INTRODUCTION TO ASSISTIVE DEVICES
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
A Person may Require an Assistive Device:
To improve _______ mobility
To enhance ________
To assist with ______
To compensate for impaired ____, decreased ____, alteration in coordinated movements, pain during WB on one or both of the LE, absence of a LE (with or without prosthetic replacement), or altered stability
To improve functional mobility
To enhance body functions
To assist with fracture healing
To compensate for impaired balance, decreased strength, alteration in coordinated movements, pain during WB on one or both of the LE, absence of a LE (with or without prosthetic replacement), or altered stability
T or F:
The faster the person walks , the more time is spent for double support
False → less time
Assistive Device
improve a person’s stability by __________
_____ weight bearing on one or both lower extremities
permit _______
T/F : it does not help alleviate pain during ambulation
improve a person’s stability by expanding the base of support (BOS),
reduce weight bearing on one or both lower extremities
permit mobility
False → it helps relieves pain during ambulation
This is used for patients who must physiologically acclimate to an erect standing position before they can initiate an ambulation.
Tilt Table
(NOT AN ASSISTIVE DEVICE)
Order the following from GREATEST TO LEAST in amount of stability/support provided:
bilateral canes
quad canes
single crutches
walkers
hemi canes
single canes
bilateral crutches
Walkers → bilateral crutches → single crutches → bilateral canes → quad canes → hemi canes → single canes
T or F:
Initially, a patient may need to start ambulation with an aid that provides maximal stability or support that gives greater mobility.
False → restricts mobility
as the pt improves, he may able to progress to an aid that provides less stability or support and allows greater mobility.
What are your PRE-AMBULATION DEVICES ?
tilt table ( not an AD)
Parallel Bar
Supported Suspension Ambulatory Aid
PRE-AMBULATION DEVICES
_________ ( Most stable AD)
used for balance training, to teach specific gait patterns, and provide support while measuring an assistive device.
adjust the width as it should permit the hips and trunk to pass through them with clearance on both sides
the height is at the level of the _______ when the patient stands erect.
Each bar should be adjusted to provide ___ degrees of elbow flexion when the patient stands erect & grasps the bars approximately __ inches anterior to the hips.
Parallel bars
greater trochanters
20°-30° of elbow flexion
6 inches anterior to the hips.
Parallel bars
Each bar should be approximately __ inches wider than the patient’s greater trochanters when he or she is centered between the bars.
Bars can be adjusted is 2 ways → ________ (elbow flexion) when standing
2 inches wider
elbow flexion is even with greater trochanter or wrist crease (ulnar styloid process)
Parallel Bar Method for Measurement of Axillary Crutches
Have the pt stand inside with head ___ , the shoulders __ and _, UE _ the parallel bars, the trunk_ , the hips_ , the pelvis_ , the knees___, and the feet __ on the floor.
Measure from a point at the anterior axillary fold to a point on the floor approximately __ inches lateral and ___ inches anterior to the patient’s toes for the overall crutch length.
head erect → shoulders level and relaxed → UE grasping the bars → trunk erect → hips straight → pelvis level → knees slightly flexed & feet flat
2 inches lateral & 4-6 inches anterior
Parallel Bar Method for Measurement of Axillary Crutches
To determine the handpiece height, the crutch should be positioned in the patient’s ____ with the tip ____ and ___ to the patient’s toes.
approx _____ degrees of elbow flexion
allow the patient to lift or support the body by extending the elbows during the NWB or other gait pattern
axilla → tip forward and lateral
20-30° of elbow flexion
Parallel Bar Method for Measurement of Axillary Crutches
T/F: To obtain the most accurate measurement and fit, the axillary pad, handpiece pad, and crutch tip should be applied after all measurements are made and the fit is confirmed. The patient should not wear shoes.
False → patient must wear shoes & apply all things before all measurements are made
Parallel Bar Method for Measurement of Axillary Crutches
Alternative Method
same position
Using a crutch with push-button (“quick fit”) length and handpiece adjustments, position the crutch in the ___ and along the patient’s side. Adjust the hand piece at the level of the_______ (3) ;
then position the tip approximately ___ inches lateral and ___ inches anterior to the forefoot (toes) and adjust the length so that approximately _____ are present between the axillary rest and the bottom of the axilla.
