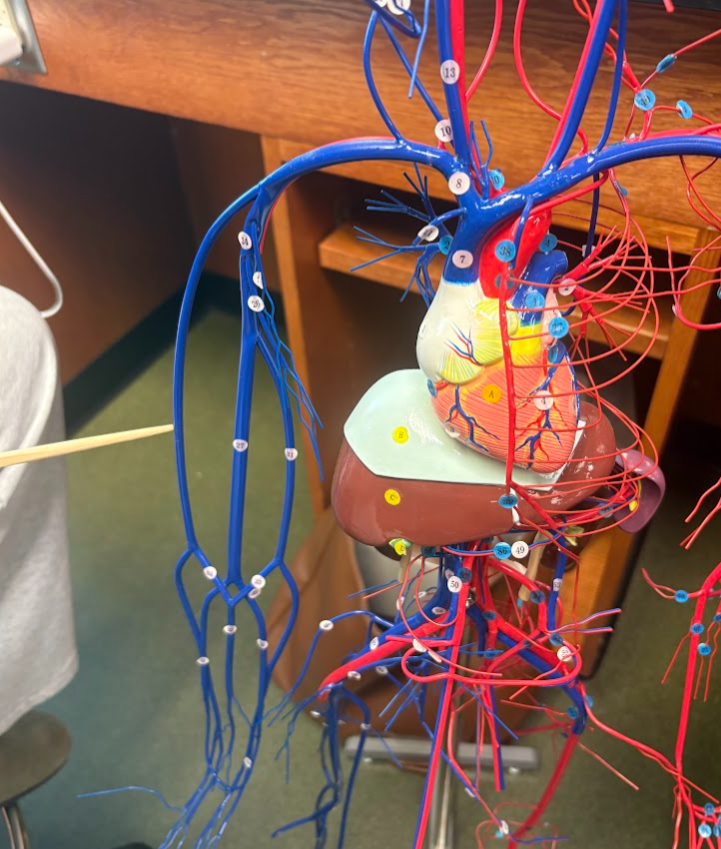
What is this?
Median cephalic vein (34)
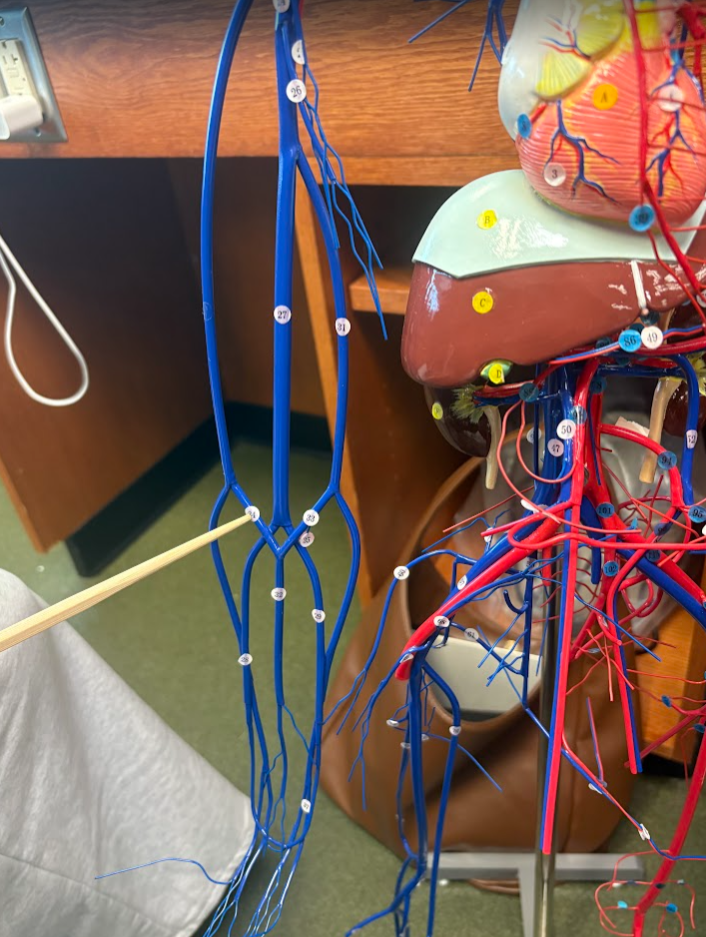


What is this?
Median antebrachial vein (32)
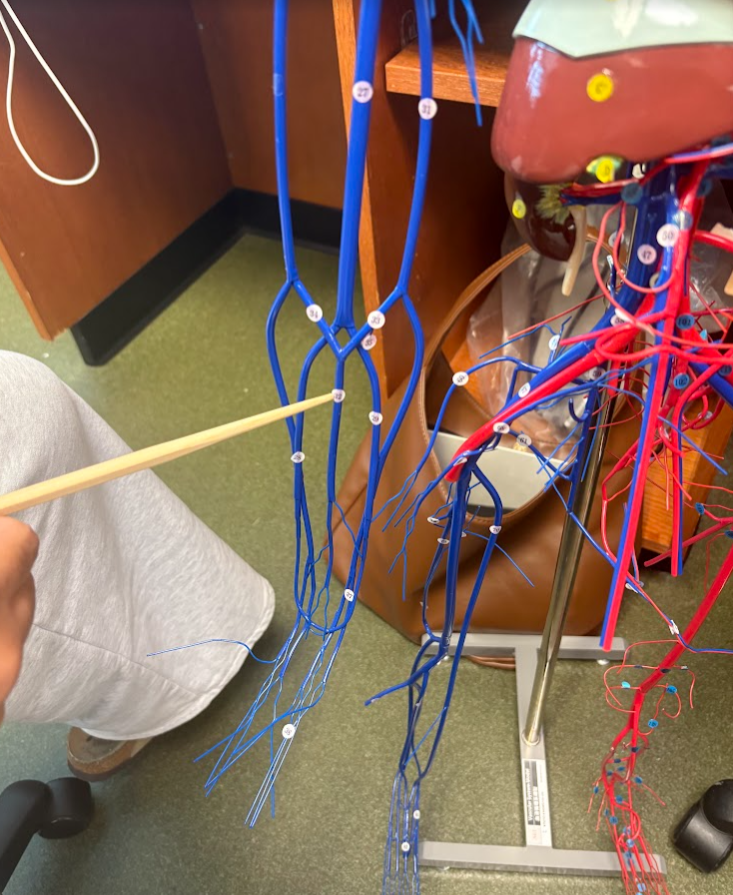
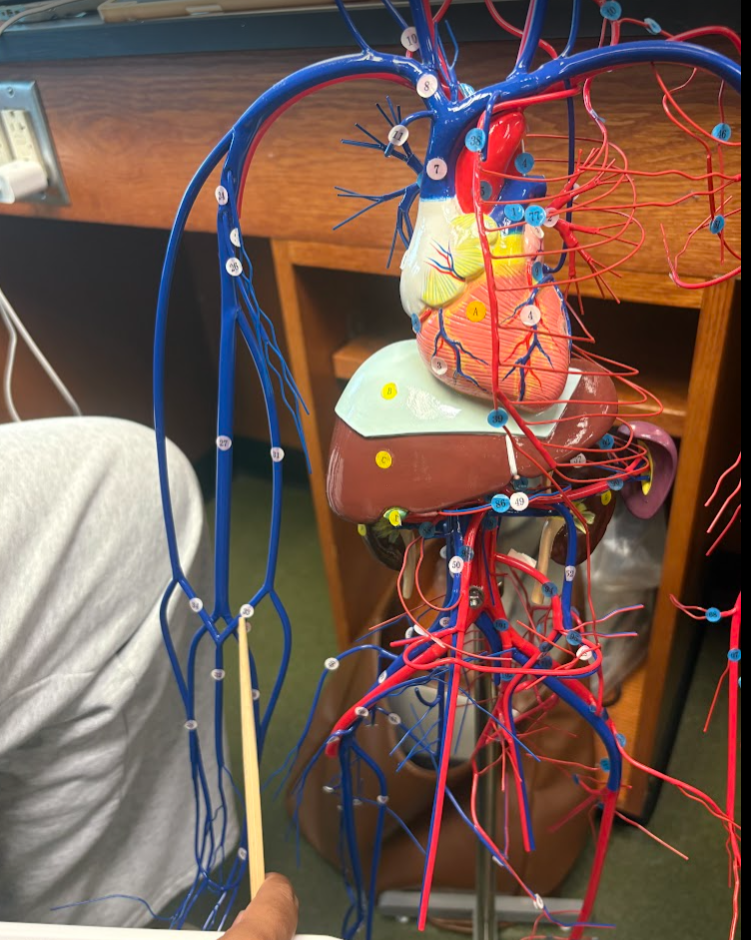


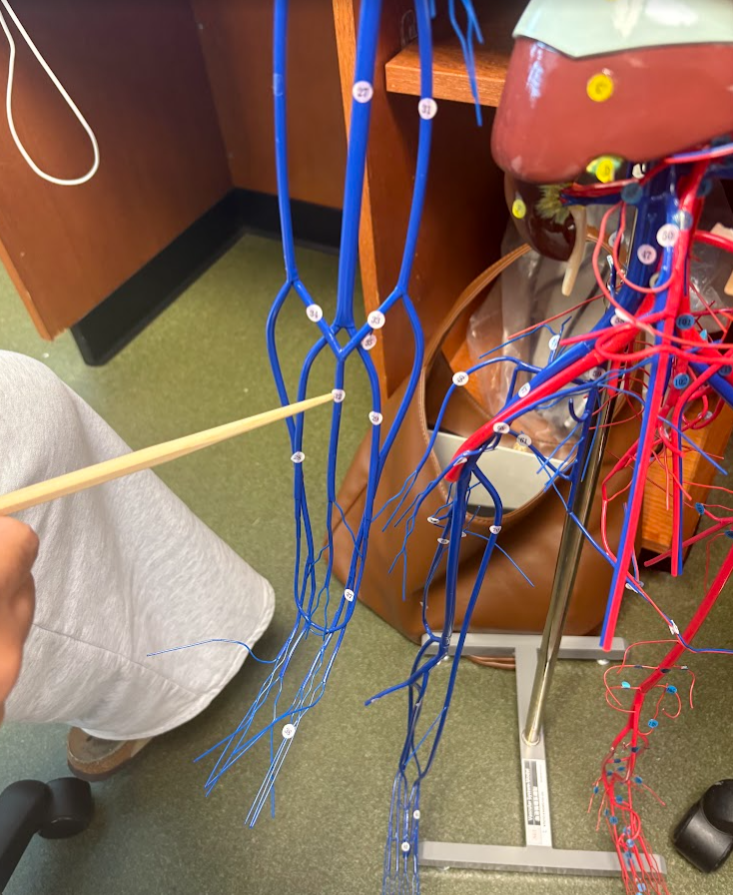
What is this?
Median cubital vein (33)
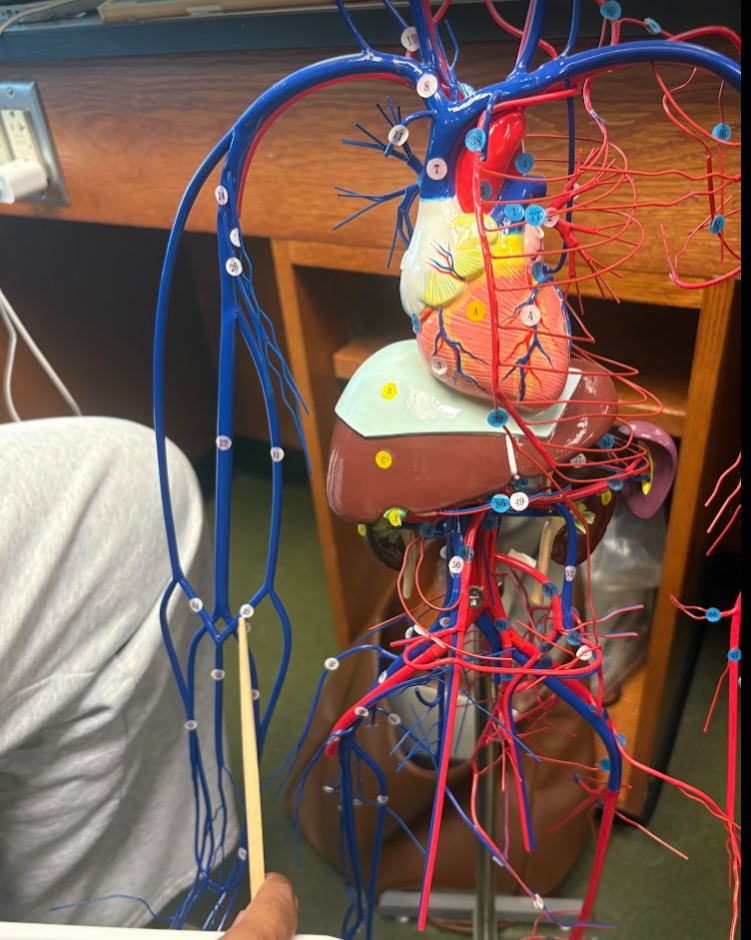

