clinical psychology
1/732
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
733 Terms
Echolalia
Psychopathological repeating of words or phrases of one person by another; tends to be repetitive and persistent.
Seen in certain kinds of Schizophrenia, particularly catatonic (CTP).
Echopraxia
Repetition by imitation of the movements of another. The action is not a willed or voluntary one and has a semiautomatic and uncontrollable quality
patient has, affect
mood is what——- and ——-is what clinician observe
gestures,
body movements,
Facial expressions
What do we observe in the body to know the affect in clinic (MSE)
anxious,
irritable,
depressed,
elevated,
euphoric,
euthymic
AIDEEE
Im MSE the quality of affect can be? (6)

Quality
Intensity
Range
.
Reactivity
Congruence with mood and thought/ communicability
appropriateness to context
.
mobility of affect,
Lability/ stability
Diurnal variation
9 Different ways to assess affect in the session?
Diurnal variation of affect
The change in affect occuring with passage of the day. (Worse in morning, Worse in the evening, Worse at night)
Orientation
State of awareness of oneself and one’s surrounding in terms of time, place and person in the clinical set up shows what?
Acceleration of thoughts
When Flow of thinking becomes rapid and increase in amount it is called
Pressure of speech
Detailed under heading of Speech Speed-
Increase in the amount of spontaneous speech, rapid, loud, accelerated speech.
Flight of ideas
Thoughts follow each other rapidly; there is no general direction of thinking; and the connections between successive thoughts appear to be due to chance factors which, however, can usually be understood
Prolixity
‘Ordered flight of ideas’ or excessive wordiness or verbosity in speech or writing? ( too much detail)
is a hallmark symptom of mania, commonly observed in bipolar disorder during manic episodes
Bradypherenia (retardation)
the train of thought is slowed down and the number of ideas and mental images which present themselves is decreased.
Seen in
Parkinson,
dementia
depression
Poverty of speech/ Laconic speech
Restriction in amount of speech used; replies might be monosymbolic..
Circumstantiality
Thinking proceeds slowly with many unnecessary and trivial details, but finally the point is reached

Tangentiality
Refers to replying to a question in an oblique, tangential or even irrelevant manner does reach answer
Goes off-topic and never returns — not intentional
Thought blocking
When there is a sudden arrest of the train of thoughts leaving the patient with a blank mind state, it is called?
Recent memory
Asking what’s your name or what medicine did you eat today is an example of testing what memory
Remote memory
asking when did you pass the graduation or when was your marriage is example of testing what memory in MSE?
Immediate Memory and New Learning
“I am going to ask you to remember three words (color, object, animal – e.g., blue, table, and horse) and I will ask you to repeat them to me in 5 minutes.
This is an example of what assessment in clinic?
form of a thought
The arrangement of parts in a thought is called its?
formal thought disorder
Disturbance in the form of thought are called?
Negative and positive type
Which are 2 types of formal disorder?
Negative type formal disorder
When the patient is looses his previous ability to think and cannot produce a concept, What is the disorder
Positive type formal disorder
When patient produces false concept by blending together incongruous elements that is —- disorder
hallmark diagnostic feature of schizophrenia and (bipolar) mania
Neologism
a newly coined word, phrase, or expression that has not yet become widely accepted or recognized in the language
Eg: "I need to fix my ‘sporkit’ today," and insists it’s a real object.”
Obsessive thoughts
The symptom of Persistent and recurrent intrusive thoughts that cannot be eliminated from consciousness by logic or reasoning.
Rumination
repetitive thinking or dwelling on negative feelings and distress and their causes and consequences. and this is less intrusive
Compulsion
Obsessional motor acts are called?
Thought alienation
Patient has the experience that his thoughts are under the control of an outside agency or that others are participating in his thinking
Hallucination
A false perception which is not a sensory distortion or a misrepresentation, but which occurs at the same time as real perceptions. (Jasper).
Stereotypy/ excitement
Symptom commonly seen in Autism, where patient shows repeated actions like rocking, flapping hands etc without any clear goal. it doesn’t change as the environment changes non-goal directed action, which is carried out in a uniform way (Fish);
Aphasia
A language disorder that affects a person's ability to communicate.
Alogia
Significant reduction in the amount of speech , often characterized by brief, concrete responses and a lack of spontaneous elaboration due to impaired thinking
Seen in schizophrenia as a negative symptom
Diffidence
an extreme lack of self-trust or self-confidence and is expressed as shyness or hesitancy to express oneself?
Seen in Avoidant PD, Social anxiety etc.
Defiance
stubbornly hold to socially unacceptable beliefs and practices simply because these beliefs and practices are unacceptable to the self.