Have the patient grasp the hand piece and evaluate the amount of elbow flexion and the length of the crutch with the crutch in the proper forward, ____ position.
Readjust the crutch as necessary to obtain the proper length and hand- piece position.
axilla
at the level of the wrist crease, greater trochanter, or ulnar styloid process
2 inches lateral → 4-6 inches ant.
2 fingerbreadths
tripod position
PRE-AMBULATION DEVICES
________
helps acclimate to an upright position as a result of a variety of conditions
prolonged recumbence, disturbance in balance, decreased proprioception, kinesthesia, LE circulation, or generalized weakness.
ability to gradually elevate a person from a horizontal to an upright position and to allow him or her to adapt or adjust to any given elevation provides a safe method for the body to accomplish physiological accommodation for upright activities
Tilt table
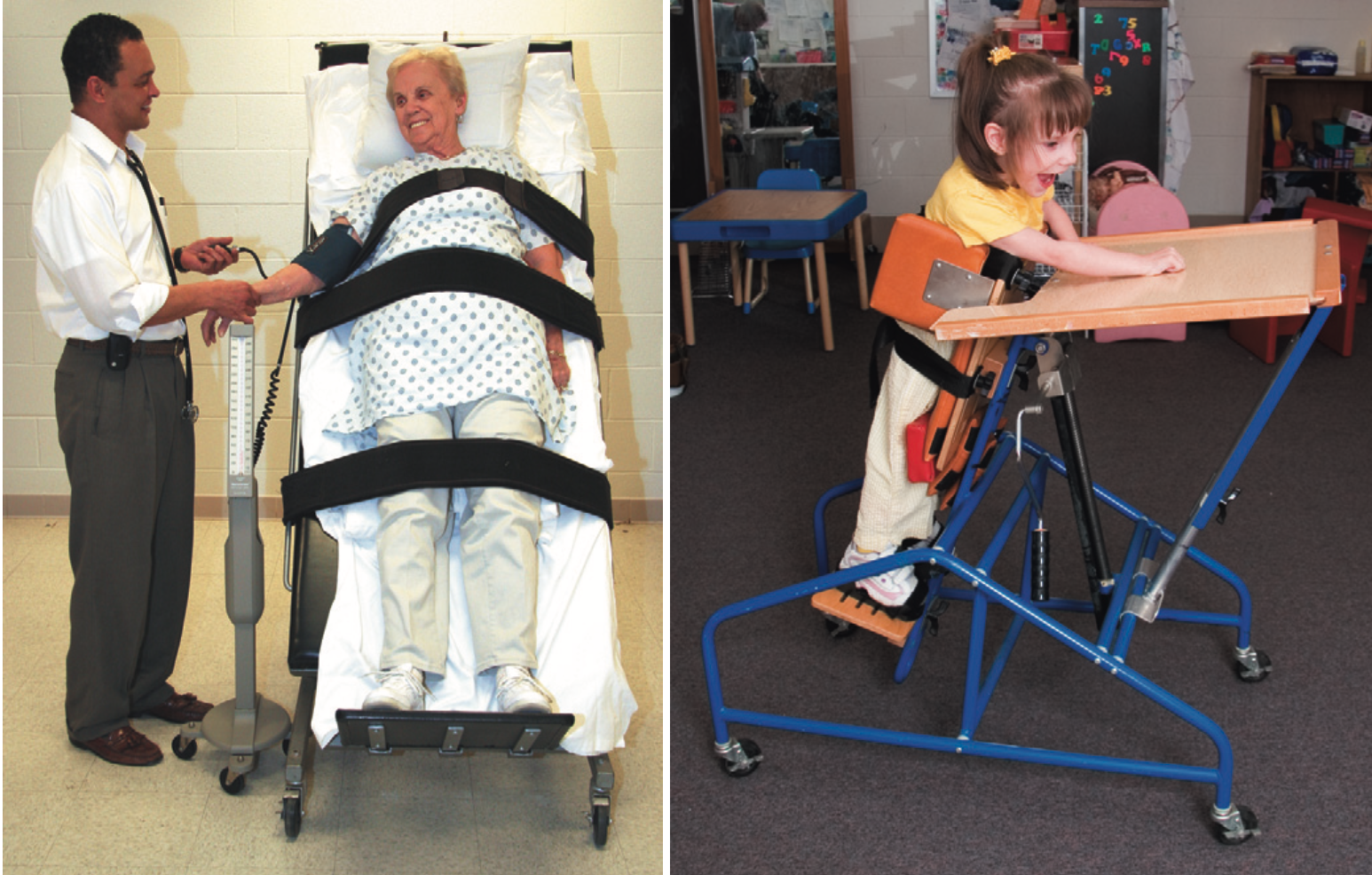
Tilt Table
measure ______ each time a progression to a higher elevation occurs
Indicates that the patient is experiencing difficulty in adapting to an upright position. → _________
Other indicators of the patient’s intolerance include
changes in consciousness, excessive perspiration, formation of edema in the lower legs, a DEC in or loss of pedal pulses, reports of nausea or numbness, a change in facial or limb color , tingling in the LE, and vertigo
VS esp BP & Pulse rate
Excessive INC or DEC in the blood pressure and pulse rate
T/F: While using a tilt table, Strengthening and ROM exercises can be performed, and lower extremity muscle groups can be positioned so a prolonged passive stretch force can be applied to them.
