EXP 5: Special Test for Saccharides
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Nitro-Chromic Acid Test
What is the test shown?

Nitric Acid (HNO3)
Potassium Chromate (K2CrO4)
What are the reagents of this test?

Oxidation
What is the process involved in this test?

Nitro-Chromic Acid Test
What is the test due to the presence of a -CHOH group?
Presence of -CHOH group/oxidation of primary alcohol
What is a positive result for the Nitro-Chromic Acid test due to?
Faint Blue
What color indicates a positive reaction for the Nitro-Chromic Acid Test?
Yeast, Sugar, Phosphate Buffer
What are the reagents of alcohol fermentation?
6.4-6.8
What is the pH of phosphate buffer?
Sucrose, Glucose, Galactose
What are the sugars used in Alcoholic Fermentation?
Bubbles
What is indicative of a positive reaction of Alcoholic Fermentation?
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
What are the bubbles of Alcoholic Fermentation due to?
Mucic Acid Test/Galactaric Acid Test
What is the test shown?

Galactose
What is the sugar tested?

Oxidation
What is the process involved?

Mucic Acid
Identify the substance.
Mucic Acid Test
What is the test for identifying galactose?
Galactose
What sugar does the Mucic Acid test identify?
Oxidation of Galactose
What is Mucic Acid formed by?
5% Galactose & Conc HNO3
What are the reagents of the Mucic Acid Test?
White Crystals
What is the result of the Mucic Acid Test?
True
True or False: Mucic Acid is an isomer of saccharide acid.
Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4)
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
Rochelle Salt
What are the components of Fehling’s solution?
0.01 M Glucose
0.01 M Fructose
0.01 M Sucrose
0.7% Starch
Water
What are the sugars and control tested in Fehling’s test?
Glucose
Fructose
What sugars test positive in Fehling’s Test?
Red Precipitate
What is a positive reaction in Fehling’s test?
Reduction of the copper ions (and oxidation of either the Aldehyde or Ketone Group)
What is the precipitate in Fehling’s test due to?
Sucrose & Starch because they are non-reducing sugars.
What sugars test negative for Fehling’s test and why?
Benedict’s Test
What is the test shown?
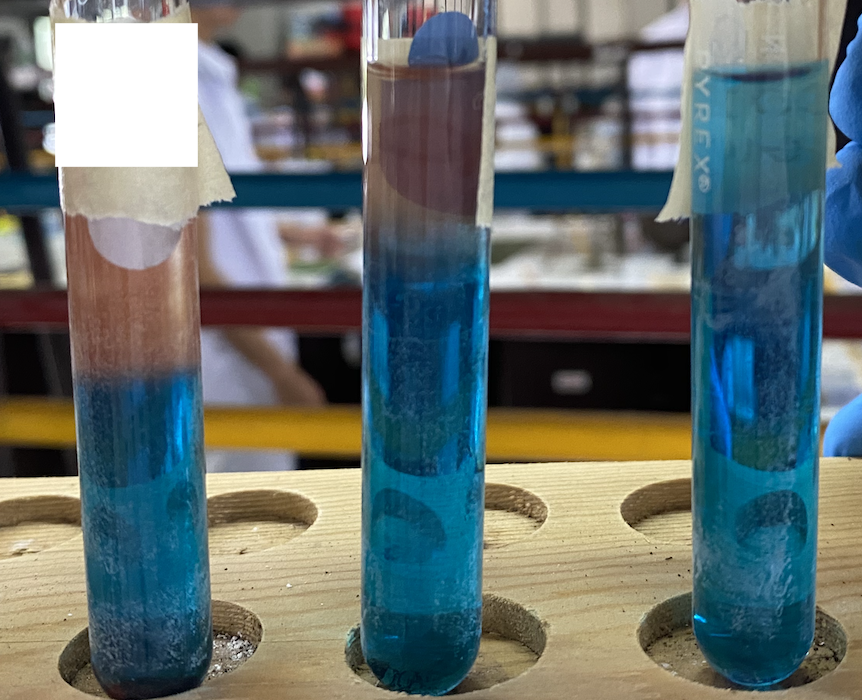

Test for glucose in urine
What is this test clinically used for?

