A&P TEST III
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
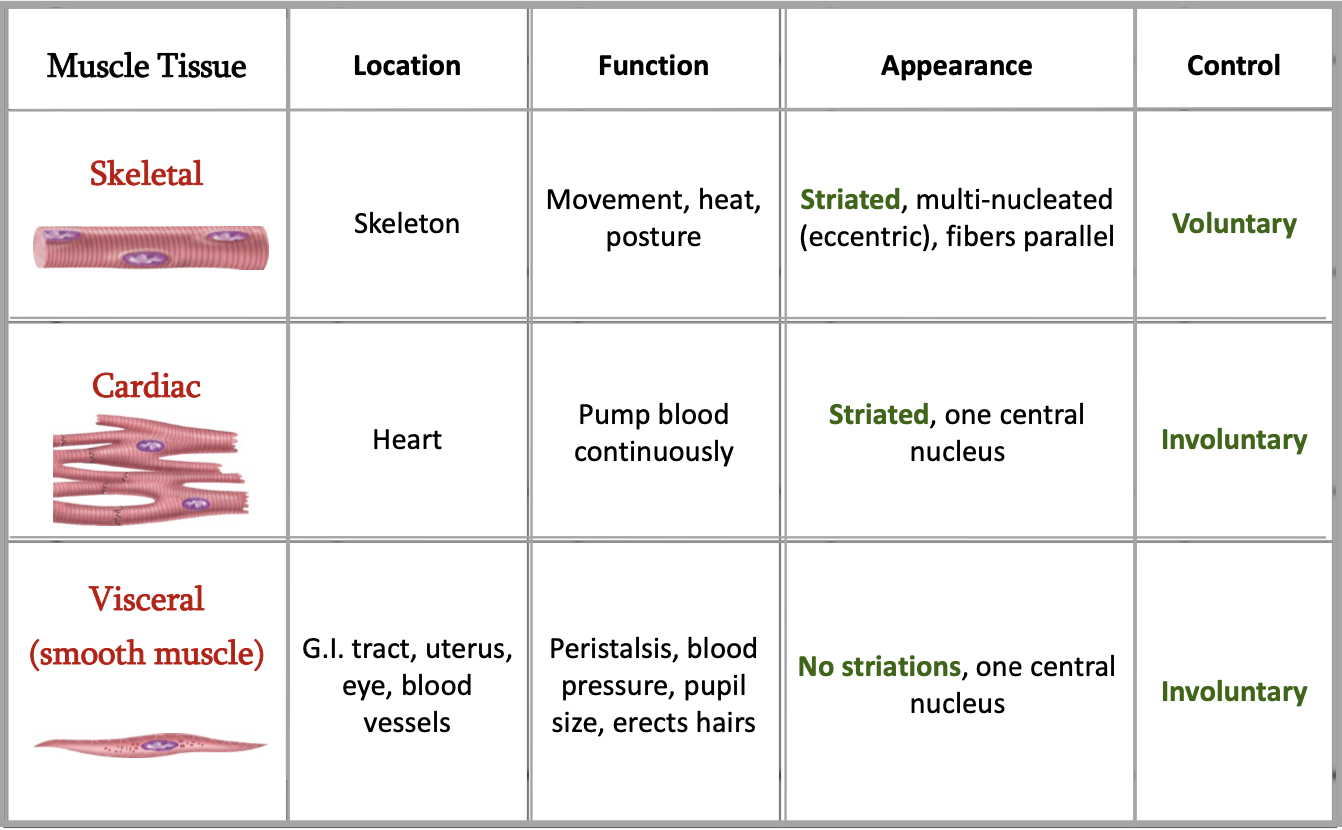
What are the three types of muscle?
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Characteristics of skeletal muscle
Moves bones
Sriated, alternating light and dark bands (striations) under microscope
Mainly voluntary
Many also controlled subconsciously
Characteristics of cardiac muscle
Found in walls of heart
Involuntary
Contraction is relaxation and initiated by node tissue called “pacemaker”
Characteristics of smooth muscle
Walls of hollow internal structures, skin, blood vessels, airways, and many organs
No striations
Involuntary
What is excitability?
