Lecture Monomers & Polymers
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Features of water?
~Water is polar
~Can form hydrogen bonds
~High specific heat capacity
Hydroxyl group example
Alcohol
Properties of hydroxyl group
~Forms hydrogen bonds with water, helping to dissolve molecules
~Enables linkages to other molecules by condensation
Is water hydrophilic or hydrophobic & why?
Water is polar so hydrophilic
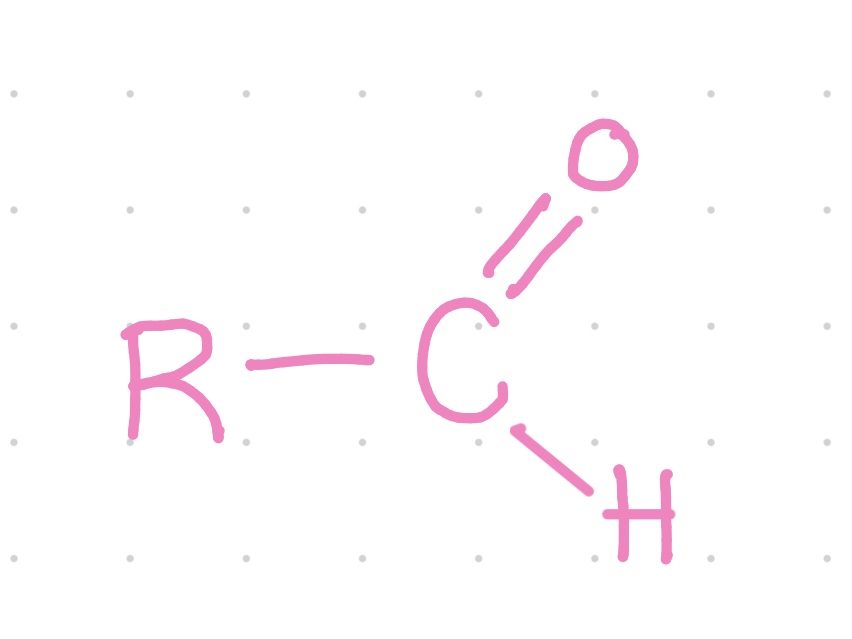
What is this functional group?
Aldehyde
Properties of aldehydes?
~ Polar
~ C=O is very reactive.
~ Important in building molecules and in energy releasing reactions
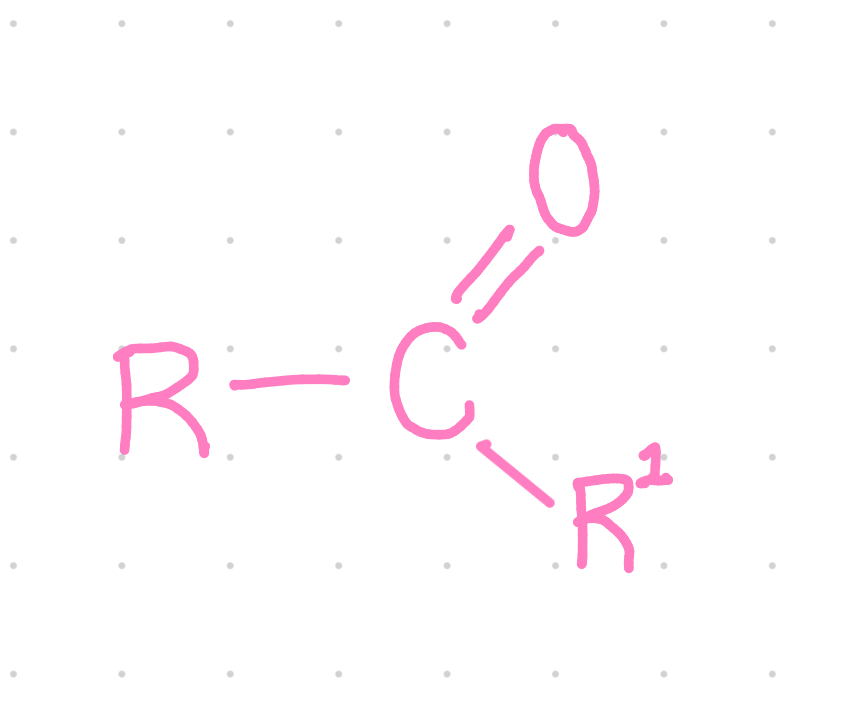
Functional group?