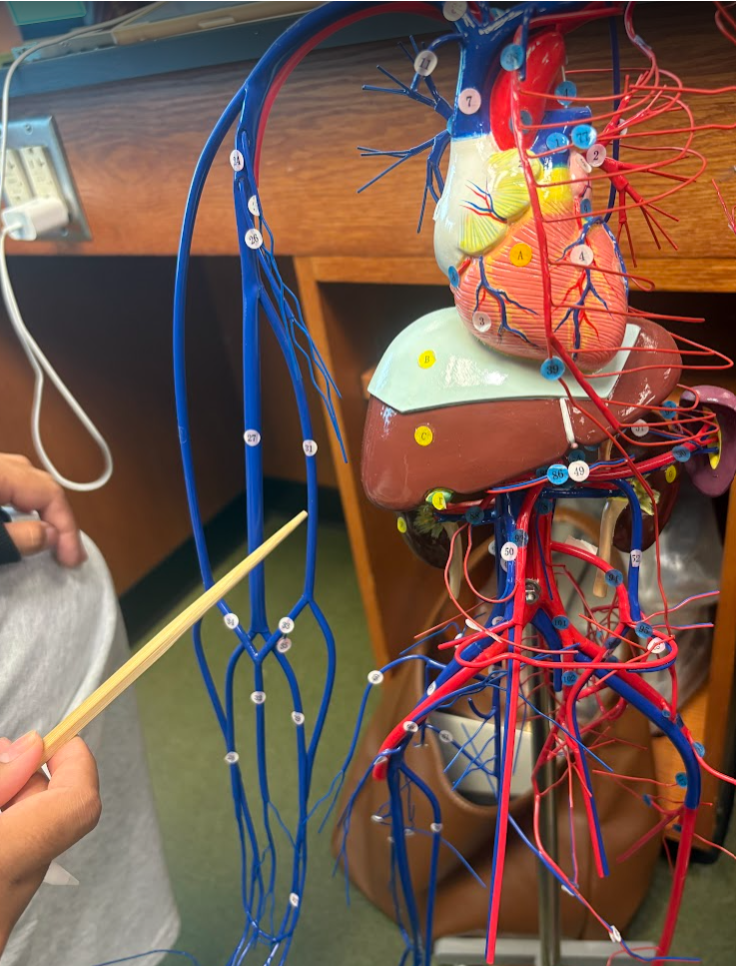
What is this?
Basilic vein (31)
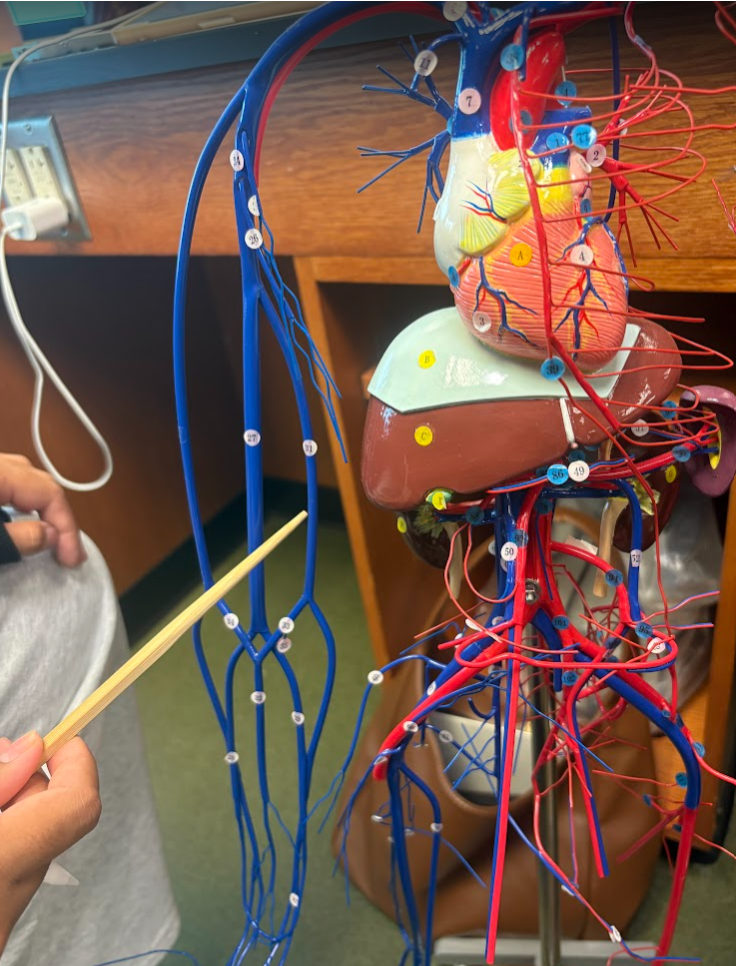
What is this?
Basilic vein (31)
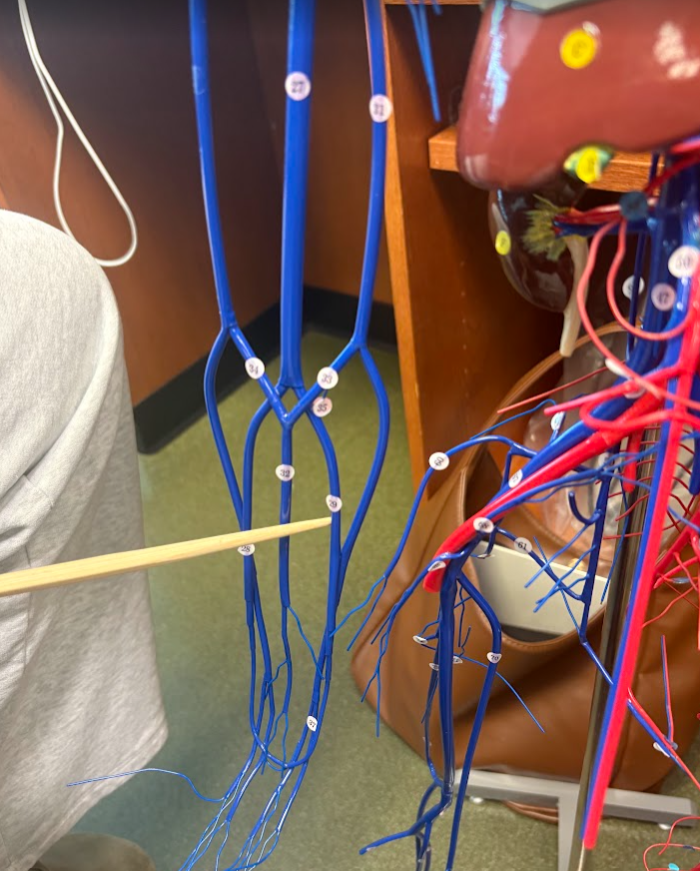
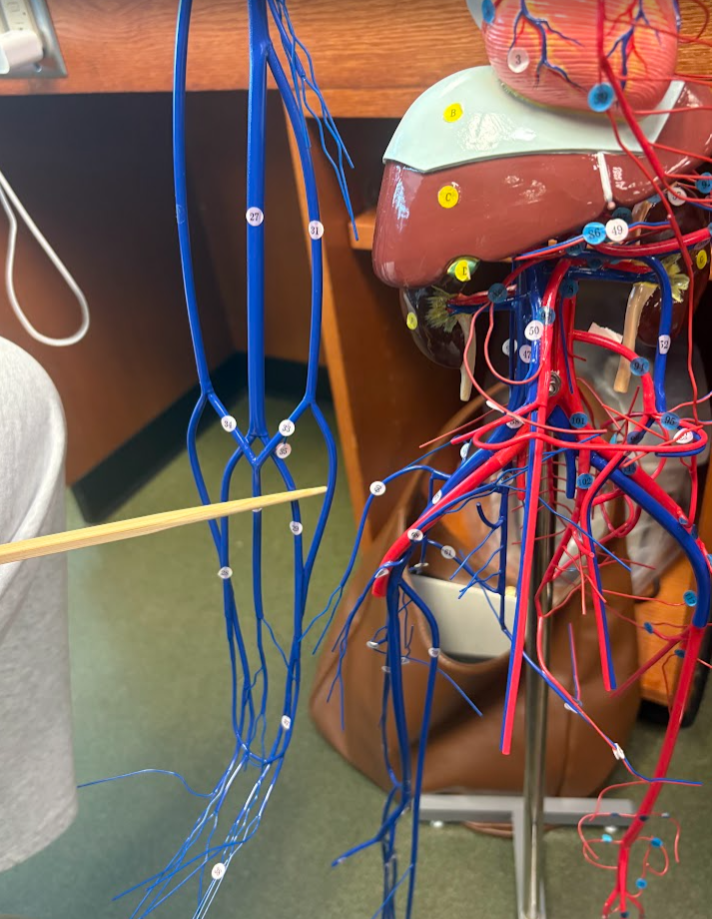
What is this?
Ulnar vein (29)
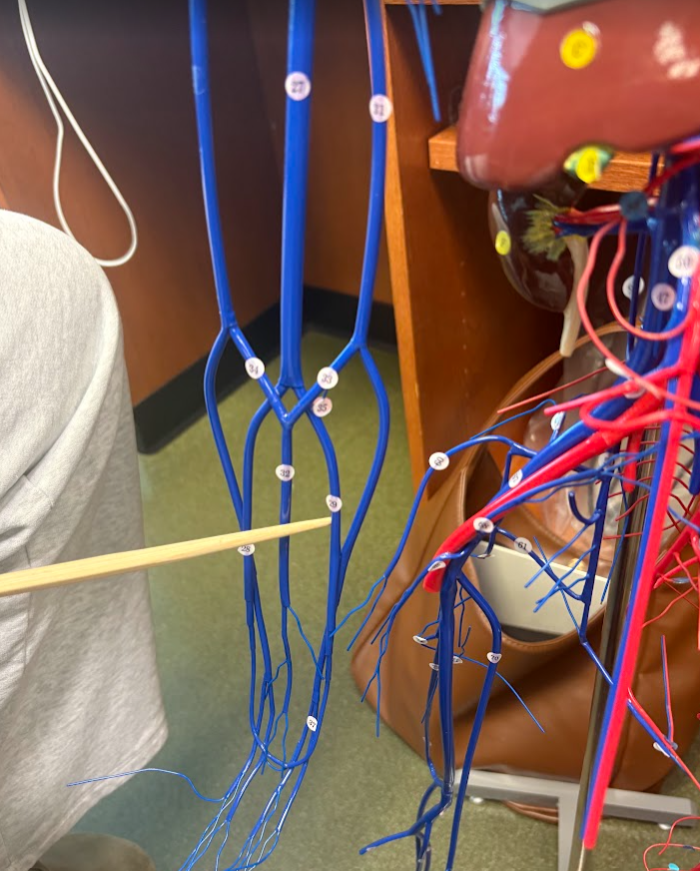
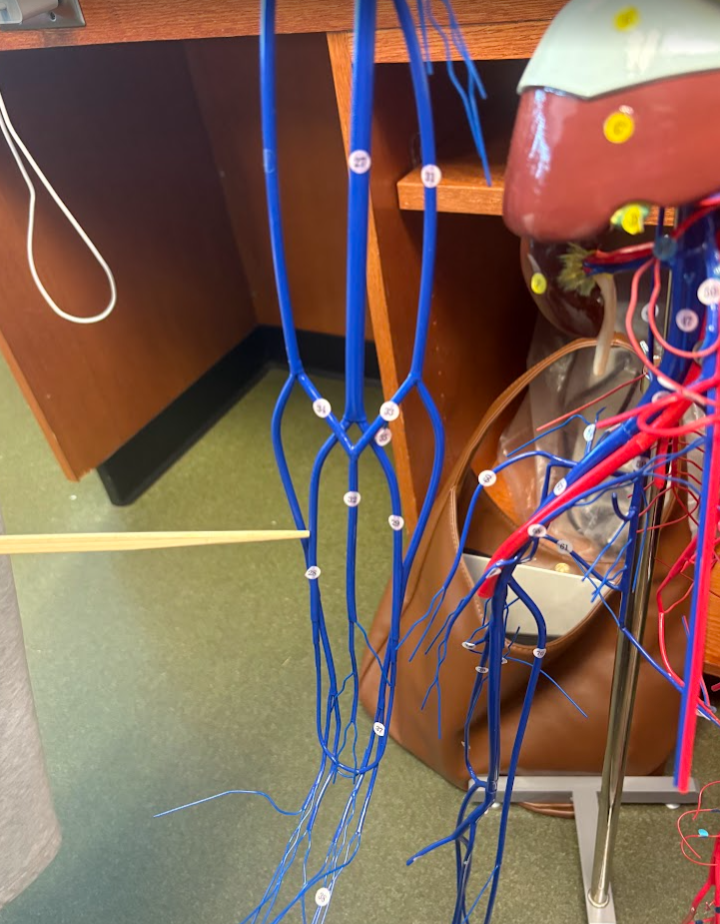
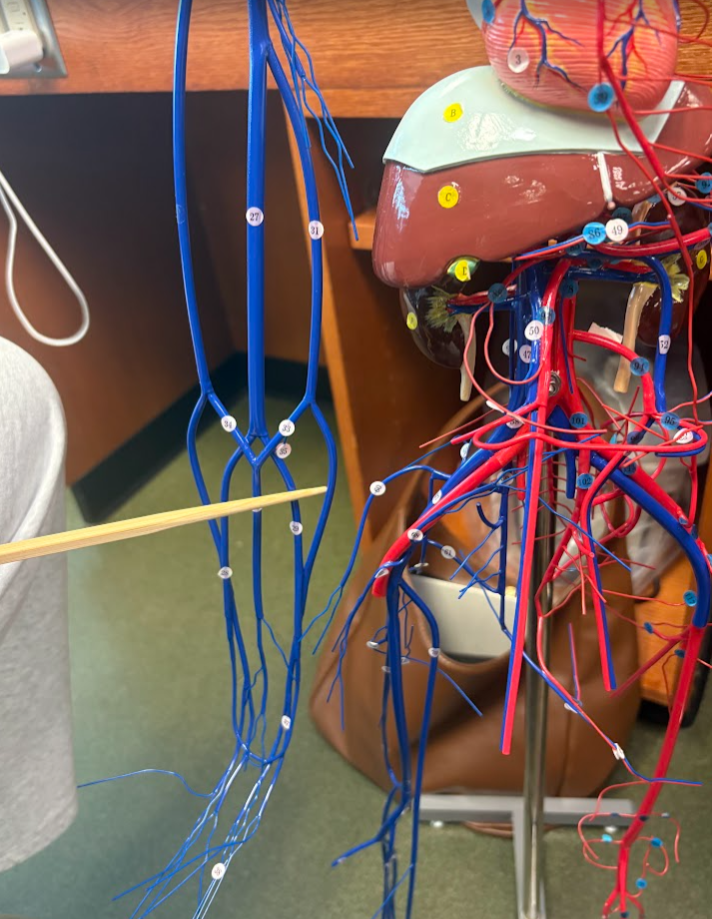
What is this?
Radial vein (28)
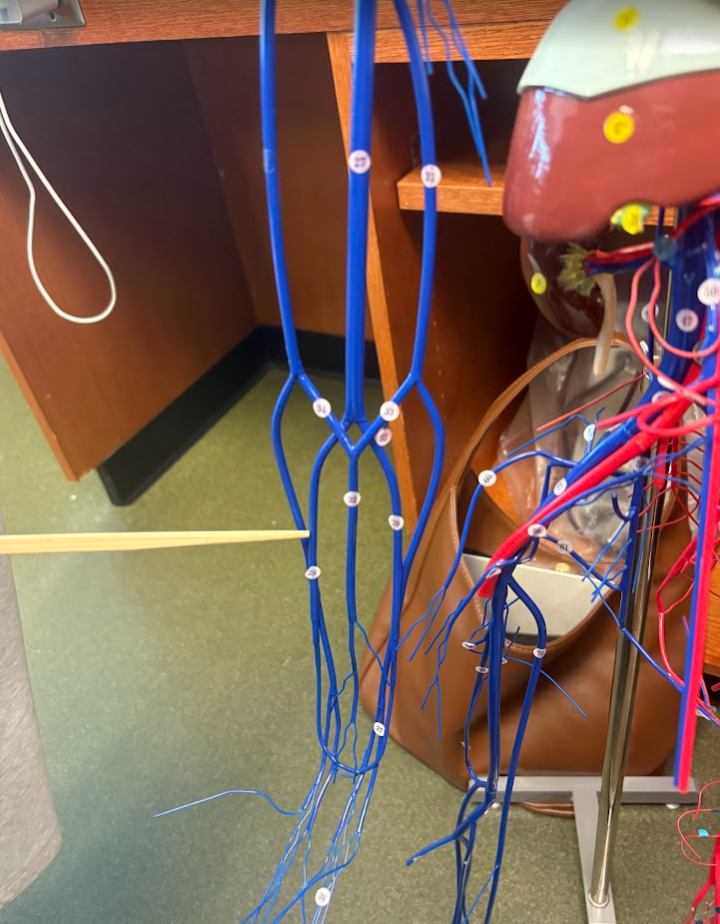
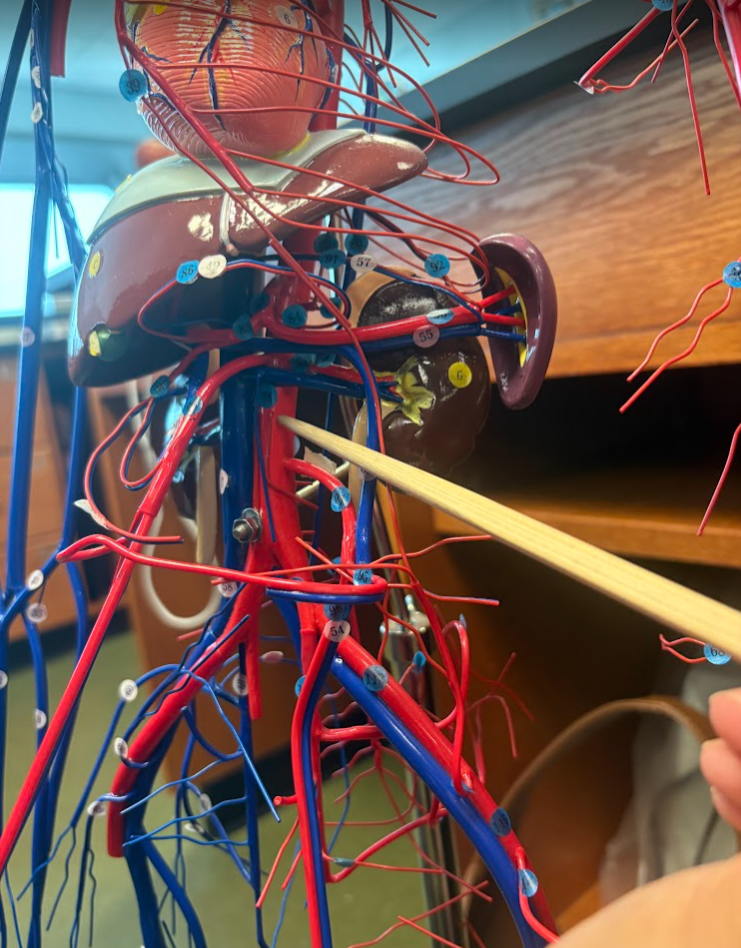
What is this?
Abdominal aorta (78)
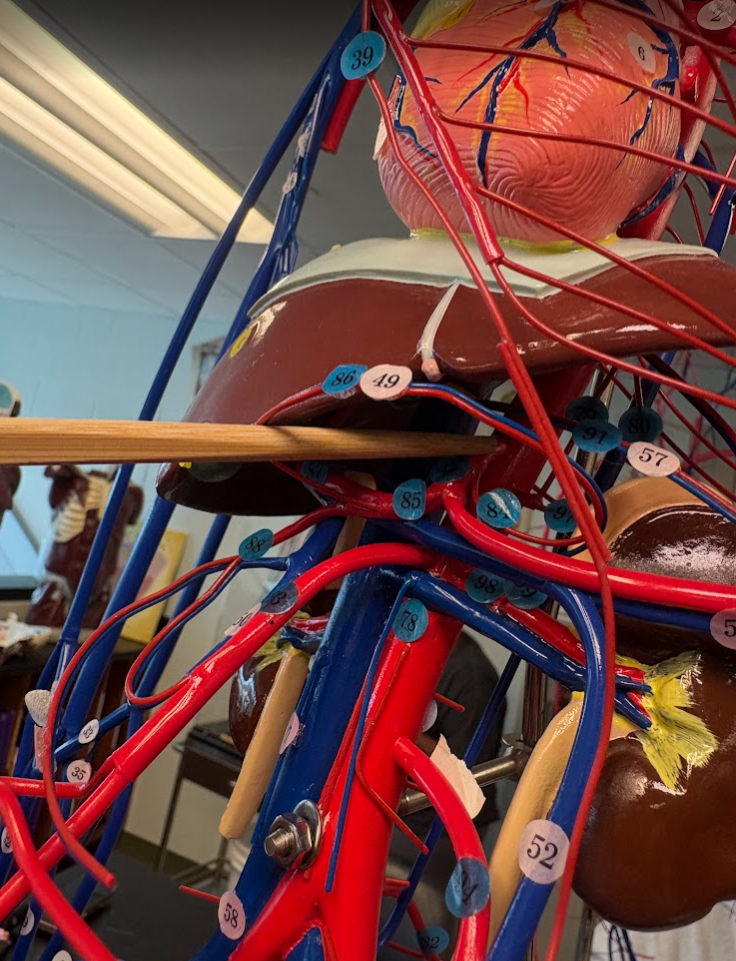
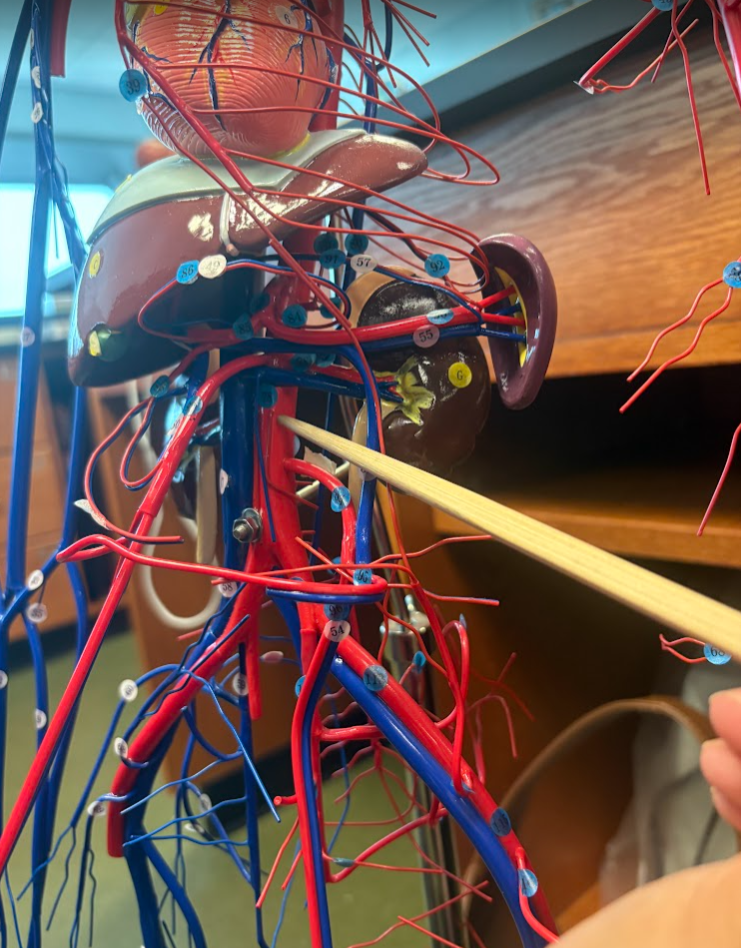