Ability to respond to stimuli
What is contractility?
Ability to contract forcefully when stimulated
Extensibility
Ability to stretch without being damaged
Elasticity
Ability to return to an original length
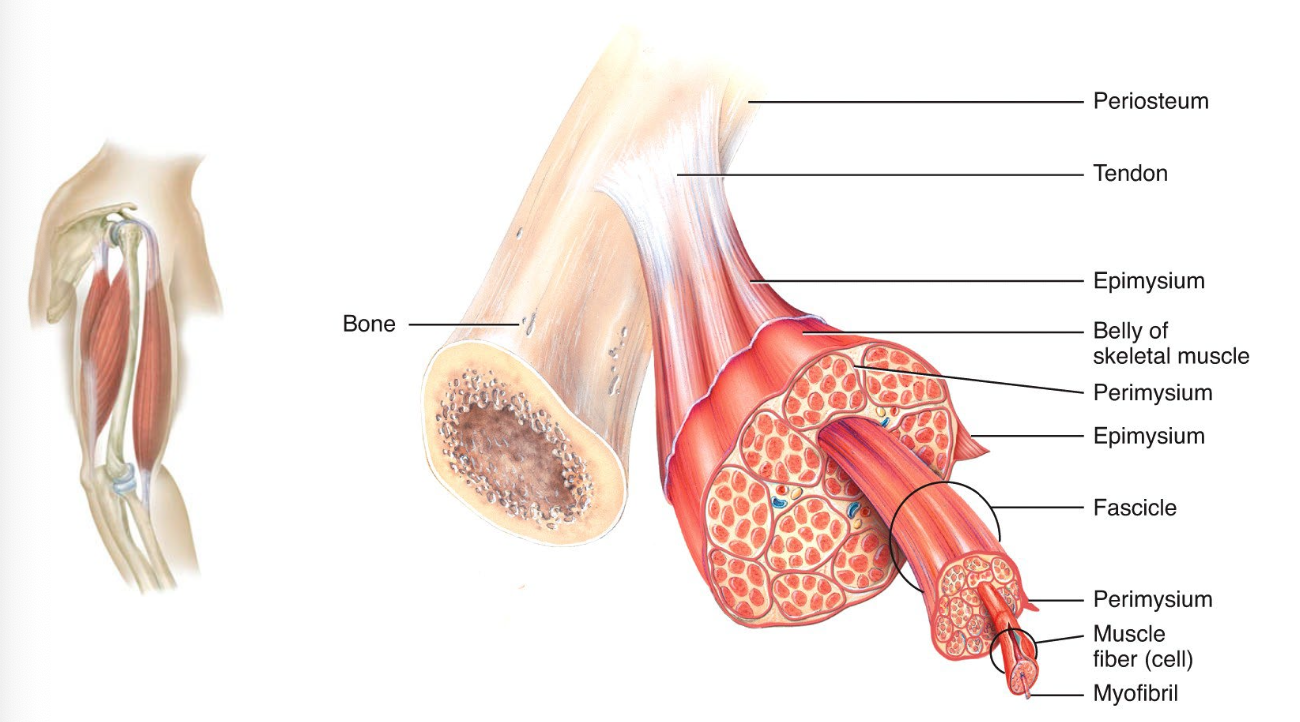
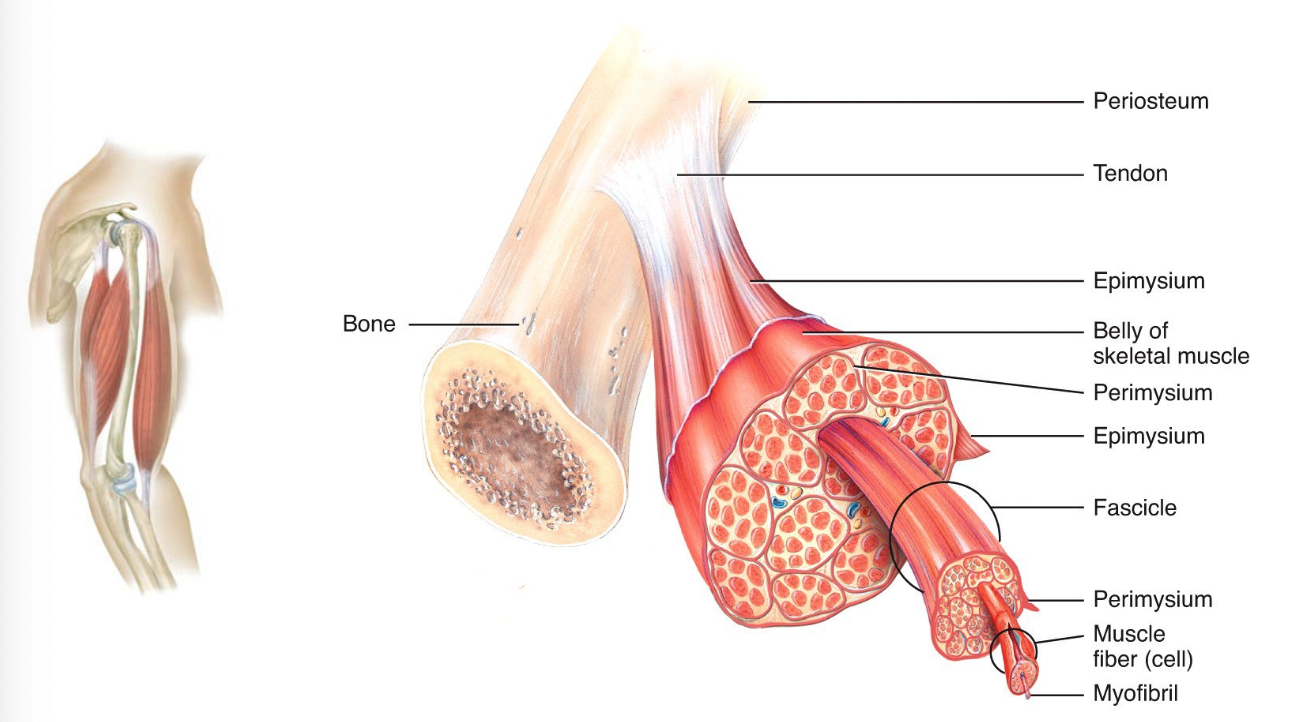
Endomysium
Encloses individual muscle fibers and separates it from another one
Perimysium
Encloses fascicles (group of 10-100 or more fibers and separating them into bundles)
Epimysium
The outermost layer encircle the whole muscle, protect and strengthen skeletal muscle
Fascia
Dense sheet or broad band of irregular connective tissue that surrounds muscles. It holds muscles and allows free movement.
Tendon
All three connective tissues make the cord like structure, called tendon which attach a muscle to a bone
Aponeurosis
Broad, flattened tendon
Myofibril
Thread-like protein which extends from ends of muscle
Muscle fiber is created by
Fusion of myoblasts
Do myoblasts continue to undergo cell division after fusion?
No
Which cells do continue to undergo cell division after birth?
Satellite cells
What is dystrophin?
Maintains shape of myofibril
What is sarcomere bounded by?