True
Tilt Table
An elevation of approx. _to_ degrees for __ minutes, for several sessions, should be sufficient
however, each person must be considered individually.
When the patient is elevated more than __ degrees, the sensation of falling forward may occur because his or her COG will be shifted forward
as a result of the pressure from the surface of the table against the back.
If the patient is elevated beyond __ degrees, a chest strap should be applied to prevent the upper body from falling forward.
necessary if the patient does not have strong _______
70°-80° for 15-20mins
>80°
>70° = Chest trap needed when pt has weak trunk extensors
Duration of Tilt Table session?
5-10 mins or 1 hr
1-2x per day or alternate days
Tilt Table Procedure

PRE-AMBULATION DEVICES
__________
Can be used for patients who need to be partially “unweighted” during gait training.
Uses adjustable suspension straps, a harness that fastens around the patient’s trunk, optional thigh straps to avoid loads to the groin area, and a type of suspension with a Y-shaped yoke that supports the patient from directly over each shoulder to maintain posture and balance.
Supported Suspension Ambulatory Aid
Some indications for use of this device are cerebral palsy, some spinal cord injuries, Parkinson disease, and severe weakness that necessitates the use of bilateral leg braces
Supported Suspension Ambulatory Aid
Supported Suspension Ambulatory Aid
Include controlled ____ and ___ to correct asymmetric movement
Facilitation of proper gait patterns, and the ability to work on balance, posture, and the _____ maneuver.
In addition, this device can ___ patients safely to the standing position from a chair or mat.
controlled WB & posture
sit to stand maneuver
lift safely
T/F: If the initial measurement is performed with the patient in a position other than standing, the fit of the aid must be evaluated and confirmed when the patient stands.
True
T/F: An aid that does not fit the patient properly will adversely affect his or her ability to perform a gait pattern and may result in an unsafe or unstable pattern.
True
Walkers
_____ BOS
Gives greater _and _ stability
Can reduce __ on one or (B) LE
For patients with debilitating conditions, fair balance or LE injury if crutches is precluded
Patient’s elbows should be maintained at _____ flexion
Height is at level of ________
Provides at least ___% of support
Widens BOS
Gives greater lateral and anterior stability
Can reduce WB on one or (B) LE
For patients with debilitating conditions, fair balance or LE injury if crutches is precluded
Patient’s elbows should be maintained at 20-30° flexion
Height is at level of greater trochanter
Provides at least 75% of support
Walkers Types
_________
Facilitate mobility in the community, cars
Portable
Less stable compared to non-folding
Folding (Collapsible)

Walkers Types
_________
Facilitate walking as a continuous movement sequence
Mobile
Contraindicated to postural disabilities (Parkinson's)
Rolling (Wheeled)

Walkers Types
_________
Has two posterior extensions and additional hand grips off of the rear legs for use on stairs
Stair Climbing Walker

Walkers Types
_________
Hinged, allows advancement on one side of the walker at a time
Mimics reciprocal gait patterns
Reciprocal Gait Pattern = Gr __ iliopsoas ( a must)
Reciprocal Walker
3/5 walker
Walkers Types
_________
Modified for use with one hand only
Stoke patients
Hemi Walker
Walker Attachments:
Fold down seats
Carrying basket
Walkers Fit Measurement
height of a walker can be determined with the patient ___ or ___.