Ketone
Properties of ketones?
~Polar
~ C=O is important in carbohydrates and energy reactions
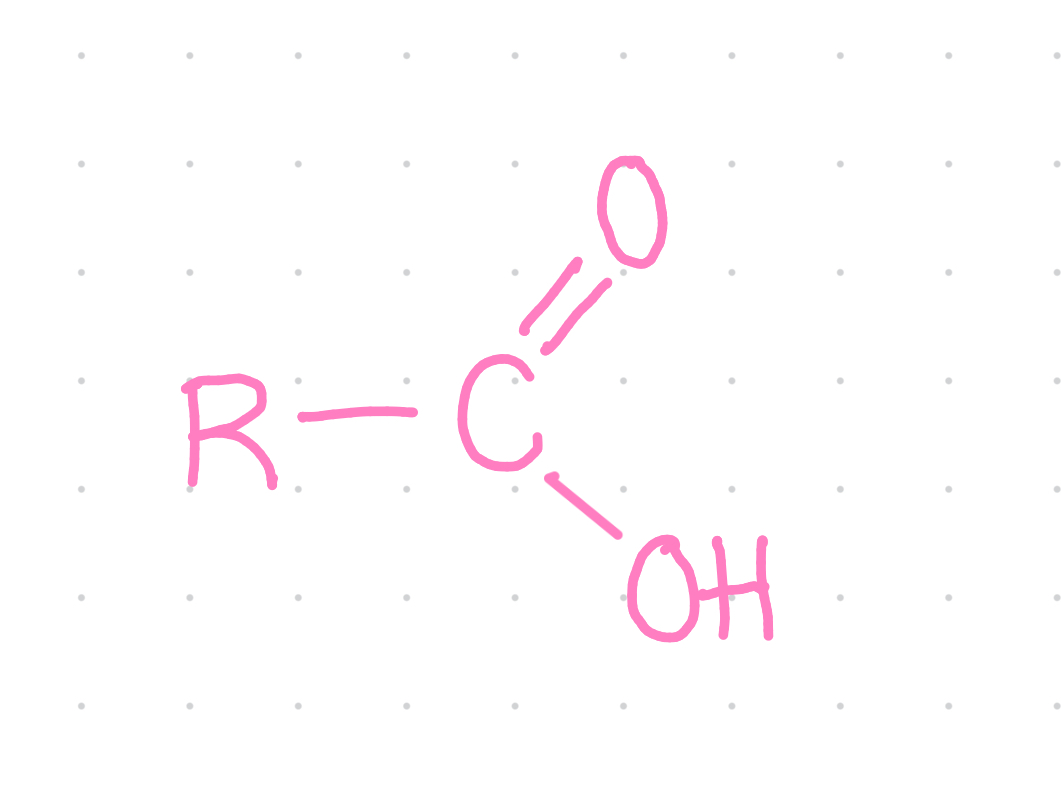
Functional group?
Carboxyl
Properties of carboxyl group?