Benedict’s Solution (Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4), Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3), Sodium Citrate)
What is the reagent of this test?

0.1 M Glucose
0.01 M Glucose
0.002 M Glucose
What sugar is in each test tube (left to right)
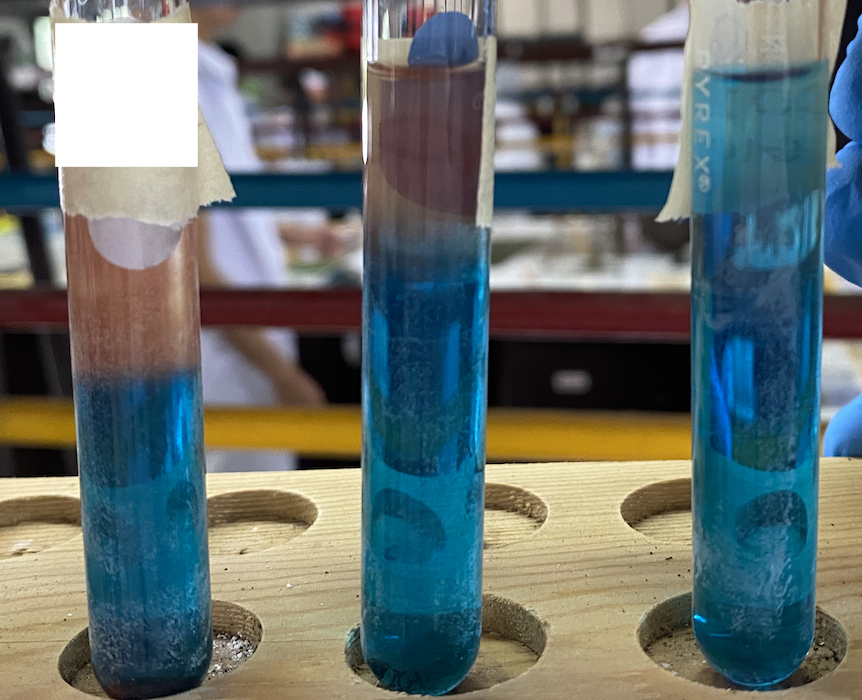

Benedict’s Test
What is the qualitative test for glucose in urine?
Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4)
Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
Sodium Citrate
What is Benedict’s solution composed of?
0.1 M Glucose
0.01 M Glucose
0.002 M Glucose
What is the order of most to least reaction in Benedict’s test?
Barfoed’s Test
What is the test to detect reducing monosaccharides, thus differentiating monosaccharides form disaccharides?
Cupric Acetate (Cu(CH3COO)2) in Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
What is in Barfoed’s Solution?
0.01 M Glucose
0.01 M Fructose
0.01 M Lactose
0.01 M Sucrose
0.03 M Glucose
0.03 M Lactose
0.03 M Sucrose
What are the sugars tested in Barfoed’s Test?
0.03 M Glucose
0.01 M Fructose
0.01 M Glucose
NR - 0.03 M Sucrose
NR - 0.01 M Sucrose
NR - 0.01 M Lactose
NR - 0.03 M Lactose
What is the order to fastest to slowest speed of reduction in BARFOED’s Test?
False (Fructose reacts faster than glucose in BARFOED’s Test)
True or False: With the same concentration, glucose reacts faster than fructose in BARFOED’s test.
Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O)
What is the product of reduction in Barfoed’s Test?
Iodine Test
What is the test for polysaccharides?
Iodine Test
What is the test shown?

Starch
Dextrin
What are the sugars in the test tube (left to right)?