Regression
psychoanalytic defense mechanism in which an individual faced with anxiety retreats to a more infantile psychosexual stage, where some psychic energy remains fixated
Repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness
phenylketonoria/ PKU
A human metabolic disease caused by a mutation in a gene coding (recessive gene by both parents) causes the genetic inability to metabolize the amino acid phenylalanine leads to accumulation of phenylalanine and mental retardation if not treated
Trait anxiety
a stable personality characteristic showing the tendency to feel consistently worried, nervousness, anxious across various situations.
Cystic fibrosis
A genetic disorder that is present at birth and affects both the respiratory and digestive systems.
Hydrophobia
Fear of water
Tay sachs
a fatal genetic disease that causes fatty material to build up in the nerves and brain
Spatial neglect
Condition where individuals have difficulty attending to or noticing stimuli on one side of space, typically due to brain damage or stroke.
It can affect perception, attention, and awareness.
commonly caused by damage to the right hemisphere of the brain,
Individuals may miss objects on their neglected side, have trouble judging distances, and experience difficulties with spatial orientation
Right visual field: able to name but not recognise
Left visual field: can recognise but can’t name since there is no communication b/w left and right
What will the response of split brain patient when objects are shown in right and left visual feild?
Split brain
A structure known as the corpus callosum connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain and enables communication between them.
Dysfunction or absence of this structure can result in a condition known as?
Labile affect
Rapid changes/Fluctuation in emotions that are often exaggerated or inappropriate in intensity.
It is commonly seen in conditions such as bipolar disorder, borderline personality disorder, and certain neurological disorders.
Self defeating personality disorder/
Masochistic Personality disorder
A proposed personality disorder characterized by patterns of self-sabotaging behavior, may resist success or reject help, ultimately hindering their own progress.
included in appendix of DSM-III-R but later excluded for it’s conceptual overlap with BPD and DPD
Avoidant personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by anxiety in social situations and personal relationships, with feelings of inadequacy and extreme sensitivity to rejection or criticism.
Dependent personality disorder
A personality disorder where the affected often feel helpless, submissive and incapable of taking care of themselves.
pattern of submissive and clinging behavior related to an excessive need to be taken care of.
Boarderline personality disorder
A personality disorder characterised by pervasive pattern of impulsivity, personal unstable relationship, trouble with self image and affect
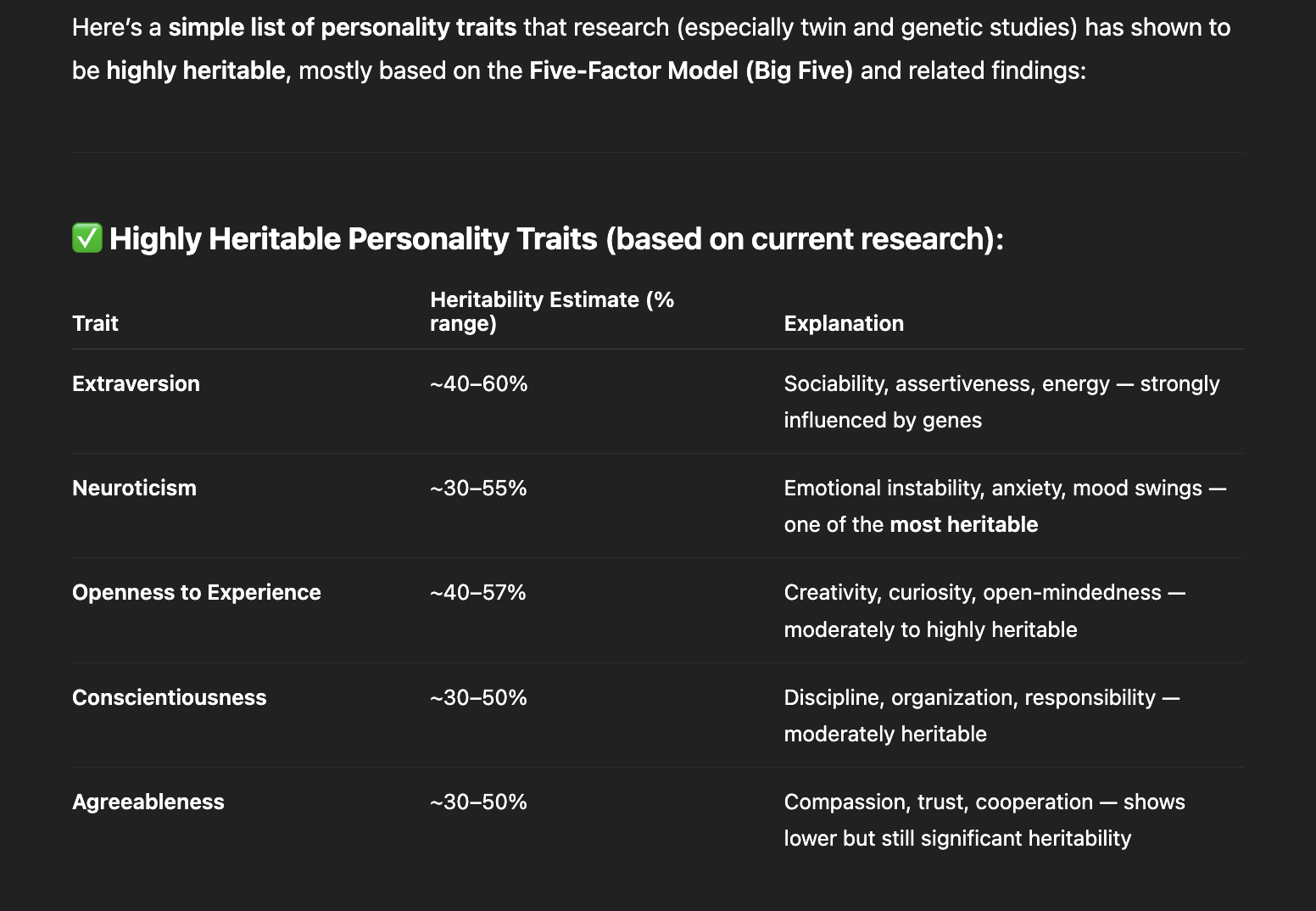
Extraversion
One personality trait that is thought to be highly heritable is?
5 chromatic 5 achromatic
How many chromatic and achromatic in rorschach cards?

Anthropometric measurement
Noninvasive quantitative measurements of the body is generally called?
Thought insertion
in schizophrenia involves somehow experiencing one's own thoughts as someone else's. thoughts being controlled or inserted into their mind by an external force or entity.
Thought withdrawal