~ charged: acidic
~ ionises in living tissues to form —COO- and H+
~ gives up —OH group to form condensation reaction
~ Some carboxylic acids are important in energy releasing reactions
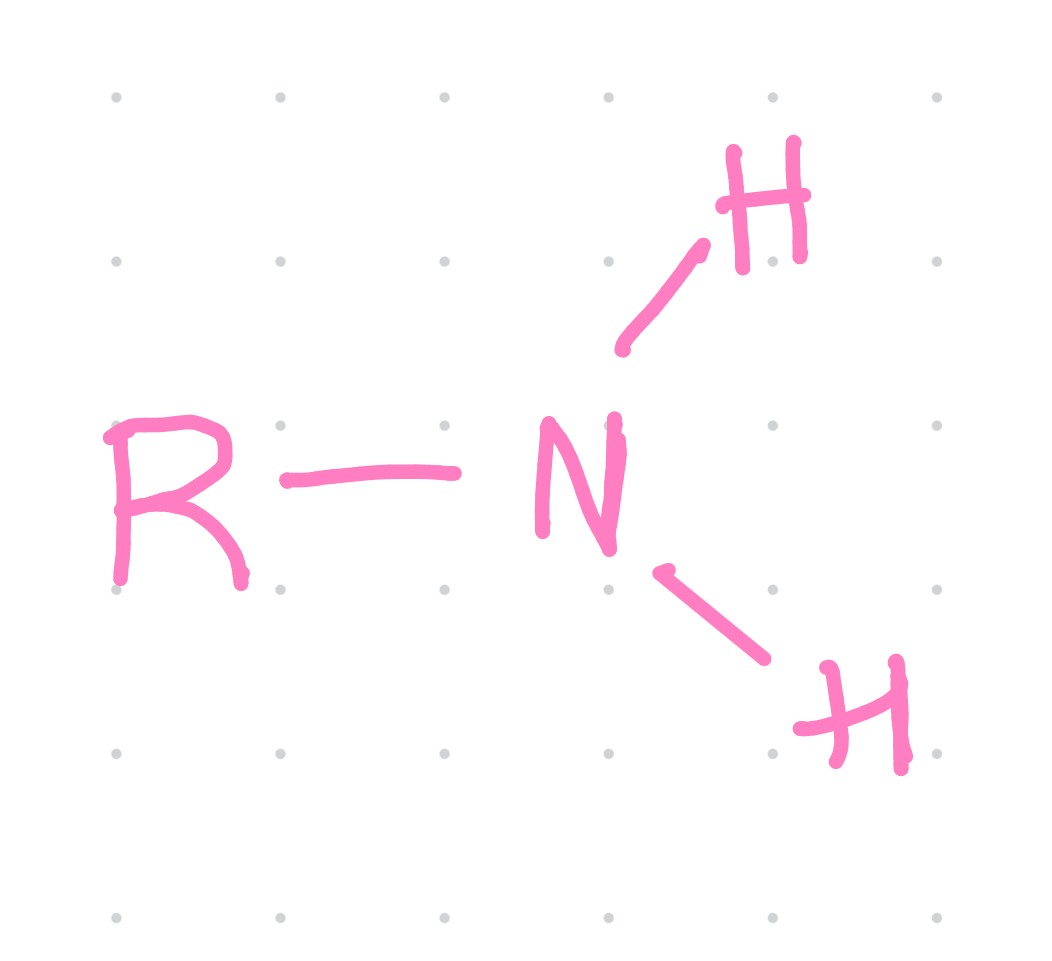
Functional group?
Amino
Example of an amino group?
Amines - methylamine
Properties of amino groups?