Starch: Colorless
Dextrin: Yellow
When heated, what color does each sugar become (left to right)?

Iodine (I2) Solution
What is the reagent added?

Starch & Dextrin
What are the sugars tested in the Iodine test?
Starch: When warmed becomes colorless but when cooled returns to original color, blue-black
Dextrin: When warmed becomes yellow but when cooled returns to original color, black-violet
What occurs to the sugars in Iodine Test when heated then cooled?
C6H8N2
Formula of phenylhydrazine
5% Glucose
5% Fructose
5% Maltose
5% Lactose
5% Sucrose
What are the sugars tested in the Phenylhydrazine reaction?
Phenylhydrazine Reaction
What is the test useful in identifying sugars with free aldehyde or ketone group?
2 phenylhydrazine hydrochloride : 3 sodium acetate
How is phenylhydrazine prepared?
Glucosazone
Fructosazone
Maltosazone
Lactosazone
NO Osazone Crystals
What is the product of the following in the Phenylhydrazine reaction:
Glucose
Fructose
Maltose
Lactose
Sucrose
A. Barfoed’s (since Barfoed’s solution contains Acetic Acid)
Which reaction occurs in an acidic environment?
A. Barfoed’s
B. Fehling’s
B. Fehling’s (since Fehling’s solution contains Sodium Hydroxide)
Which reaction occurs in an basic environment?
A. Barfoed’s
B. Fehling’s
True (In Benedict’s Test, the higher the glucose concentration, the higher the amount of red precipitate)
True or False: The degree of colors change depends on the amount of reducing sugar present.
Osazone Test
What is another name for the phenylhydrazine reaction?
Fructose (Fructosazone): 2 minutes
Glucose (Glucosazone): 4-5 minutes
Maltose (Maltosazone): Soluble in hot water
Lactose (Lactosazone): Soluble in hot water
Sucrose without Hydrolysis: N/A (No crystals form unless Sucrose is hydrolyzed)
Time or Solubility for each osazone formation?
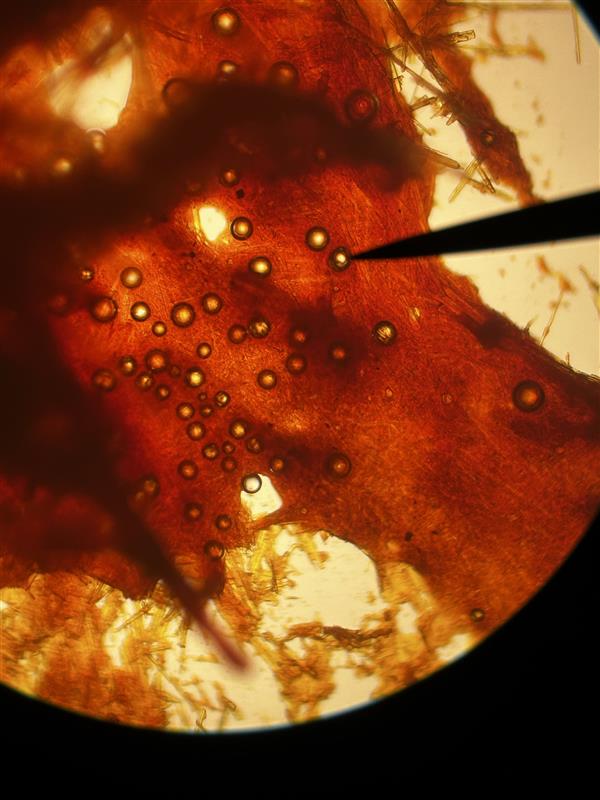
Glucosazone; Needle-Like
Identify name and describe the osazone.
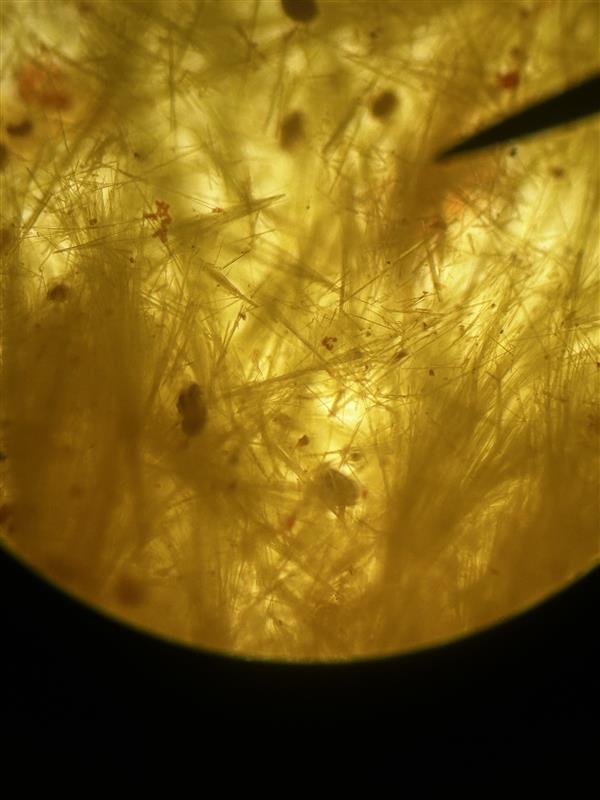
Fructosazone; Needle-like
Identify name and describe the osazone.
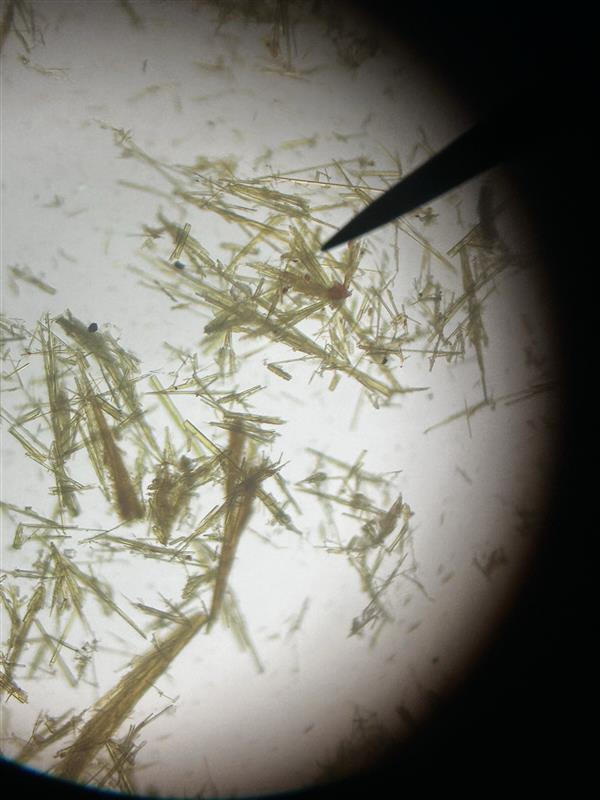
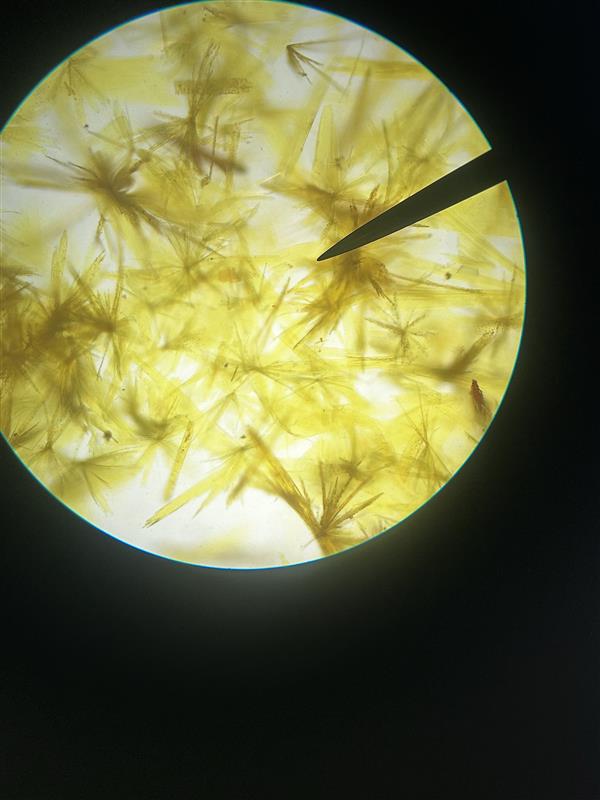
Maltosazone; sunflower-shaped
Identify name and describe the osazone.

