Lectures 1 & 2 - Endocrine System
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What hormone does the liver produce?
Angiotensin
What hormone does the thymus produce?
Thymosin (promotes T-cell development)
What hormone does the heart produce?
BNP (Brain natriuretic peptide)
What hormones does the kidney produce?
Renin and erythropoetin
What hormone dos the stomach produce?
Gastrin
What hormones does the duodenum produce?
Secretin and CCK (Cholecystokinin)
What hormone does the skin produce?
Some species make vitamin D3 in their skin, which has the properties of a hormone
What hormone does the placenta produce?
Relaxin
What type of hormone needs a carrier to travel through the blood? (ex. hydrophilic or hydrophobic/lipophilic)
Hydrophobic/ Lipophilic
What type of hormone attaches to receptors on the cell surface? (ex. hydrophilic or hydrophobic/lipophilic)
Hydrophilic
What type of hormone attached to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus? (ex. hydrophilic or hydrophobic/lipophilic)
Hydrophobic/ Lipophilic
What type of hormone travels freely through the blood? (ex. hydrophilic or hydrophobic/lipophilic)
Hydrophilic
Is a steroid hormone hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic/ Lipophilic
Is an amine hormone hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
Is a peptide hormone hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
Is a protein hormone hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
What are the different types of intercellular communication?
- Endocrine;
- Paracrine;
- Autocrine;
- Synaptic;
- Neuroendocrine
What is endocrine signalling?
Hormones are released into the bloodstream and travel to distant target cells
What is paracrine signalling
Hormones or signalling molecules act on nearby cells without entering the bloodstream
What is autocrine signalling?
A cell releases signals that act on itself to regulate its own activity
What is synaptic signalling?
Neurotransmitters are released across a synapse to communicate with a neighbouring neuron or target cell
What is neuroendocrine signalling?
Nerve signal stimulates hormone release
How are hydrophilic hormones broken down?
They are broken down by the liver or filtered out by the kidneys
How are hydrophobic/lipophilic hormones broken down?
They last longer in the blood than hydrophilic hormones. Some free hormones dissolve in the plasma. They are then broken down by the liver or filtered out by the kidneys
What hormones does the hypothalamus create and release?
- GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone);
- CRH (Corticotropin releasing hormone);
- TRH (Thyrotropin releasing hormone);
- GHRH (Growth hormone releasing hormone);
- PRH (Prolactin releasing hormone);
- Oxytocin;
- ADH (Antidiuretic hormone)
What hormones does the posterior pituitary create and release?
None - the posterior pituitary only stores and releases hormones created by the hypothalamus
What hormones does the posterior pituitary store and release?
Oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
What organ does oxytocin act on?
Mammary glands and uterus
What does ADH (antidiuretic hormone) do?
Acts on the kidney to stimulate water reabsorption
What hormones does the anterior pituitary produce and release?
- ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone);
- FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone);
- LH (Luteinizing hormone);
- TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone);
- Prolactin;
- GH (Growth hormone)
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone)?
CRH (Corticotropin releasing hormone)
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (Luteinizing hormone)?
GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone)
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone)?
TRH (Thyrotropin releasing hormone)
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of Prolactin?
PRH (Prolactin releasing hormone)
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of GH (Growth hormone)?
GHRH (Growth hormone releasing hormone)
What organ does ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) act on?
Adrenal cortex
What organ does FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (Luteinizing hormone) act on?
The gonads (testes and ovaries)
What organ does TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone) act on?
Thyroid gland
What organ does Prolactin act on?
Mammary glands
What organ does GH (Growth hormone) act on?
Liver and all of body
What actions does GH (growth hormone) have on the body?
- Bone/muscle growth in young animals;
- Regulation of protein, carbs, and lipids in all cells;
- Anabolism of proteins;
- Catabolism of lipids in fat;
- Increases hepatic gluconeogenesis;
- Inhibits cells from using glucose
What disease is associated with too much GH (growth hormone)?
Acromegaly (anterior pituitary tumour)
What disease is associated with too little GH (growth hormone)?
Pituitary dwarfism
What is another name for growth hormone?
Somatotropin
What action does prolactin have?
Begins and maintains lactation
What type of feedback loop is associated with prolactin release?