the delusion that thoughts have been taken out of the patient's mind. It often accompanies thought blocking. The patient may experience a break in the flow of their thoughts believing that the missing thoughts have been withdrawn from their mind by some outside agency.
Thought broadcasting/ Thought diffusion
A delusion that before we talk about what we think, everybody knows it. Everybody has access to the thought
Thought insertion,
Thought withdrawal,
thought broadcasting
What are types of thought alienation ?
(symptom of psychosis where individuals experience a loss of control over their thoughts)
Schneiderian first-rank symptom/ first-rank phenomena/ first rank symptom / FRS
- - - - symptoms are considered important in the diagnosis of schizophrenia because they are highly specific to psychotic disorders and are less likely to occur in other psychiatric conditions.
Schneiderian first-rank symptom/
first-rank phenomena/ first rank symptom /
FRS
Any form of thought alienation is a ———symptom, highly indicative of schizophrenia.
Eudemonia
A state of well-being encompasses a sense of purpose, fulfillment, and optimal functioning across various domains of life focusing personal growth, virtue, and fulfilling one's potential.
hedonic wellbeing
The wellbeing and the type of happiness or contentment that is achieved when pleasure, satisfaction of desires, and self-interests are obtained and pain is avoided.
pleasure, meaning/Virtue)
Hedonic is something that pursues —- to achieve happiness. Eudaimonic is something that pursues —— to achieve happiness long term.
Hedonic
Maximizing pleasure
Prioritize enjoyable experiences
Short-term gratification are examples of —— well being
emotional wellbeing
What focuses on emotions and feelings and Refers to the state of one's emotions, including happiness, contentment, and ability to manage stress and challenges effectively.
emotional wellbeing
a good Emotional regulation, stress management, positive emotions, coping strategies are examples of —- wellbeing
Social wellbeing
- —— well being focuses on social Relationships and social connections and refers to the quality of relationships, social support networks, and sense of belonging in communities or groups.
Psychological wellbeing
what well being refers to overall mental health and resilience, including self-esteem, purpose in life, personal growth, and sense of autonomy and control.
Psychological wellbeing
What is the term of wellbeing given to 'autonomy or being determining, independent and able to resist social pressures to think and act in certain ways ?
Auditory, olfactory, tactile, visual, Gustatory
What are the primary modes of hallucination
Thought echo,
Third person voice (voice talking about the person)
running commentary
What are the 3 common types of auditory hallucination occurring in psychosis (schneiderian first rank symptoms)
Somatic passivity
The belief that outside influences are playing on the body. The patient is a passive and invariably a reluctant recipient of bodily sensations imposed upon him by some external agency
Volition
What do one check in MSE about how a person feels about the actions and behaviours related to their body
Made act
The patient has a cognitive beleif that he experiences his actions as being completely under the control of an external influence. The movements are initiated and directed throughout by the controlling influence, and the patient feels he is an automaton, the passive observer of his own actions.