What is this?
Celiac artery (83)
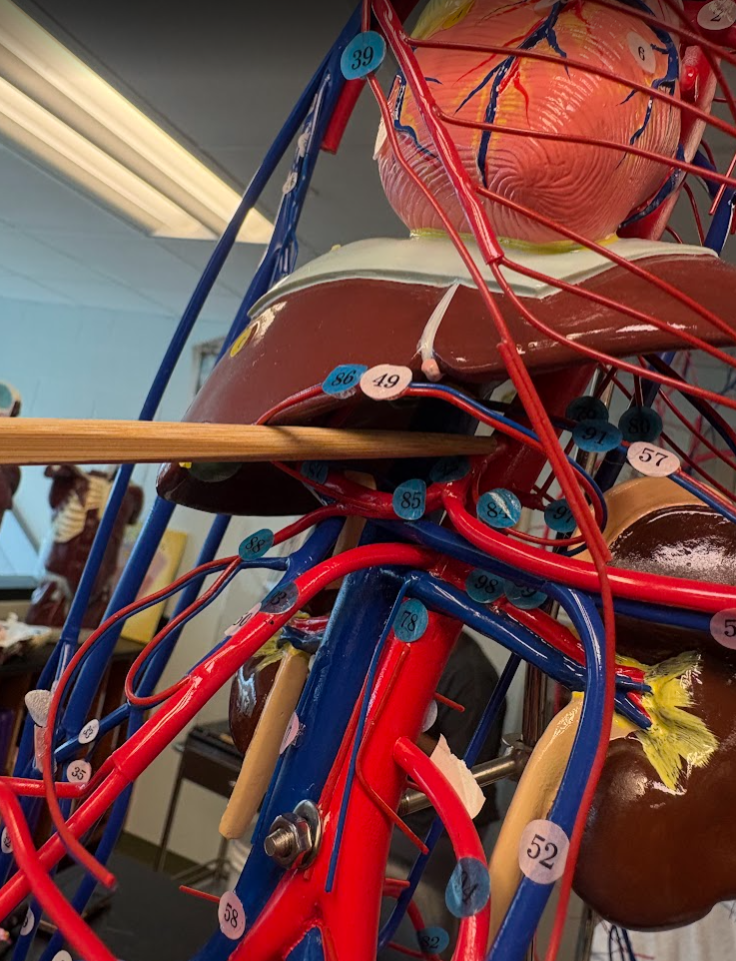

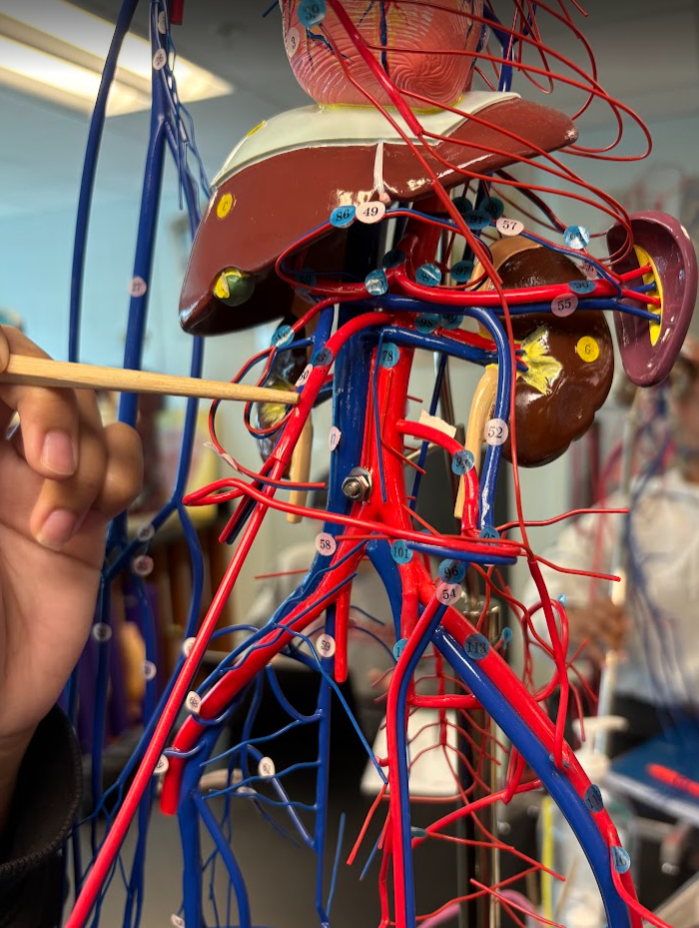
What is this?
Superior mesenteric artery (93)
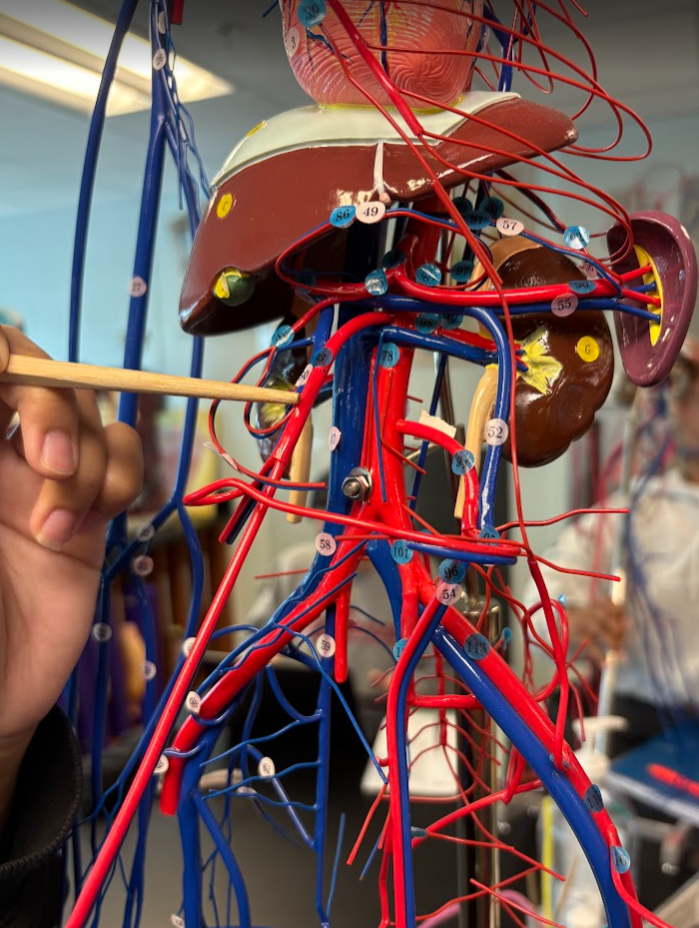
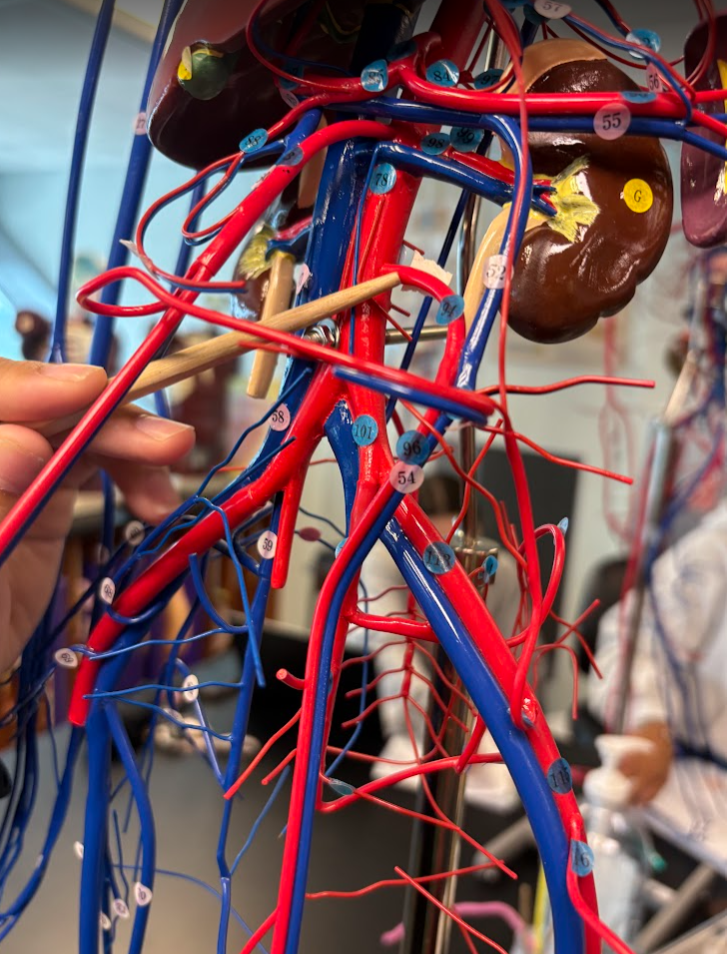
What is this?
Inferior mesenteric artery (94)
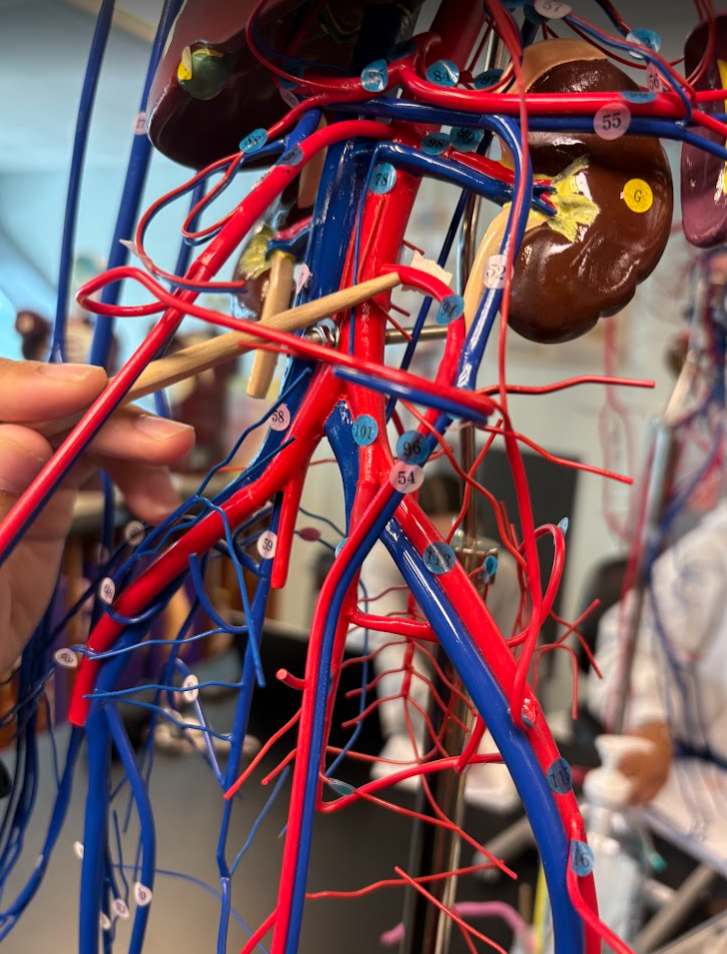
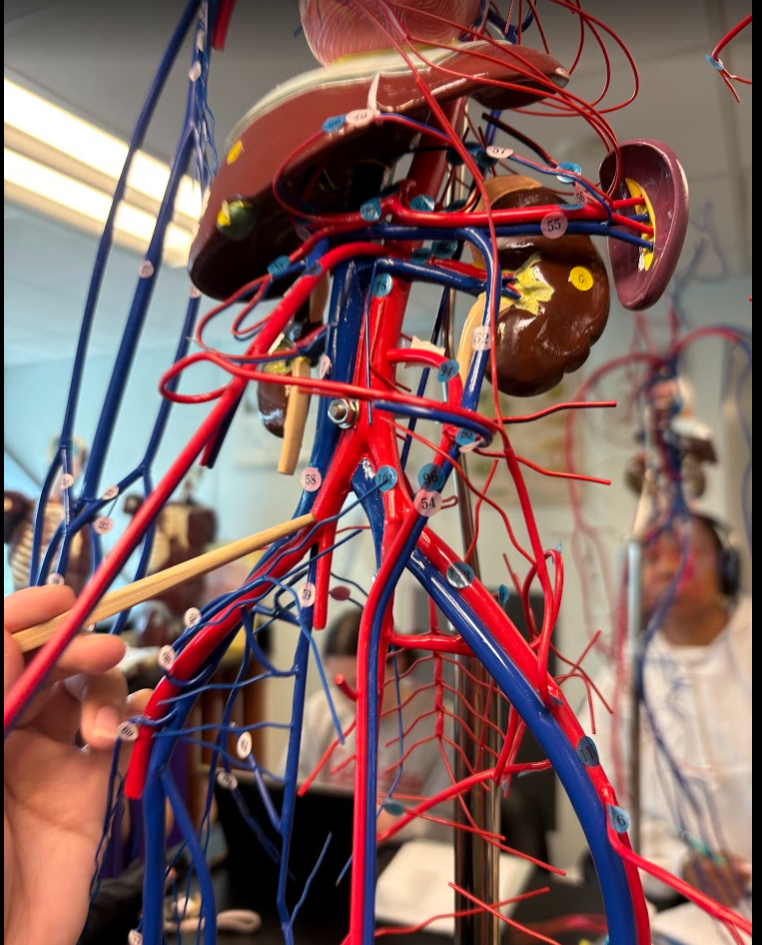
What is this?
Common iliac artery (101)
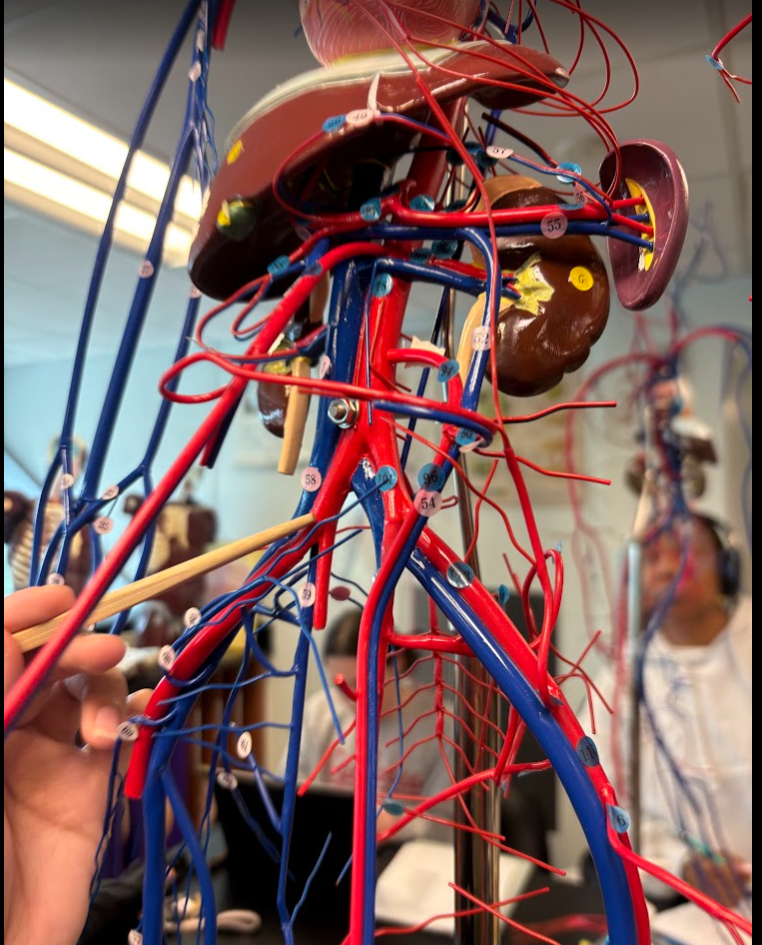
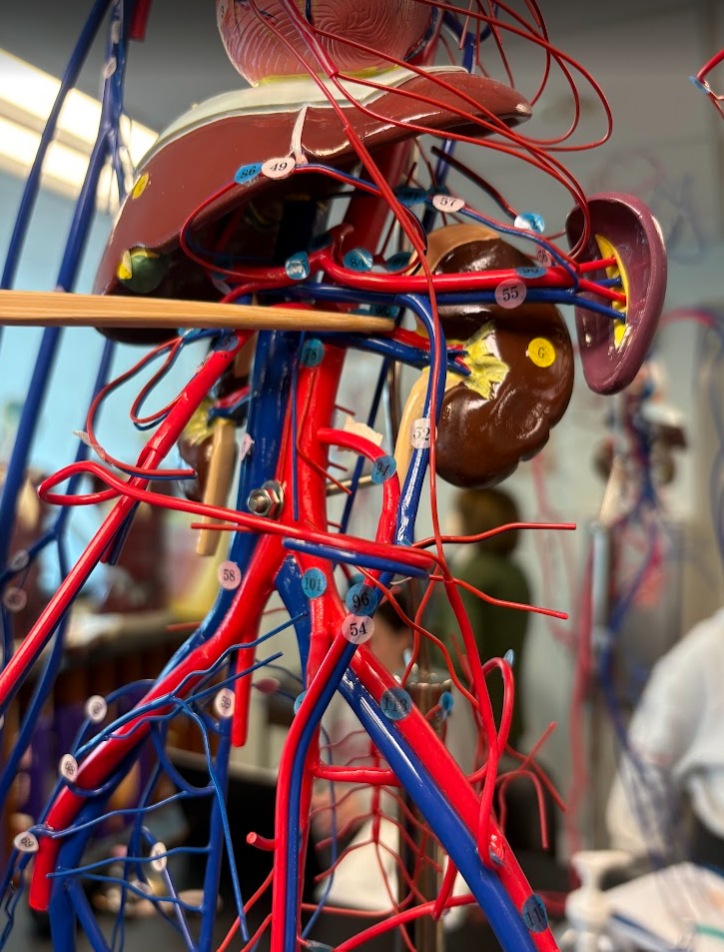
What is this?
Renal artery
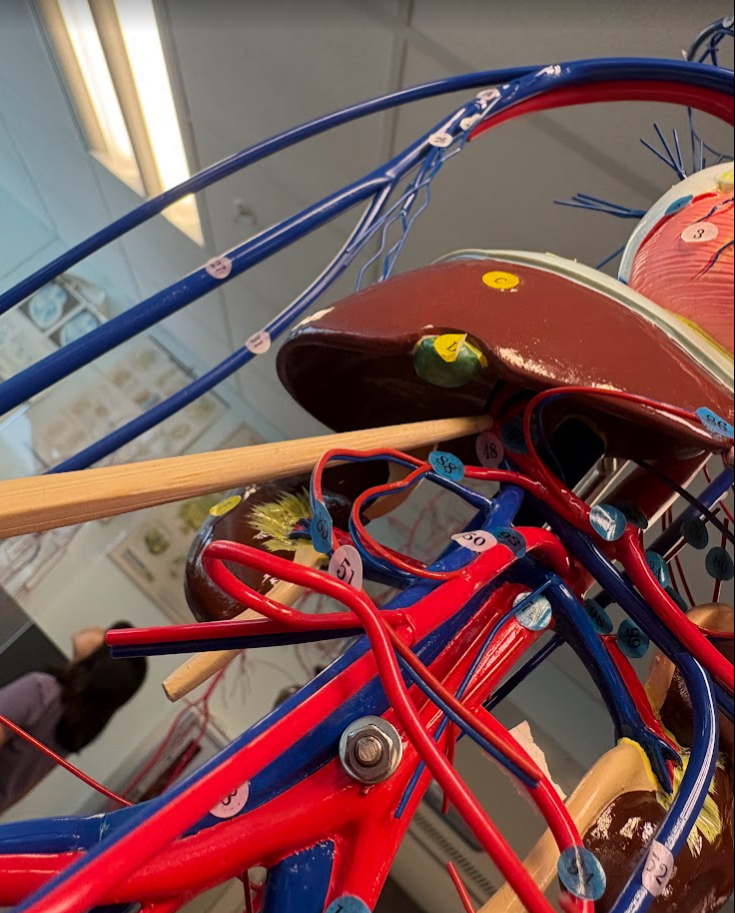
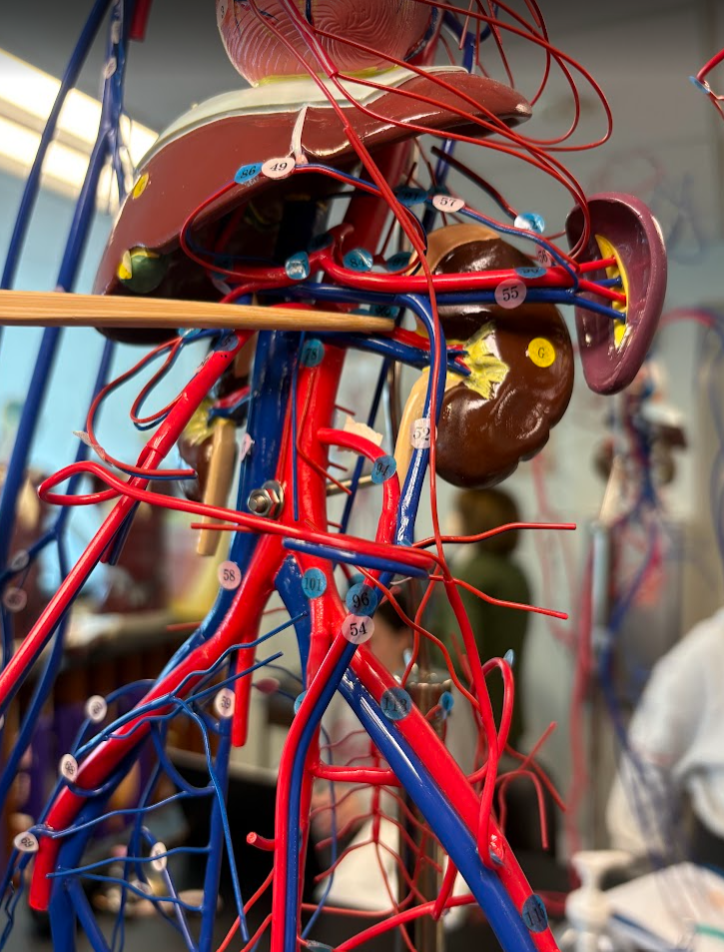

