Muscles of the head and neck NOT DONE
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Action and innervation of the sternocleidomastoid
Unilateral = contralateral rotation (right sided contraction → head moves left)
Bilateral = flexion
Innervation: Accessory nerve (CN XI)
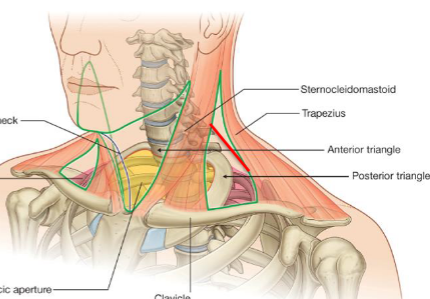
How do approximate the accessory nerve?
In the posterior triangle
Approx. 1/3 down SCM to 1/3 up trapezius
What are the Suboccipital muscles?
Rectus capitis posterior major: C2 spinous process to lateral inf. NL
Rectus capitis posterior major: Post. tubercle C1 to medial inf. NL
Obliquus capitis superior: C2 spine to C1 transverse process
Obliquus capitis inferior: C1 (TP) to occiput laterally
Insertion of the trapezius muscle
From sup. nuchal line + nuchal ligament to scapula spine, acromion + lateral 1/3 clavicle
Action and innervation of the trapezius muscle
unilateral contraction: lateral flexion and contralateral rotation of the head
bilateral contraction: extension of the head
Innervation: Accessory nerve (CN XI)
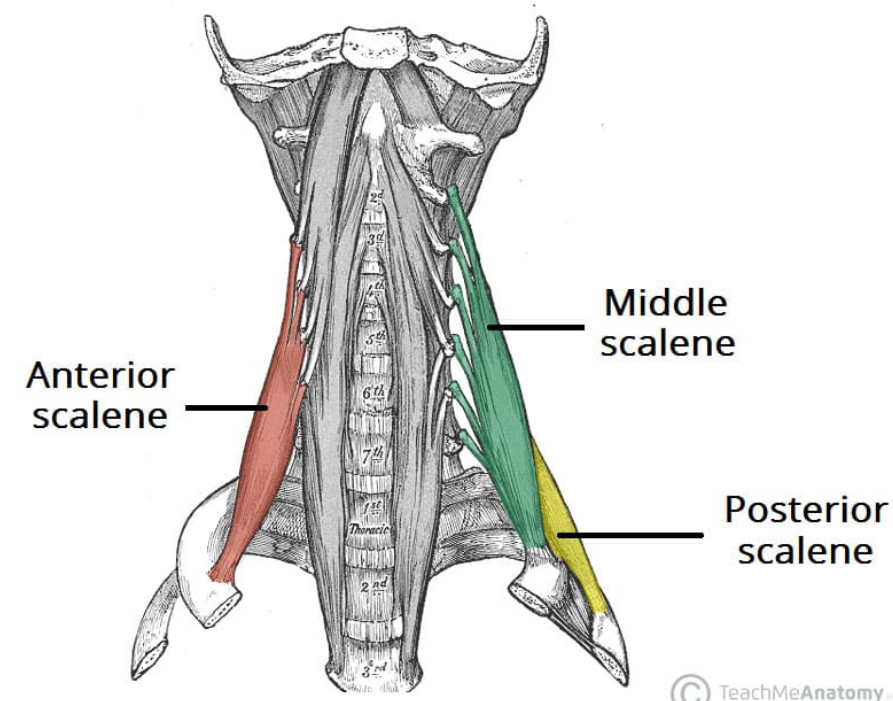
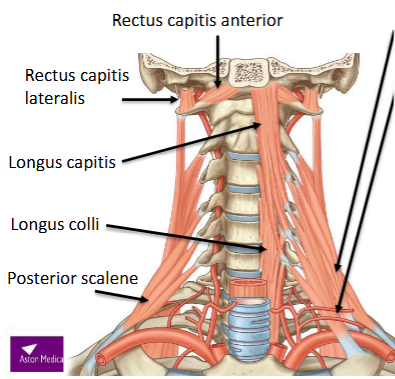
