Motion Graphs
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
motion
when an object's distance from another object is changing
reference point
a place or object used as comparison to tell if motion has occurred
speed
the distance traveled in a certain amount of time
velocity
speed in a certain direction
acceleration
the rate at which velocity changes (how fast you change velocity)
instantaneous speed
speed at that moment (how fast you are going right now)
average speed
the TOTAL distance traveled in the TOTAL time it took, even thought you may have gone faster or slower)
constant speed
speed that does not change
m/s2
the unit for acceleration
time
this is on the x-axis on a velocity graph
distance
this is on the y-axis on a velocity graph
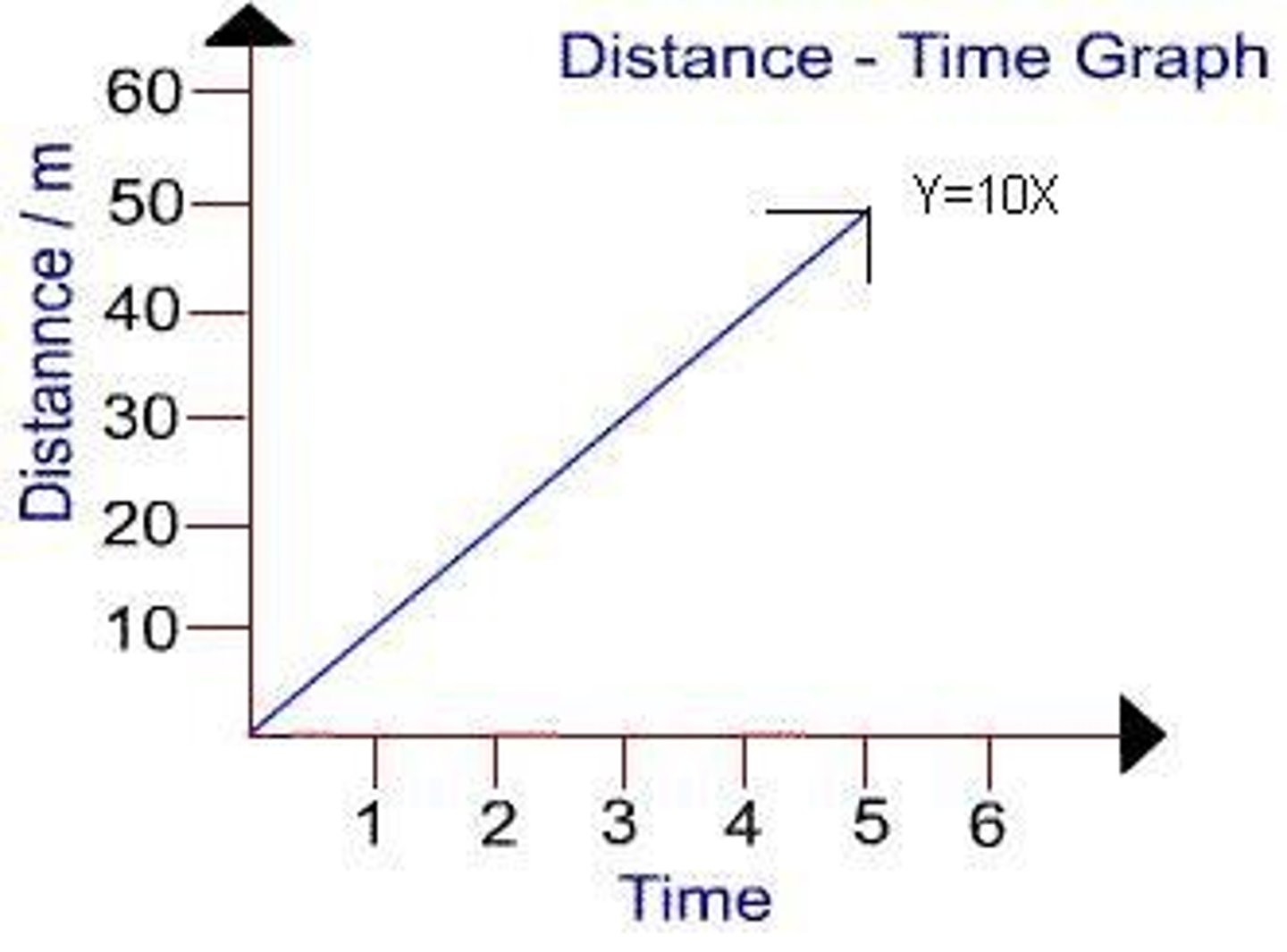
10 m/s
what is the velocity of this object?
b
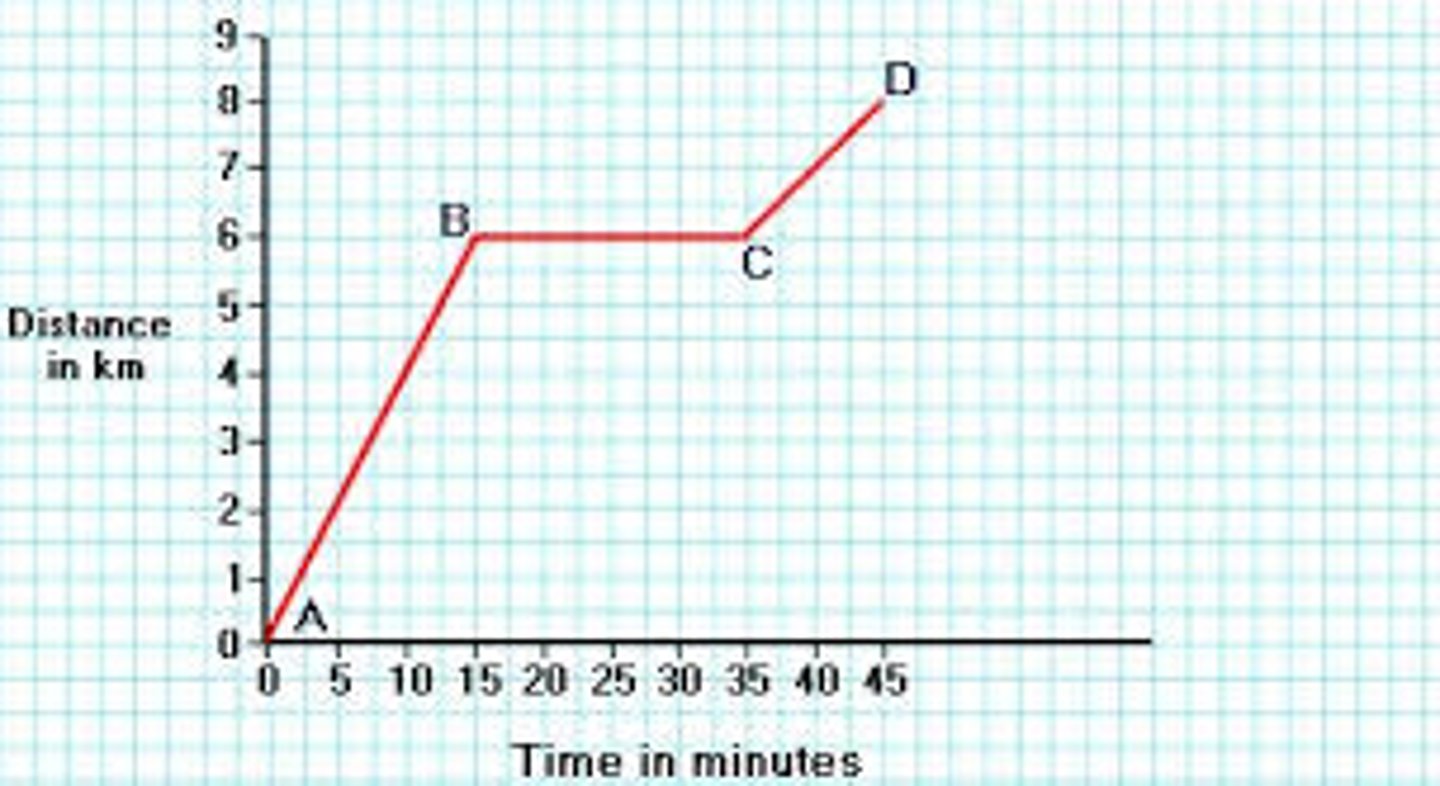
Shows the object has stopped moving
a. A-B
b. B-C
c. C-D
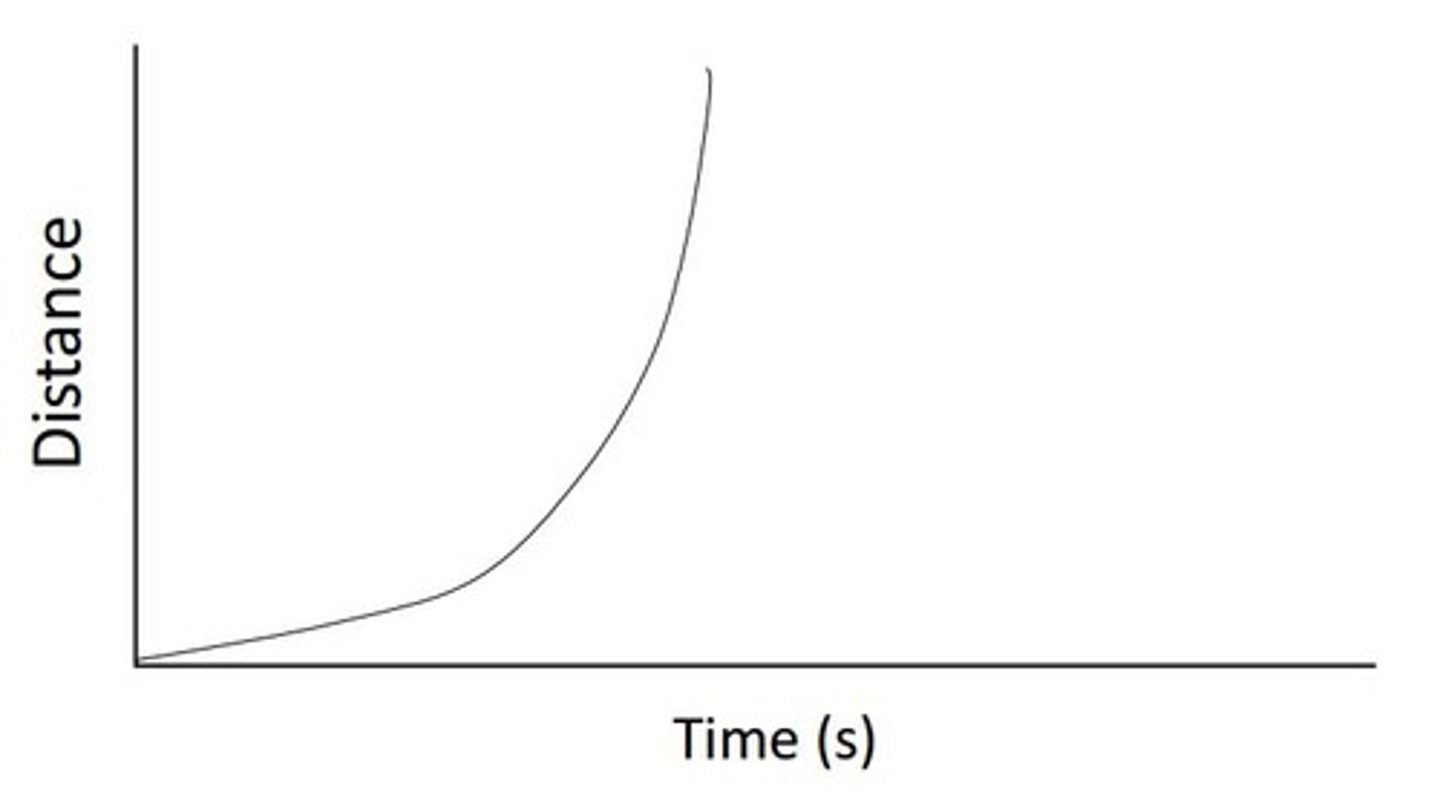
a
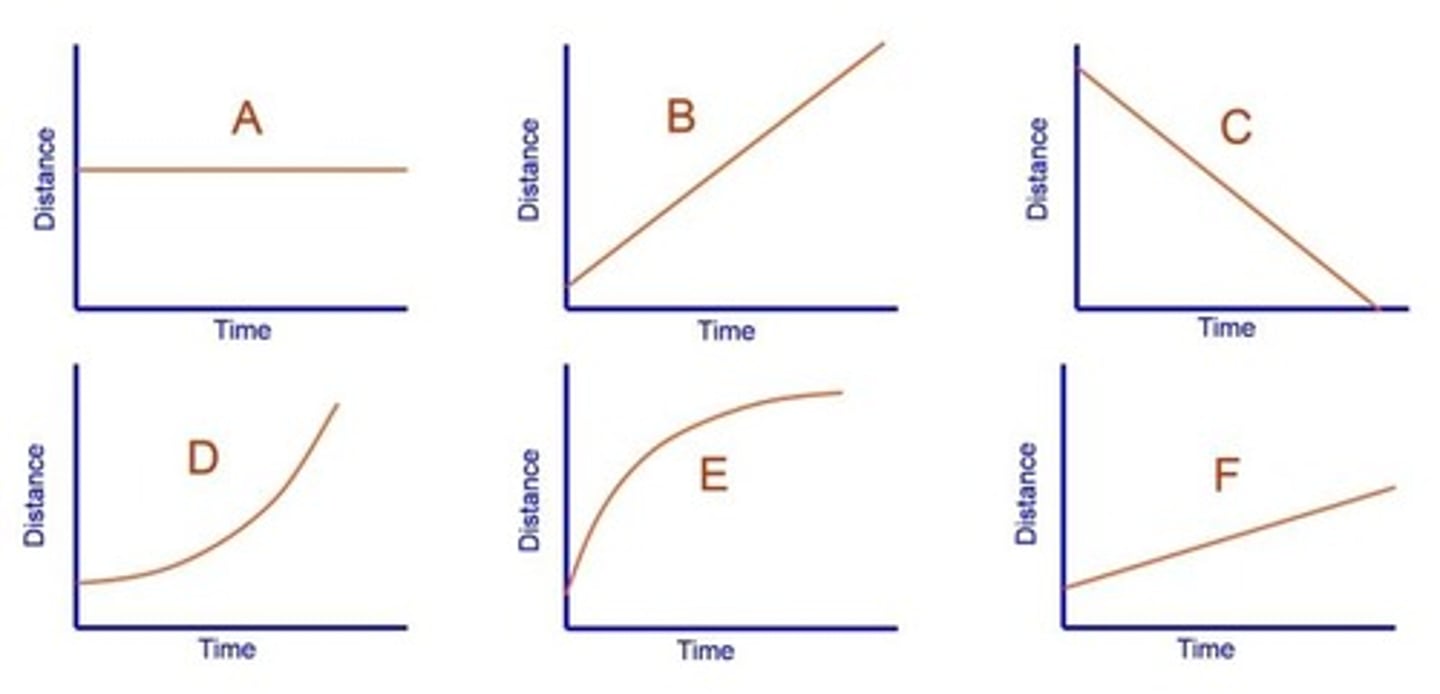
This line shows that the object is:
a. increasing speed
b. decreasing speed
c. going constant speed
d. changing direction
instantaneous speed
This tells your:

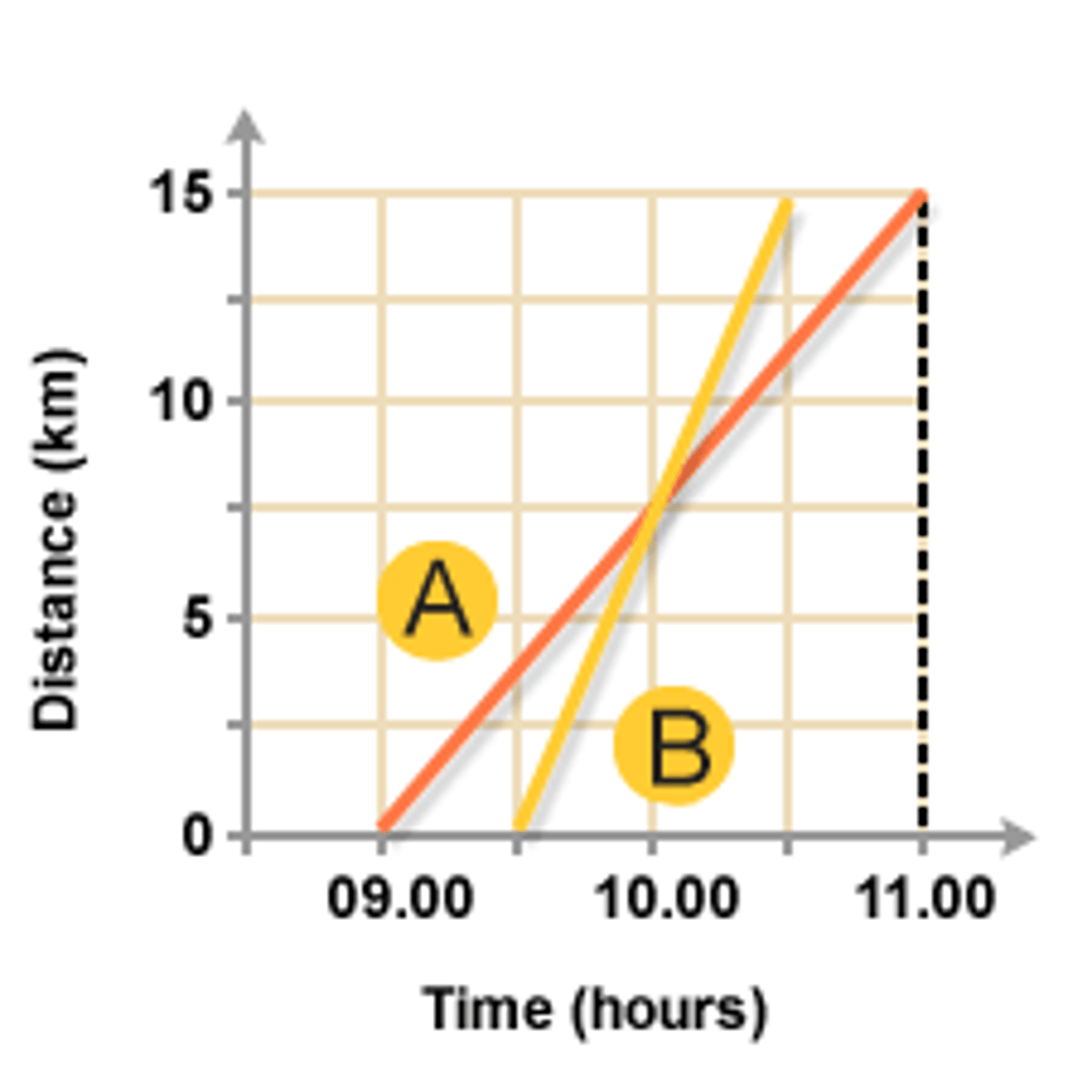
10
At what hour are A and B in the same place at the same time?
c
What does vi stand for in this equation?
a. integral velocity
b. instantaneous velocity
c. initial velocity
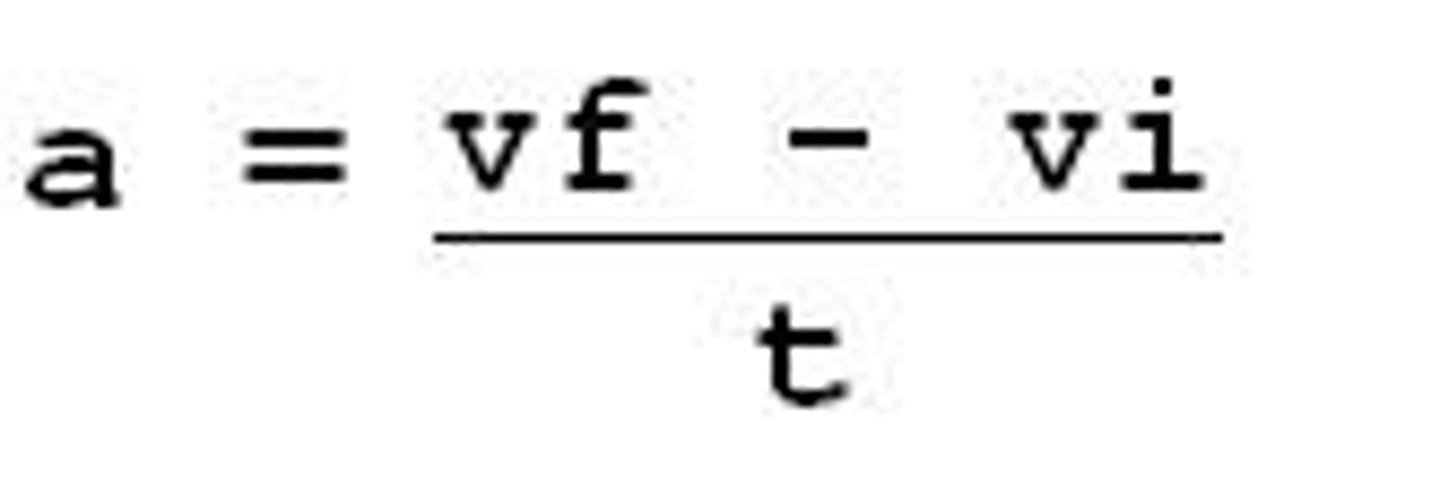
speed up, slow down, change direction
Three ways to accelerate are:
d
How can an object moving at constant speed be accelerating?
