MRI Artifacts
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
A radiologist notes that the chemical shift artifact along the vertebral endplates is much more severe on images from their new 3T scanner compared to their old 1.5T scanner. This is because the artifact is worse on the:
A. 0.5T resistive magnet
B. 0.23T permanent magnet
C. 1.5T superconducting magnet
D. 3T superconducting magnet
D. 3T superconducting magnet

A ________ artifact occurs when a tendon or ligament is approximately 55 degrees to the direction of the main magnetic field, and a short TE value pulse sequence is utilized
A. Magic angle
B. Dielectric
C. Aliasing
D. Annefact
E. Parallel Imaging
A. Magic angle

Ensuring adequate door suction in the MR scan room will aid in preventing which artifacts from appearing in an MR image?
A. Wraparound artifacts
B. Parallel imaging artifacts
C. Chemical shift
D. RF zipper
E. Cross talk
D. RF zipper

A decrease in the voxel volume yields:
A. Aliasing artifacts
B. An increase in partial volume averaging
C. A decrease in partial volume averaging
D. An increase in overall signal to noise
C. A decrease in partial volume averaging

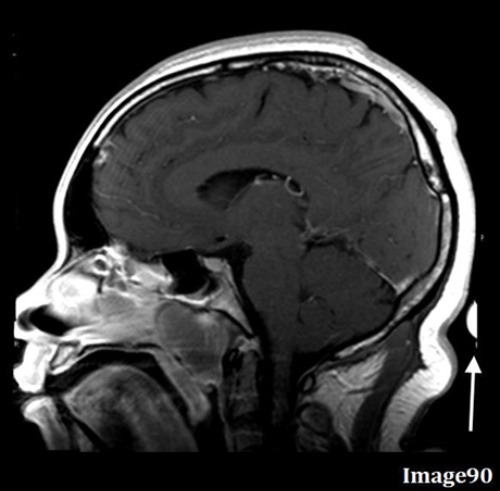
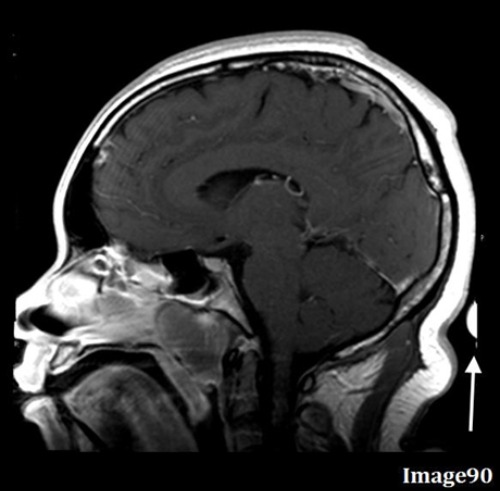
What is the most direct way to correct for the wrap-around artifact seen in Image 90?
A. Increase parallel imaging factor
B. Reduce FOV
C. Increase voxel size
D. Enable flow compensation
E. Increase FOV
E. Increase FOV

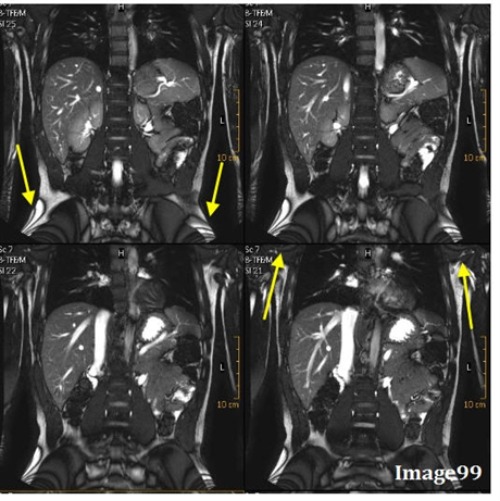
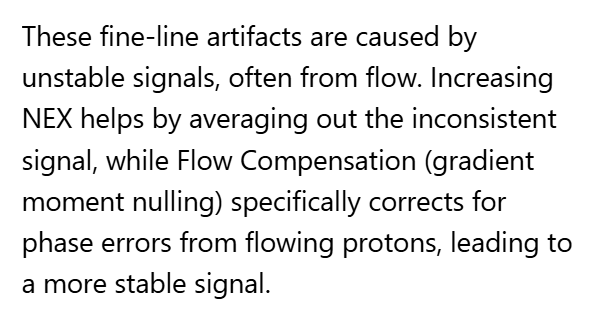
The artifact in Image 99 is caused by:
A. Interference of aliased signals at different phases
B. When a small matrix is used, it incompletely digitizes the echo by the end of the acquisition
C. Undersampling
D. Differing frequencies of fat and water
A. Interference of aliased signals at different phases