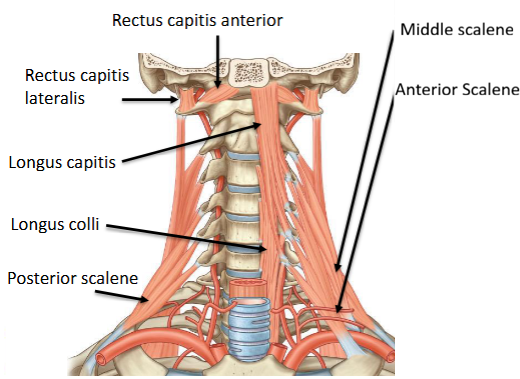
Origin and insertion of the scalene muscles
Posterior: Post. tubercles C5-7 to 2nd rib
Middle: Post. tubercles C2-7 to 1st rib
Anterior: Ant. tubercles C3-6 to 1st rib (scalene tubercle)
Action of the scalene muscles
Anterior:
Elevation of the first rib
Ipsilateral contraction causes ipsilateral lateral flexion of the neck
bilateral contraction causes anterior flexion of the neck
Middle:
Elevation of the first rib
Ipsilateral contraction causes ipsilateral lateral flexion of the neck
Posterior:
Elevation of the second rib
ipsilateral lateral flexion of the neck
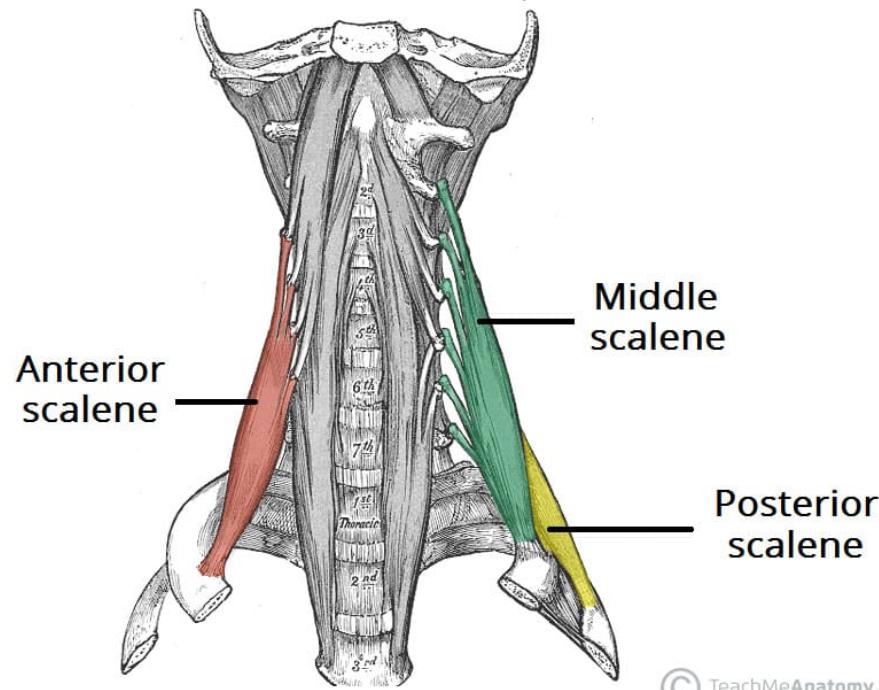
Innervation of the scalene muscles
Anterior: Anterior rami of C5-C6
Middle: Anterior rami of C3-C8
Posterior: Anterior rami of C6-C8
What passes between the anterior and middle scalene?
The brachial plexus and subclavian artery
What passes the anterior scalene?
subclavian vein and phrenic nerve pass anteriorly to the anterior scalene
subclavian vein courses horizontally across it
the phrenic nerve runs vertically down the muscle
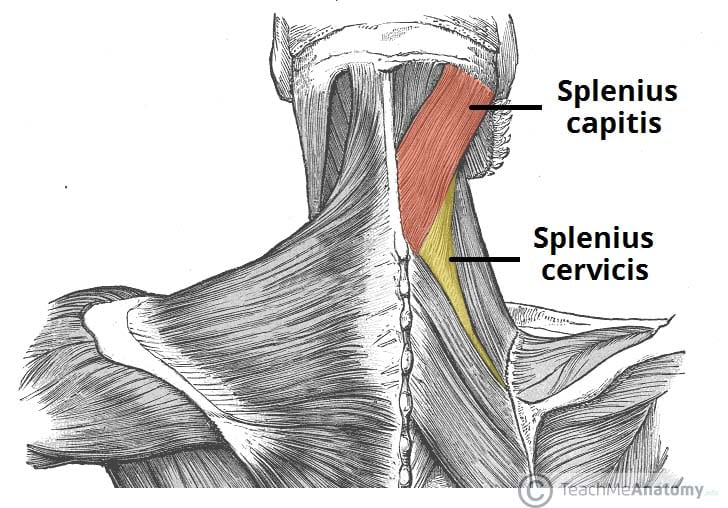
What is the function of the splenius muscles?