hand grip should be placed level with the ____________ (3)
walker positioned in front and along patient sides with patient arms straight
feet of walker should be resting on the floor or even with the heels, the hips and knees should be ____, and shoes should be _____.
height → standing or supine
wrist crease, ulnar styloid process or greater trochanter
straight and shoes are worn

Ambulatory Devices
__________
Used to increase the BOS, provide moderate degree of stability, or relieve WB on the LE
Correct measurements and fitting is needed to prevent nerve damage
Allows ___% of support
Crutches
50%
Crutches
_______
Provide increase UE WB over FA crutches
May be difficult to use in small areas
Disadvantage
Prolonged leaning on the axillary bar can result in vascular and/or nerve damage (axillary artery/radial nerve)
Axillary Crutches
Axillary Crutches
Measurement = ______ of elbow flexion is a must
Standing
Pt’s ht - ___ inches then multiply pt height to __%
Or base of ___ - __inches
Front (big toe) = __inches lateral
20-30° of elbow flexion
Height of pt - 16 in → x77%
base of axilla - 6in
2 inches lateral
Axillary Crutches
Sitting:
UE is _____ at shoulder level, one elbow is ____, the other elbow is flexed to __°
Measure from olecranon of flexed elbow to fingertips of extended arm
abducted → one elbow extended while 90° flexed yung isa
Axillary Crutches
Hand Piece
Top of forearm cuff should be ~___ inches distal the olecranon process
handgrips should be adjusted to level of _____ or _____
approx. 1-1.5 in distal to olecranon
wrist crease or olecranon process
Axillary Crutches Length
with the pt standing, tips of crutches approx ___ inches lateral and ____ inches anterior to toe of patient shoes
crutches should rest on the floor at a ____° angle
space between axillary rest and floor of axilla should be approx ___ inches or fingerbreadths