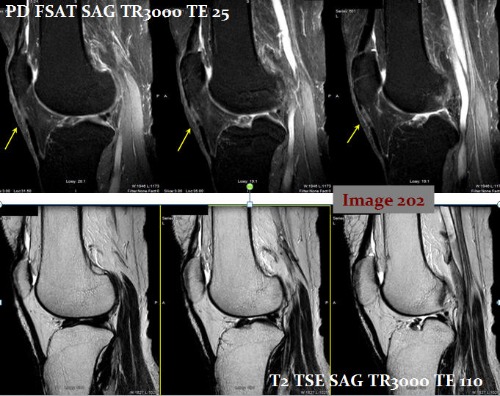
The yellow arrows in Image 202 are pointing to an artifactual increase in signal within the supraspinatus tendon. This is known as:
A. Magic angle
B. Dielectric
C. Aliasing
D. Annefact
A. Magic angle

The white arrow in Image 90 points to anatomy from the top of the head being wrapped to the bottom of the image. What is this artifact?
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. RF zipper
D. Wraparound (aliasing)
E. Magnetic susceptibility
D. Wraparound (aliasing)

To correct for the wrap-around (aliasing) artifact seen in Image 89, the technologist should:
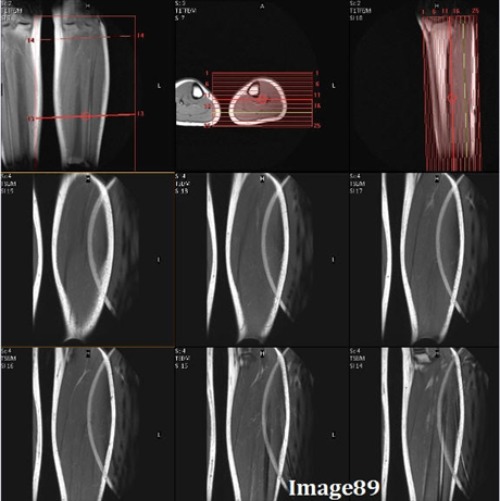
A. Utilize oversampling
B. Utilize undersampling
C. Enable anti-aliasing option
D. Enable flow compensation
E. A and/or C
F. B and/or C
E. A and/or C
The yellow arrows in Image 201 display what type of MRI artifact?
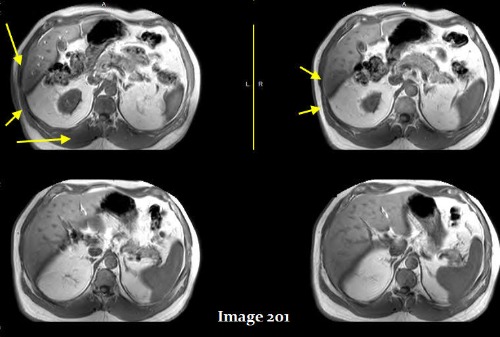
A. Annefact
B. Aliasing
C. Dielectric effects
D. Fine line / FID
C. Dielectric effects

During a shoulder MRI, the patient’s opposite shoulder is wrapped into the image, obscuring the anatomy of interest. This aliasing occurs because tissue outside the selected FOV is:
A. Oversampled
B. Undersampled
C. Not sampled
D. Chemically Shifted
B. Undersampled