What is this?
Hepatic artery (2 under liver) (85)
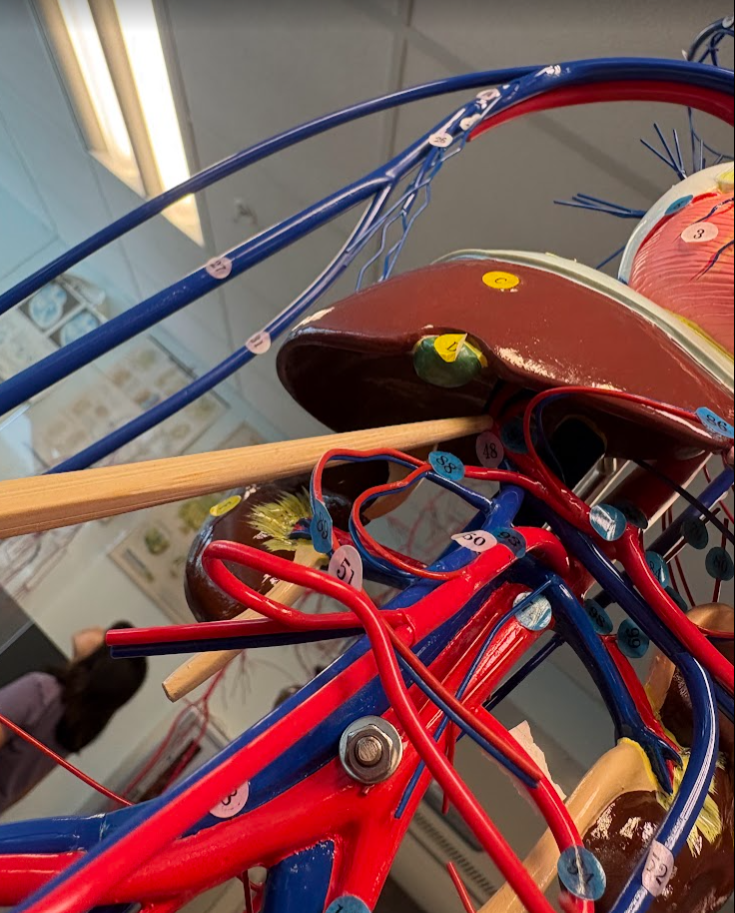


What is this?
Splenic artery (90)
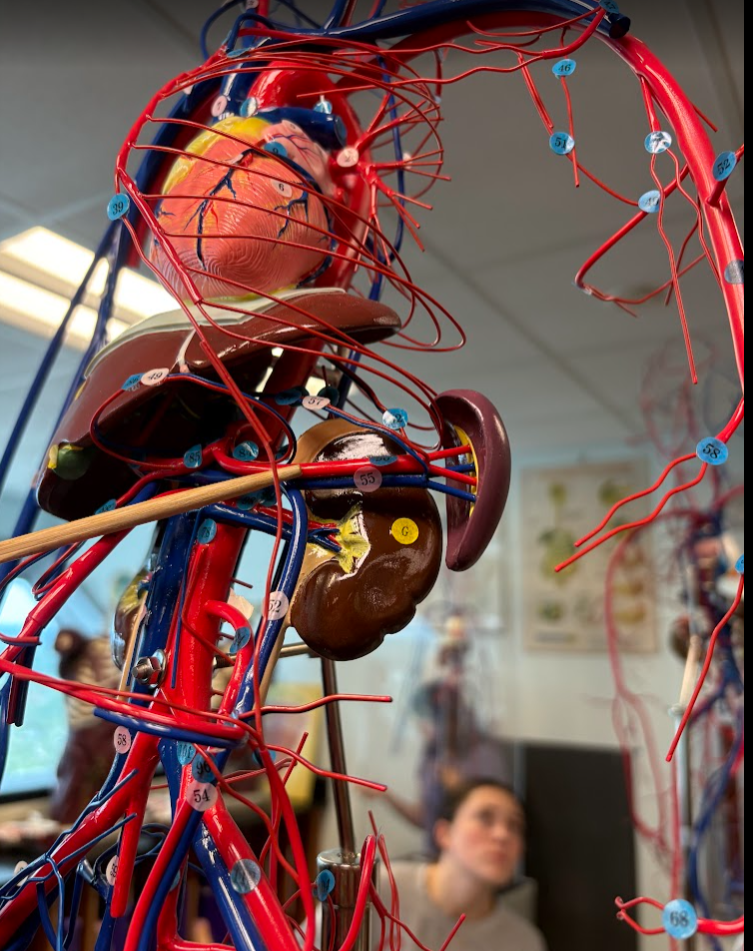
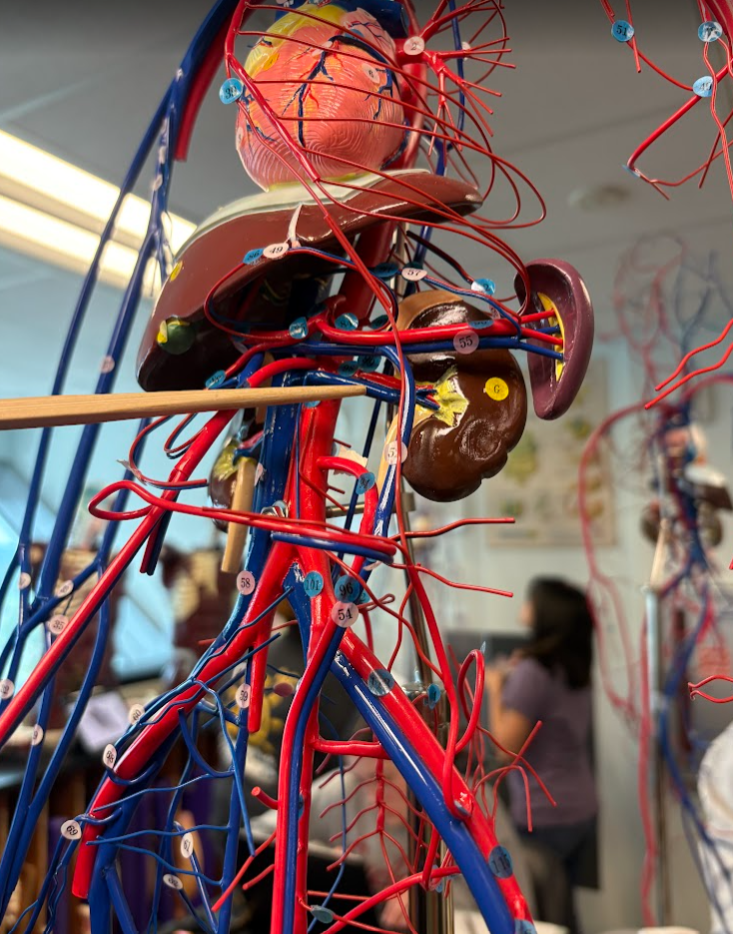


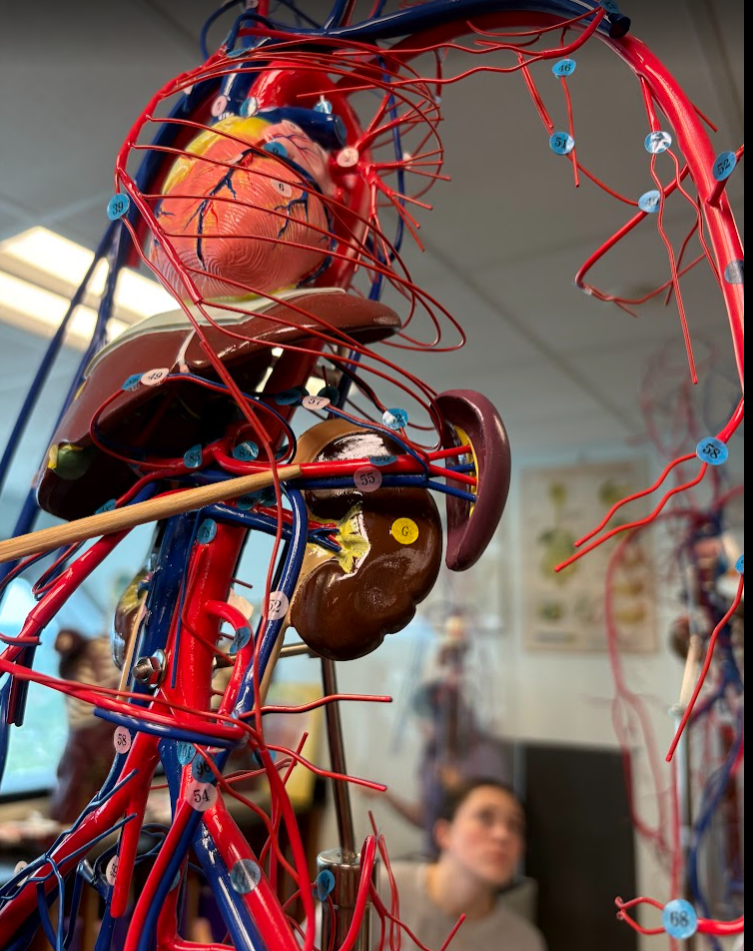
What is this?
Renal vein (46)
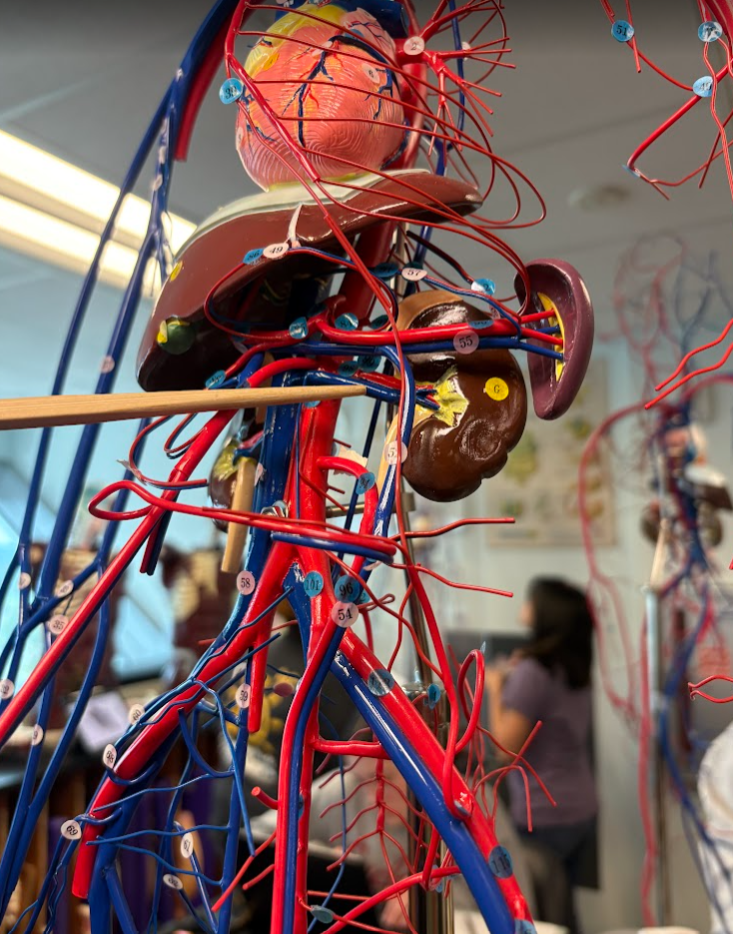

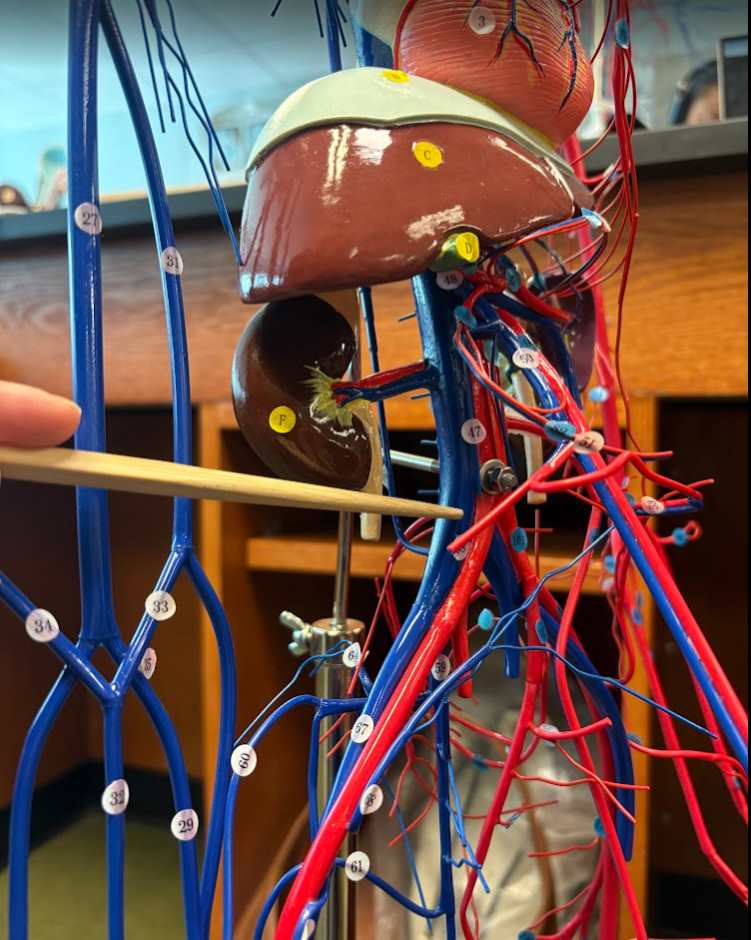
What is this?
Common iliac vein (58)
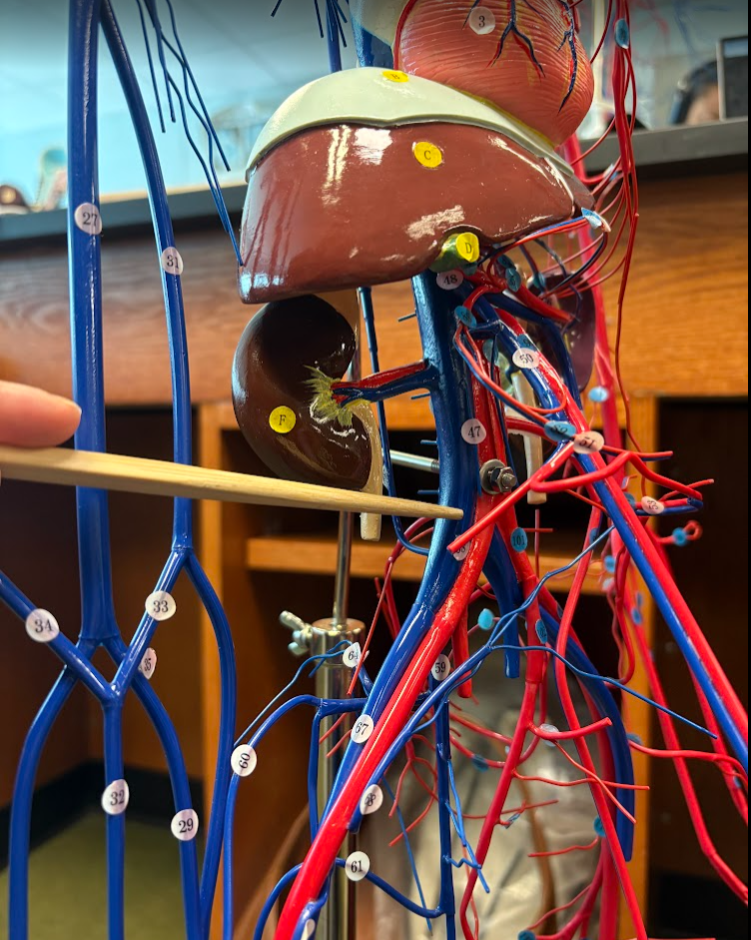
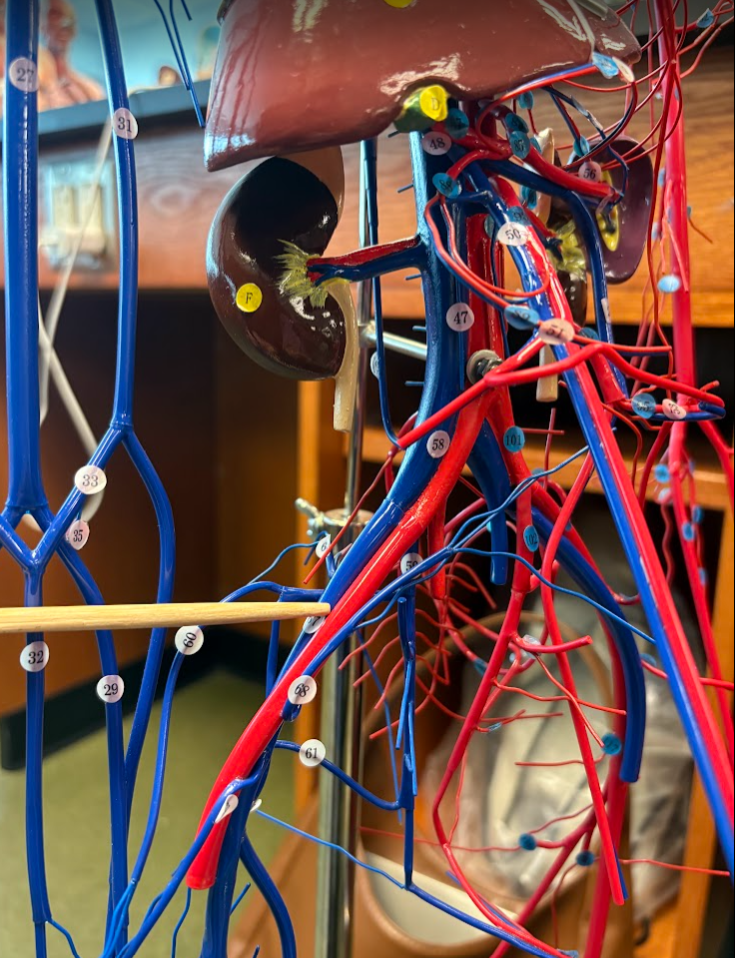
What is this?
External iliac vein (67)
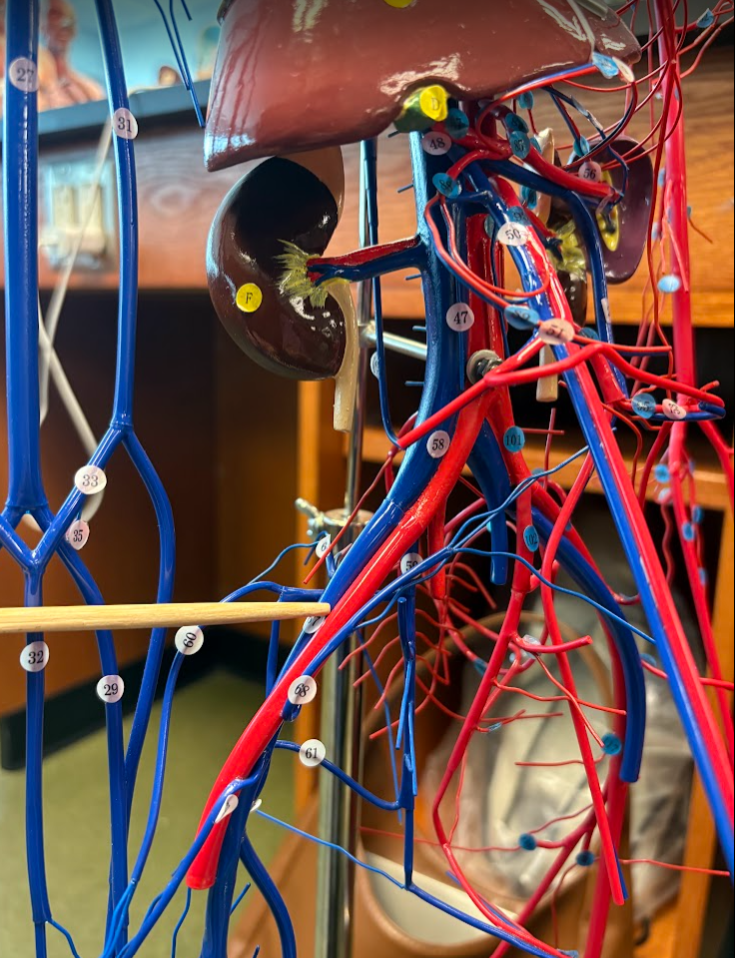
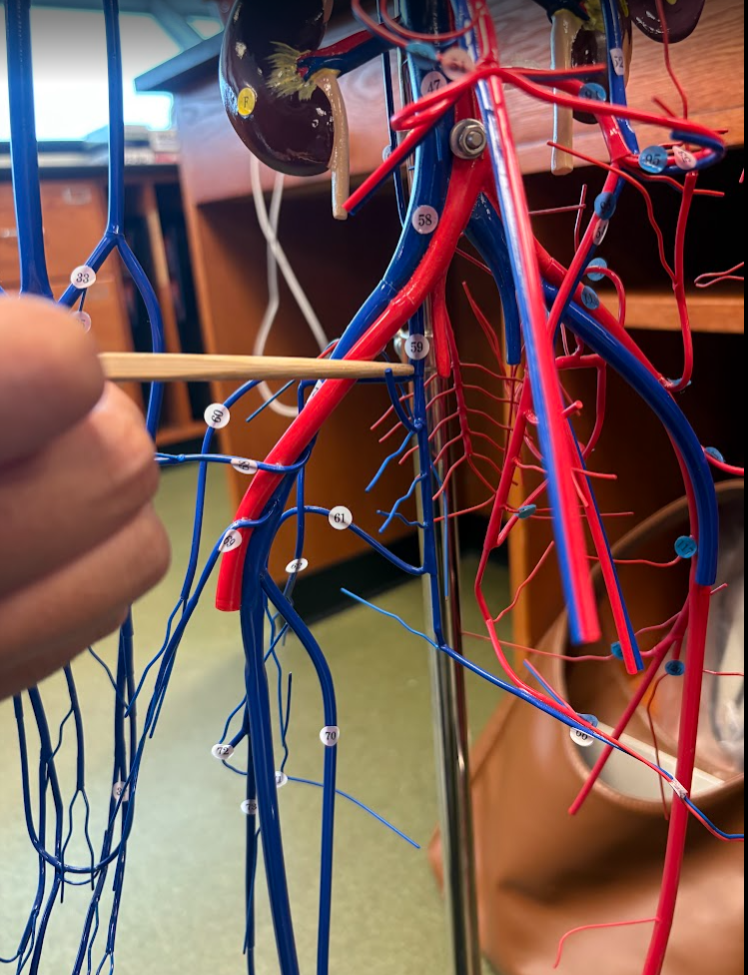
What is this?
Internal iliac vein (59)
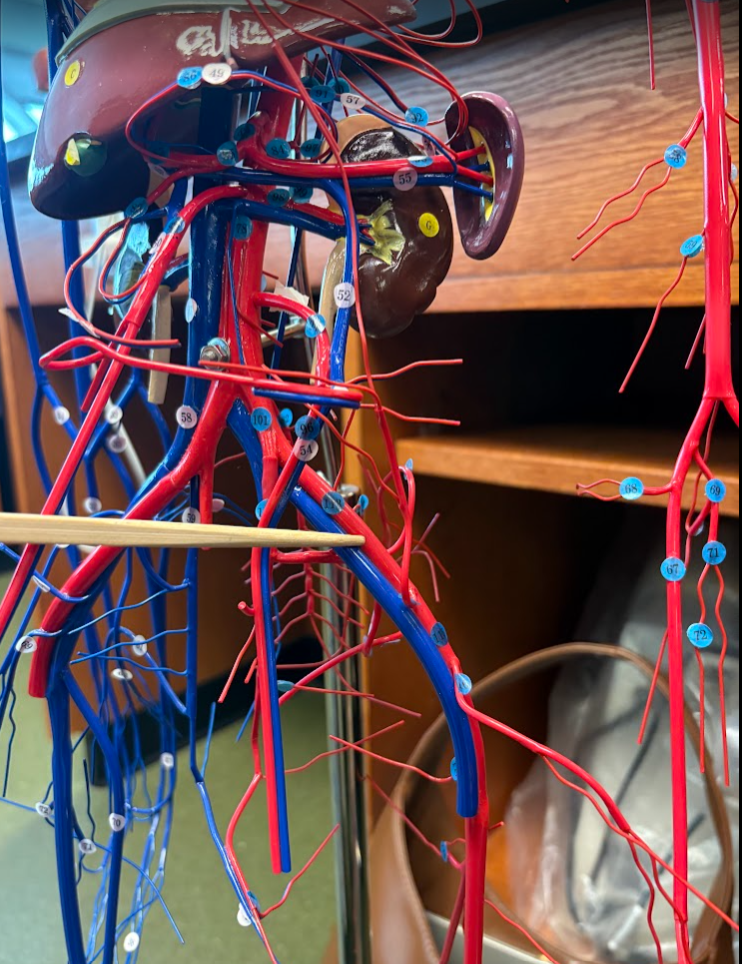
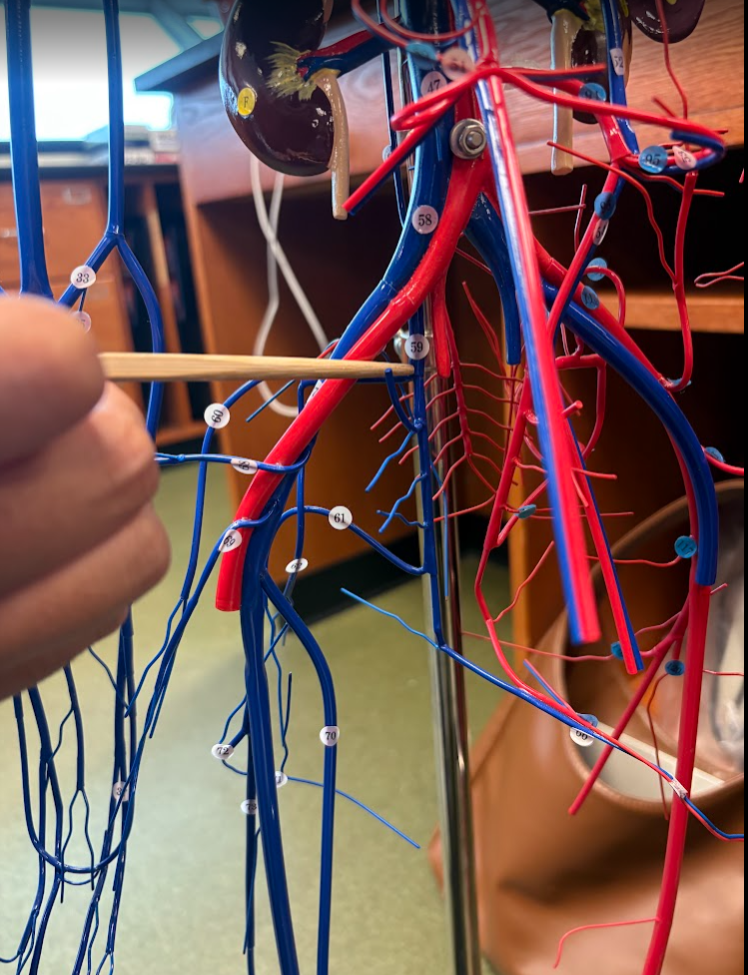