2 inches lateral and 4-6inches anterior
45° angle
2 inches or fingerbreadths
Forearm Crutches Types
_________
Has a forearm cuff and a hand grip
Provides less stability but increase ease of movement
Frees hands for use w/o dropping the crutch
Lofstrand Crutches
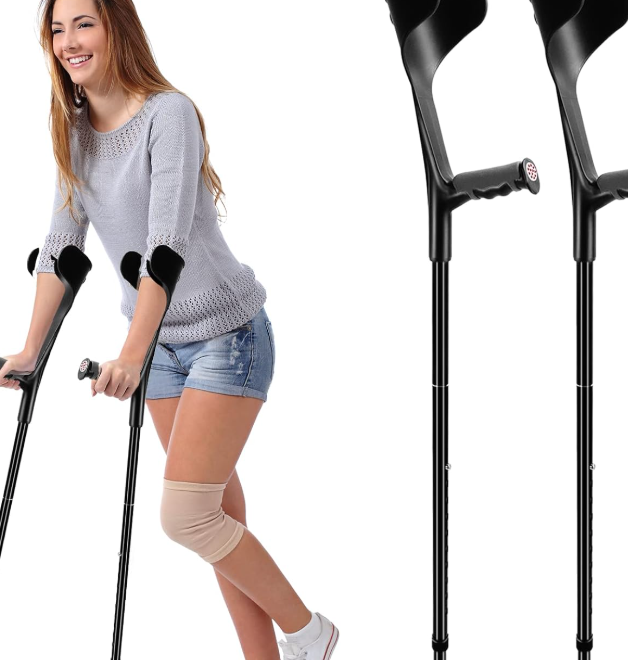
Forearm Crutches Types
_________
Allow WB on the FA, used for pts who are unable tp WB through their hands
Forearm Platform Crutch

Forearm Crutches Add Ons
________
Rubber ~1.5 inches in diameter
Provide suction, minimize slippage
Crutch Tips
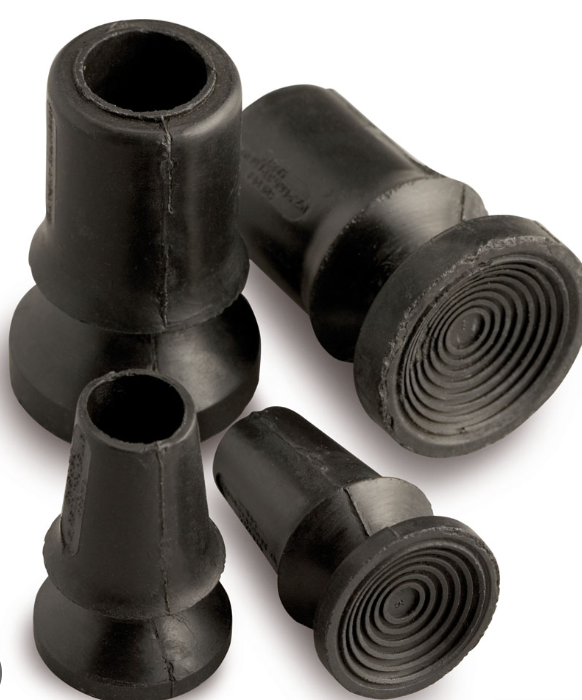

Forearm Crutches Types
The cuff should cover the proximal third of the FA ~____inches below the elbow
when the patient grasps the handpiece with the cuff applied to the forearm and the wrist in neutral flex-ext
1-1.5 inches below the elbow
T/F: The initial fit of the aid may be revised after the patient has ambulated several times. As he becomes stronger, more skilled and more efficient, initial fit wont be comfortable
True
Common Errors in Fitting Assistive Devices

Ambulatory Device
_______
Widen the BOS to improve balance
Provide limited stability and unweighting
Used to relieve pain
Provides ___% support
Canes
25% support
Cane Types
______
Adjustable with push pin lock
_____
Single point cane
_____
re-distributed force in WB = easier to use for some patients
Wood / Aluminum
Standard
C angled handles
Cane Measurement
______ of elbow flexion
Greater trochanter to a point __ inches to the side of the toes
In Supine
a tape measure can be used to measure the distance from patients ____ to the ____ with hip and knee extended
20-30°
6 inches
Greater Trochanter → heel with hip & knee extended
Cane Types
_________
4 contact points with the ground
Provides increased stabilisty but slows gait
_________ (SBQC) = stairs
__________ (WBQC) = not fit for stairs
Quad Cane