Z-disc to Z-disc
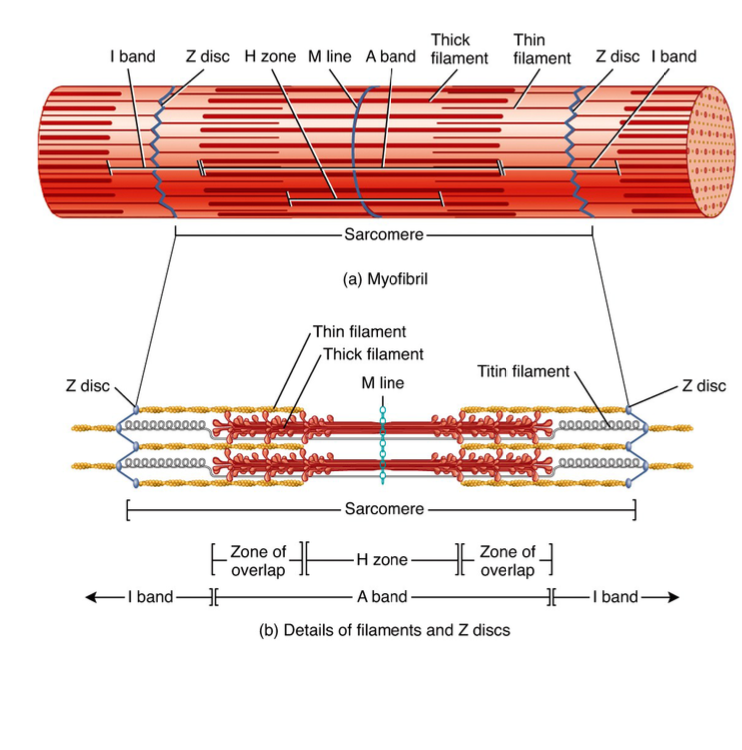
What is thin band?
Actin
What is thick band?
Myosin
What constitutes the A zone?
Myosin
What is titin?
Supports myosin
What is the I band?
Only actin
What is the H zone
Actin and myosin
Myosin
Thick filament which functions as motor protein and can achieve motion
Convert ATP to motion
Having two heads and one tail
Actin
Thin filaments which provide a site where a myosin head can attach
Tropomyosin and troponin are also part of the thin filament
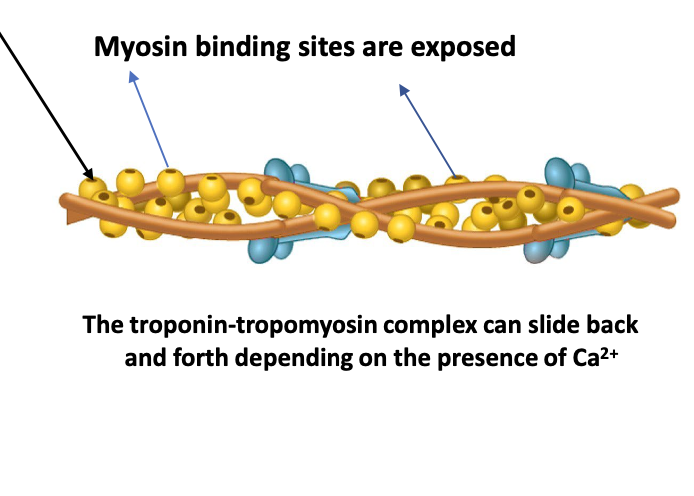
What happens when Ca binds to tropomyosin
Tropomyosin and troponin move to expose myosin binding sites on actin
What happens after tropomyosin and myosin move?