What is this?
External iliac artery (113)
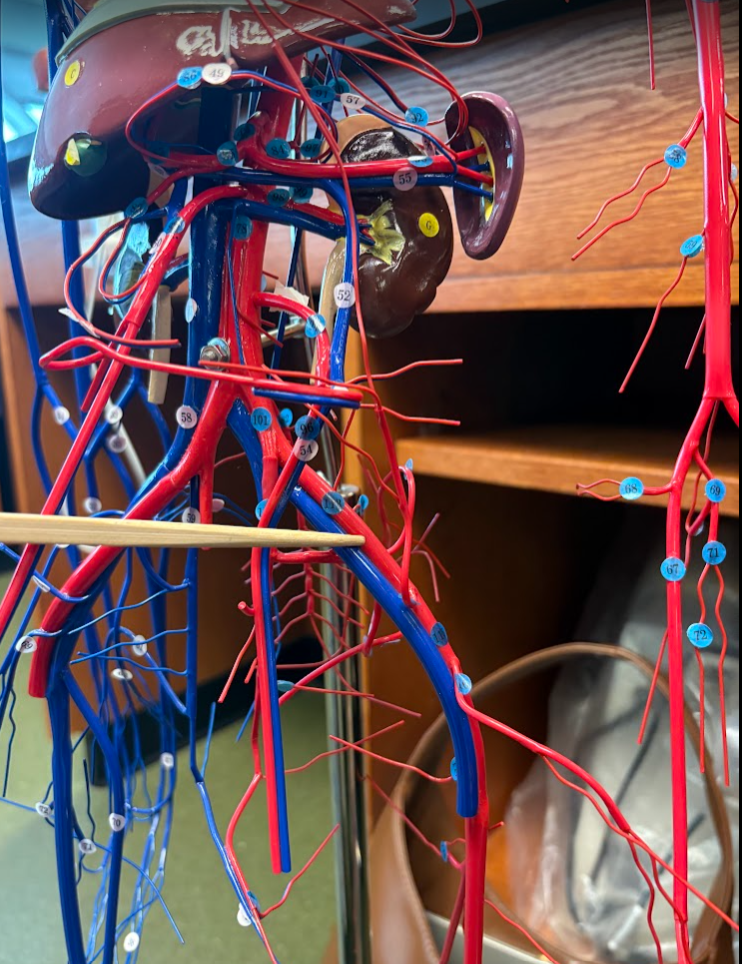
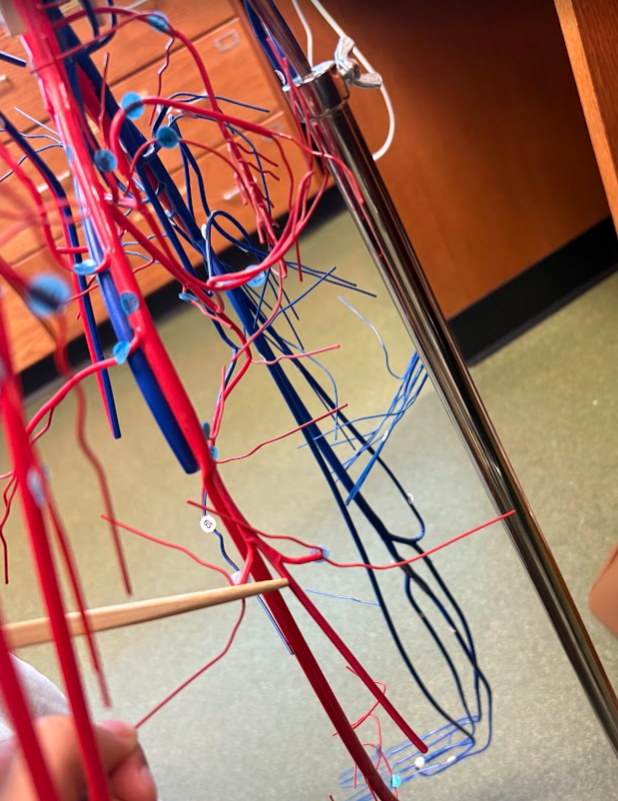


What is this?
Deep femoral artery (118)
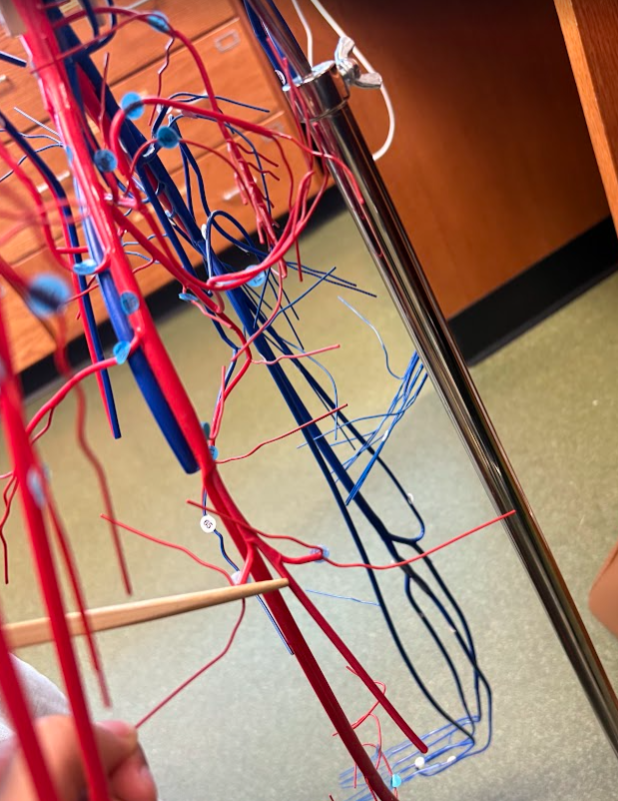


What is this?
Femoral artery (115)
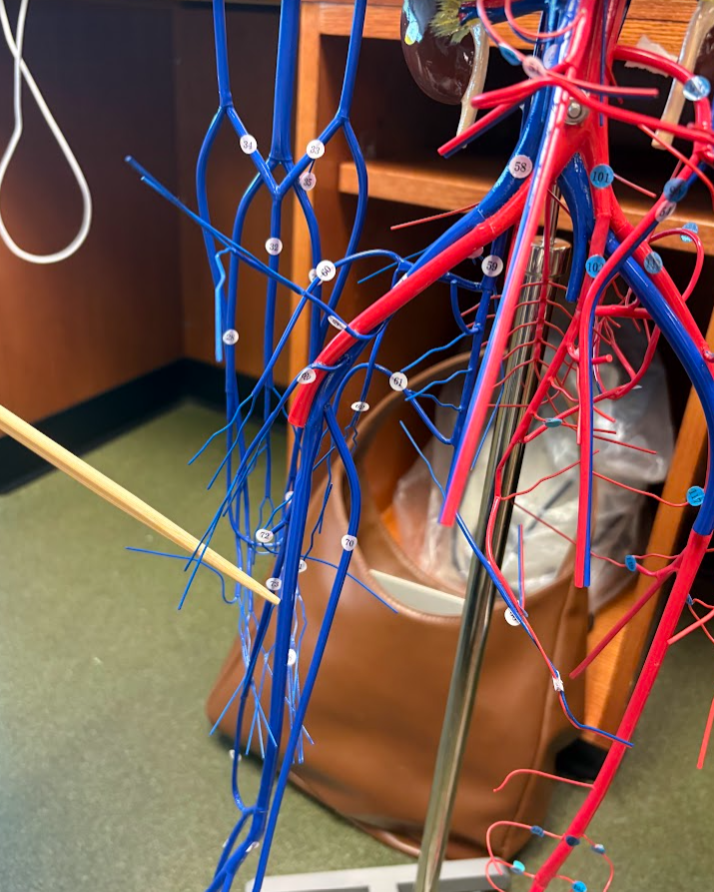


What is this?
Femoral vein (75)
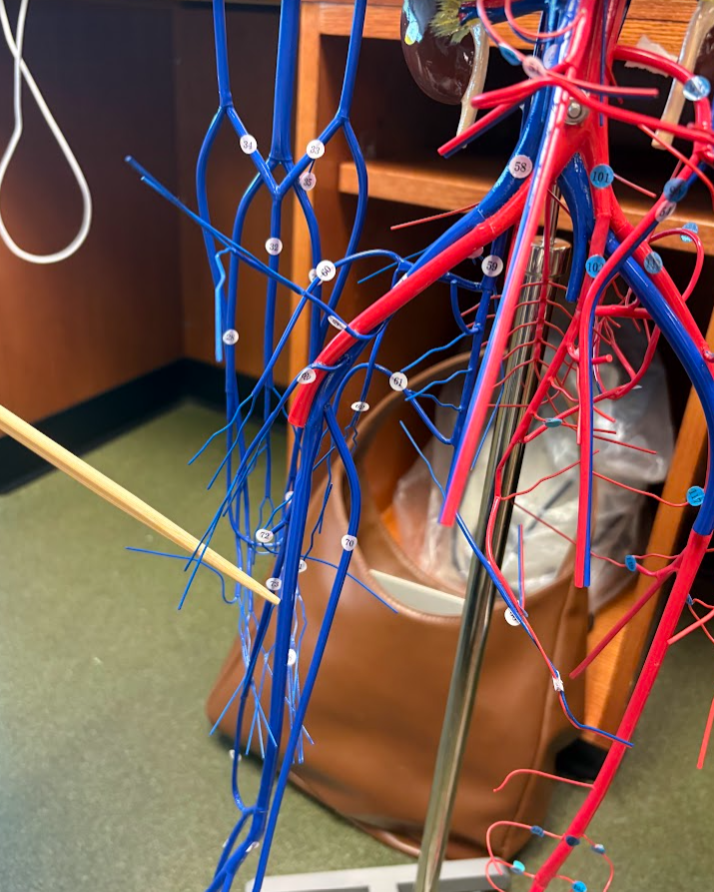
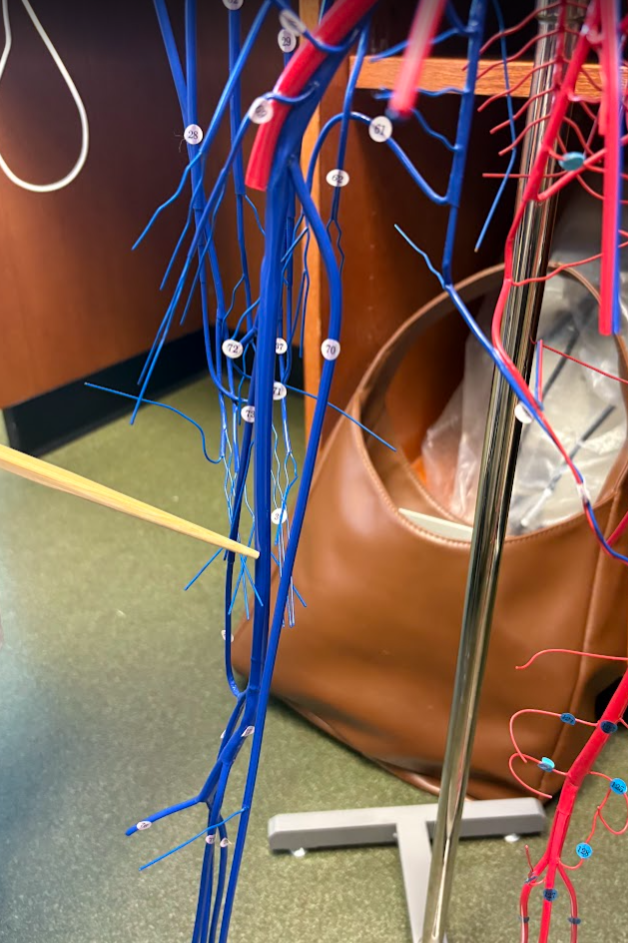


What is this?
Popliteal vein (77)
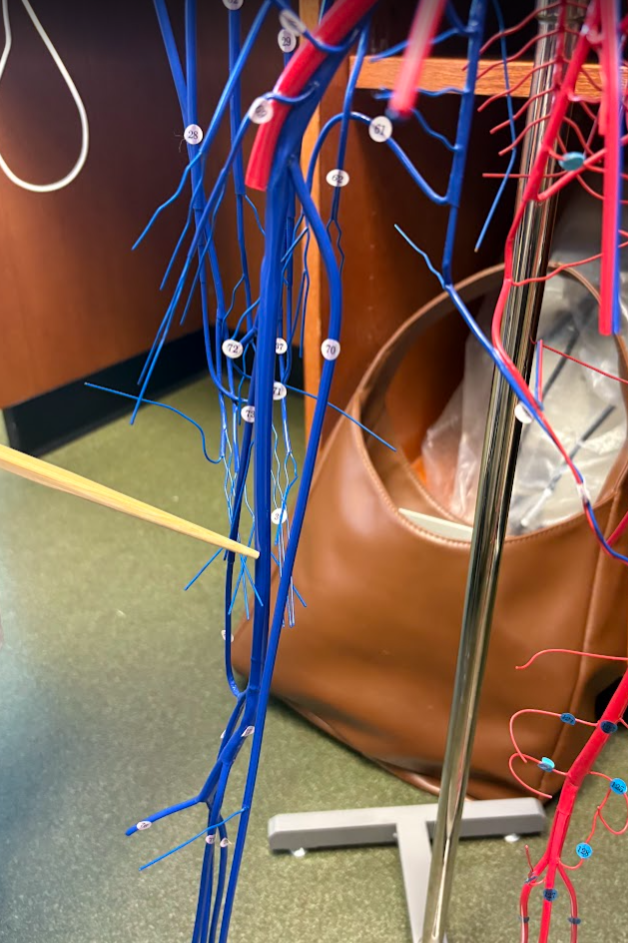
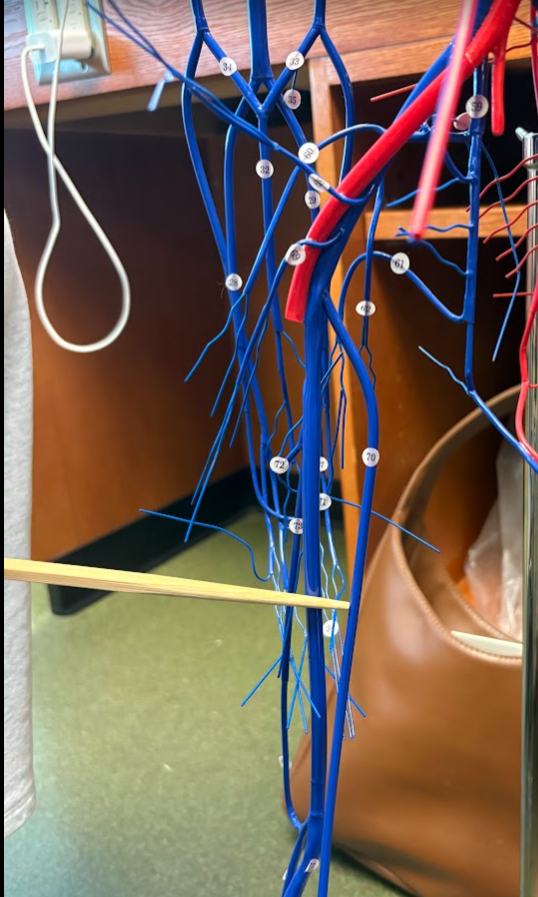