~ charged: basic
~ accepts H+ in living tissues to form NH3+
~ enters into condensation reactions by giving up H+
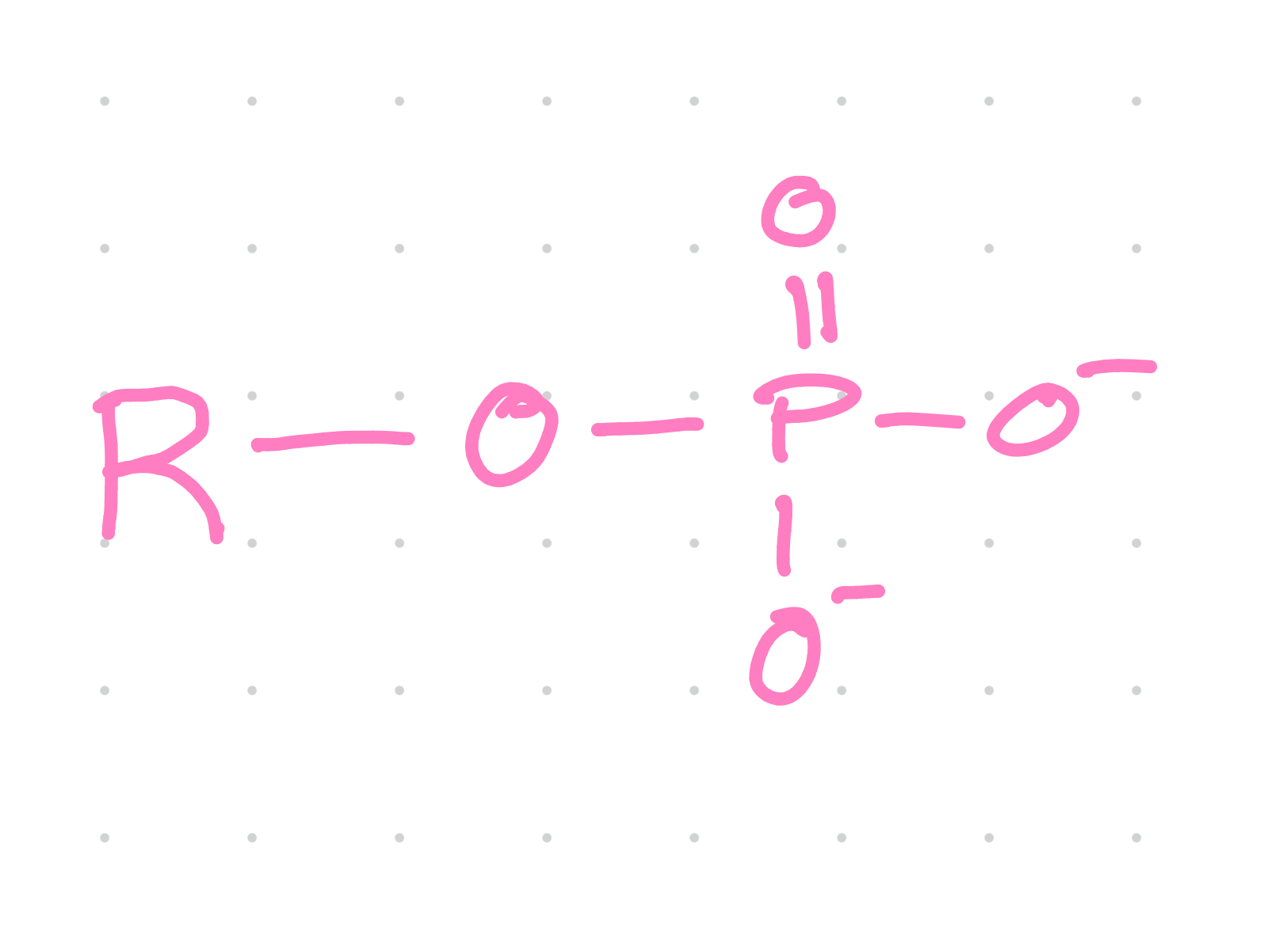
Functional group?
Phosphate
Properties of phosphates?