Unilateral contraction: lateral flexion and ipsilateral rotation of the head and neck
Bilateral contraction: extension of the head and neck
What are the 2 splenius muscles?
Splenius capitis and cervicis
Action and innervation of the longus colli muscle
Bilateral contraction: Neck flexion
Unilateral contraction: Neck contralateral rotation, neck lateral flexion (ipsilateral)
Innervation: Anterior rami of spinal nerves C2-C6
Action and innervation of the Longus capitis muscle
Bilateral contraction - head flexion
Unilateral contraction - head rotation (ipsilateral)
Innervation: Anterior rami of spinal nerves C1-C3
Name the Prevertebral muscles
longus capitis
longus colli
rectus capitis anterior
rectus capitis lateralis
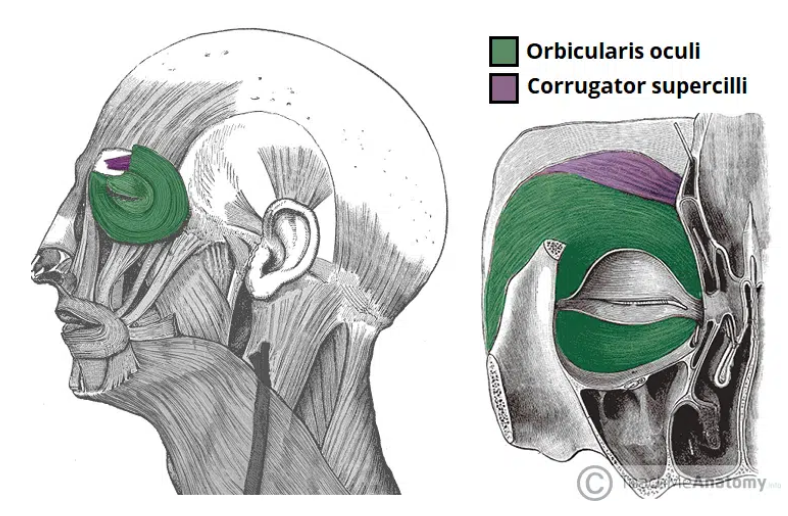
Actions and innervation of the oribucularis oculi
Palpebral part – gently closes the eyelids.
Lacrimal part – involved in the drainage of tears.