Small-based quad cane (SBQC) = stairs
Wide-based quad canes (WBQC) = not fit for stairs

Walker in General
Axillary Crutches In general


Forearm Crutches in General
Canes in General

Gait Patterns : NON-WB
The walker is picked up and moved forward about an______
Weight is then transferred through the_____ to the walker
The involved NWB limb is held anterior to the pt’s body but does not make ________
The uninvolved limb is moved ______
The cycle is repeated
The walker is picked up and moved forward about an arm’s length
Weight is then transferred through the UEs to the walker
The involved NWB limb is held anterior to the pt’s body but does not make contact with the floor
The uninvolved limb is moved forward
The cycle is repeated
Gait Patterns : PWB
The walker is picked up and moved forward about an arm’s length
The involved PWB limb is moved _____, and body weight is transferred partially through the ___ to the walker
The uninvolved LE is moved _______ past the involved limb
The cycle is repeated
MD determines amount of weight-bearing
Train pt by feeling the amount of weight in comparison to the non-affected LE
The walker is picked up and moved forward about an arm’s length
The involved PWB limb is moved forward, and body weight is transferred partially through the UEs to the walker
The uninvolved LE is moved forward past the involved limb
The cycle is repeated
MD determines amount of weight-bearing
Train pt by feeling the amount of weight in comparison to the non-affected LE
Gait Patterns : Full-WB
The walker is picked up and moved forward about an arm’s length
The ______ is moved forward
The _______ is moved forward past the ____
The cycle is repeated
NOTE: stronger leg is always ________ to the weaker leg
The walker is picked up and moved forward about an arm’s length
The first LE is moved forward
The second LE is moved forward past the first
