Biotechnology
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Helpful videos: https://youtu.be/L3r4njvKsNQ, https://youtu.be/p_6ds_6mYLk?si=VwtIzT5OCeooj9jQ
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
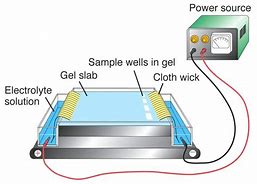
Electrophoresis
a way to separate fragments of DNA based on their size
The electric field causes the molecules to migrate through the gels with smaller and more negatively charged molecules move faster than larger less negatively charged molecules
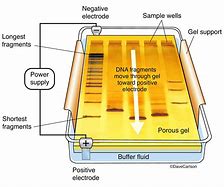
Genetic Engineering
the combining of genetic information from two or more organisms to create a “transgenic” organism that expresses new traits
this involves restriction enzymes and vectors
Reporter genes
genes in vectors that enable detection of successful transfer
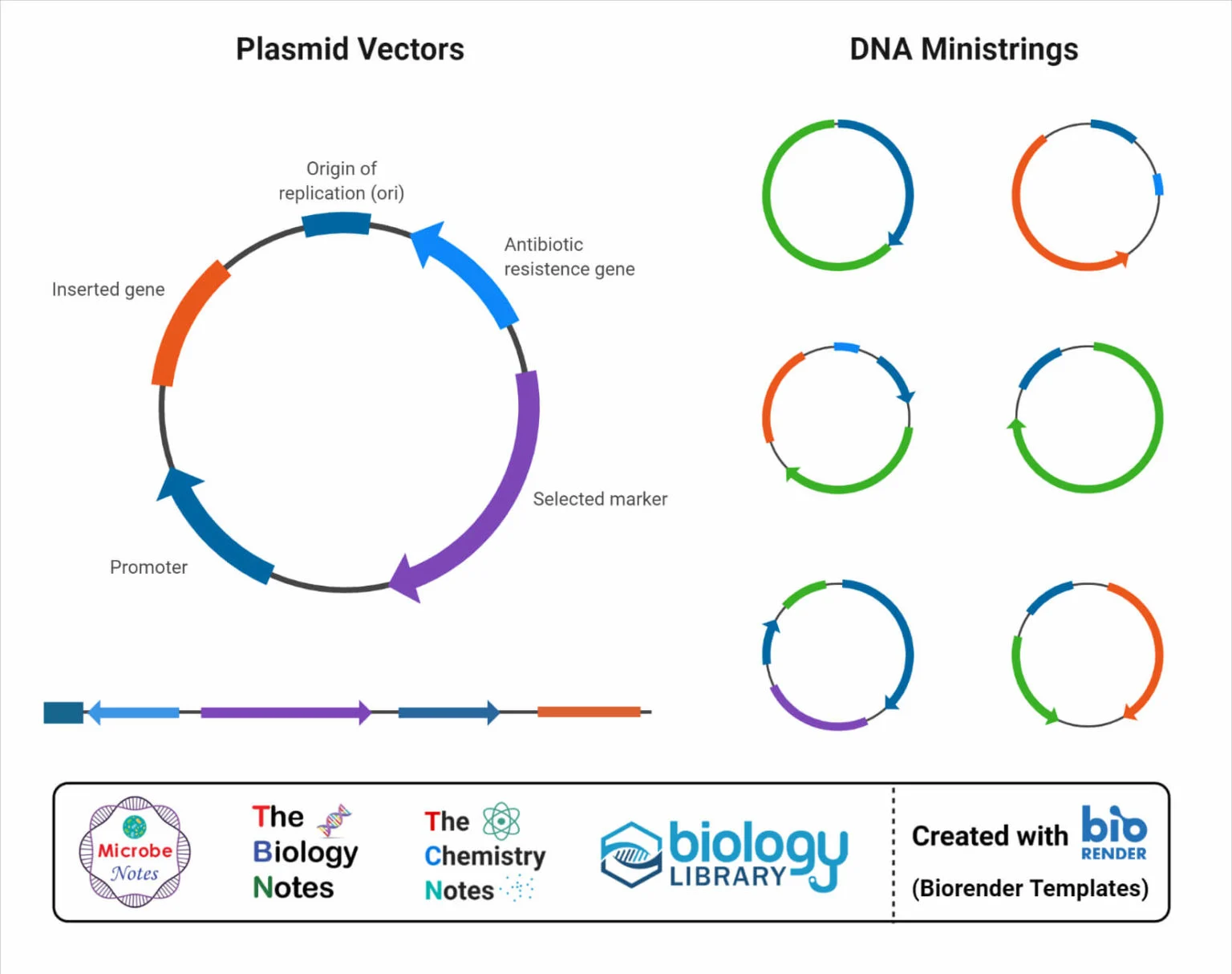
Vectors
are DNA molecules that are used to transport and introduce foreign genetic material into a host cell
