C1- Chlamydomonas: a model system
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
what type of organism is Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
eukaryotic green algae
what distinct feature does chlamy have not found in animals
cell wall
average size of chlamy
10 µm (microns)
is chlamy larger or smaller than the average bacteria
larger
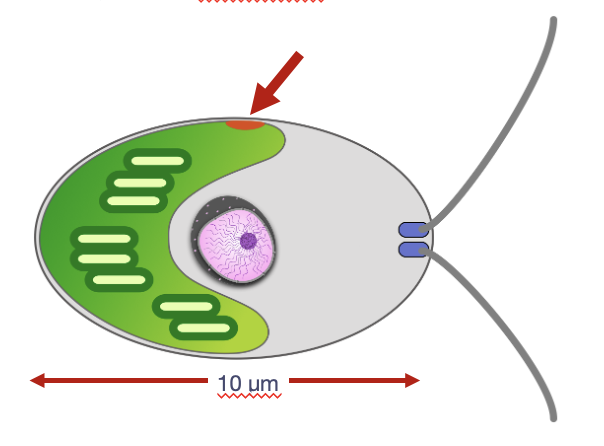
identify the structure & its general function
eyespot
enables swimming away from or towards a light source
common environment of chlamy
fresh-water systems
common environmental temperature range of chlamy
24-28ºC
asexual division mechanism of chlamy
binary fission
T/F- chlamy is a microbe
T
T/F- binary fission is found in multicellular organisms
F
binary fission is common in which organism type
prokaryotes
generation time of chlamy under optimal conditions
10 hours
impact of temperature on growth rate of chlamy
lower temp = lower growth rate
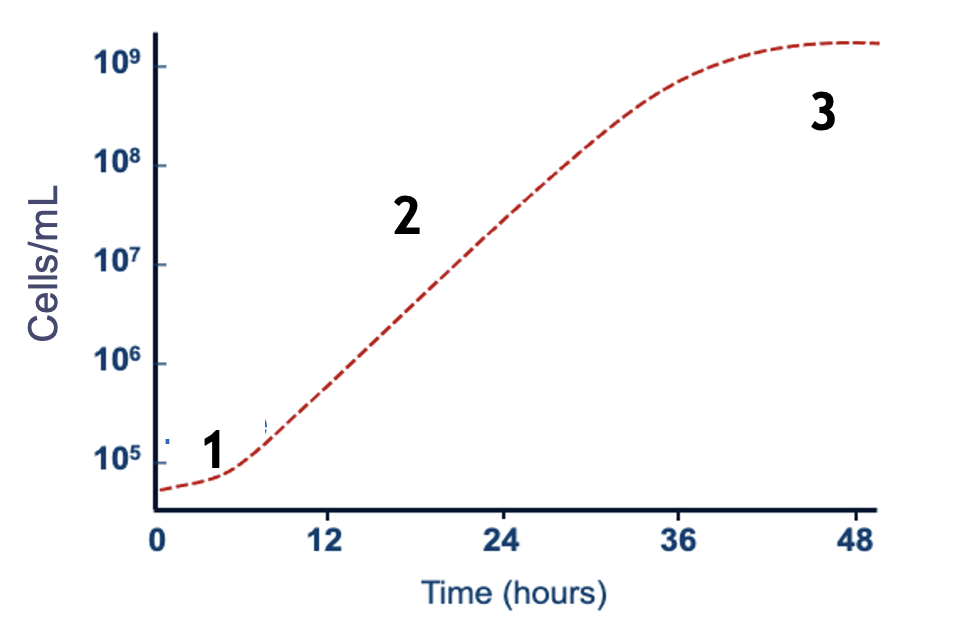
identify the growth phases
1- lag phase
2- exponential phase
3- stationary phase
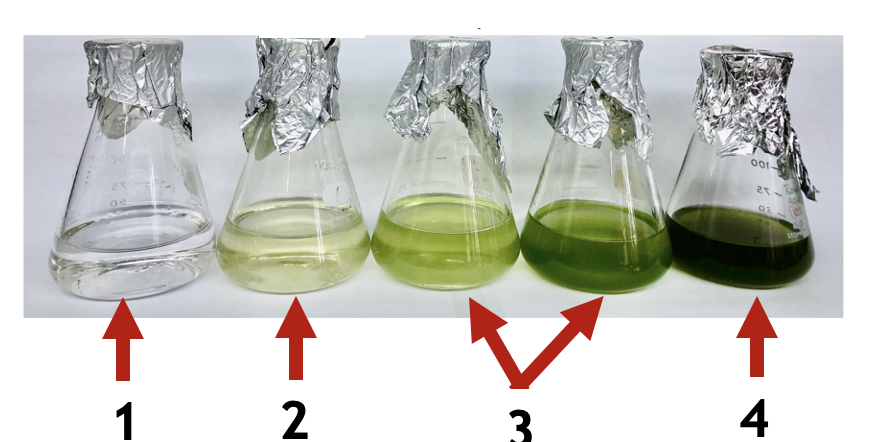
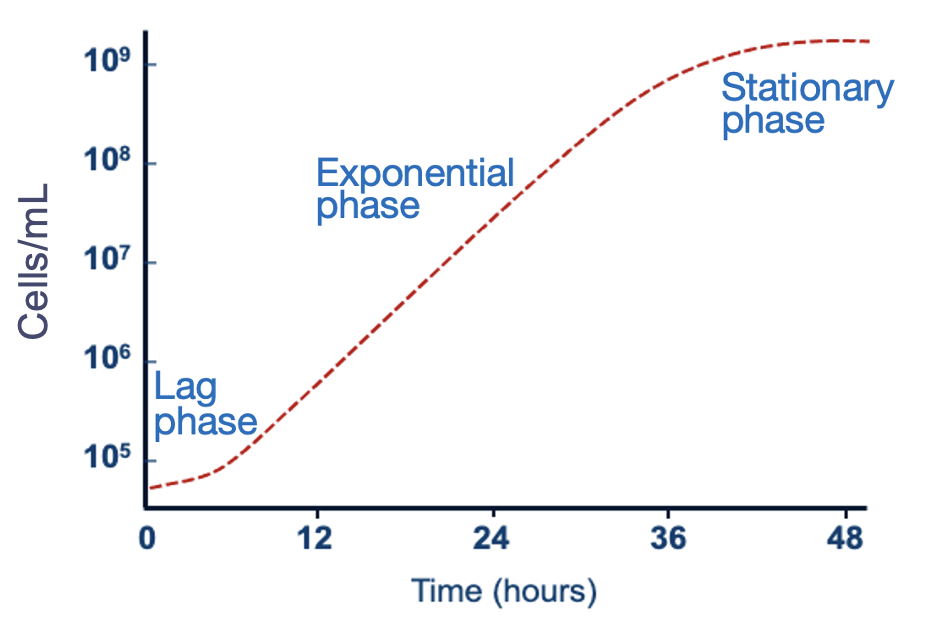

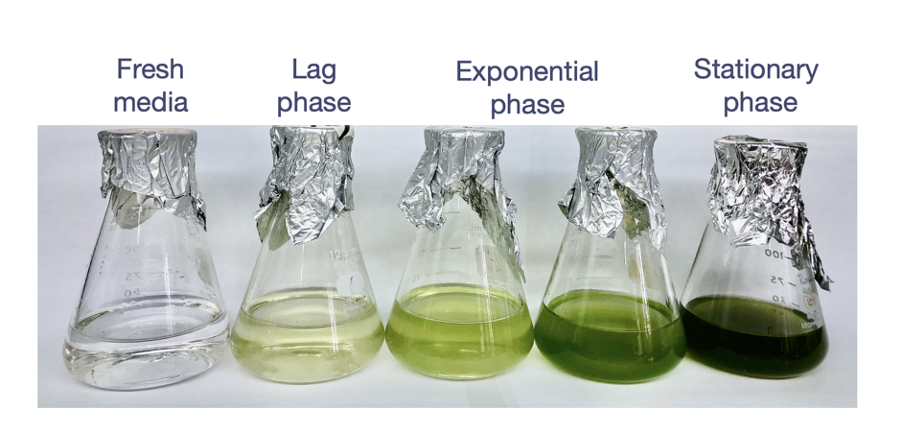
identify the growth phases
1- fresh media
2- lag phase
3- exponential phase
4- stationary phase

what growth phase has the maximum growth rate
exponential
name for this graph
microbial growth curve
how is this growth rate calculated
change in cell # divided by change in time
why is there no growth in stationary phase
a nutrient runs out
what nutrients commonly cause stationary phase (2)