The cycle is repeated
NOTE: stronger leg is always posterior to the weaker leg
Ambulation Patterns
2-Point Gait Pattern
Use of bilateral assistive devices such as _____ or _____ is required
uses a simultaneous_______ placement of the AD and patient’s opposite LE
Use of this gait requires ______ (G to normal)
It is relatively ____ and performed more _____ than 4 point gait
Use of bilateral assistive devices such as crutches or canes is required
uses a simultaneous reciprocal forward placement of the AD and patient’s opposite LE
Use of this gait requires better balance (G to normal)
It is relatively stable and performed more rapidly than 4 point gait
Ambulation Patterns
2-Point Gait Pattern
_____ energy expenditure and very similar to normal gait pattern
requires coordination by pt to move one ____ and its opposite ___ forward simultaneously
appropriate for ______ patient affecting both LE
patient can ambulate more ____ but with less ____ than 4 point pattern
Requires Gr___ /5 Illiopsoas
low energy expenditure and very similar to normal gait pattern
requires coordination by pt to move one UE and its opposite LE forward simultaneously
appropriate for antalgic gait patient affecting both LE
patient can ambulate more rapidly but with less stability than 4 point pattern
3/5 illiopsoas
Ambulation Patterns
3-Point Gait Pattern
During forward progression of involved extremity, weight is borne _____ on both crutches and on the affected extremity
____ gait pattern, NWB (amputated leg) is advanced with the crutch
During forward progression of involved extremity, weight is borne partially on both crutches and on the affected extremity
Shadow gait pattern, NWB (amputated leg) is advanced with the crutch
Ambulation Patterns
4 Point Pattern
This pattern provides ___, __ gait as three points of floor contact is maintained