~Charged: acidic
~ enters into condensation reaction by releasing —OH
~ when bonded to another phosphate hydrolysis releases much energy
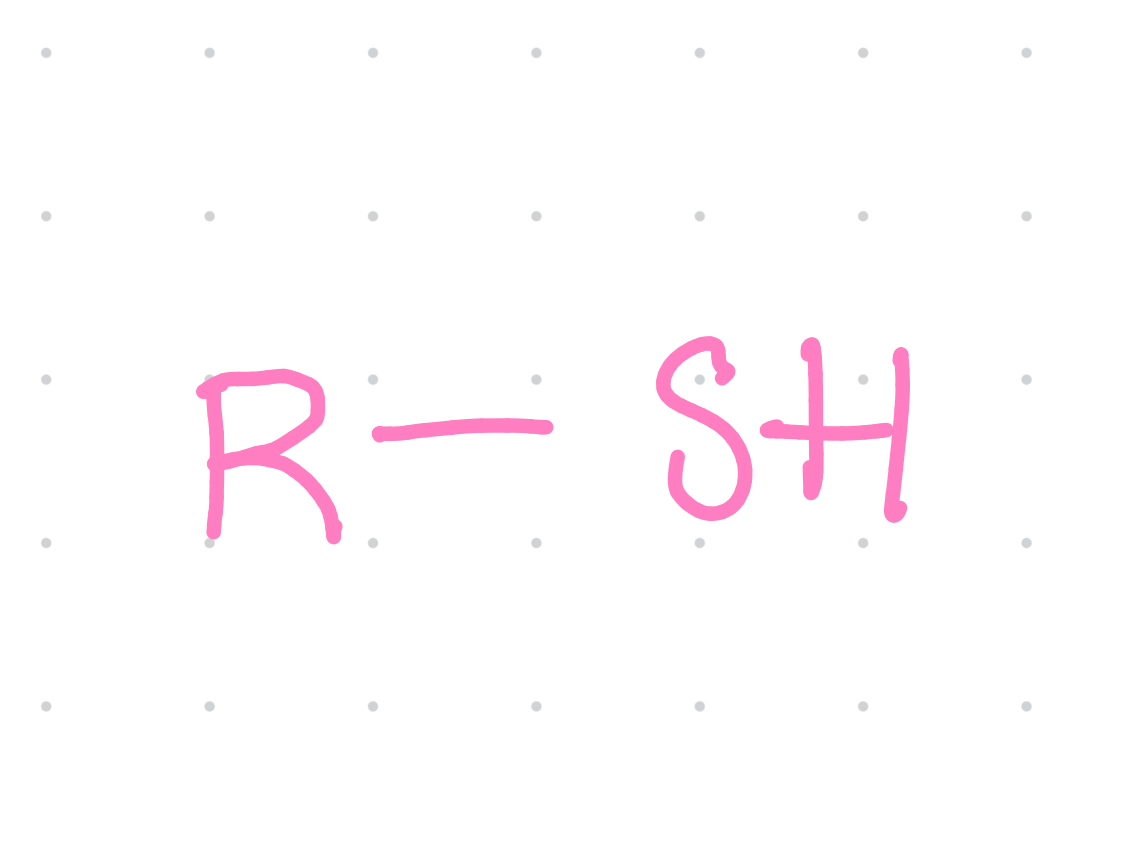
Functional group?
Sulfhydryl