Made affect
When a patient feels whatever they are feeling is putting by some external source
Made impulse
The distorted cognitive belief of a patient that the impulse to carry out some action is not felt to be his own, but the actual performance of the act is admitted to be the patient’s own.
Insight
What is the patient’s current awareness about their condition is called—— in MSE
delusion of reference
The delusion says neutral or unrelated events, objects, or actions in the environment are somehow specifically directed at them or have a special significance related to them personally.
Agoraphobia
fearing and avoiding places or situations that might cause panic and feelings of being trapped, helpless or embarrassed.
Agoraphobia (inescapable situation)
- shares more kinship with panic disorders than phobic disorders
Anomia
The inability to name objects is called?
primary affected area is left Temporal lobe
Acetylecholine
Most current Alzheimer’s treatment are done by altering levels of ——
Personality and psychological disorders
MMPI measures?
test to measure intelligence of recruits
Clinical psychologies major contribution to WW1 (World war 1) was?
Grade 1- complete denial of illness
Grade 2- Slight awareness but denying at the same time.
Grade 3- illness due to external or physical factors.
Grade 4- due to something unknown in self.
Grade 5-Intellectual insight
Grade 6 - Emotional insight
What are different 6 levels of insight scale in MSE?
Grade 5/Intellectual insight
awareness of being ill and that the symptoms are due to own particular irrational feelings/ thoughts; yet doesn’t apply this knowledge to the current/ future experiences.
Eg: A person is chronic smoker, know it is not good for family or them but does not really take action to stop it.
Grade 6/ emotional insight
When a patient’s awareness of their own motives and deep feelings leads to a change in their personality or behaviour patterns, what do we call it?
It is the deeper level of understanding of the problem with due motivation to bring about a positive change in behaviour or personality.
Catatonic negativism
The tendency to actively resist or oppose suggestions, instructions, for movements.
no neurological reason but a behavioural response only
sometimes doesn’t follow commands (passive) sometimes actively do the opposite to show resistance( active)
Verbigeration
This involves obsessive repetition of meaningless word or phrases without any stimulus.
Associated with schizophrenia and other thought disorders
eg: utter nonsensical syllables or such as “dog cat ate car work,” without any coherent meaning.
Automatic obedience
A psychomotor symptom and tendency to comply with commands without true understanding or volition. A classic symptom of catatonia
Patients may follow commands but without any apparent awareness or intention.
Waxy flexibility
A psychomotor symptom in catatonia where a person’s limbs remaining in a position for an unusually long time after being placed there by someone else.
limbs show slight resistance when moved but can be easily positioned and will maintain that position until moved again.
Perseveration
A self initiated involuntary repetition or continuation of a behavior or thought pattern beyond its original context or purpose starting as a response to some cue.
Kempt and tidy
MSE word for Trimmed (beard) & combed (hair) Orderly and neat in appearance. Usually found in normal individuals, Obsessive Compulsive personality disorder.
Overtly made up
What do we write in MSE if we observe Exaggerated concern or preoccupation with appearance and dress.
found in
Mania/Hypomania;
Histrionic and Narcissistic personality disorder;
some cases of Schizophrenia.

Sickly/
Neglected appearance under general appearance scale
Term in MSE Refers to a patient who looks ill or has complete neglect of his health. This may be found in Substance abuse disorders, severe and long-standing Dementia.
Perplexed
A confusional state in which a patient has inability to decide on a task, state of confusion, bewilderment, or an inability to make sense of one's surroundings, experiences, or thoughts. or a solution, is noted as what in MSE?
often seen in
psychotic disorders,
delirium,
dementia,
severe anxiety or dissociation.
cooperative
Helps the examiner conduct the interview smoothly.
Attentive: Patient pays attention to the interviewer. It is a normal response. then the patient can be noted as?
Defensive
It is the kind of behaviour that turns the examiner’s attention away from one’s deficiencies, or behavior that might cause him guilt or embarrassment. Seen in Paranoid Schizophrenia, Delusional disorder.
Frank/
Cooperativeness and Openness
This behaviour helps to conduct an open conversation that includes all the deficiencies without guilt or embarrassment.
hostile
What is characterized by behaviour of covert aggression, tends to create strong negative feelings or anger in the examiner or towards the examiner.
Seen in Paranoid Schizophrenia, Antisocial personality disorder