a. it can stop
b. it can be staying at the same speed
c. it can be slowing down
d. it can be turning

velocity
What is this formula used to calculate? d/t
b
Why is this car accelerating?
a. It is decreasing speed
b. It is increasing speed
c. It is stopped
d. It is going constant speed
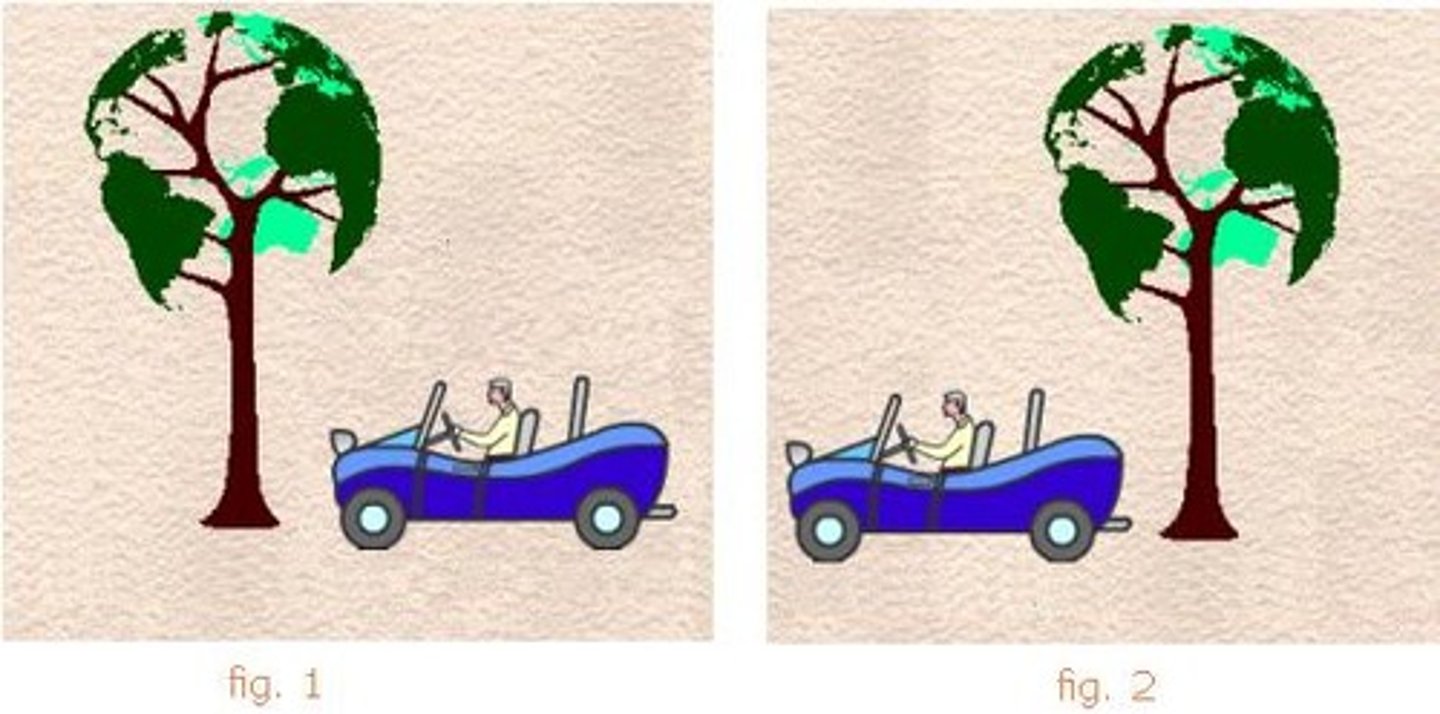
reference point
To tell if the car is in motion you use the tree as a:
add them
To find the resultant velocity of two objects moving in the same direction you:
subtract the smaller velocity from the larger velocity
to find the resultant velocity of two objects moving in opposite directions you:
60 m/s north
An action hero is running on top of a train traveling at 55m/s north. If our hero is moving
toward the front of the train at a speed of 5 m/s, what is our hero's resultant velocity?
4 m/s2