What class of compound is a sulfhydryl compound found in?
Thiols
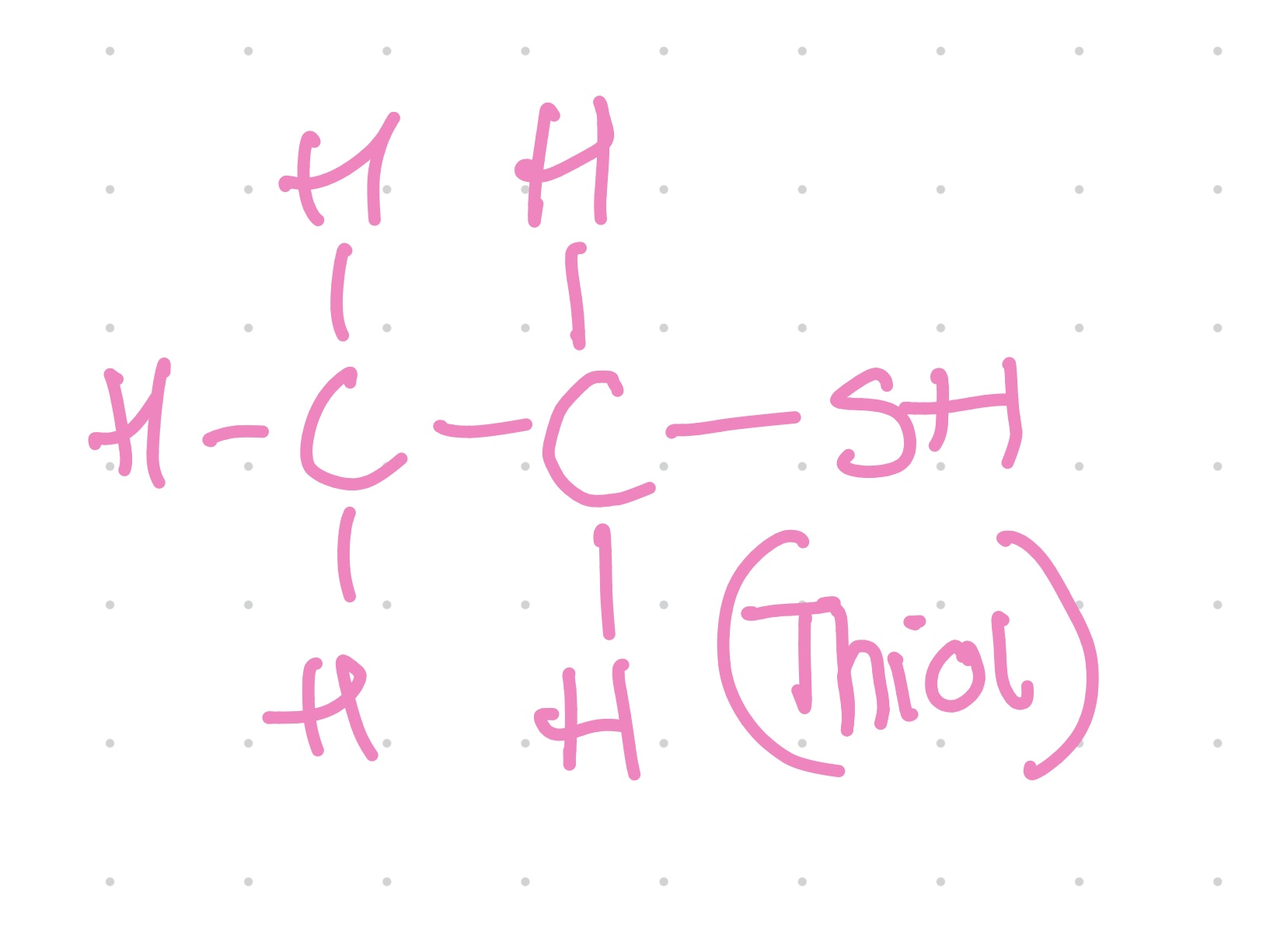
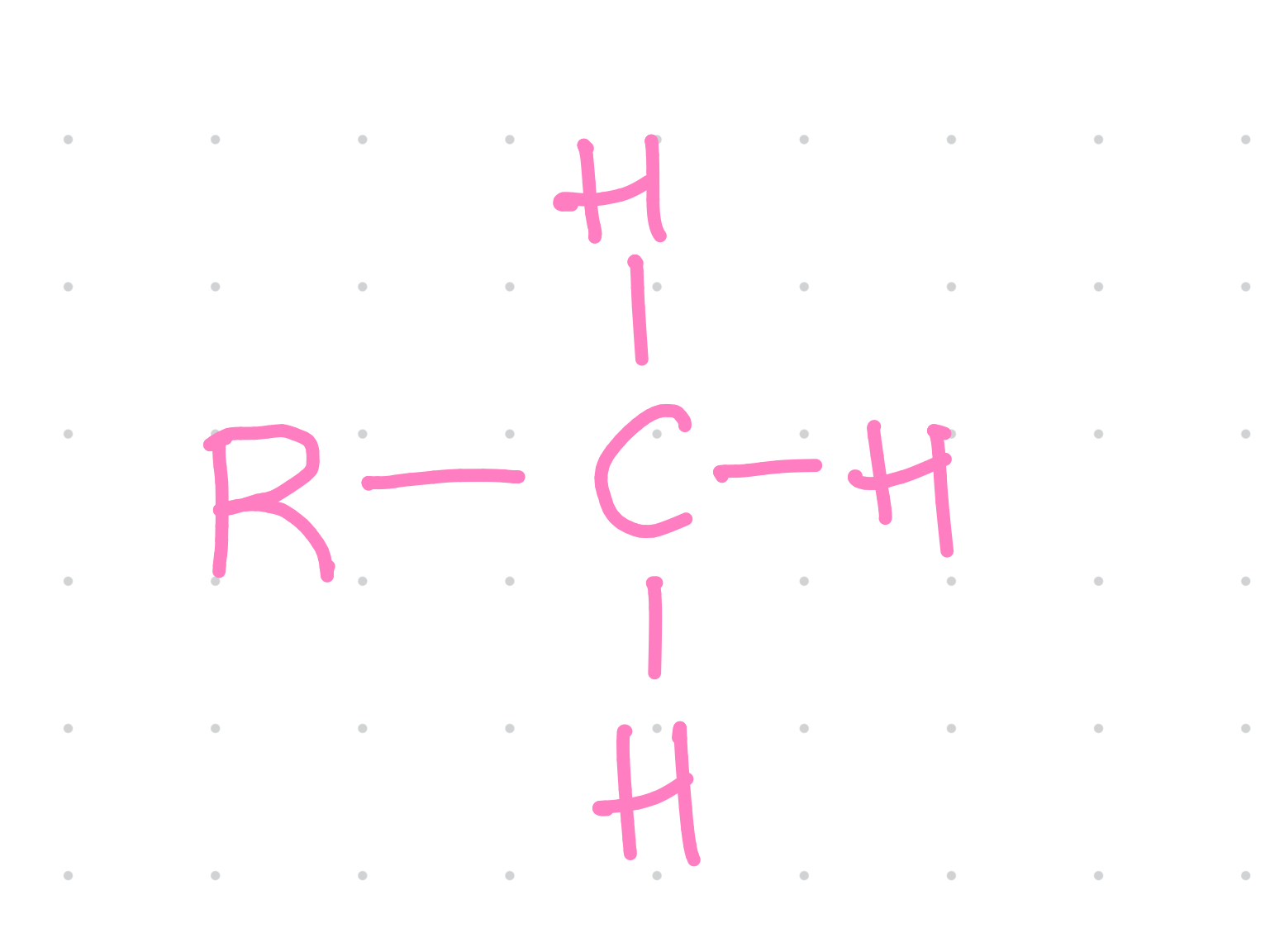
Functional group?
Methyl
What compound is methyl group found in?
Alkyl
Properties of methyl group?
~ Nonpolar
~ Important in reactions with other nonpolar molecules and in energy transfer
Key macromolecules?
~Proteins
~Carbohydrates
~Lipids
~Nucleic Acids
What is a protein's monomer?
Amino acids
Amino acid structure?