nitrogen
phosphorus
T/F- we need the same nutrients as chlamy
T
how many essential macronutrients and micronutrients does chlamy need
macro-nutrients: 4
micronutrients: 7
why is nitrogen an essential nutrient (3)
makes proteins
makes RNA
makes DNA
how long ago did algae and plants diverge
1 billion years ago
T/F- chlamy and human flagella are identical
T
why did plants lose flagella
no need for them (stationary)
why did prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells both evolve flagella
easiest way to move
T/F- bacteria & eukaryotes have homologous flagella
F- analogous
what is the only structural difference between cilia & flagella
cilia are shorter
what is a microtubule
a protein polymer made from tubulin subunits
what are eukaryotic flagella microtubules made of
alpha & beta tubulin dimers
what causes microtubules to bend
dynein
what is dynein
a motor protein
main consequence of the bbs4 mutant chlamy
can’t swim
what are ciliopathies
distinct diseases linked to mutations in genes involved in cilia structure/function
the 2 types of cilia
motile
non-motile
why is chlamy a good model system
many human diseases are caused by mutations or defects in flagella & cilia
other name for non-motile cilium
sensory cilium
what issues are linked to defective/mutated motile cilia (2)
male infertility
lung issues
how are flagella in eukaryotes bound
by plasma membrane
what is comparative proteomics
comparison of the entire set of proteins (the proteome) between different biological samples to identify differences in which proteins are present