ATP in myosin head breaks down (lysis) and creates crossbridge
Contractile proteins
Myosin and actin generate force during contraction
Regulatory proteins
Troponin and tropomyosin help switch the contraction process on and off
Structural proteins
Titin and dystrophin keep thick and thin filaments in proper alignment and link the myofibrils to the sarcolemma and extracellular matrix
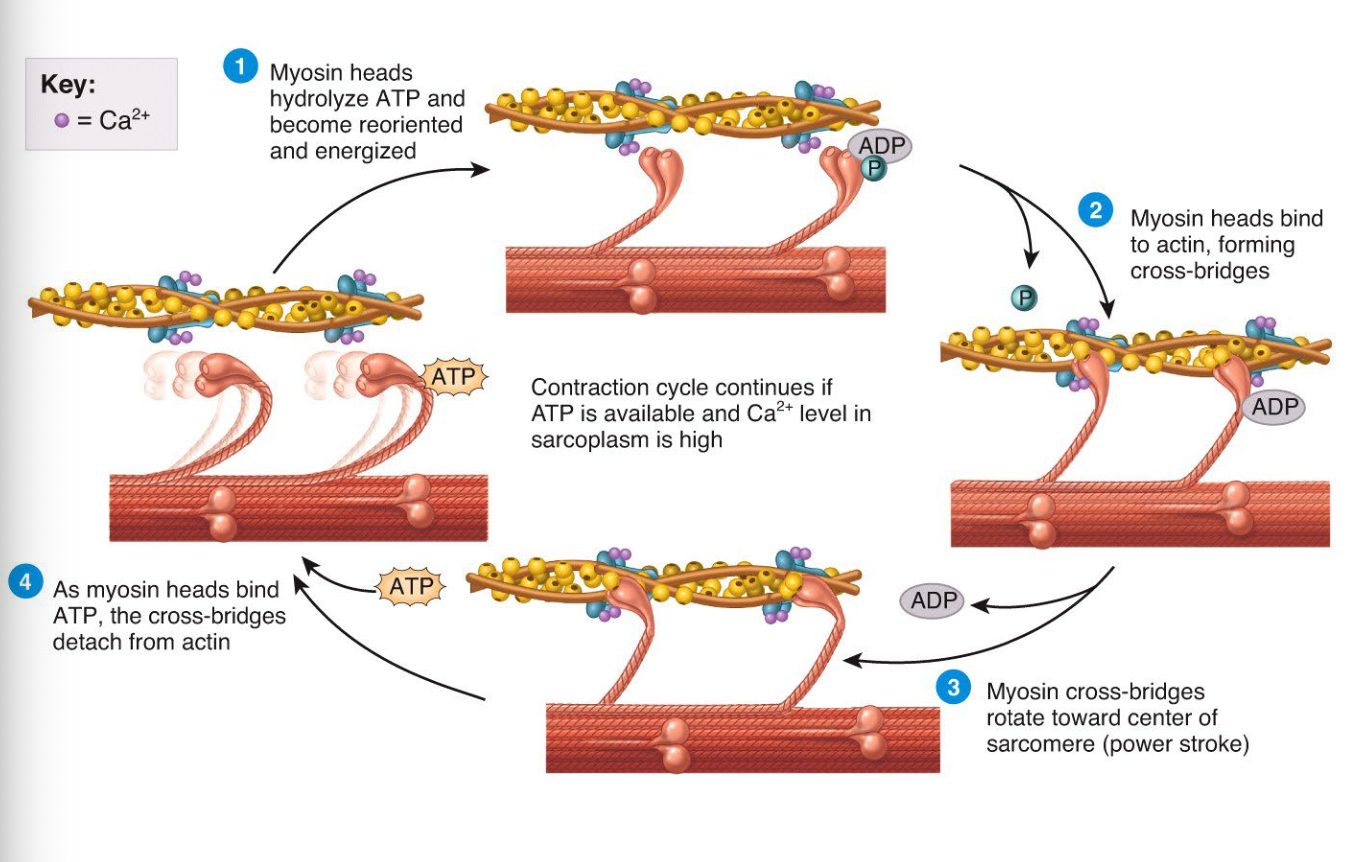
The contraction cycle
Excitation
Sarcoplasmic reticular contains CA to return back to the SR, decreasing calcium ion levels
Inside the SR, molecules of calcium binding protein called calsequestrin bind to the CA to be sequestrated or stored within the SR
Concentration of Ca is 10,000x higher in SR than in cytosol in a relaxed muscle fiber
As the Ca level in the cell drops, myosin-binging sites are covered tropomyosin and the muscle relaxes
What is the neuromuscular junction?
Motor neurons have a thread like axon that extends from the brain or spinal cord to a group of muscle fibers
What is a synapse
Region where communication occurs between somatic motor neuron and muscle fiber
What is the synaptic cleft
Region where communication occurs between a somatic motor neuron and a muscle fiber
What is a synaptic cleft
Gap that separates the nerve cell from the muscle cell
What is a neurotransmitter
Chemical released by the initial cell communicating with the second cell
What is the synaptic vesicle
Sacs suspended within synaptic end bulb containing neurotransmitter
Motor end plate
The region of the muscle cell membrane opposite the synaptic end bubbles which contain acetylcholine
What kind of channel is NA
Ligand gated
What kind of channel is K?
