type I diabetes mellitus
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
what is type I diabetes mellitus?
inability to produce or secrete insulin
which age group does TIDM usually present in?
children and adolescents
where is insulin produced and secreted from?
beta cells in the islets of langerhans
what happens to the beta cells in T1DM?
destroyed
when does hyperglycaemia usually occur in terms of beta cell destruction?
when up to 90% of the beta cell mass has been destroyed
what is thought to be the main reason for beta cell destruction?
autoimmunity
what is the main auto-antibody identified in pts with TIDM?
anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (anti-GAD)
what type of hypersensitivity reaction is T1DM?
IV
what are the genetic associations with TIDM?
certain human leucocyte antigens (HLA)
- DR3
- DR4
(remember 4-3=type 1 diabetes)
what other autoimmune conditions are associated with TIDM?
- autoimmune thyroid disorders
- coeliac
- addison's
- pernicious anaemia
what is thought to trigger onset of the autoimmune attack of the beta cells?
external triggers:
- viral infections
- vit D deficiency
how is insulin activated?
from proinsulin cleaved into insulin and C-peptide
what stimulates insulin release from pancreas?
- increased blood glucose
- glucagon-like peptide (GLP) from L cells in small intestine
what are the functions of insulin?
- increases glycogenesis and glycolysis
- inhibits gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
- increases glucose uptake in peripheral tissues
- decreases lipolysis
- increases fatty acid and triglycerol synthesis
- increases protein synthesis
- decreases protein degradation
which hormones counter-regulate insulin action?
- glucagon
- adrenaline
- growth hormone
- cortisol
what do counter-regulatory hormones do?
- promote glucose production in liver
- inhibit peripheral uptake of glucose
what does a decrease in insulin from TIDM lead to?
- increase rate of glucose production in liver
- reduced peripheral glucose uptake
= hyperglycaemia
what happens as this blood gets to the kidneys?
osmotic diuresis
what does osmotic diuresis cause?
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- dehydration
- electrolyte derangement
what is polydipsia?
extreme thirst
what else can the decreased peripheral glucose uptake cause?
increase muscle and fat breakdown = weight loss
as the body cannot use glucose as an energy source what does it resort to?
fatty acids
what happens to the fatty acids?
taken up by hepatocytes and converted into ketone bodies
what happens to the ketone bodies?
released back into circulation
what is the process of metabolising fatty acids called?
ketosis
what can excess ketosis lead to?
metabolic acidosis (diabetic ketoacidosis)
what can high circulating ketones lead to?
vomiting - which further exacerbates dehydration and electrolyte derangement
what happens as the acidosis becomes more severe?
pH-dependent enzyme systems fail
what happens in diabetic ketoacidosis if left untreated?
potentially fatal:
- acute kidney injury
- cerebral oedema
- acute respiratory distress syndrome
what is it called when T1DM develops in adulthood?
latent-onset autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA)
what are the symptoms of T1DM? (5)
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- weight loss
- vomiting
- lethargy
what are the signs of T1DM? (2)
- mild-moderate dehydration
- BMI<25 (adults)
what is the diagnostic investigation for T1DM?
either:
associated signs and symptoms and 1 abnormal random blood glucose reading
OR
2 abnormal random blood glucose reading
what random blood glucose level would indicate diabetes?
>11.1mmol/L
what investigations are done for T1DM?
autoantibody testing
which autoantibodies can be tested for? (4)
- islet cell antibodies (ICA)
- glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)
- insulin antibodies (IAA)
- IA-2 antibodies
what further testing can be done?
c-peptide
what are the levels of c-peptide in T1DM?
low
what should you test for in pts >60 presenting with new-onset diabetes?
pancreatic cancer - CT/MRI
what is the main management of T1DM?
life-long exogenous insulin
what are the other features of T1DM management? (4)
- blood glucose monitoring
- treatment targets
- monitoring for complications
- education
how is exogenous insulin usually administered?
subcutaneously
what are some types of exogenous insulin? (5)
- rapid-acting
- short-acting
- intermediate-acting
- long-acting
- mixed (short and intermediate)
what is an example of rapid-acting insulin?
novorapid
what is an example of short-acting insulin?
humulin R
what is an example of intermediate-acting insulin?
humulin N
what is an example of long-acting insulin?
lantus
what is an example of mixed insulin?
humulin 70/30
what are the three main insulin regimes for T1DM?
- basal-blous
- one, two or three injections per day
- continuous insulin infusion via a pump
what is the basal-bolus regime?
- rapid- or short-acting insulin before meals
- long-acting preparation for basal requirements
what is the one, two or three injections per day regime?
using both short-acting and intermediate-acting insulin multiple times a day
what is the continuous insulin infusion via a pump regime?