Orbital part – tightly closes the eyelids
Innervation: Temporal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve
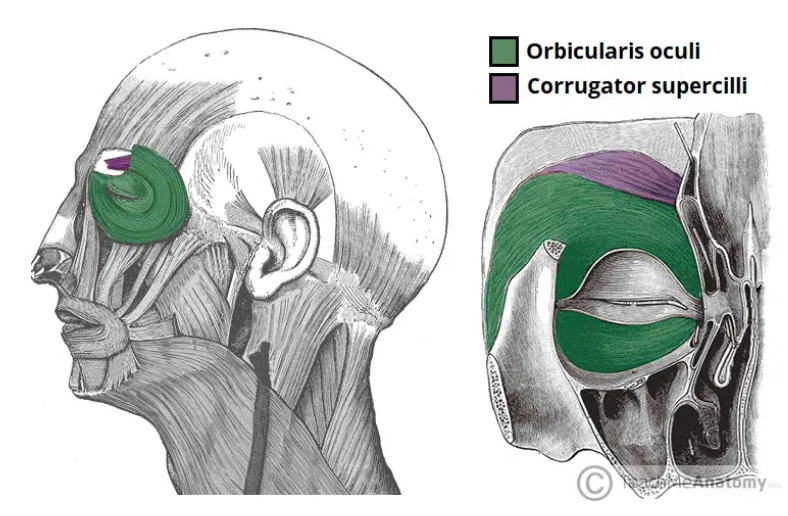
Action and innervation of the Corrugator Supercilii
Draws the eyebrows together, creating vertical wrinkles on the bridge of the nose (associated with frowning)
Innervation: Temporal branches of the facial nerve
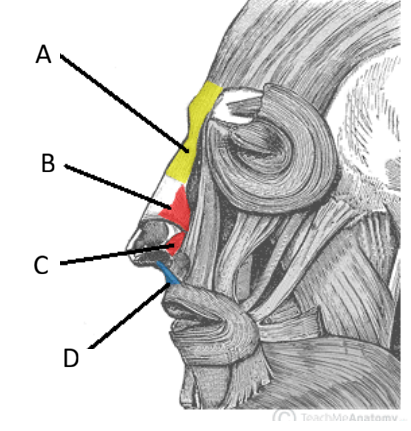
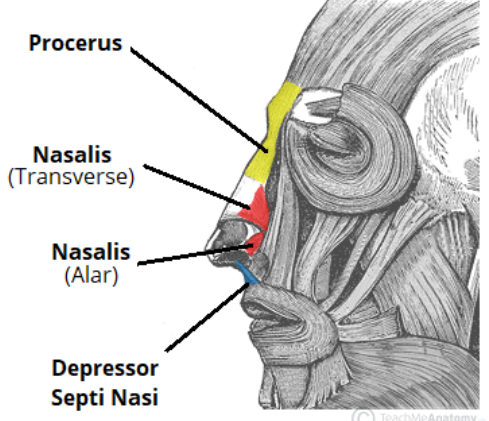
Action and innervation of the Orbicularis Oris
Closes the lips to narrow the oral opening
Innervation: Buccal branches of the facial nerve
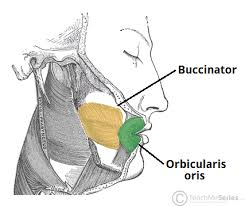
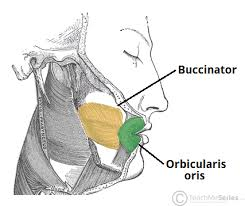
Action and innervation of the buccinator muscle
Pulls the cheek inwards against the teeth, preventing accumulation of food in that area
Innervation: Buccal branches of the facial nerve
Action and innervation of the platysma muscle
Depresses mandible and angle of mouth, tenses skin of lower face and anterior neck
Innervation: Cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII)
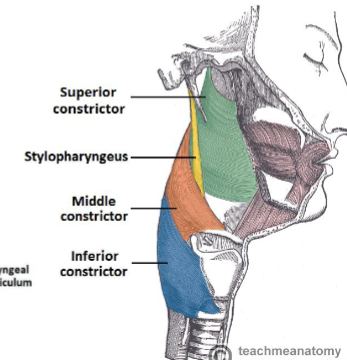
Location of the pharyngeal constrictors
Superior constrictor
Posterior: from base of occiput
Anterior: from mandible, pterygomandibular ligament, + pterygoid hamulus
Inserts as a midline raphe
Middle constrictor
From hyoid bone + stylohyoid ligament
Inserts as a midline raphe
Inferior constrictor – two parts:
Thyropharyngeus: from thyroid cartilage
Cricopharyngeus: from cricoid cartilage
What is Killian’s dehiscence?