Leak
What is ATP needed for
Power the contraction cycle and pump Ca into the SR
What are the ways muscle fibers create ATP
Creatine phosphate, anaerobic cellular respiration (break down of glycogen), and aerobic cellular respiration (presence of oxygen)
What is muscle fatigue?
Inability of muscle to maintain force of contraction after prolonged activity
Factors that contribute to muscle fatigue
Inadequate release of calcium from SR
Depletion of creative phosphate
Insufficient oxygen
Depletion of glycogen and other nutrients
Buildup of location acid and ADP
Failure of the motor neuron to release enough ACH
Twitch contraction
Brief contraction of all the muscle fibers in a motor unit in response to a single action potential
Latent period
A brief delay between the stimulus and muscular contraction
The action potential sweeps over the SR and Ca is released from SR
Contraction period
Ca binds to troponin
Myosin binding sites on actin are exposed
Cross bridges form
Relaxation period
Ca is transported back into the SR
Myosin-binding sites are covered by tropomyosin
Myosin heads death from actin
Tension decreases
Refractory period
The period of loss excitability
Skeletal has refractory of 5 miliseconds
Cardiac has refractory of 300 milliseconds
Muscle tone
Tension in the muscle due to weak contractions of motor units
Small groups of motor units are alternatively active and inactive in a constantly shifting pattern to sustain muscle tone
Muscle tone keeps skeletal muscles firm
Isotonic contraction
The tension developed remains constant while muscle changes its length
Used for body movements and for moving objects
Picking a book up off a table
Isometric contraction
The tension generated is not enough for the object to be moved and the muscle does not change its length
Holding a book steady using an outstretched arm
Red muscle fibers
Have a high myoglobin content
Appear darker
Contain more mitochondria, more energy stores
Supplied by more blood capillaries
White muscle fibers
Have a low content of myoglobin, less mitochondria, less blood supply
Apply lighter
Three muscle fiber classifications
Slow oxidative fibers, fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers, fast glycolytic fibers
Slow oxidative fibers
Smallest in diamter
Least powerful
Sark red
Aeorobic
Slow speed of contraction
Prolonged contractions
Endurance type
Fast-oxidative
Intermediate diameter
Large amounts of myoblobin
Dark red
Generate ATP aerobic
Moderately high resistance
Generate some ATP anaerobic
Faster
Walking and sprinting
Fast glycolytic
Fastest
Largest in diameter
Low myoglobin
Few mitochondria
White
Generate ATP by glyocolysis
Fatigue quickly
Weightlifting or throwing ball
Types of Fibers
Most muscles are mixture of all three types of muscle fibers
Proportions vary, depending on the action of the muscle, the person’s training regimen, and genetic factors
Postural muscles of neck, back, and legs have SO fibers
Muscles of shoulders and arms have FG fibers
Leg muscles have large numbers of both SO and FOG fibers
Intercalated discs
Unique to cardiac
Connects ends of cardiac muscle fibers
Allow muscle APs to spread from one to another
Cardiac muscle tissue contracts when stimulated by what
Its own rhythmic muscle fibers (node)
What respiration does cardiac muscle depend on
Aerobic
Requries lactic acid produced by skeletal muscle fibers to make ATP
How are APs spread in smooth muscle
Gap junctions
How are smooth muscles stimulated?
Neurotransmitter/hormone, or autonomic signals
Anatomy of smooth muscle
Thick and thin filaments
Not arranged with orderly sarcomeres
No regular pattern
Lack T tubules
Dense bodies
Dense bodies
Thin filaments attach to structures called dense bodies which function similar to Z-discs in skeletal muscle
Filaments pull on dense bodies causing a shortening of muscle fiber
Physiology of smooth muscle
Contractions last longer
Initiated by Ca
Ca move slowly out of the muscle fiber delaying relaxation
Able to sustain long-term muscle tone
Important in gastrointestinal tract and walls of blood vessels
What do smooth muscles respond to?