Positive feedback loop
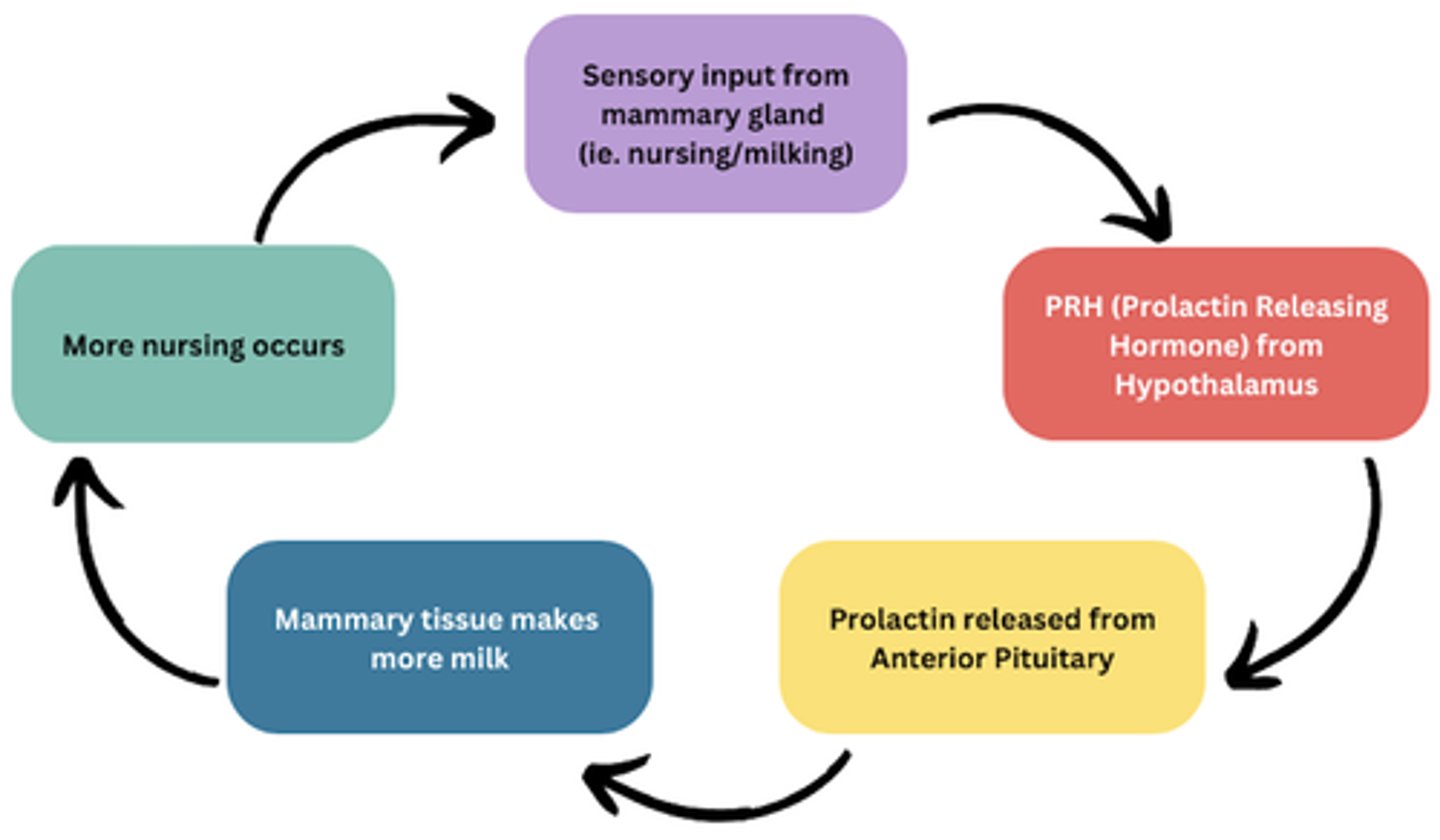
What action does oxytocin have on the mammary glands?
Milk let-down
What action does oxytocin have on the uterus?
Contraction of the uterus for parturition and fertilization
What is another name for TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)?
Thyrotropic hormone
What action does TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) have?
Acts on thyroid gland to produce and release T3 and T4
What type of feedback loop is associated with TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) release?
Negative feedback loop
Where is the thyroid gland located?