can be mortified to store and replicate other DNA sequences
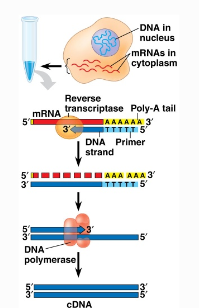
cDNA
“Complementary DNA”
DNA copies of RNA molecules (produced using reverse transcriptase)
increases stability, removes introns for prokaryotic expression of eukaryotic genes
expresses a specific protein in a cell that isn’t normally expressed
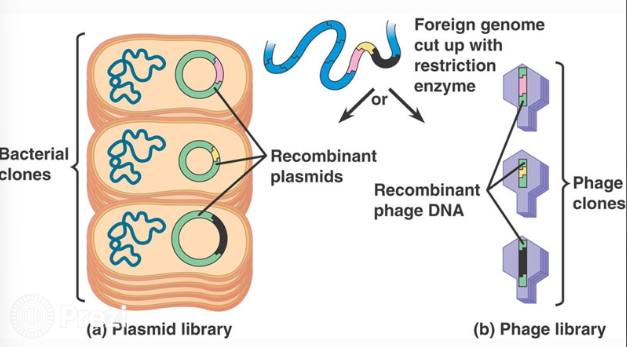
Gene Libraries
are collections of DNA sequences, stored in vectors
large sequences are cut into smaller pieces
the pieces are placed into vectors
the vectors are introduced into cells
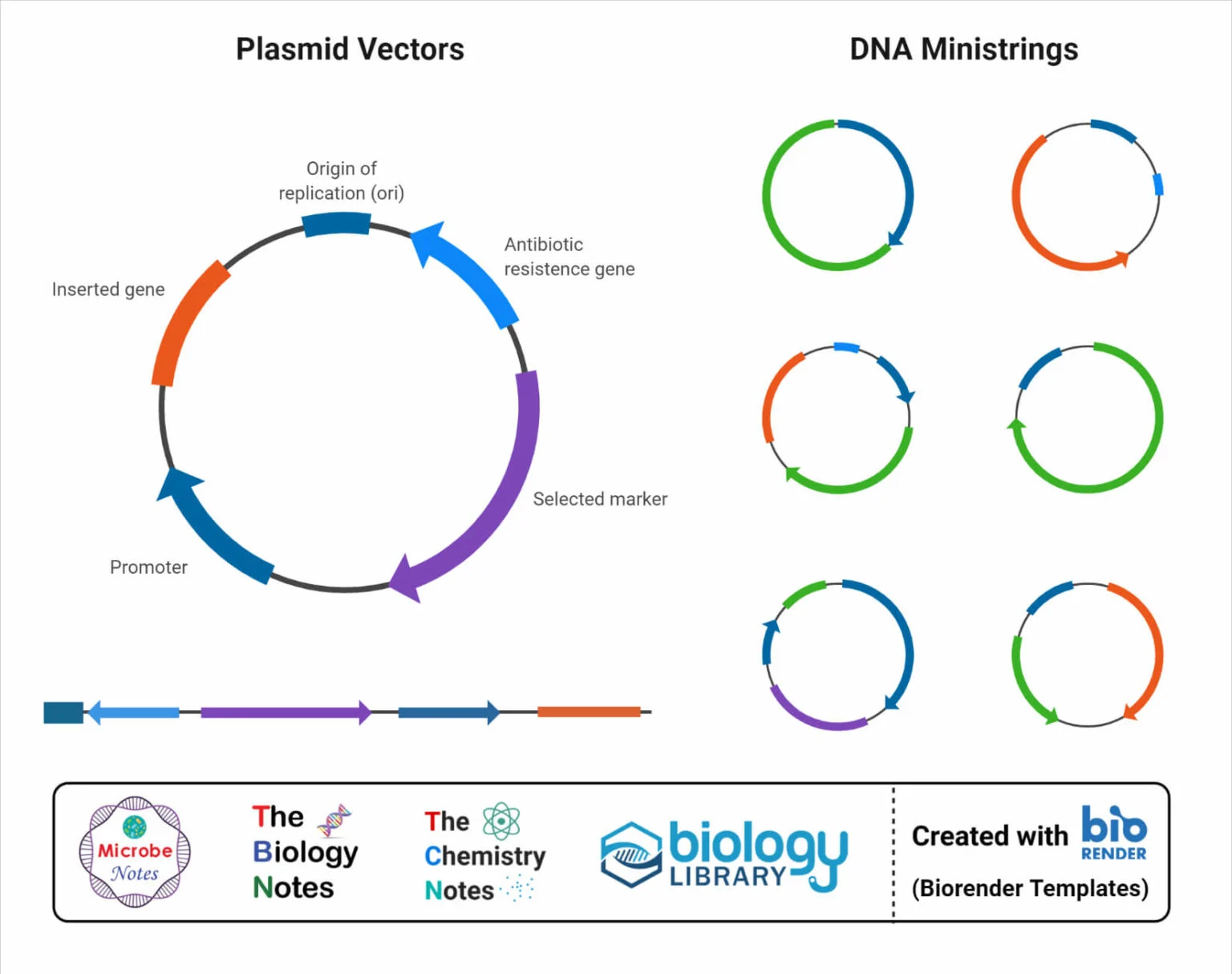
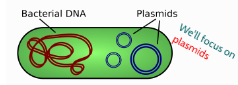
Plasmids
small circular pieces of DNA that replicate independently from chromosomal DNA and are mainly found in bacteria.
small circular double stranded DNA molecules that act as delivery vehicles or vectors to introduce foreign DNA into bacteria.
DNA Sequencing