weakness between the 2 inferior pharyngeal constrictors
The herniation of mucosa through Killian's dehiscence results in a Zenker's diverticulum (or pharyngeal pouch) → dysphagia, regurgitation, halitosis, cough
Innervation to the pharyngeal muscles
All muscles of the pharynx = CN X
Except stylopharyngeus = CN IX
Except Thyropharyngeus = CN Vc
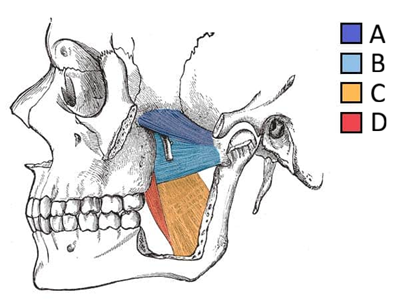
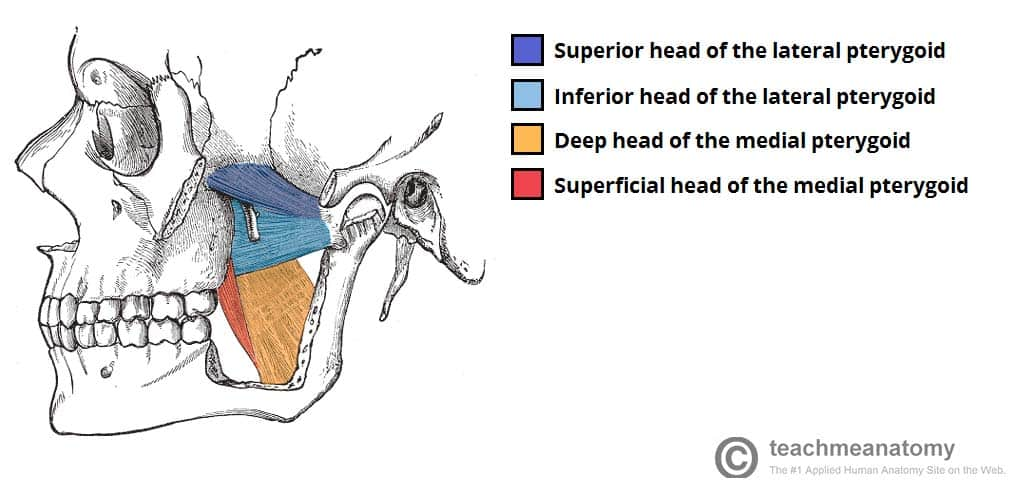
What are the muscles of mastication and their action and innervation
Four muscles – move the TMJ:
Masseter – elevates
Temporalis – elevates and retracts
Medial pterygoid – elevates
Lateral pterygoid – protracts
Innervated: Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
Name the intrinsic muscles of the tongue and their innervation
Superior and inferior longitudinal
Transverse
Vertical
Innervation: hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
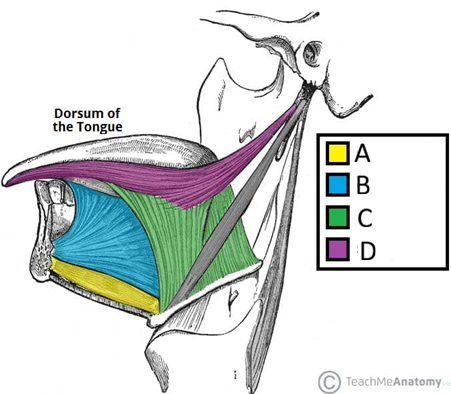
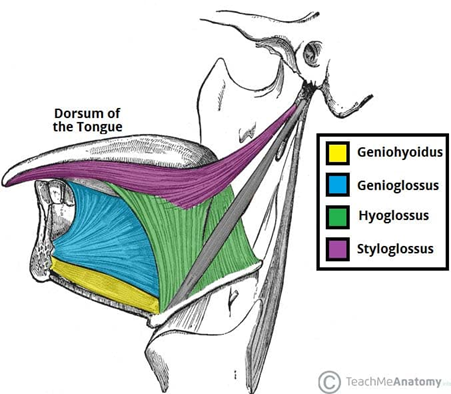
Name the extrinsic muscles of the tongue and their innervation
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Palatoglossus
Innervation: hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), except palatoglossus innervated by vagus nerve (CN X) (via branches of pharyngeal plexus)
Action of the intrinsic tongue muscles
Superior and inferior longitudinal: retracts and broadens tongue, elevates (superior) / lowers (inferior) apex of tongue
Transverse: narrows and elongates tongue
Vertical: broadens and elongates tongue
Action of the extrinsic tongue muscles
Genioglossus: depresses and protrudes tongue (bilateral contraction); deviates tongue contralaterally (unilateral contraction)
Hyoglossus: depresses and retracts tongue
Styloglossus: retracts and elevates lateral aspects of tongue
Palatoglossus: elevates root of tongue, constricts isthmus of fauce
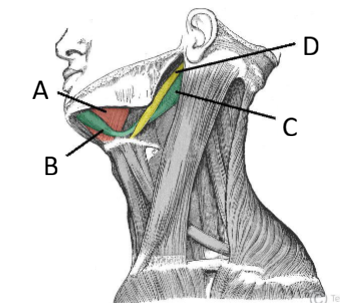
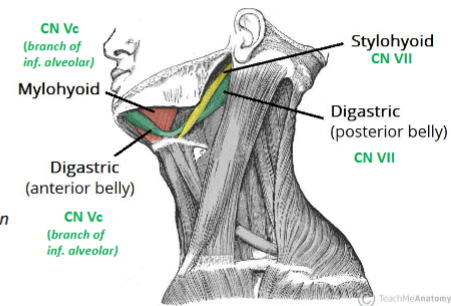
What are the Suprahyoid muscles and their actions?