APs from autonomic, stretching, hormones, changes in pH, oxygen, and CO2
Hyperplasia
Increase in number of fibers (unusual)
Smooth muscles in uterus retain capacity for vision and can grow by hyperplasia
Hypertrophy
Enlargement of existing cells
Satellite cells divide slowly and fuse with existing fibers to grow muscle and repair
Cardiac muscle can undergo hypertrophy (like in athletes) due to increased workload
What term-layer does muscle come from?
Mesoderm
Cardiac and smooth are from migrating mesoderm cells
Aging in muscle
Loss of muscle mass
Decrease in strength
Slowing of muscle reflexes
Loss of flexibility
Largest muscle
Gluteus maximus
Muscle behind neck
Levator scapulae
Muscle of thigh
Adductor Magnus and tensor tympani
Muscle of calf
Fivularis longus (top) and fibulas braves (bottom) of fibia
Muscle of abdomen
Transversus abdominus
Muscle of arms
Biceps and tibialis anterior
What is origin of muscle
Non-moveable part
What is the fleshy part of muscle?
Belly
What is moveable part of muscle?
Insertion
What is origin, insertion, and action of biceps brachia?
Origin is scapula, radius is insertion, action is pronate and flex arm
Origin, insertion, and action of triceps brachia
Scapula is origin, upper and lateral posterior sites of humerus and posterior surface of humerus. Insertion is back of olecranon process of ulna. Action is straighten
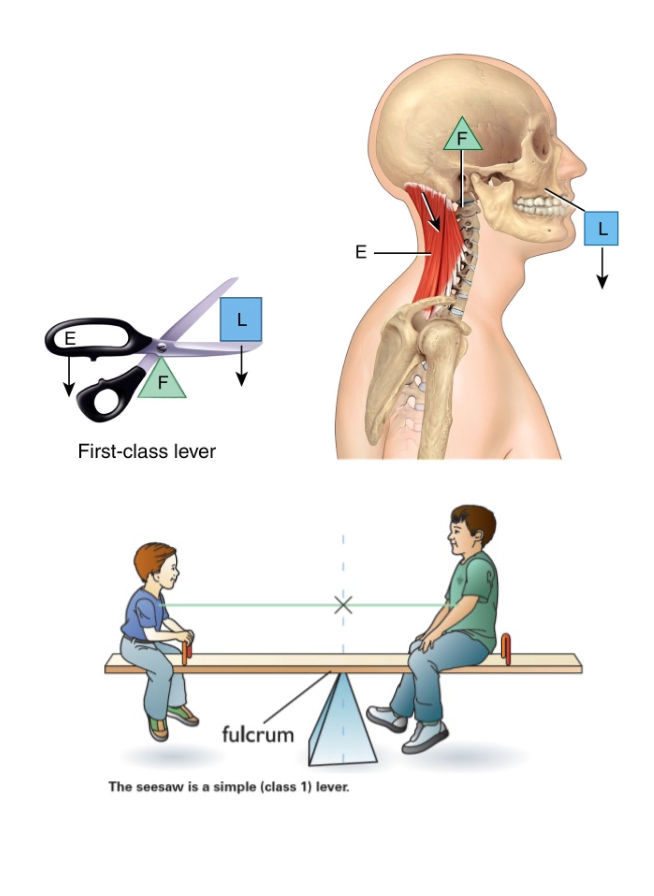
What is a lever?
Rigid structure that can move around a fixed point is called a lever.