You take a shopping cart that is not moving and race it down the grocery isle at 10 m/s
in 2.5 seconds. What is your acceleration?
11 m/s north
A river flows at a speed of 12 m/s from north to south. A powerboat can move at a speed of 23 m/s. What is the resultant velocity of the boat traveling against the current)?
35 m/s south
A river flows at a speed of 12 m/s from north to south. A powerboat can move at a
constant maximum speed of 23 m/s What is the maximum velocity of the boat if it goes WITH the current?
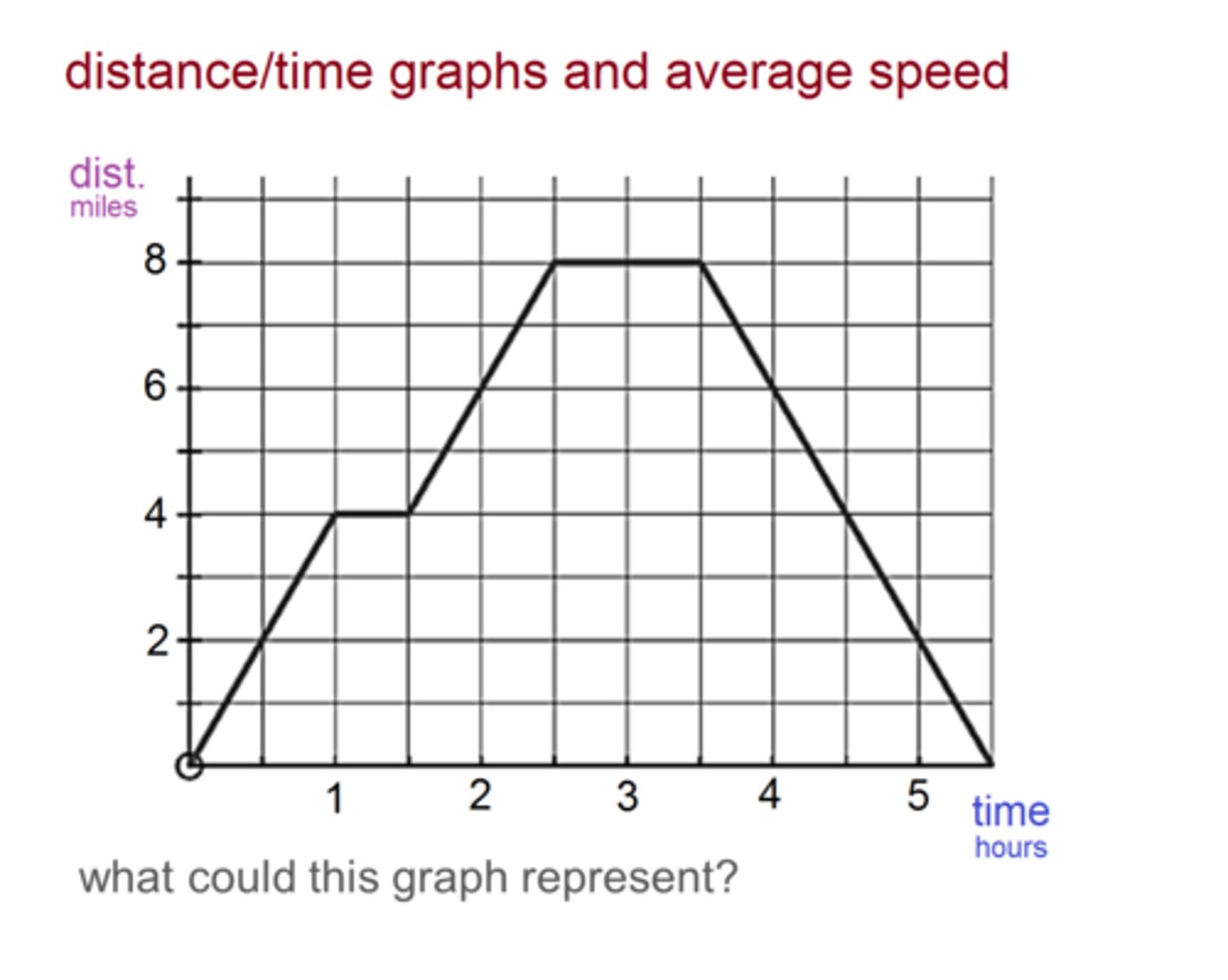
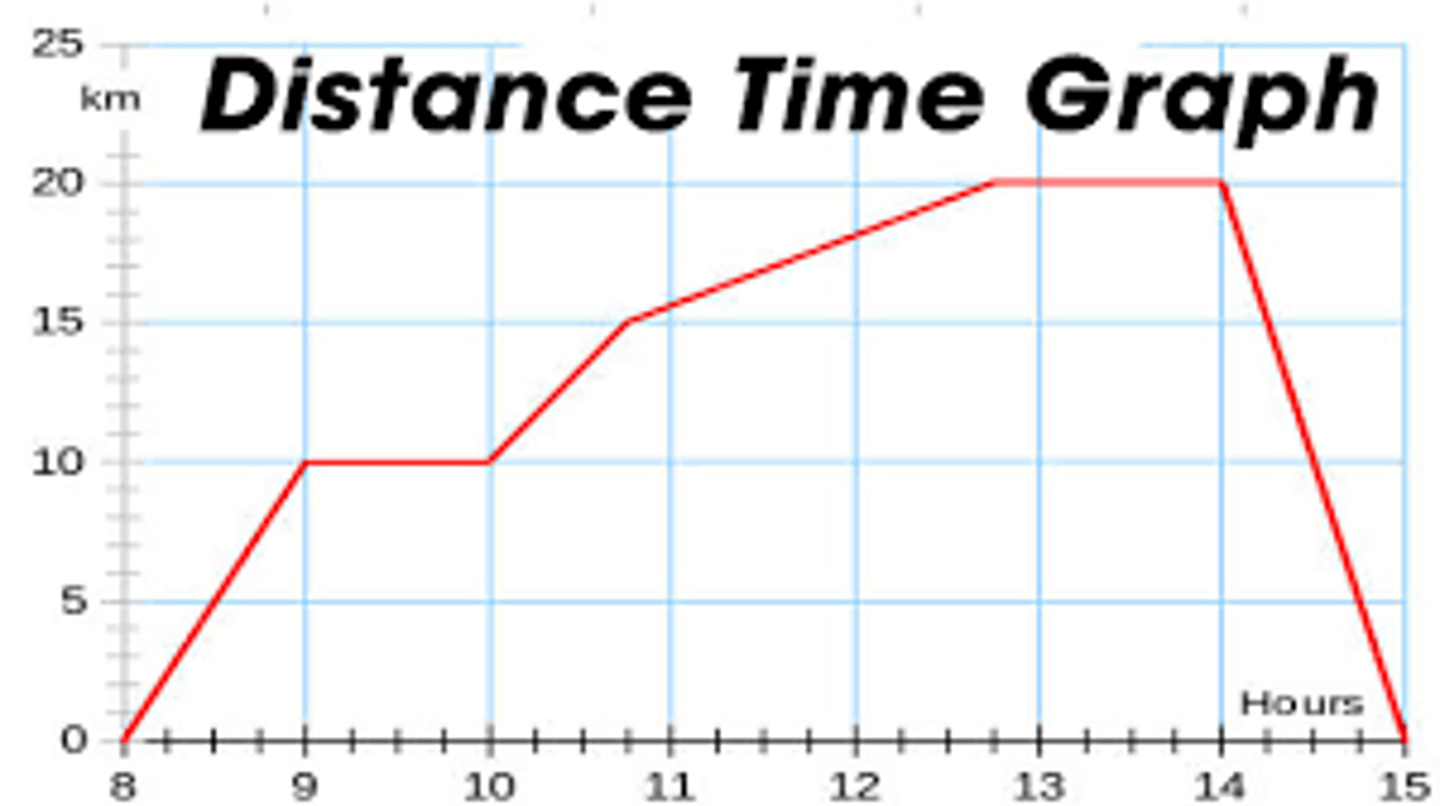
1.5 hours
What is the total time that this object was stopped?
a
When is this object moving the slowest while still moving?
a. A-B
b. B-C
c. C-D
d. E-F
d
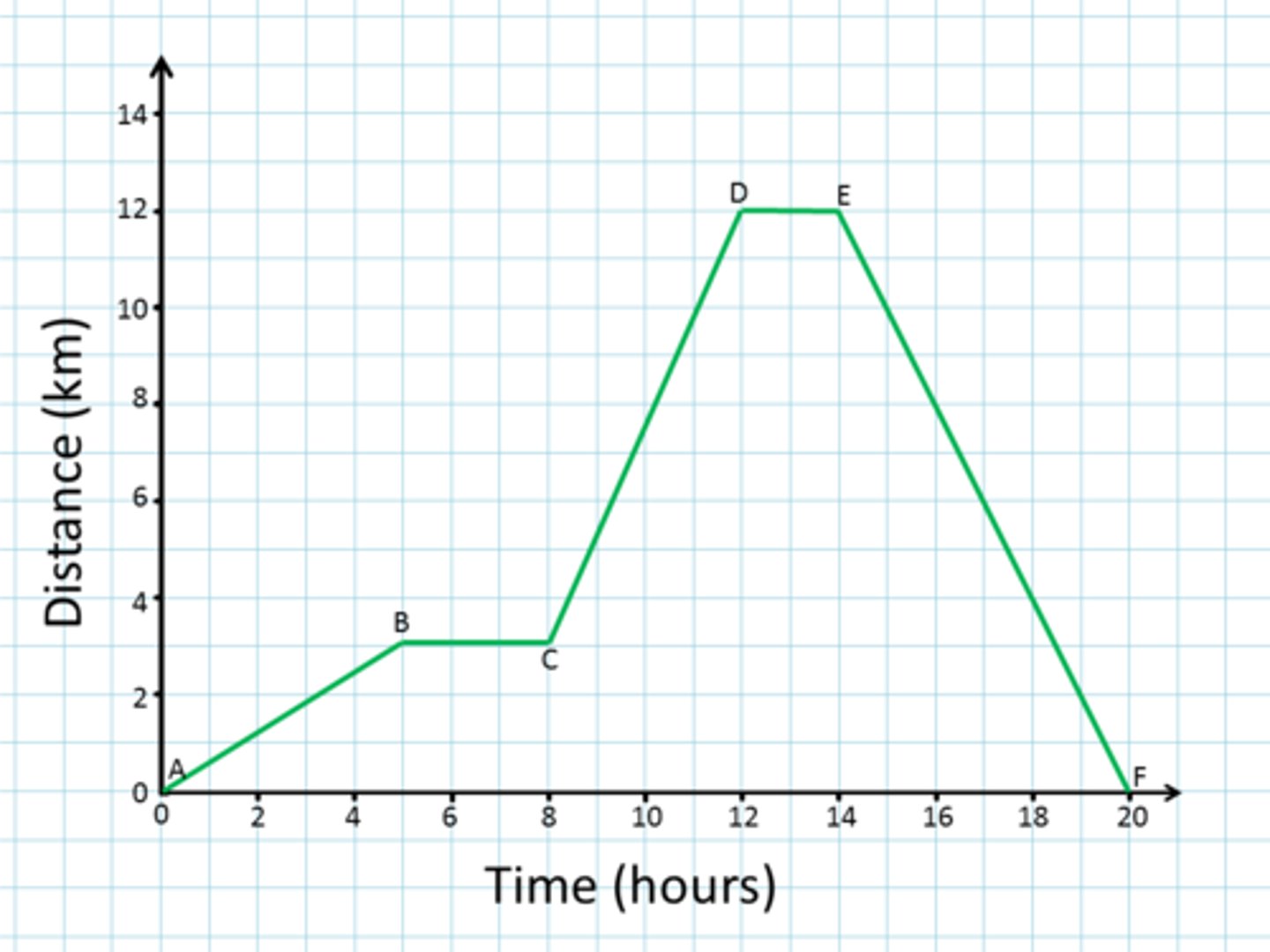
Which graph(s) show acceleration?