What is this?
Great saphenous vein (70) (Lower limb)
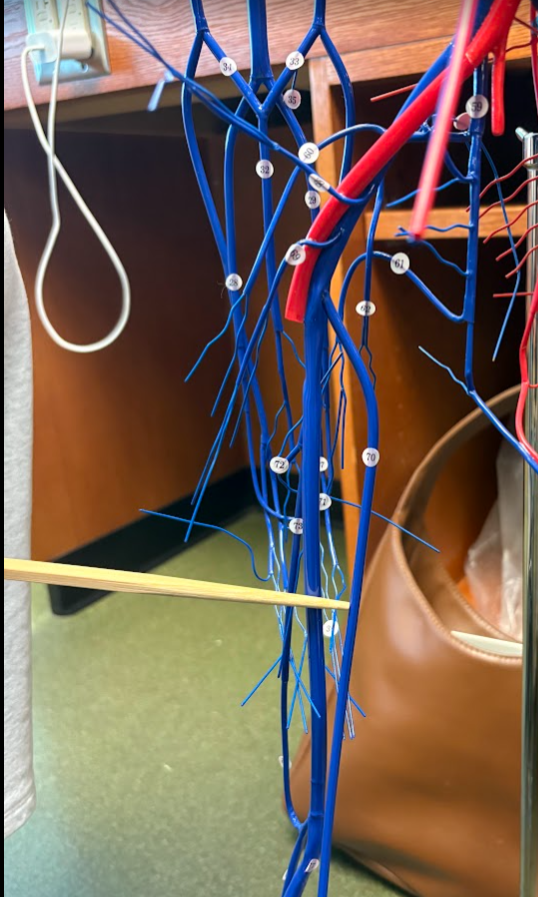


What is this?
Fibular vein (76)
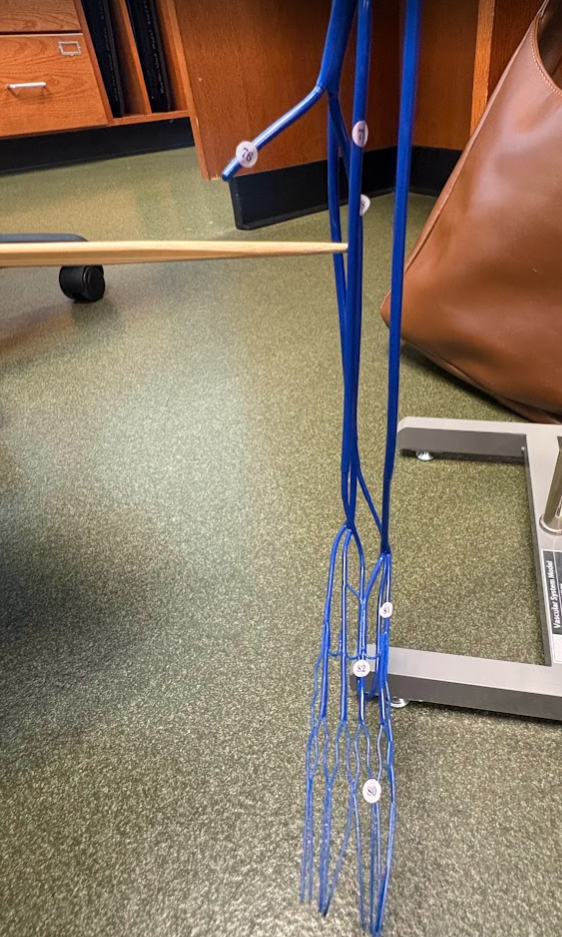


What is this?
Anterior tibial vein (79)
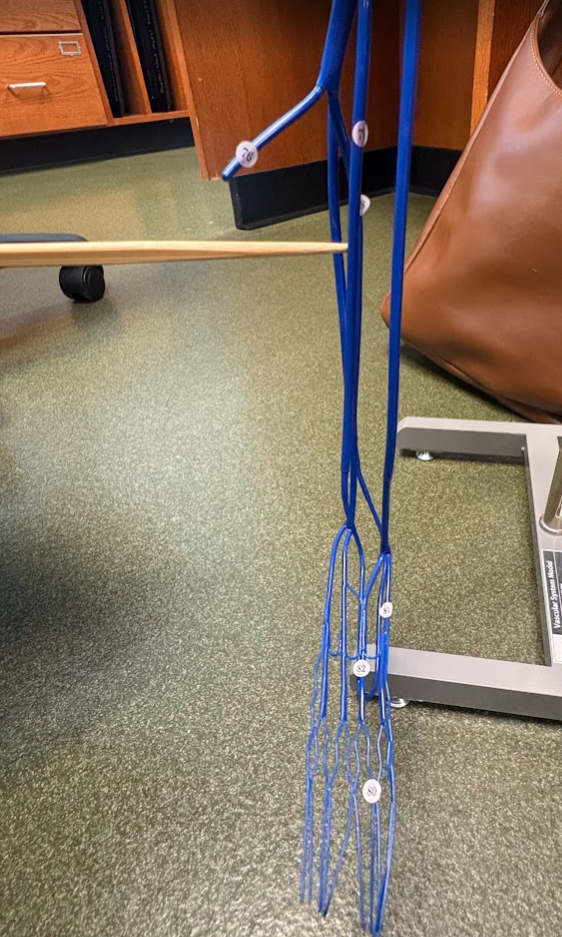

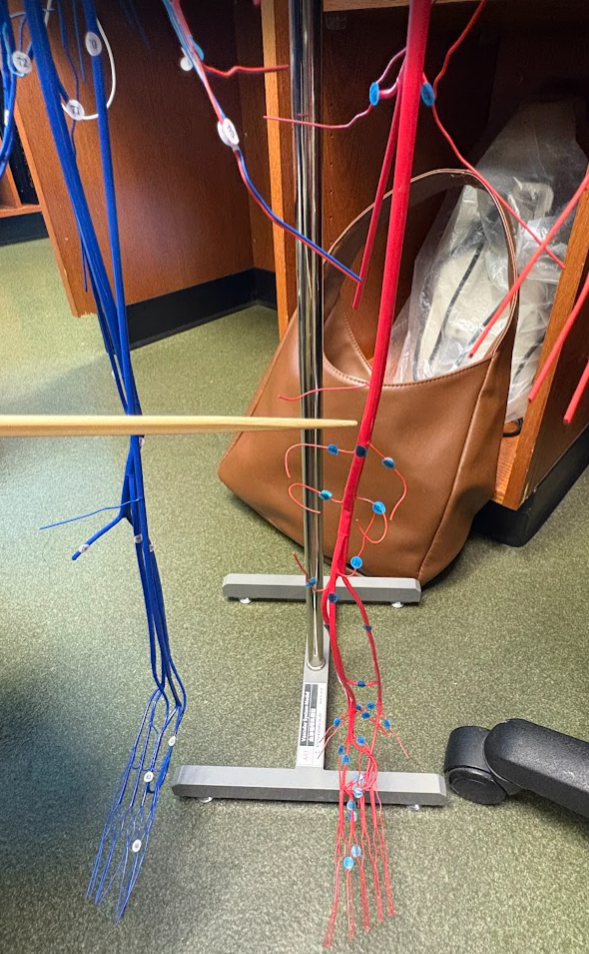
What is this?
Popliteal artery (122)
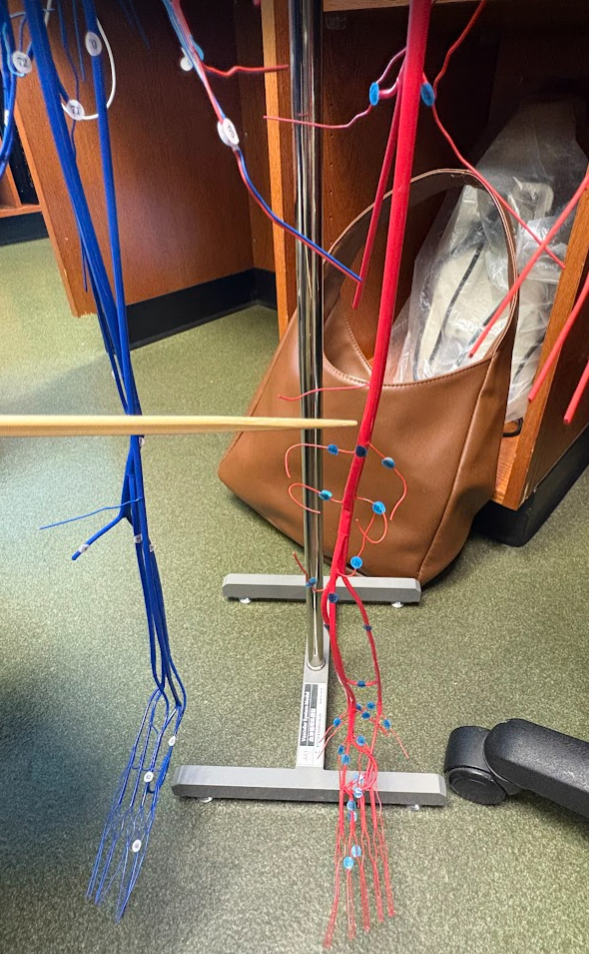
What is this?
Anterior tibial artery (127)
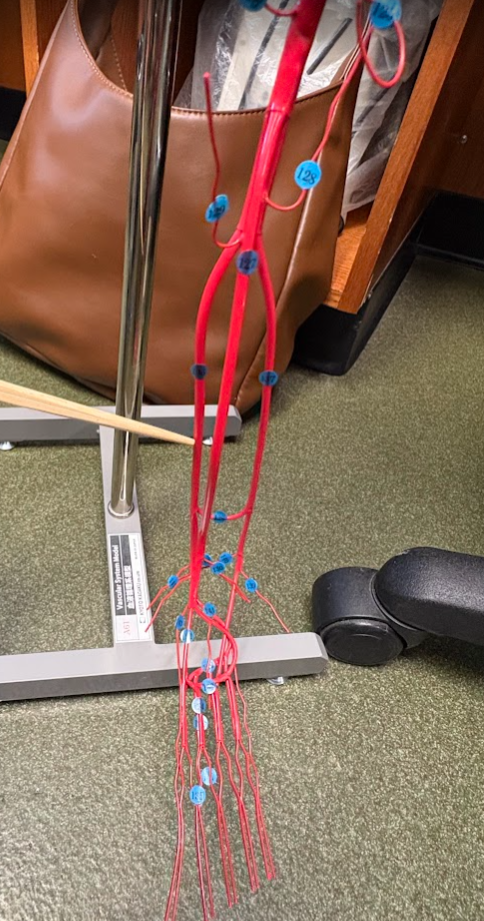
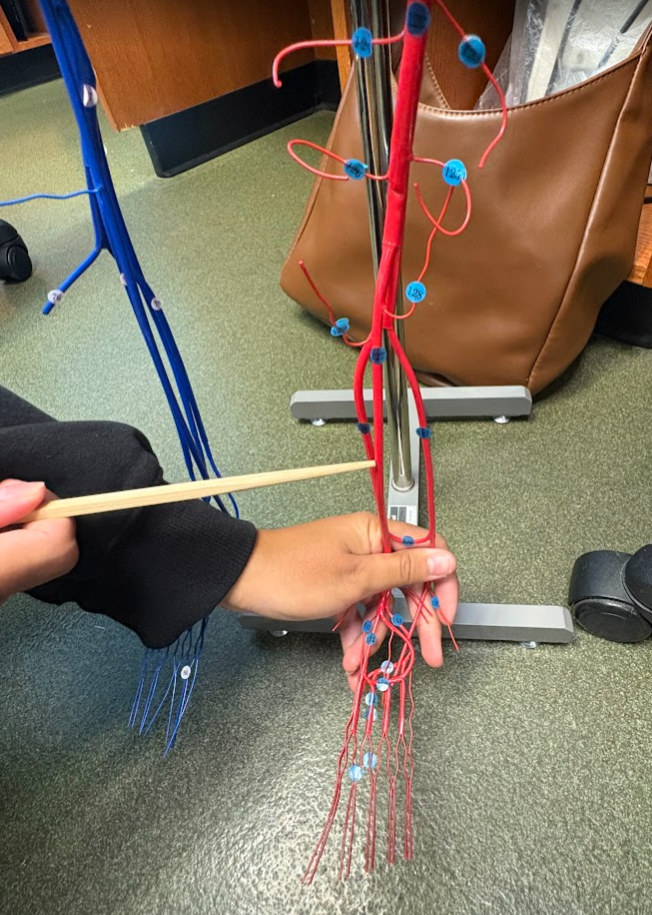

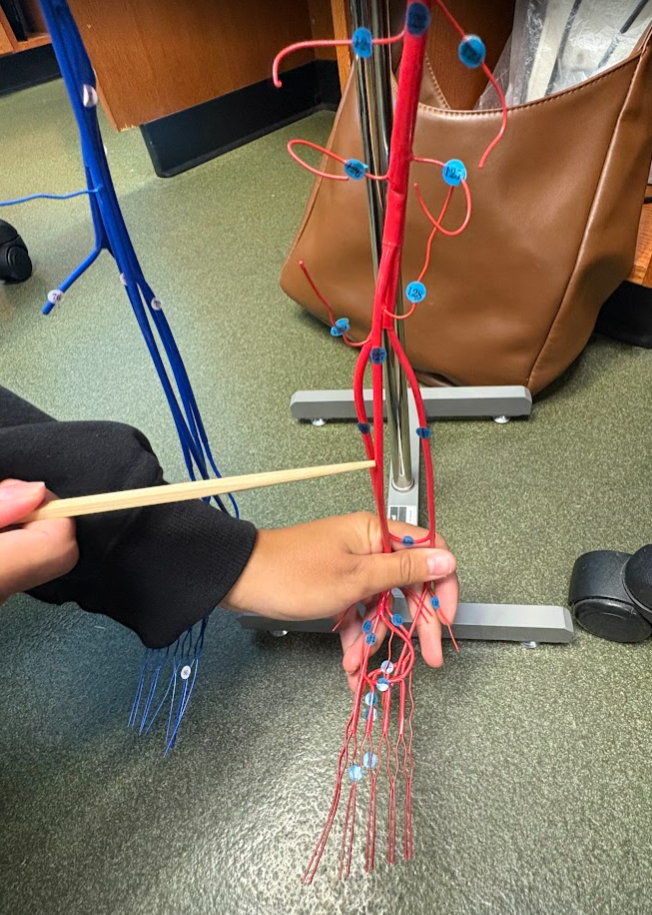
What is this?
Posterior tibial artery (136)
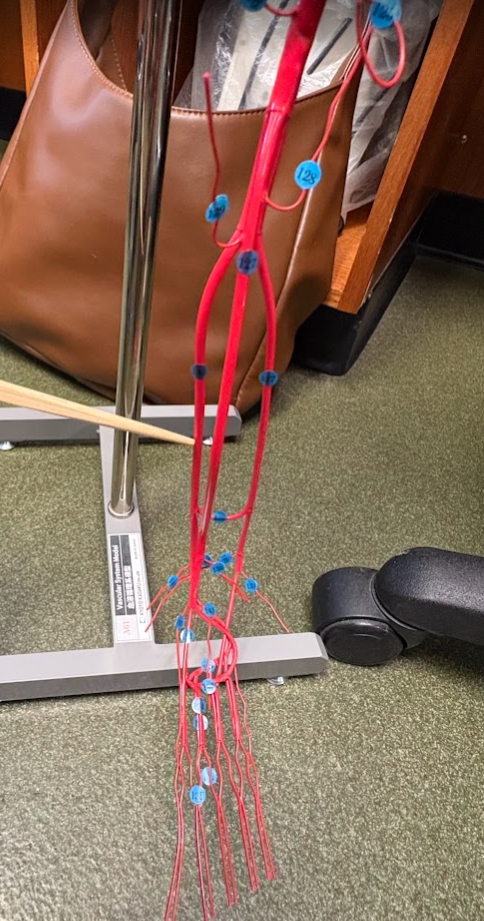

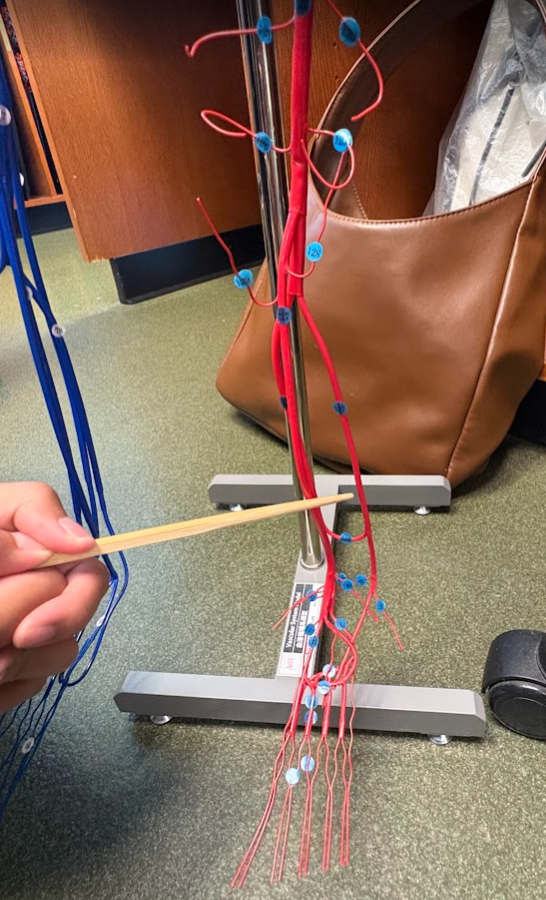
What is this?
Fibular artery (137)
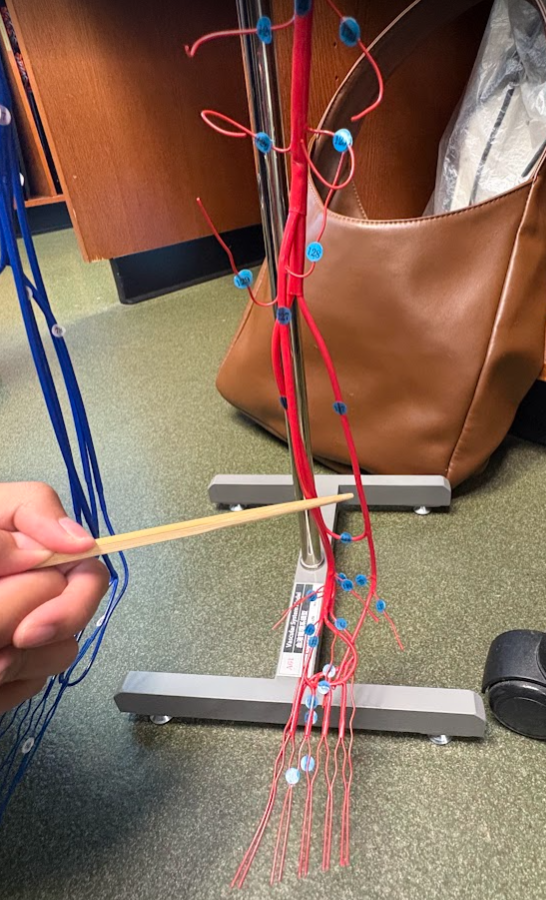