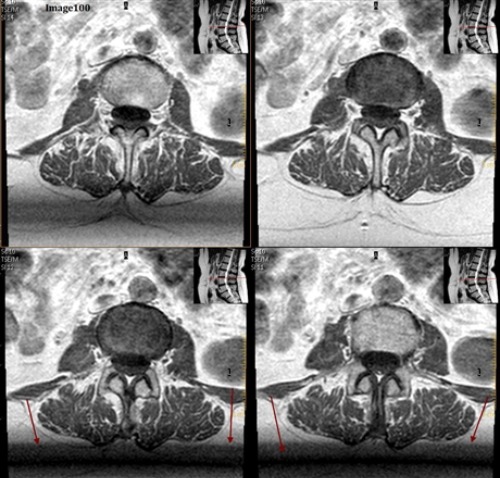
To correct for the Gibbs truncation artifact (white arrows) seen in the spinal cord in Image 85, the technologist should:
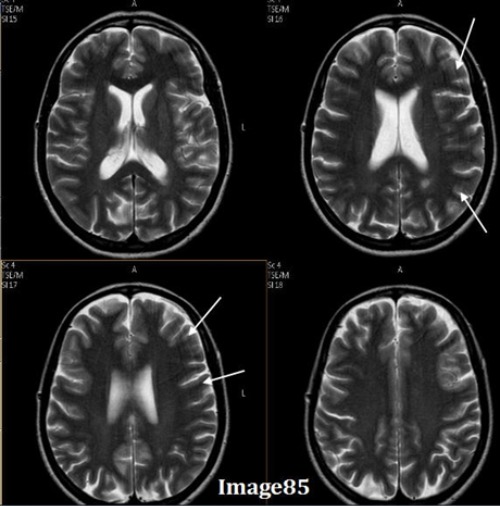
A. Decrease phase matrix
B. Increase phase matrix
C. Increase voxel size
D. Enable flow compensation
E. Utilize gating techniques
B. Increase phase matrix

The red arrows in Image 172 are indicative of which type of MRI artifact?
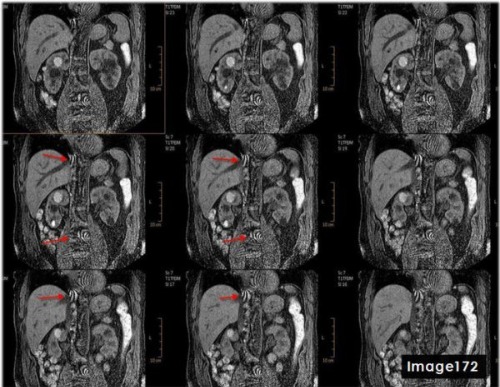
A. Wraparound
B. Annefact
C. Dielectric effects
D. Parallel Imaging
D. Parallel Imaging

A technologist observes a streak artifact across the image. After checking the scanner room, they realize the door was not fully sealed. This leak in the RF shielding typically appears as:
A. A zipper artifact in the frequency direction
B. A bright spot in the center of the image
C. A black outlining of anatomy with fat and water frequencies in the same pixel
D. A ghosting of anatomy along the image edge
A. A zipper artifact in the frequency direction

What is the term used to describe gradient field interactions as visual light flashes, or “seeing starts”?
A. Magnetophosphenes
B. Magnetohydrodynamic effect
C. Magnetopolar spin
D. ferromagnetic effect
A. Magnetophosphenes

This image is degraded by a sharp line of noise running through the center. What is this artifact called?
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. Dielectric effects
D. RF zipper
E. Magnetic susceptibility
D. RF zipper