a. F
b. D
c. B & C
d. D & E
20 km
How many km does this object cover when it is moving the fastest?
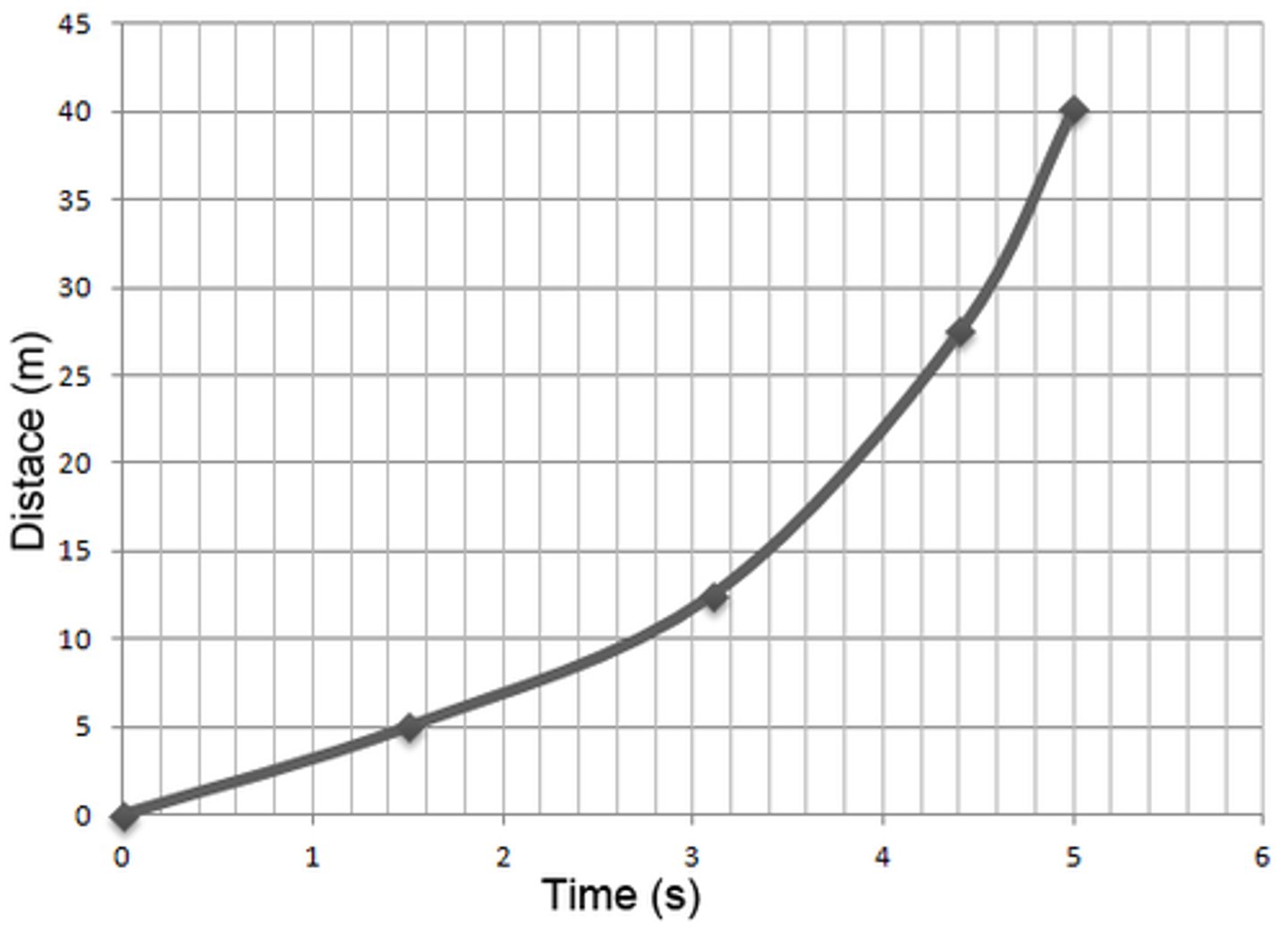
false
This object is slowing down: true or false
car
Which object goes constant speed?