DNA is replicated in the presence of dideoxynucleotides (ddNT’s)
Plasmids need to be successful:
an origin of replication
a region containing many restriction sites (a “multiple cloning site”)
gene/genes that enable screening of cells that have successfully taken up the plasmid
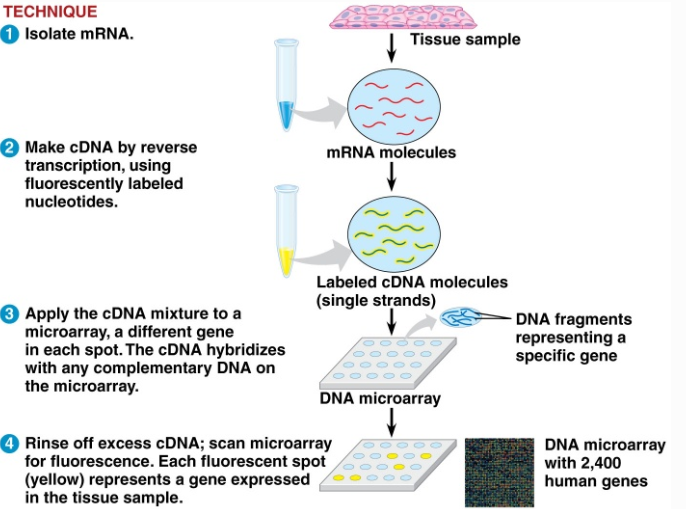
microarray technique
isolate mRNA
Make cDNA by reverse transcription, using fluorescently labeled nucleotides
Apply the cDNA mixture to a microarray, a different gene in each spot. The cDNA hybridizes with any complementary DNA on the microarray
Rinse off excess cDNA; scan microarray for fluorescence. Each fluorescent spot represents a gene expressed in the tissue sample
Bacterial Transformation
a process where bacteria take up and expresses DNA from outside the cell (change in phenotype and genotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell). The DNA is either integrated into the bacterial chromosome or simply exist as a plasmid.