Weight is borne on ______ and typically is used with bilateral involvement due to poor balance, incoordination, or muscle weakness
In this gait pattern, one crutch is _____ and then the opposite LE is _____
This pattern provides slow, stable gait as three points of floor contact is maintained
Weight is borne on both LEs and typically is used with bilateral involvement due to poor balance, incoordination, or muscle weakness
In this gait pattern, one crutch is advanced and then the opposite LE is advanced
Ambulation Patterns
4 Point Pattern
requires use of ______ assistive devices like crutches or cranes
very ____ and performed ____
safest pattern used in crowded areas
low energy expenditure & used to reduce pain in LE from ______ gait or INC balance strategies
disburses weight bearing forces
requires significant amount of coordination and diminishes speed of ambulation
requires use of bilateral assistive devices like crutches or cranes
very stable and performed slowly
safest pattern used in crowded areas
low energy expenditure & used to reduce pain in LE from antalgic gait or INC balance strategies
disburses weight bearing forces
requires significant amount of coordination and diminishes speed of ambulation
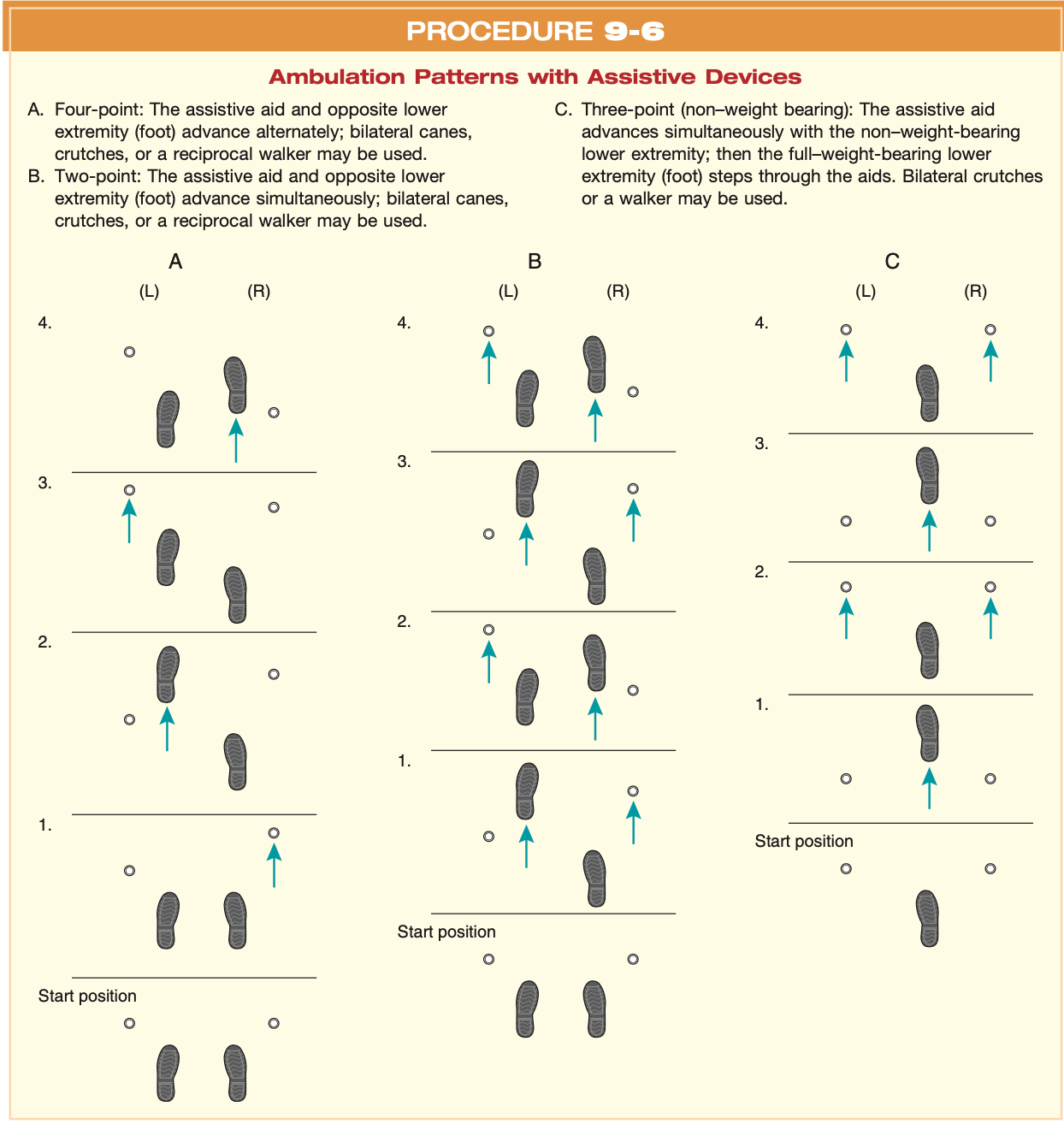
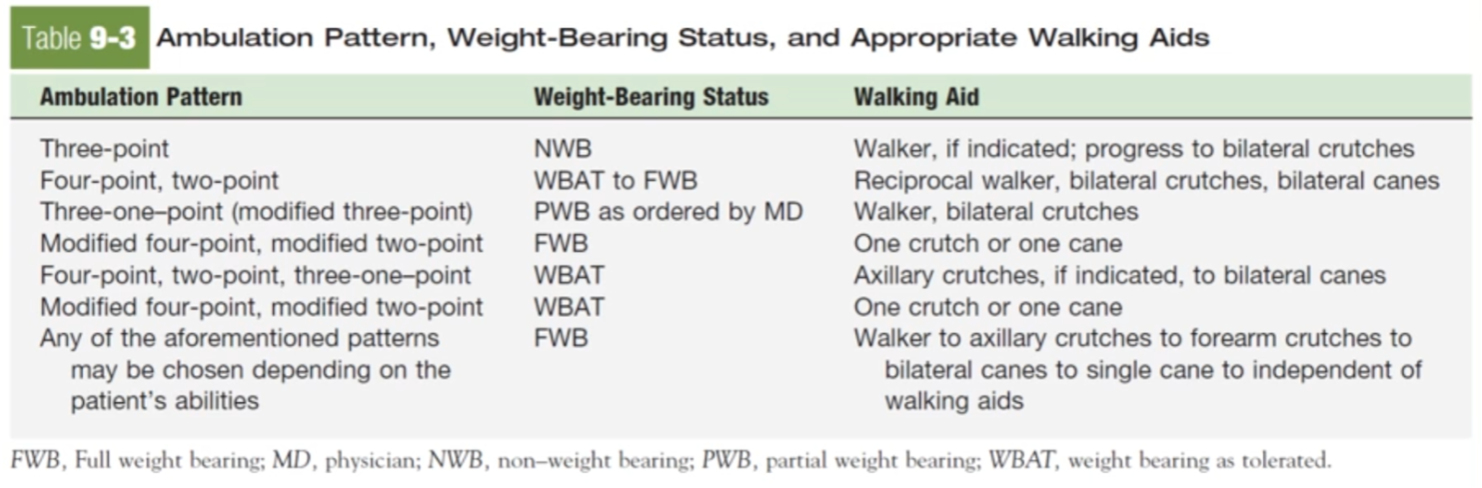
Ambulation Patterns with Assistive Devices
Ambulation Patterns with Assistive Devices—cont’d
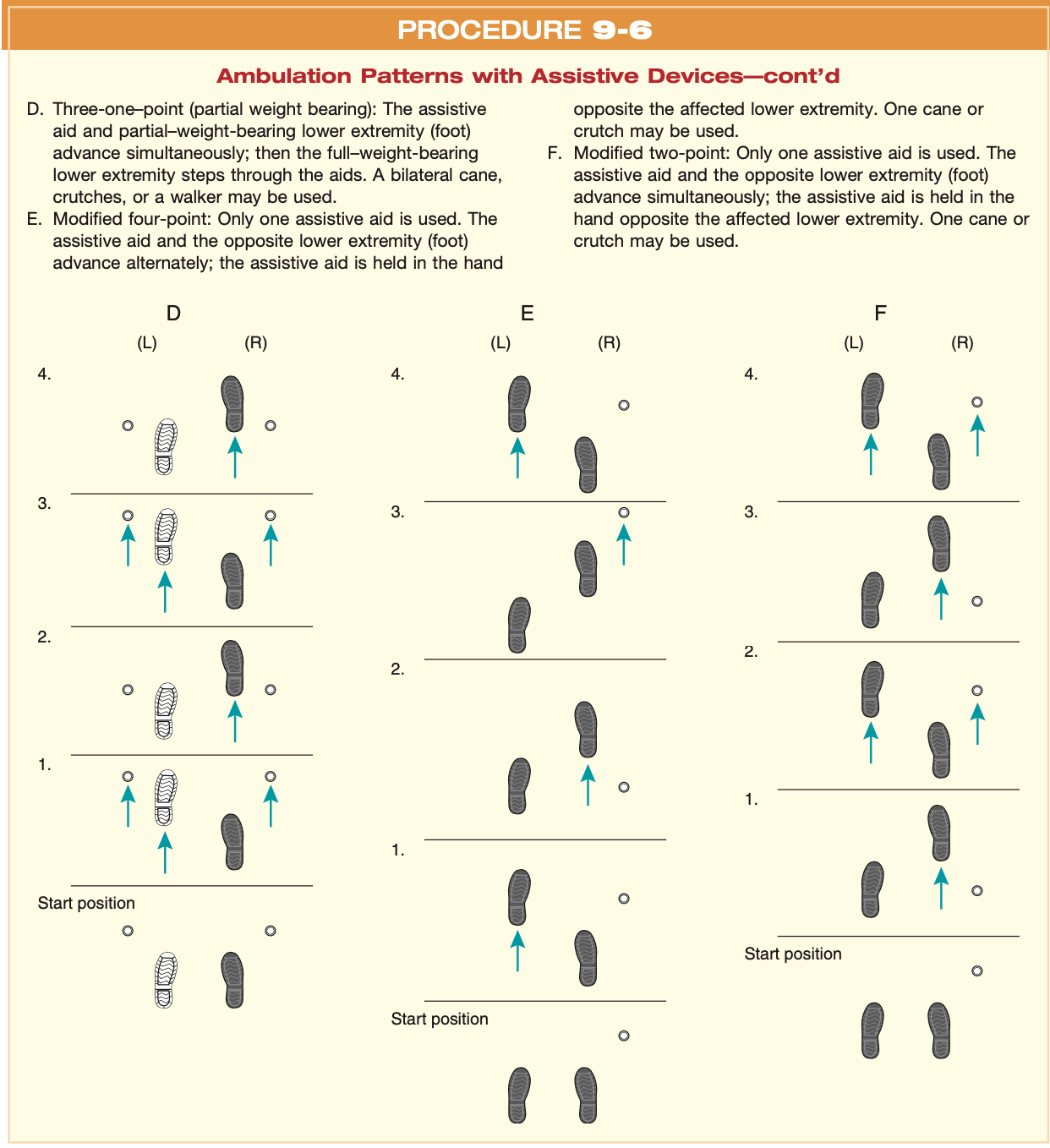
Stair Climbing and Guarding
Ascent = ___________ (steps)
Descent =___________ (steps)
“Good leg goes to heaven, bad leg goes to hell”
uninvolved → AD → involved
AD → involved → uninvolved
“Good leg goes to heaven, bad leg goes to hell”
Guarding ( PT)
Ascent = PT _____ posterolateral to involved side
Descent = PT in _____ posterolateral to involved side
PT behind
PT infront
READ DA TABLE
“Good leg goes to heaven 😇
bad leg goes to hell” 👹