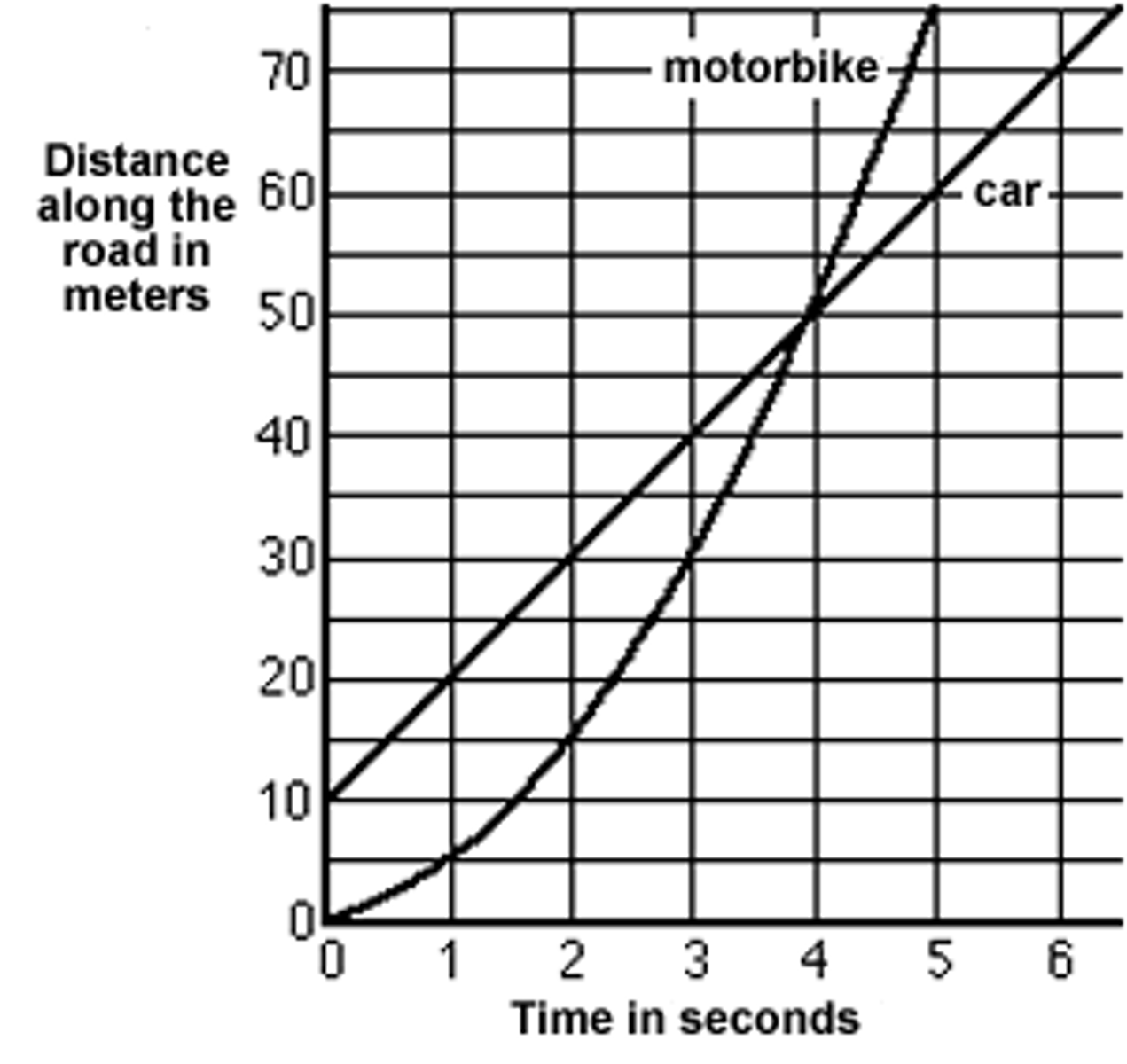
green
Which object, green or red, won the race?
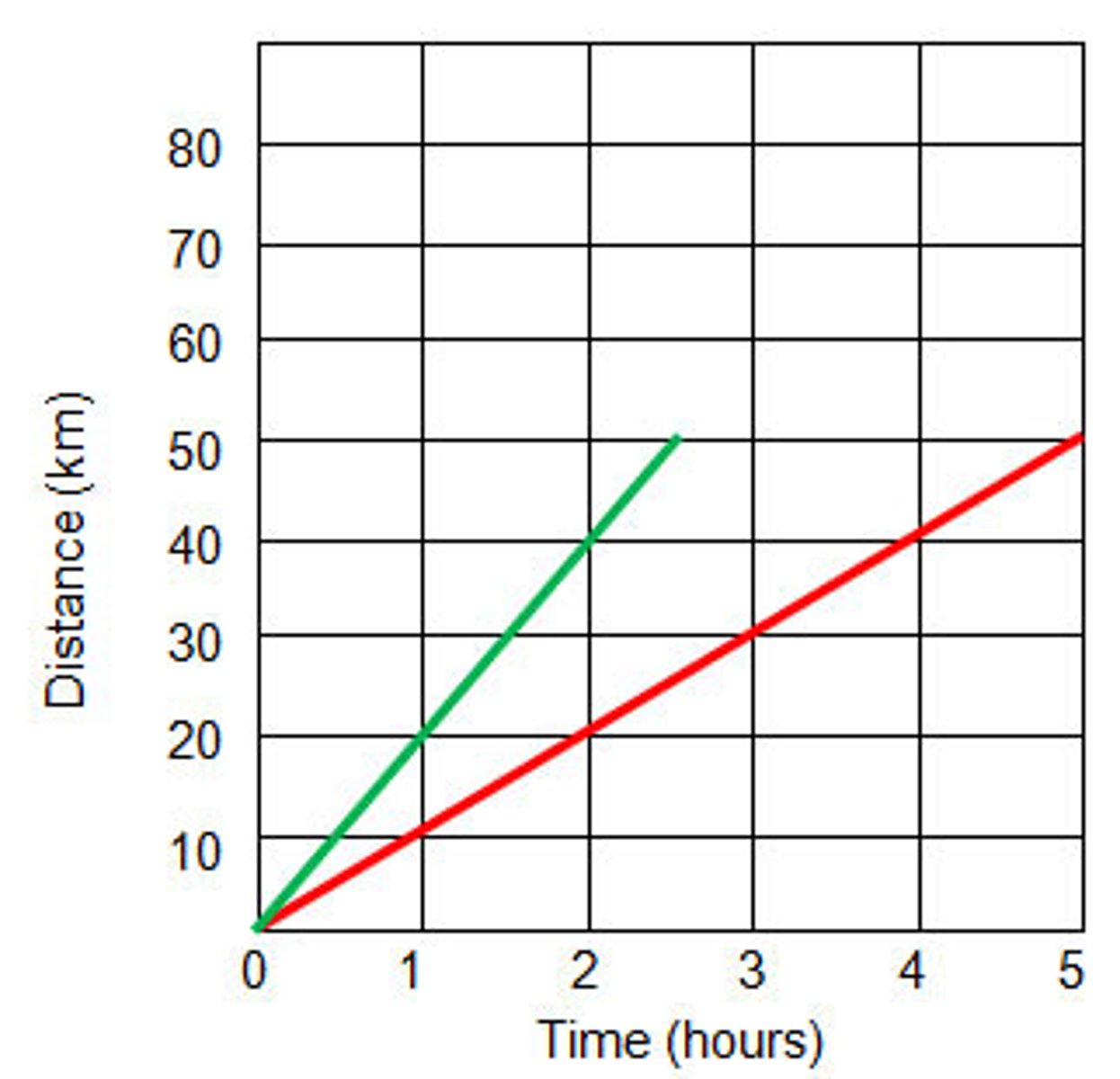
10 m/s
Calculate the velocity from 2-5 minutes
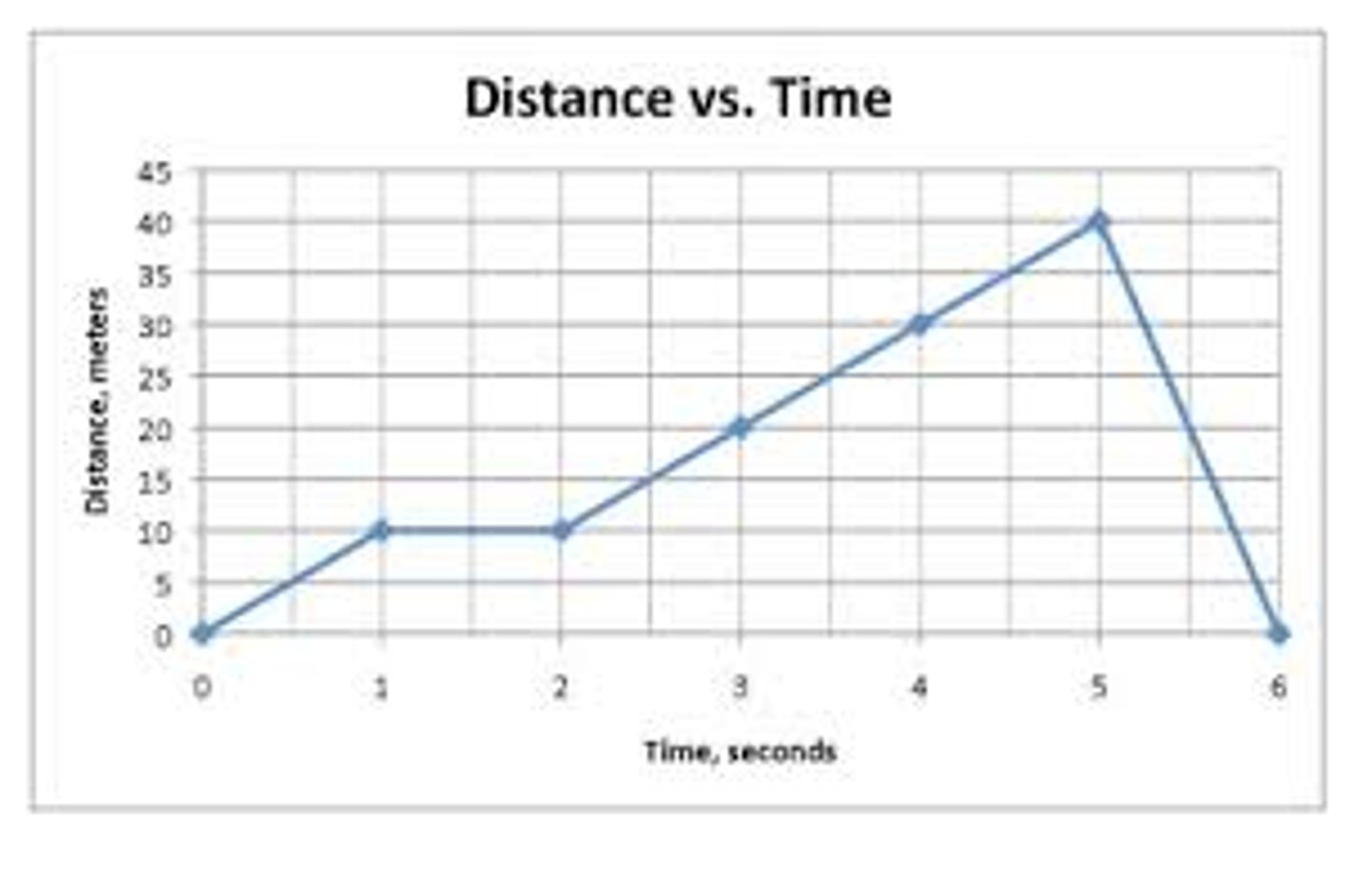
3 m
How many meters away from Ms. D's classroom are you when you begin to walk away down the hallway?
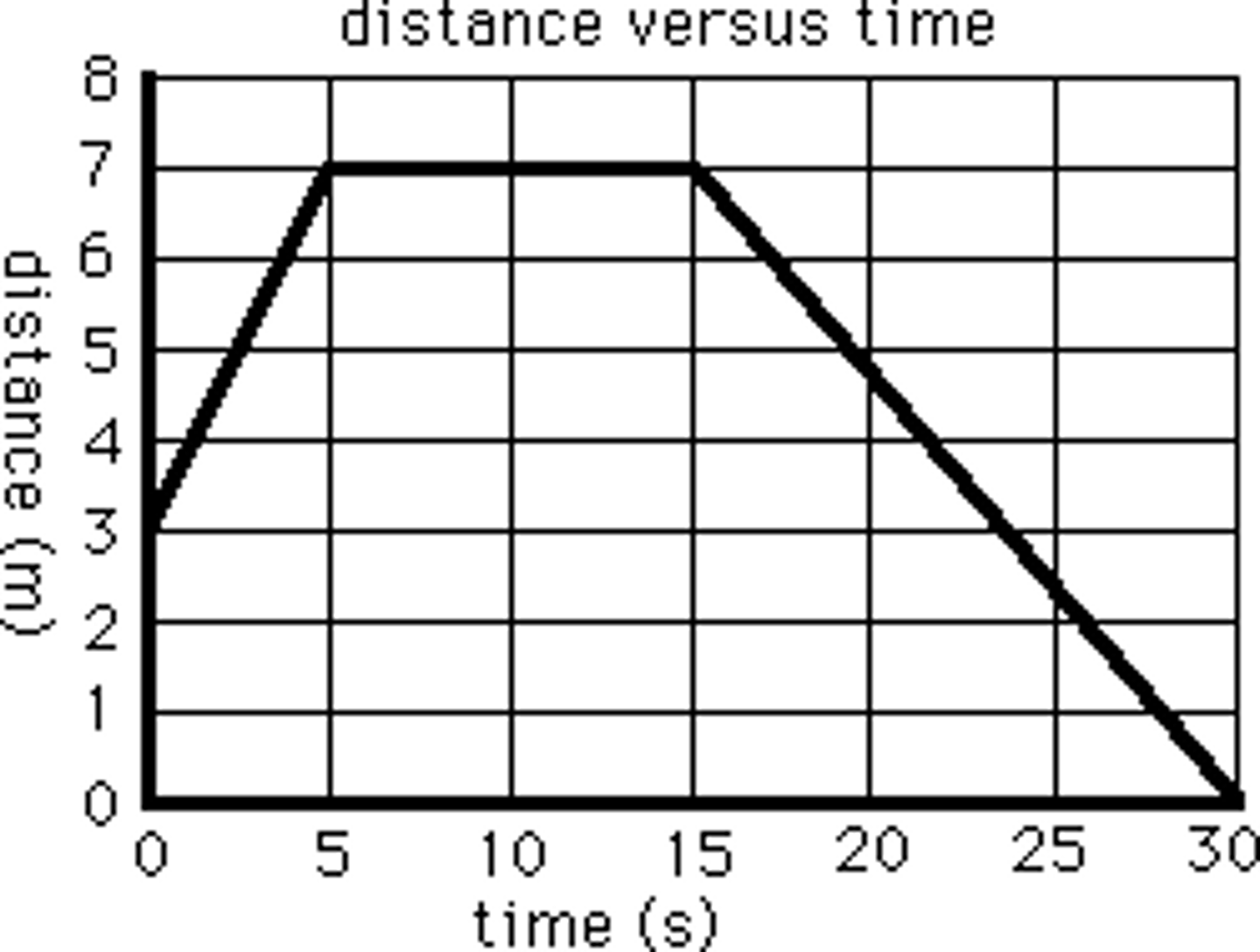
moving backwards
Is this object moving forwards, moving backwards, increasing speed or decreasing speed?
distance
the space between two points
time
what happens between two events
30 seconds
You are in TROUBLE! If you walk 45 m to Dr. Cohen's office at a velocity of 1.5 m/s, how long will it take you to get there?
1.67 m/s
How fast are you riding your bike if you ride 20 m in 12 seconds?
99 m
How far away is the lunchroom from Ms. Crowley's room if you walk at 1.8 m/s and it takes you 55 seconds to get there?
9.62 m/s
What is the velocity of a runner who travels 100 m in 10.4 seconds?