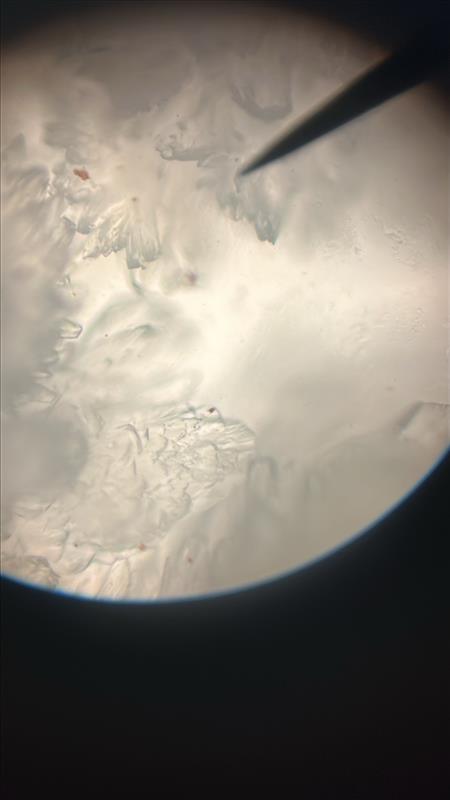
Lactosazone; cotton-ball like
Identify name and describe the osazone.
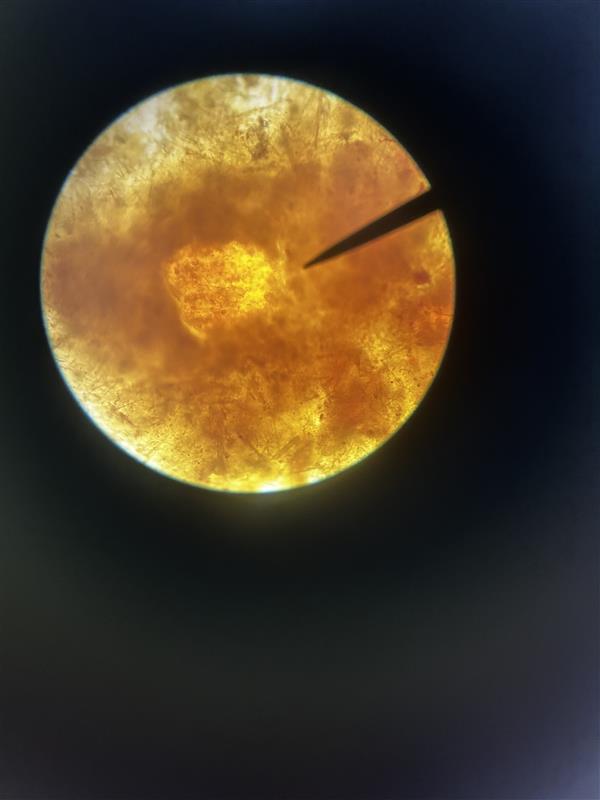
N/A; No osazone has formed
Identify name and describe the osazone.