- rapid- or short-acting insulin throughout the day
when would the continuous insulin infusion via a pump regime need to be used?
when pts are experiencing hypoglycaemic episodes with the other regimes
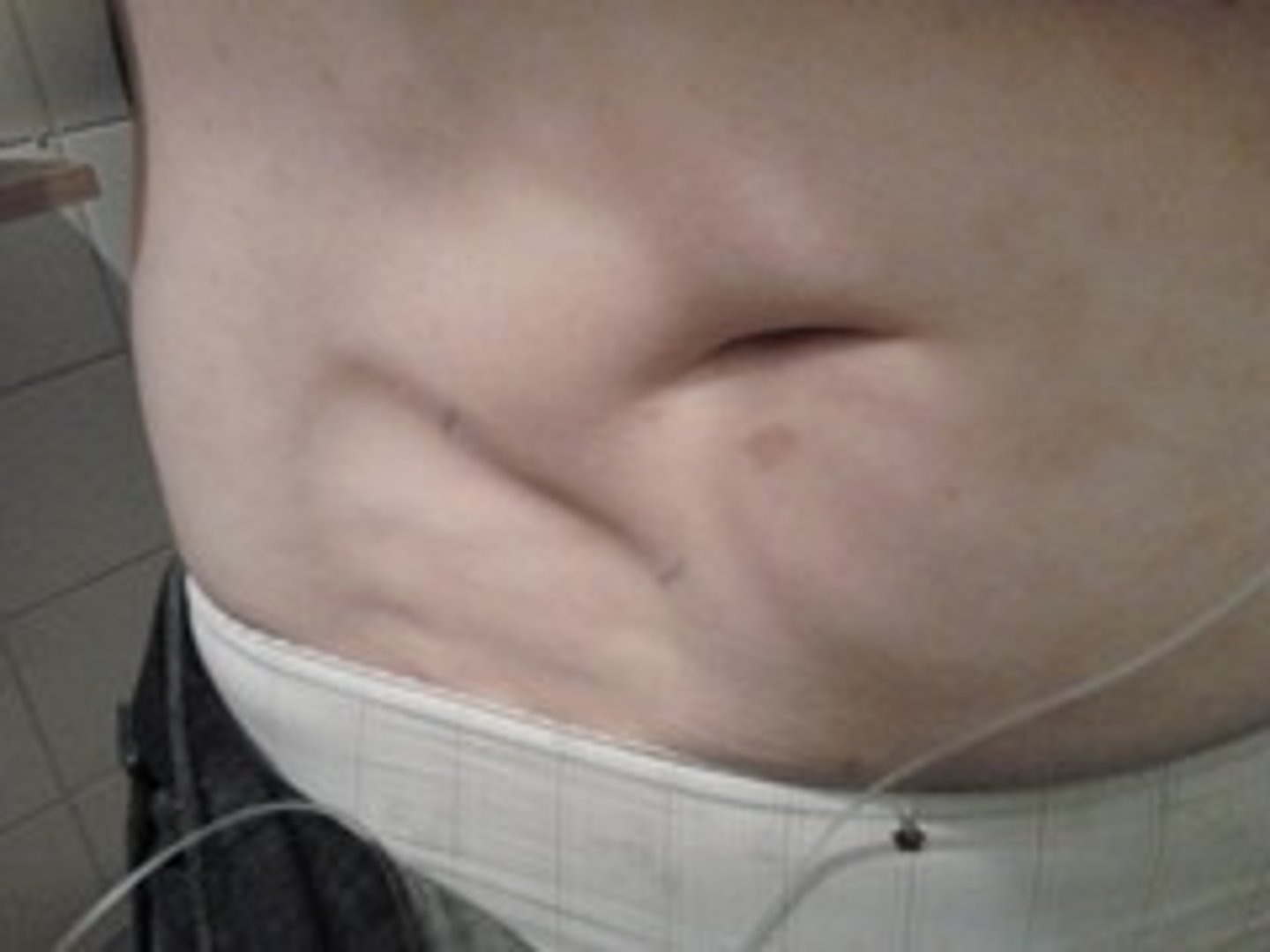
what can ongoing insulin injections given in the same place cause?
lipodystrophy
what is lipodystrophy?
atrophy of subcutaneous tissue (lumps)
what are the other side effects of insulin therapy?
- weight gain
- hypokalaemia
- hypernatraemia
how does insulin cause hypokalaemia and hypernatraemia?
stimulates the Na+/K+ ATPase pump
(think about treatment for hyperkalaemia)
what is used to monitor blood glucose?