Digastric
Stylohyoid
Mylohyoid
Geniohyoid
Action: elevate the hyoid
What innervates the suprahyoid muscles
Digastric:
Anterior belly: Nerve to mylohyoid (of inferior alveolar nerve (CN V3))
Posterior belly: Digastric branch of facial nerve (CN VII)
Stylohyoid:
Stylohyoid branch of facial nerve (CN VII)
Mylohyoid:
Nerve to mylohyoid (of inferior alveolar nerve (CN V3))
Geniohyoid:
Anterior ramus of spinal nerve C1 (via hypoglossal nerve CN XII))
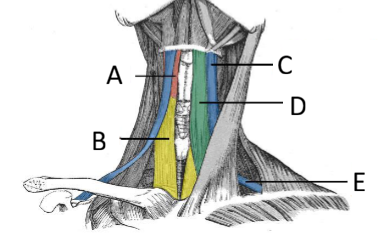
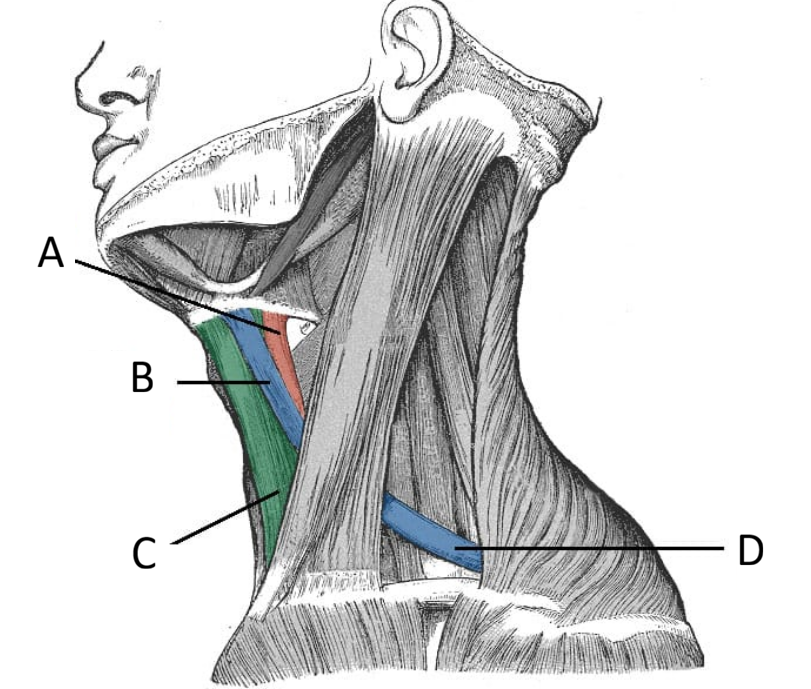
Name the infrahyoid muscles and their actions
Omohyoid (sup. and inf. bellies)
Sternothyroid: + depresses larynx
Thyrohyoid: + elevates larynx
Sternohyoid
Action: depress the hyoid
Innervation to the infrahyoid muscles
Anterior rami of spinal nerves C1-C3 (via ansa cervicalis):
Nerve to Omohyoid (sup. and inf. bellies)
Nerve to Sternothyroid
Nerve to Sternohyoid
Anterior ramus of spinal nerve C1 (via hypoglossal nerve):
Nerve to Thyrohyoid