On either side of the trachea
What hormones are produced and released by the thyroid gland in response to TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)?
T3 and T4
Which of the two thyroid hormones (T3 or T4) is a pro-hormone that circulates freely in the blood?
T4
Which of the two thyroid hormones (T3 or T4) is the active form of the thyroid hormone?
T3
What are the effects of thyroid hormone?
- Increases the rate of calorie usage;
- Controls body temperature;
- Development of the CNS;
- Growth and development of muscles and bones;
- Anabolism (synthesis) of proteins;
- Increased gluconeogenesis
What disease is associated with an iodine deficiency?
Goiter
What disease is associated with too much thyroid hormone?
Hyperthyroidism
Which species (cats or dogs) is more prone to hyperthyroidism?
Older cats
What disease is associated with too little thyroid hormone?
Hypothyroidism
Which species (cats or dogs) is more prone to hypothyroidism?
Some dog breeds
How can goiter be treated?
Dietary iodine supplementation
How can hyperthyroidism be treated?
Surgery, medication, limited iodine diet, or radioactive iodine
How can hypothyroidism be treated?
Thyroid hormone supplementation
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of calcitonin?
None! Calcitonin is released from C-cells in the thyroid gland and is under control of the C-cells directly
What effect does calcitonin have?
Decreases blood calcium levels (puts calcium into the bones)
What is another name for parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Parathormone
What hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
None! Parathyroid hormone is released from the parathyroid gland in response to low blood calcium levels
What effect does parathyroid hormone (PTH) have?
Increases blood calcium levels (takes calcium out of the bones)
What are some diseases associated with too much parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
- Rubber jaw (secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism);
- Secondary renal hyperparathyroidism;
- Primary hyperparathyroidism (parathyroid gland tumour)
What effect does FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) have in a female?
- Stimulate oogenesis;
- Superovulation;
- Cycle timing;
- Stimulates follicle lining to make estrogen
What effect does FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) have in a male?
Stimulates spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules
What effect does luteinizing hormone (LH) have in a female?
Stimulates estrogen production in the follicle
What type of feedback loop is associated with estrogen?
Positive feedback loop (dec. FSH and inc. LH)
What effect does lutenizing hormone (LH) have on the male?
Stimulates interstitial cells in testes to make testosterone
What is another name for lutenizing hormone (LH) in the male system?
ICSH (Interstitial cell stimulating hormone)
What are the three types of hormones released by the ovaries?
Estrogens, progestins, and relaxin
What is the primary type of estrogen released by the ovary?
Estradiol
What effect does extradiol have?
Causes physical and behavioural chances to prepare for breeding and pregnancy
What is the primary type of progestin released by the ovary?
Progesterone
What part of the ovary releases progesterone?
Corpus luteum
What effect does progesterone have?
Maintains pregnancy
What part of the ovary makes relaxin?
Corpus luteum (or uterus or placenta in some species)
What effect does relaxin have?
Relaxes ligaments of birth canal for parturition
Which ovarian hormone can be used as a pregnancy test factor in dogs?
Relaxin
Where is testosterone made?
Interstitial cells
What hormone stimulates the production of testosterone?
FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone)
What effect does testosterone have on the body?
Development of accessory sex glands and growth of penis
Which hormones are produced by and released from the adrenal glands in response to ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) from the anterior pituitary?
Mineralocorticoids (ex. aldosterone), glucocorticoids, and androgens/estrogens (sex hormones)
What are two primary examples of glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex?
Cortisol and cortisone
What effect do glucocorticoids have?
Increases blood glucose levels and long term stress
What disease is associated with too much glucocorticoid production?
Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism)
What disease is associated with too little glucocorticoid production?
Addison's disease (Hypoadrenocorticism)
What is an example of a mineralocoriticoid released by the adrenal gland?
Aldosterone
What effect does aldosterone have on the body?
Increases blood pressure and volumte by acting on the kidneys
What hormones are produced and released by the adrenal medulla?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
What type of stress is associated with epinephrine and norepinephrine?
Short term stress
What effect does ADH (antidiuretic hormone) have on the body?
Tells the kidneys to reabsorb more water
What is a disease associated with too much ADH (antidiuretic hormone)?
Diabetes insipidus
What hormone is released by the pinealo gland?
Melatonin