What is this?
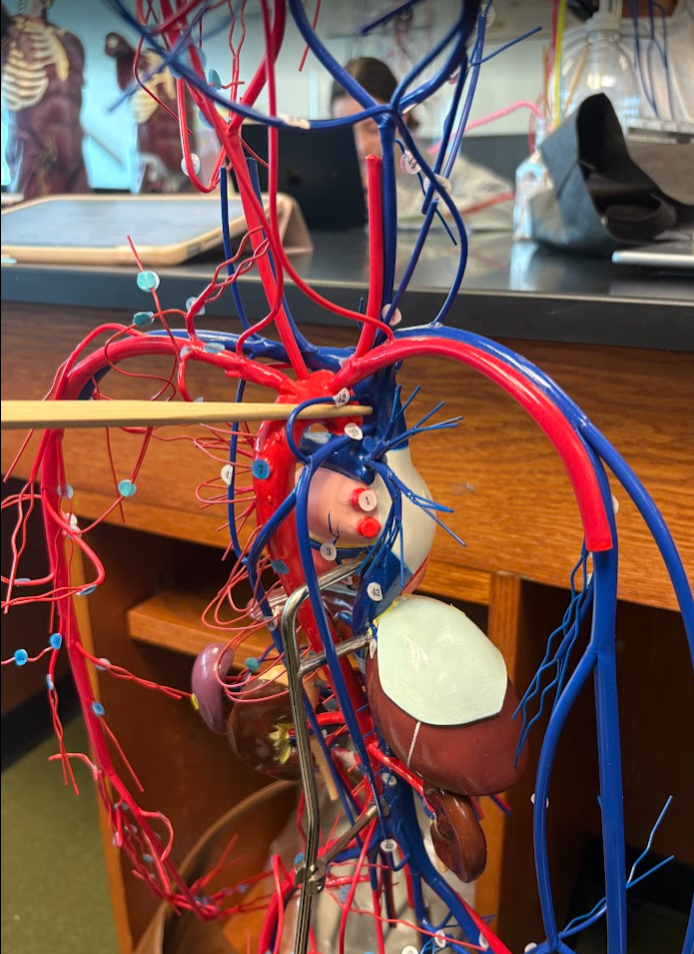
Superior vena cava
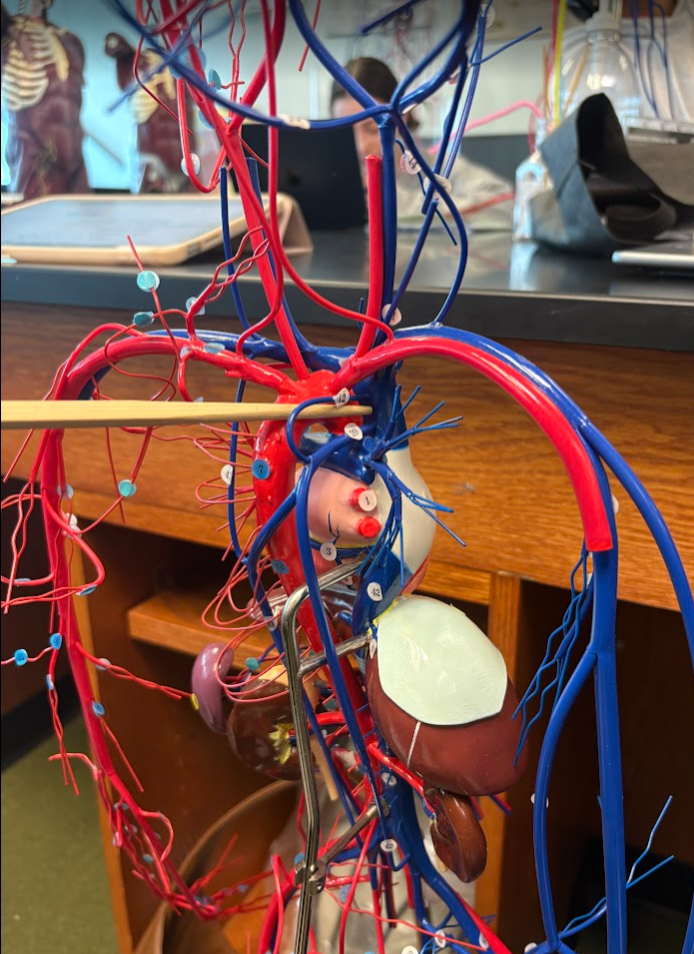
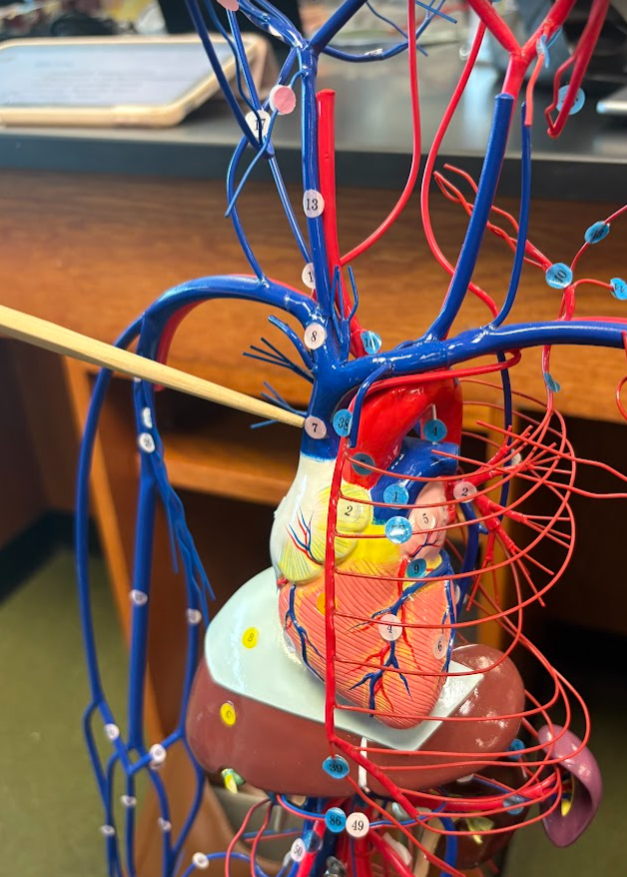


What is this?
Superior vena cava (7)
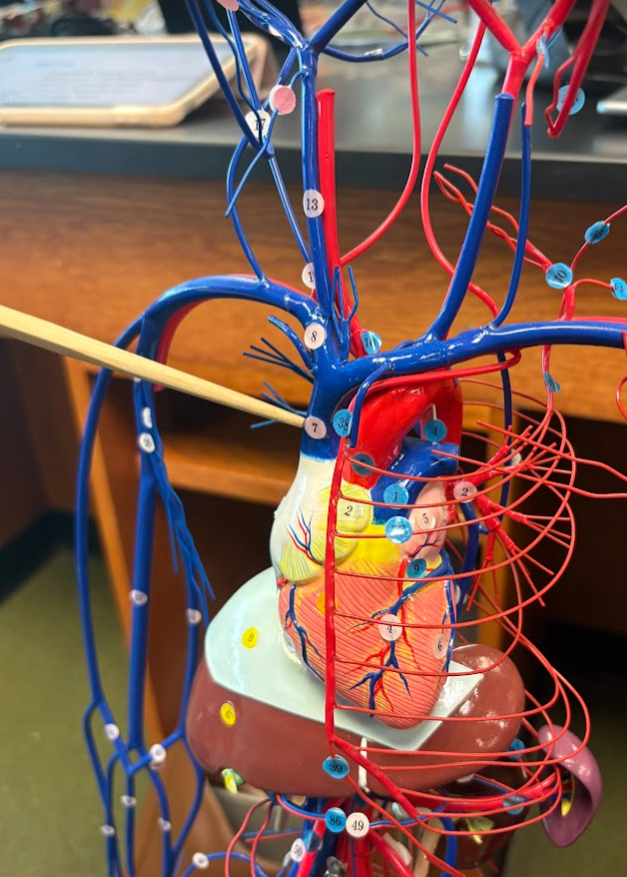

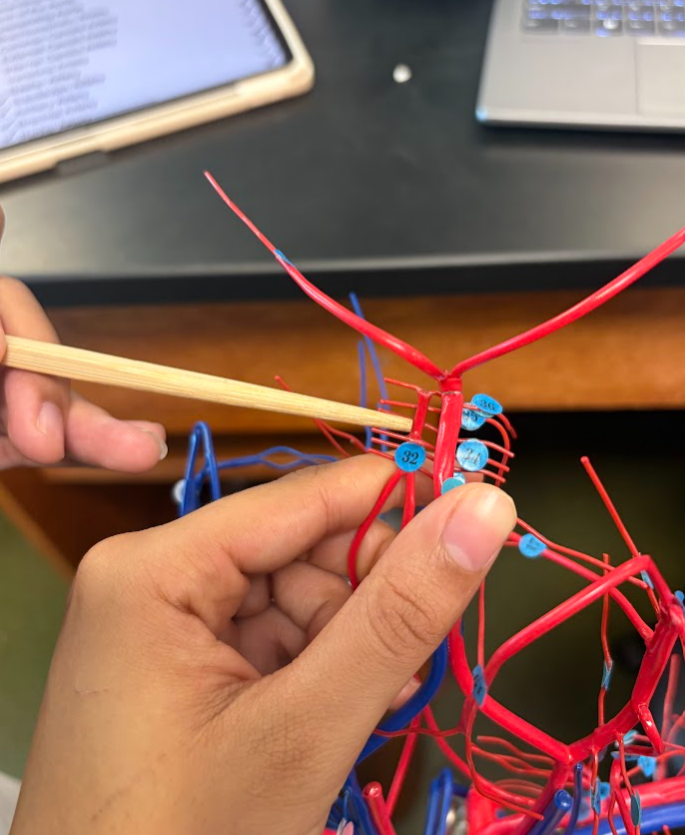
What is this?
Basilar artery (32)
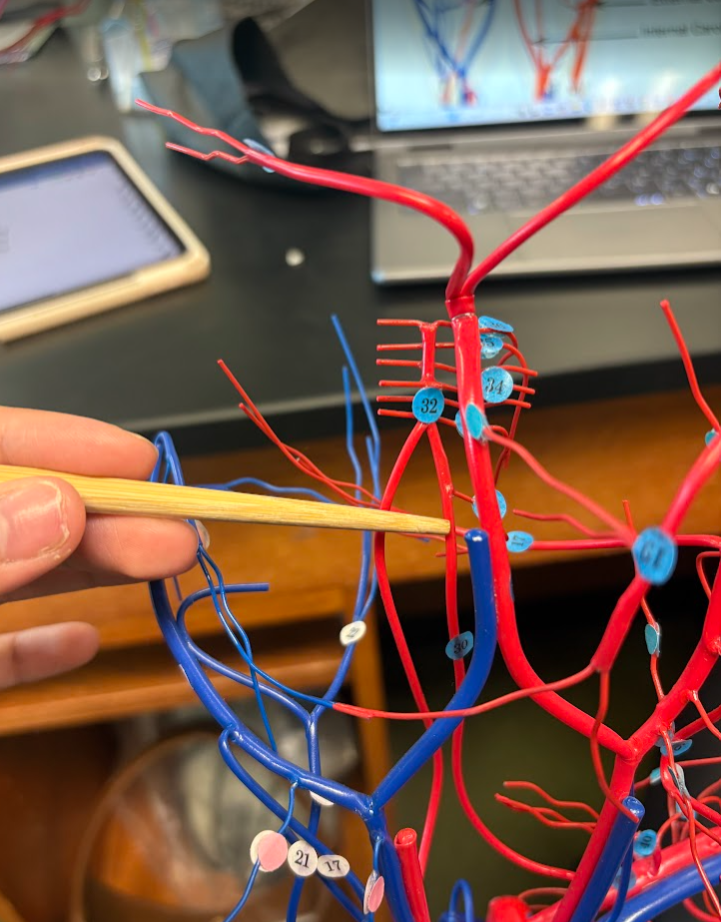
What is this?
Vertebral artery (another on other side) (30)
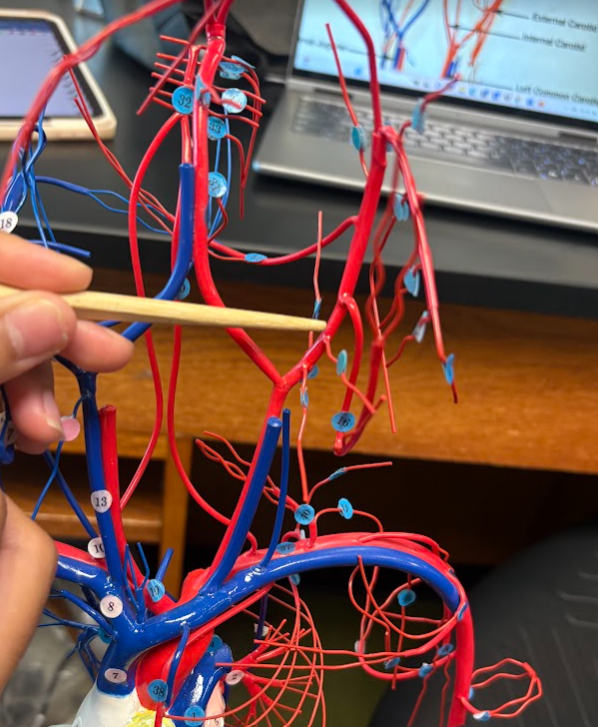
What is this?
External carotid artery (12)
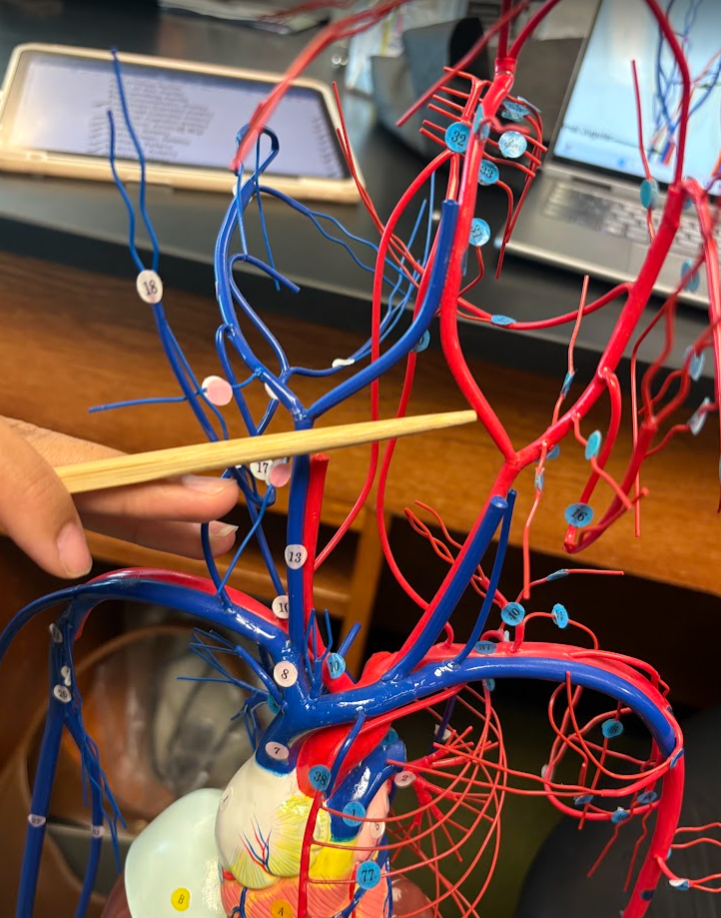
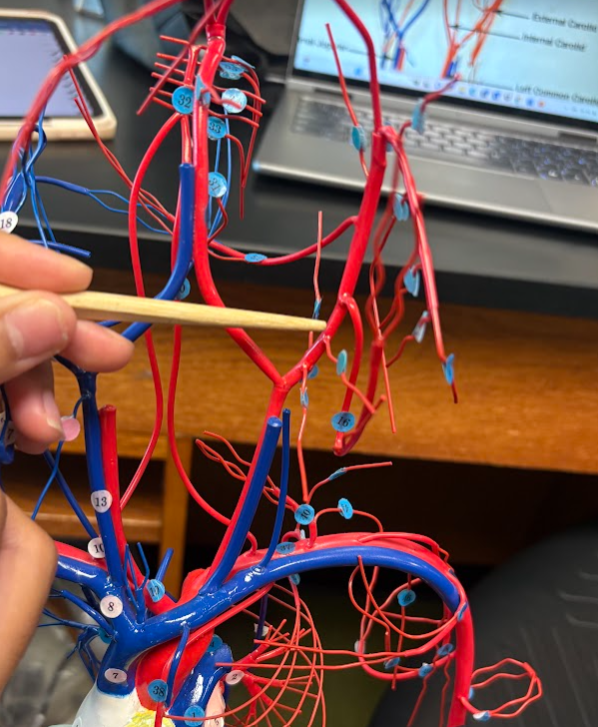

What is this?
Internal carotid artery (26)
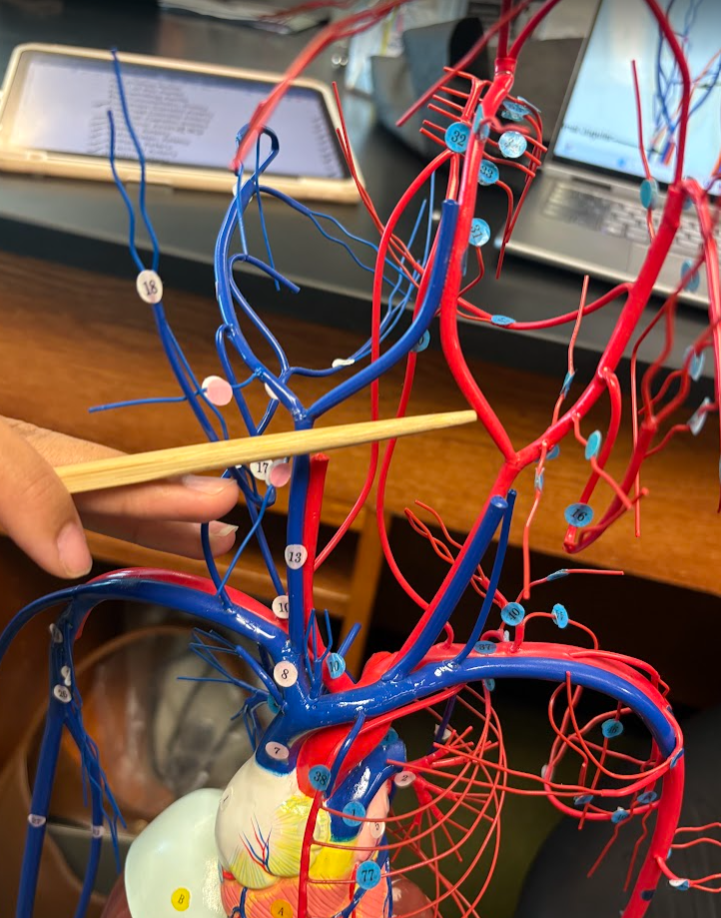
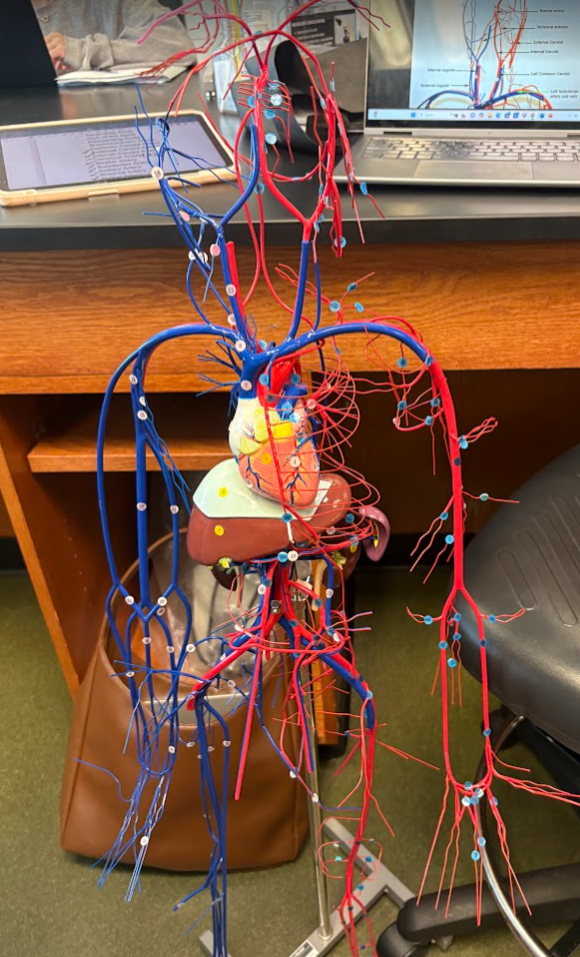