CGM - continuous blood glucose monitoring
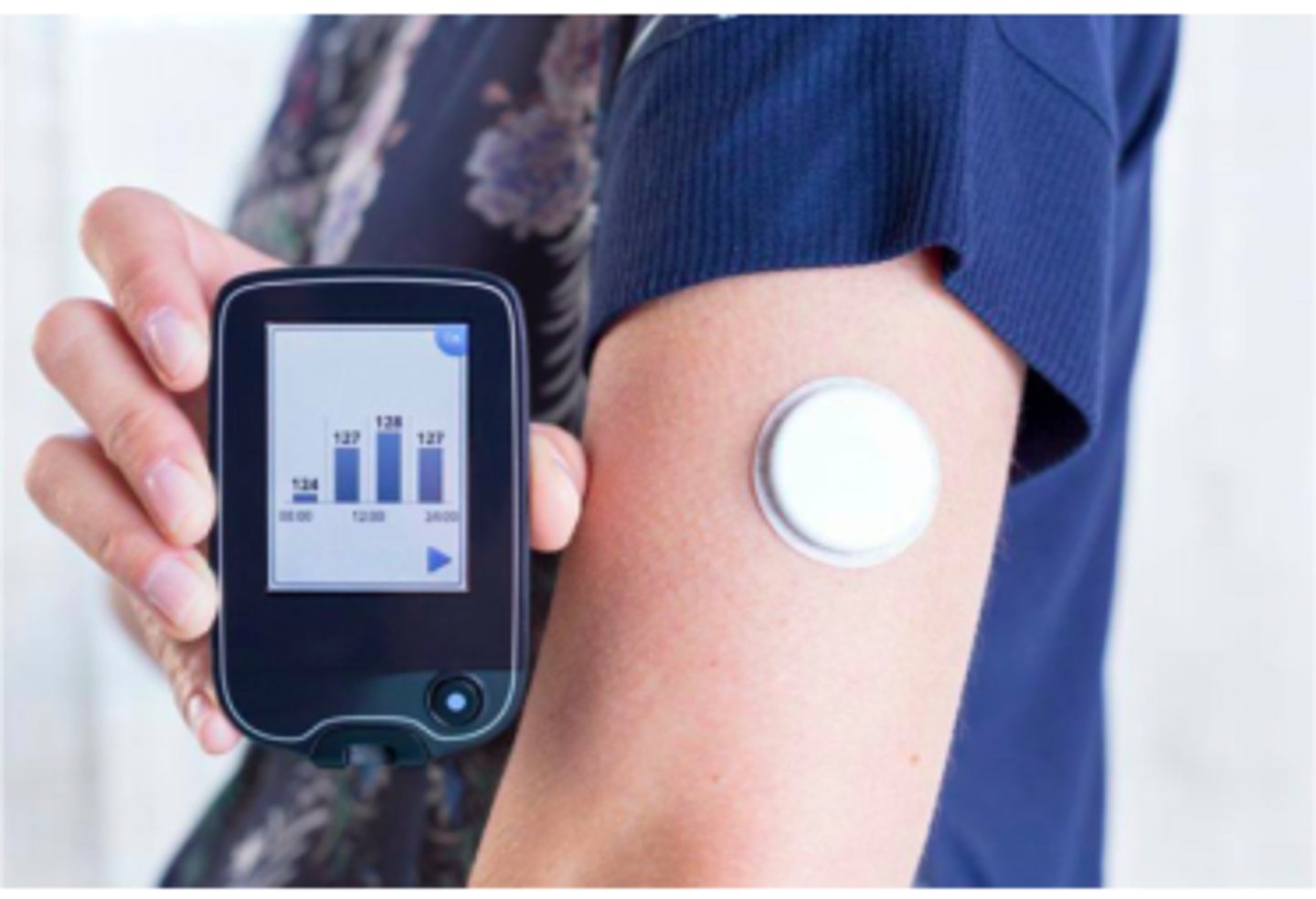
what are the two types of CGM?
- real-time continuous CGM
- intermittently scanned CGM
what is real-time continuous CGM?
latest blood sugars automatically recorded and shown on a mobile device
what is intermittently scanned CGM?
a recording is made only when you scan a device over a sensor
what is the option for pts who do not want to use a CGM?
traditional capillary finger prick glucose - 4 times a day
what is the blood glucose target for waking up?
5-7mmol/L
what is the blood glucose target for before meals?
4-7mmol/L
what is the blood glucose target for after meals?
after 90 minutes - 5-9mmol/L
how is long-term blood glucose measured?
HbA1c
what is HbA1c measuring?
glycated haemogobin - average of over the past 3 months
what is the target HbA1c?
<48mmol/mol (6.5%)
what programme aims to educated pts with T1DM about calculating their insulin levels correctly?
The Dose Adjustment For Normal Eating (DAFNE) programme
how often do pt with T1DM need a review?
annually
what is recommended for pts with T1DM and BMI ≥ 25?
metformin