Point of movement (fulcrum) is acted on by two different forces: effort (muscle) and load (resistance)
First class lever
Fulcrum (atlanto-occipital joint)
Load (facial bones)
Effort (muscles of the back of neck
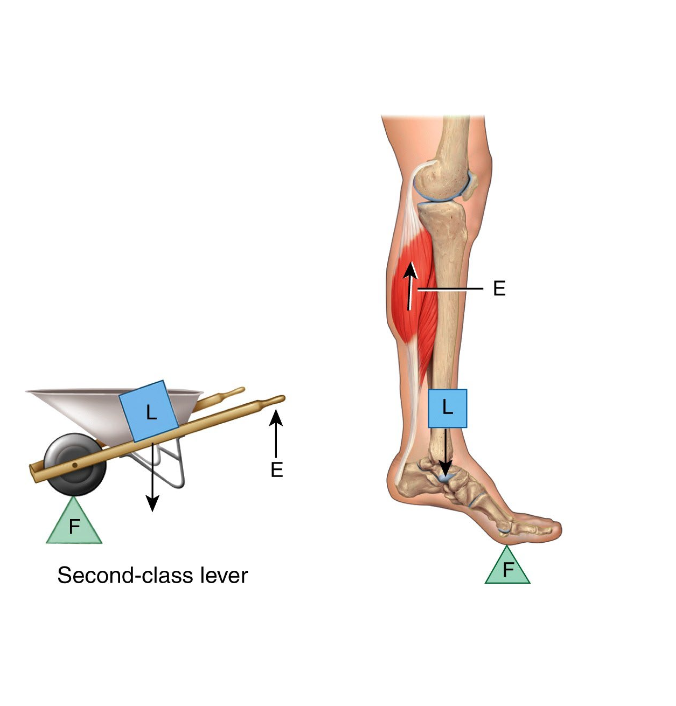
Second class lever
Compares with wheelbarrow.
Fulcrum (metatarsophalangeal joints)
Effort (gastrocnemius)
Whole body weight is resistance
Third class lever
Fulcrum (elbow joint)
Effort (biceps brachii)
Load (bones of hand)
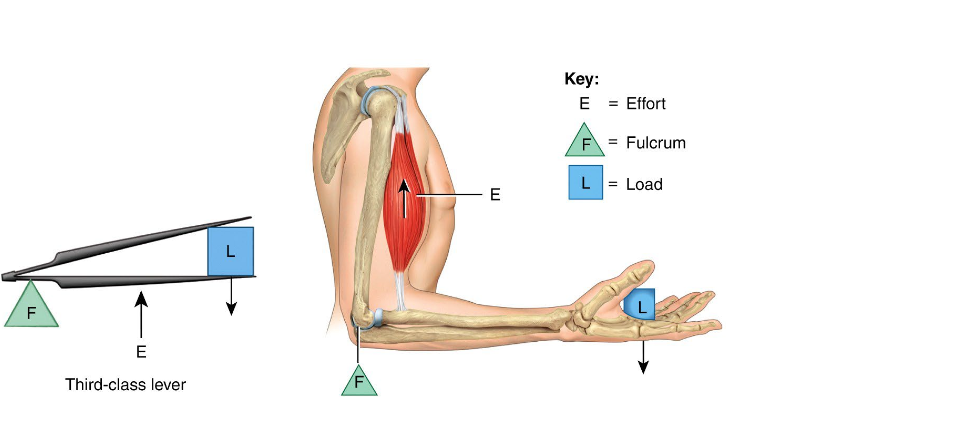
What is coordination of moving muscles?
Agonist )prime mover ) and antagonist (stretches or yields)
EX. Brachialis is prime mover and agonist is triceps brachia
What is synergistic muscle
Muscles used to aid of assist in movement (biceps move with brachialis)
What is the fixator?
Synergist muscle used to steady or fix the proximal joints of prime mover
EX. shoulder stabilizes for the forearm flexors
Muscles of mastification
Masseter, temporalis, medial and lateral pterygoid
Orbicularis oris
Mouth
Muscles of facial expression (muscle to skin)
Orbicularis oris
Orbicularis oculi
Occipitofronatlis
Zygomaticus major
Zygomaticus minor
Buccinator
Bells Palsy
Facial paralysis wherein person is unable to wrinkle forehead, close eye, or pucker lip on the affected side
What moves eyeball
Extraocular muscle
Muscle of chest
Pectoral’s major and minor
Anterior abdominal muscle group
Latissimus dorsi
Biceps brachii
Diaphragm
Trapezius
Deltoid