Which side is the left and which side is the right of the model?
Remember, the left side is red and the right side is blue.
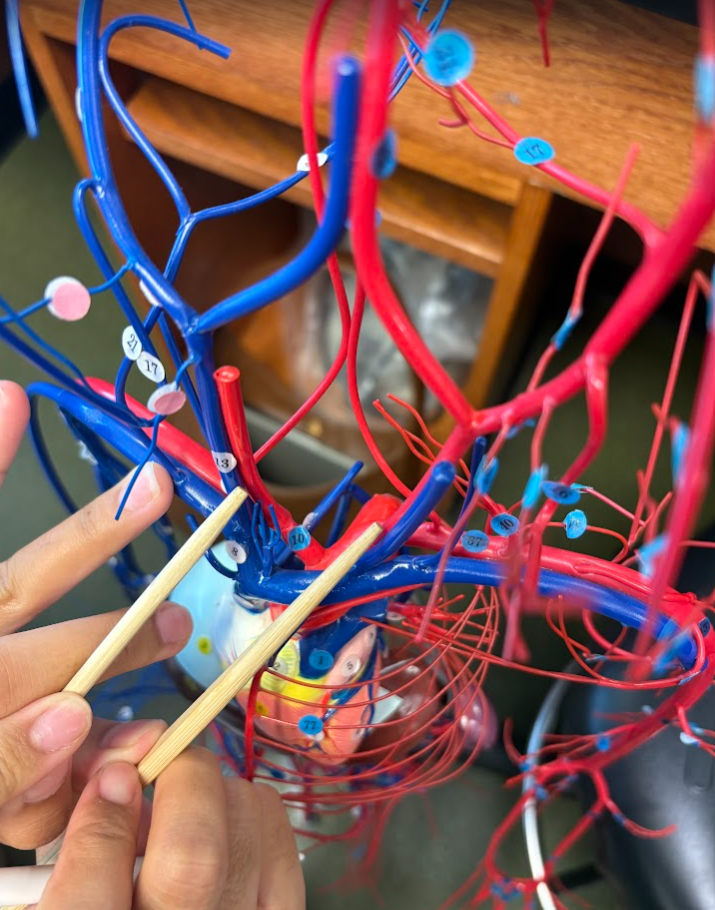

What is this?
Common carotid artery (both sides) (11)
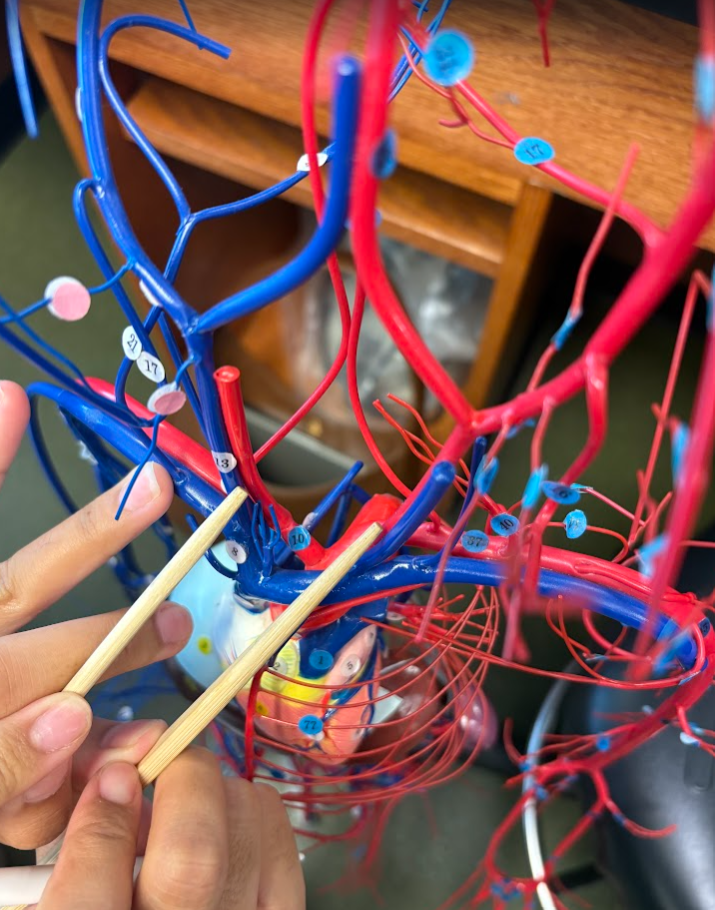

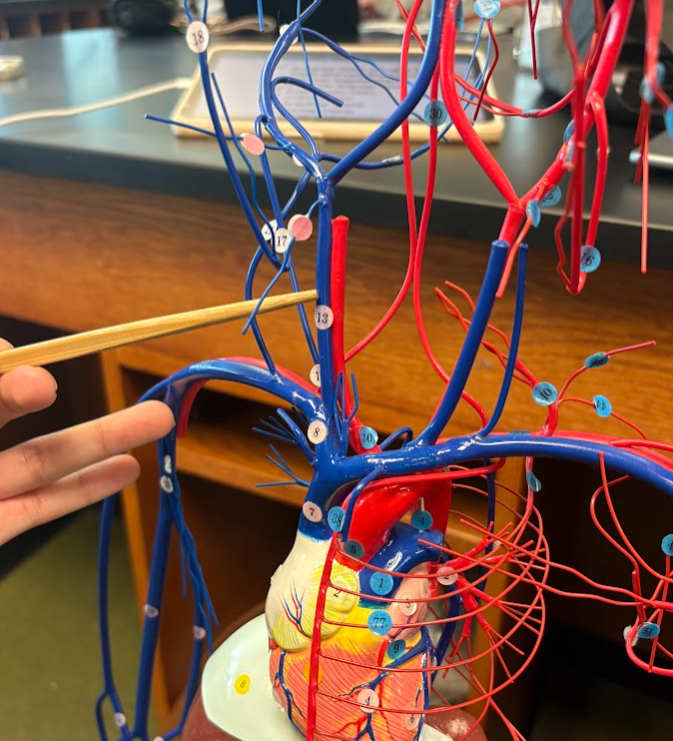
What is this?
Internal jugular vein (13)
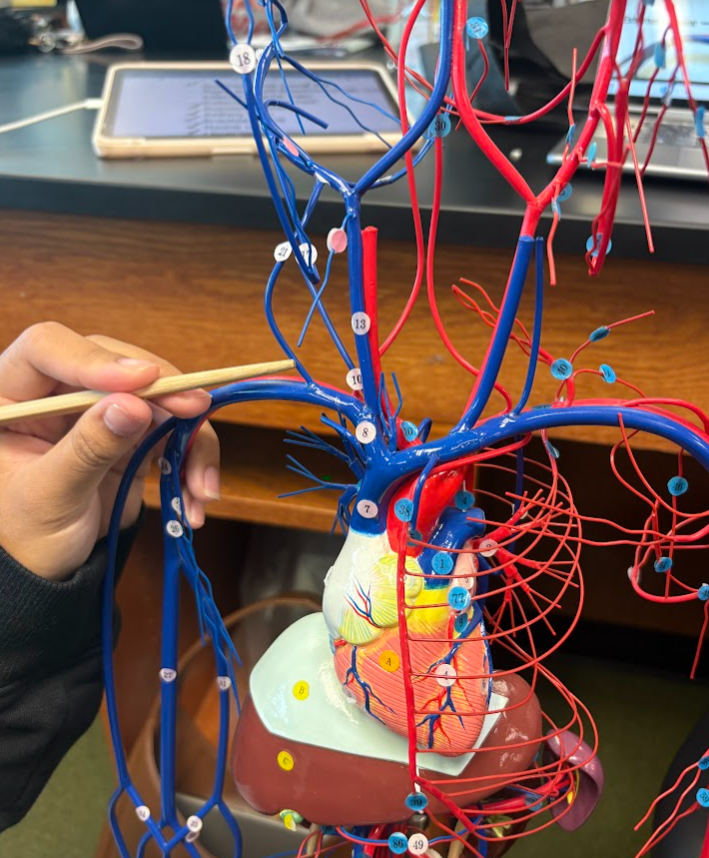
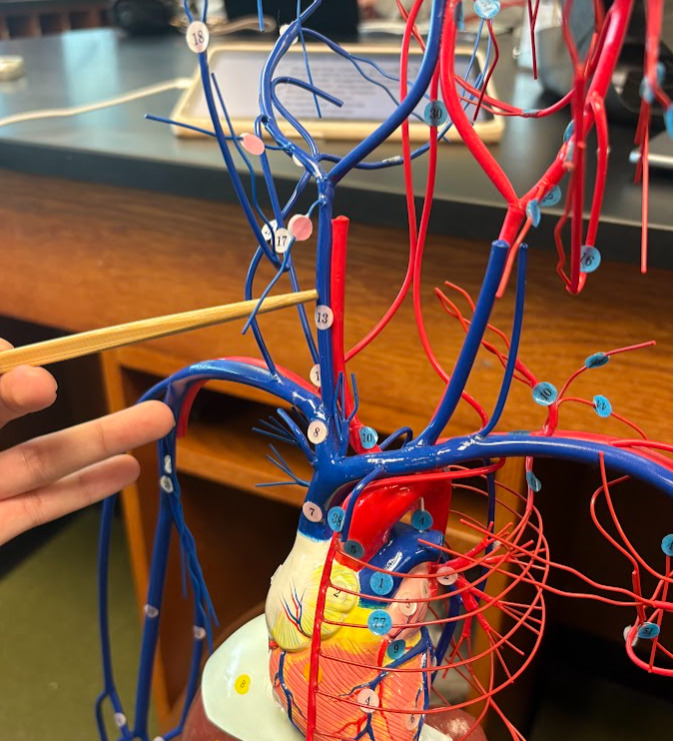

What is this?
External jugular vein (21)
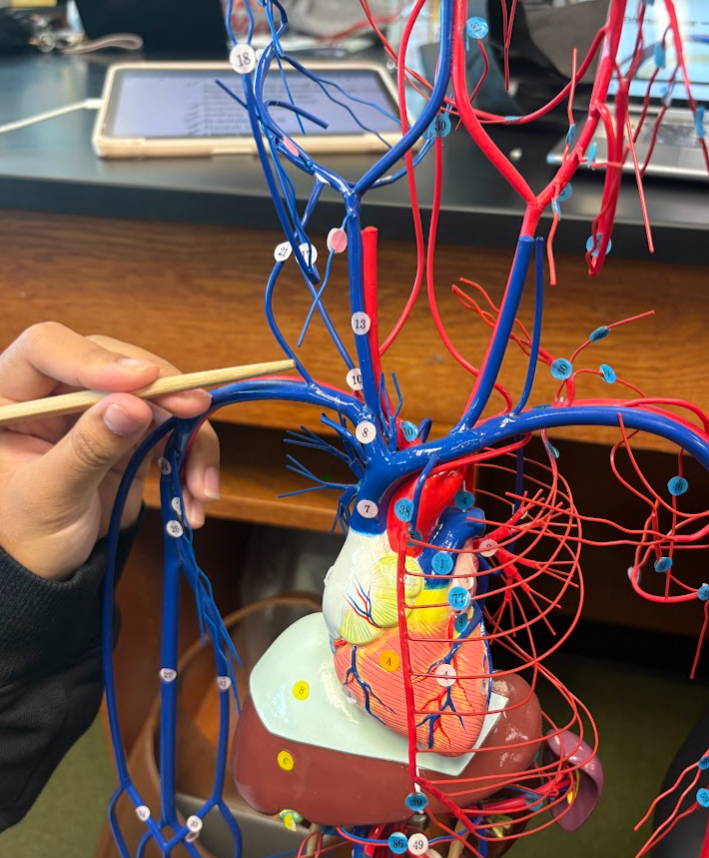

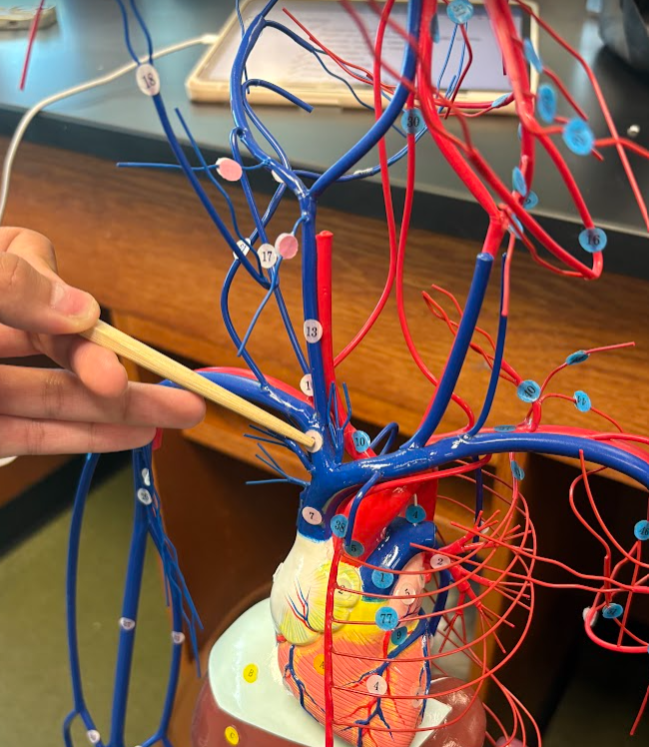
What is this?
Right and left brachiocephalic veins (8)
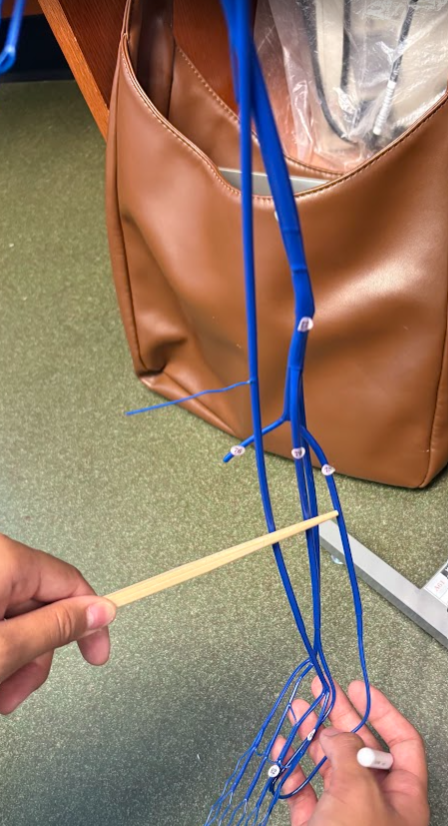
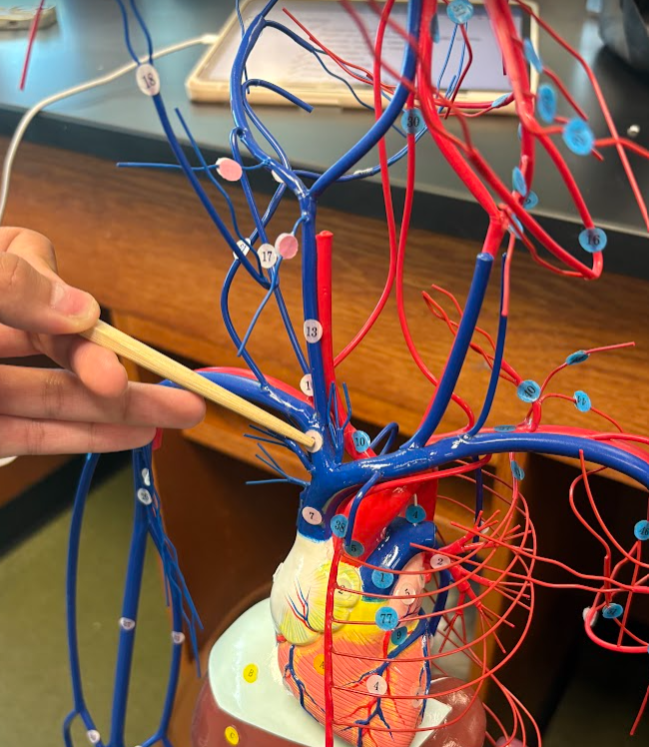

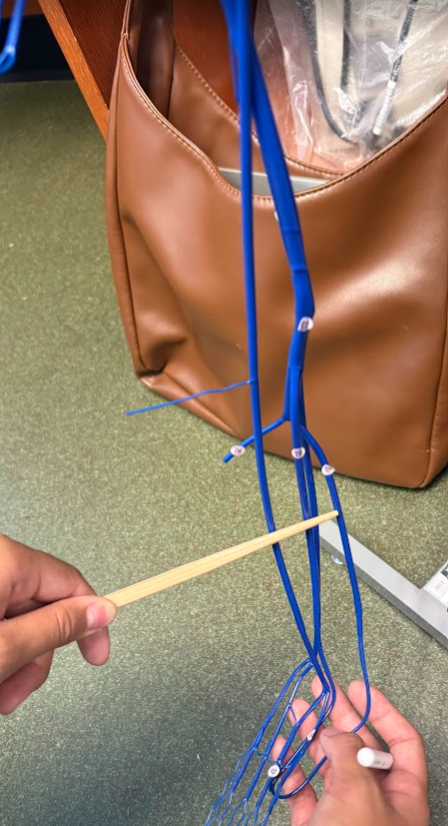
What is this?
Posterior tibial vein (78)
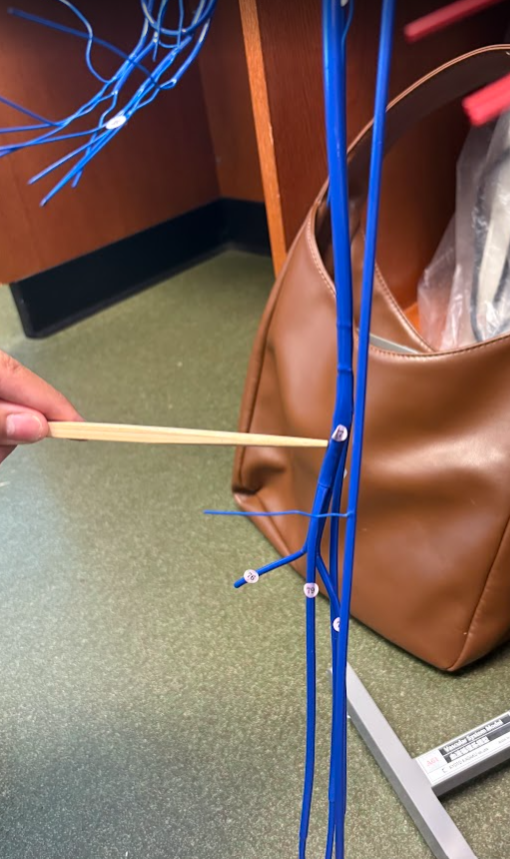


What is this?
Popliteal vein (77)