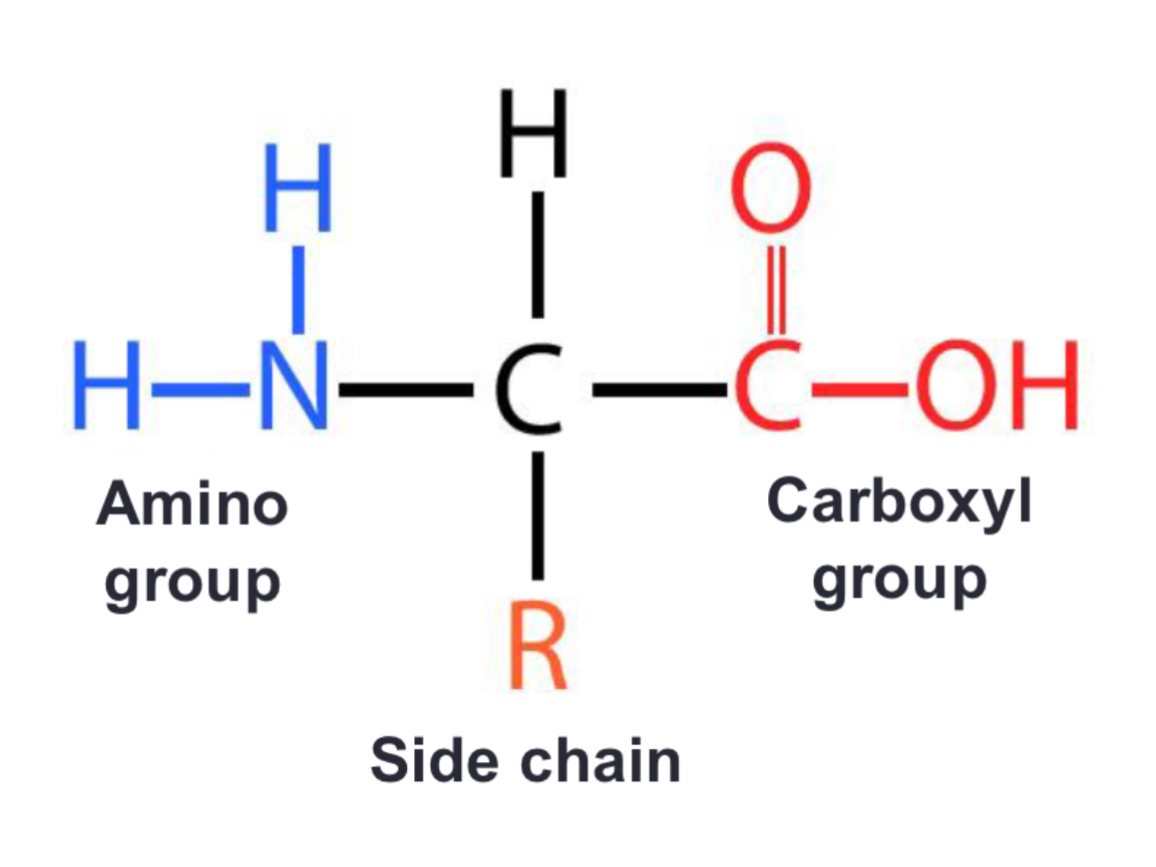
Amino acid properties?
~Nonpolar, hydrophobic
~Polar, hydrophilic
~Acidic and basic
What is the start codon?
AUG- encodes for methionine
Chemical formula for generic molecule of carbohydrate?
(CH2O)n )n
(CH2O)1 Example and function
Formaldehyde
Carcinogen
(CH2O)2 example and function
Glycoaldehyde
Highly reactive
(CH2O)3 example and function
Triose- Glyceraldehyde
Glycolysis pathway
(CH2O)4 example and function
Tetroses- Erythrose & Threose
Rare in mammalian biology
(CH2O)5 example and function
Pentoses
DNA & RNA
(CH2O)6 example and function
Hexose
Energy and monomer for polysaccharides
Carbohydrate polysaccharide examples?
~Cellulose
~Starch
~Glycogen
Where are carbohydrate disorders found?
X chromosome
Most common lipids?
~ triglycerides
~ phospholipids
Name the 7 lipid groups
~ Fatty acyls
~ Glycerolipids (Triglycerides)
~ Glycerophospholipids
~ Sterol lipids
~ Prenol lipids
~ Saccharolipids
~ Polyketides
What makes a fat saturated?
No carbon carbon double bonds
What is a triglyceride?
~ 1 glycerol
~ 3 fatty acids
What is a phospholipid?
~ 1 phosphate group
~ 1 glycerol
~ 2 fatty acids
Phospholipid bilayer has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail.
Importance of lipids?
Small uncharged molecules (e.g. glycerol, water, ethanol) can pass through the hydrophobic lipid bilayer.
Large polar molecules and ions can’t pass through the lipid bilayer.
Steroid examples
Cholesterol
Testosterone
Oestrogen