allows for the bacteria to express new proteins like antibiotic resistance
Competent Bacteria
are in a special physiological state where the cell wall is permeable to DNA molecules from outside the cell; necessary for bacterial transformation to occur
heat shocking serves what purpose
it facilitates the entry of DNA through the pores of the bacteria cell wall, transforming the bacteria’s genome.
induces the competent state of bacteria
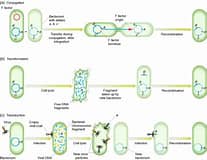
Steps of Transformation in bacteria
Competence development: Bacteria enter the competent state which allows for DNA to be absorbed from the surroundings
DNA binding, uptake, and processing: Bacteria take in a plasmid from another organism and gene expression is decided by the plasmid’s DNA
Integration into the host genome: The plasmid characteristics are expressed in the newly transformed bacteria
The bacteria’s plasmid is cut into with the restriction enzyme. The foreign DNA is cut in two as well and then those sticky ends will attach to give us recombinant DNA. DNA ligase joins the ends together to form a recombinant plasmid. The bacteria encounter many lab-based techniques to make the bacterial cell competent so that the bacteria can take in the new plasmid. Then the bacteria is transformed.
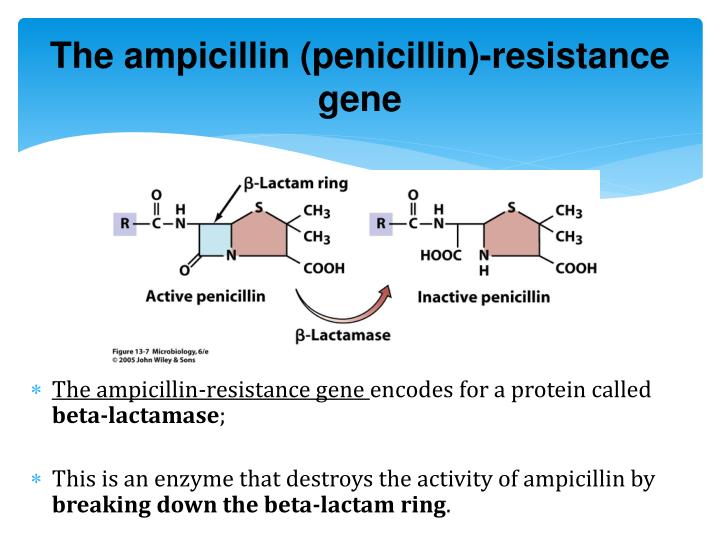
Ampicillin resistant gene
detroys the activity of ampicillin by breaking down the beta-lactam ring.
ampicillin
an antibiotic that kills off bacteria that is used on the recombinant bacteria to test if the bacteria is resistant to the antibiotic.
What direction does the DNA go in gel electrophoresis
towards the positive end
large to small
Recombinant genes
artificial DNA molecules that are created by combining genetic material from different sources
Main types of Recombination
Transformation (uptake of free genetic material from the environment)
Conjugation
Transduction
Bacterias contain
bacterial chromosome and potentially many plasmids
Restriction Enzymes
enzymes that cut DNA at specific recognition sites that are usually 4 to 8 base pairs in length
sometimes palindromic
Marker
a sample of DNA that we know the exact fragment lengths of placed in the very first well during gel electrophoresis