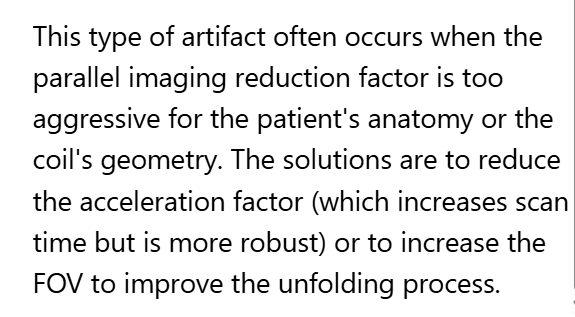
To correct for the central aliasing artifact shown in Image 172, which is characteristic of parallel imaging reconstruction error, the MRI technologist would:
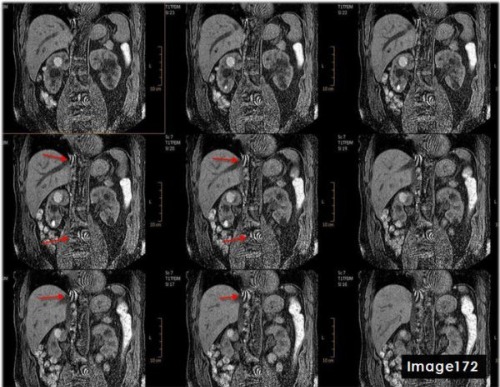
A. Reduce parallel imaging factor
B. Increase parallel imaging factor
C. Increase FOV
D. A and/or C
D. A and/or C (Reduce parallel imaging factor and/or Increase FOV)
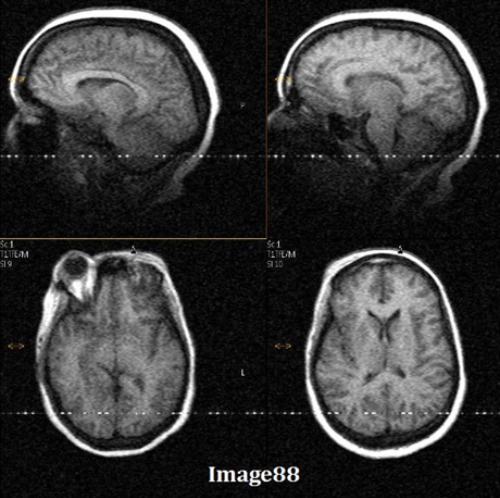
An MRI of the brain is performed to rule out an acoustic neuroma. The DWI images are degraded by susceptibility artifact near the internal auditory canals. How can this artifact be minimized?
A. Increasing FOV
B. Increasing parallel imaging acceleration factor
C. Decreasing parallel imaging acceleration factor
D. Reducing flip angle
B. Increasing parallel imaging acceleration factor

To reduce an RF zipper artifact:
A. Increase FOV
B. Oversample phase encoding steps
C. Enable flow compensation
D. Close scan room door and ensure adequate door suction
D. Close scan room door and ensure adequate door suction

In an MRI of the orbit, you notice a dark outline on one side of the optic nerve and a bright outline on the other. This chemical shift artifact occurs because:
A. The field strength is lower than desired
B. Data is undersampled in the phase encoding direction
C. RF leaks cause streak artifacts
D. Fat and water precess at different frequencies
D. Fat and water precess at different frequencies

Which artifact mimics a syrinx in the spine?
A. Zipper
B. FID artifact
C. Truncation
D. Aliasing
C. Truncation

The _________ magnetic field poses risks to patients and staff, due to the torpedo effect when a ferromagnetic object becomes magnetized and attracts to the large magnet.
A. Gradient
B. Main static
C. radiofrequency
D. Phased array
B. Main static

A patient with dental braces requires a brain MRI. Which pulse sequence would be most severely affected by magnetic susceptibility artifact from the braces?
A. Spin echo sequences
B. Fast spin echo
C. Inversion recovery
D. Gradient echo
D. Gradient echo

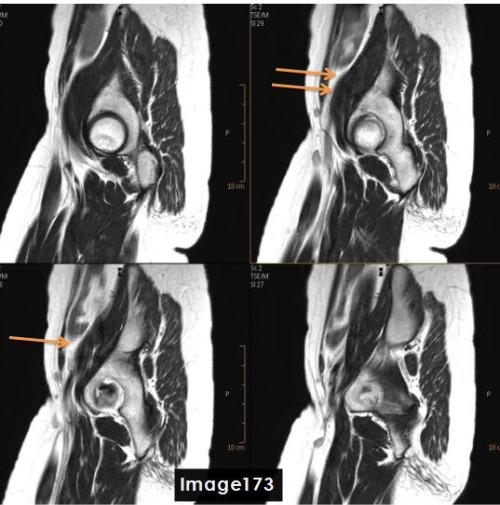
The arrows in Image 100 are pointing to bands of signal variation where adjacent slices appear to be affecting one another. This is an example of:
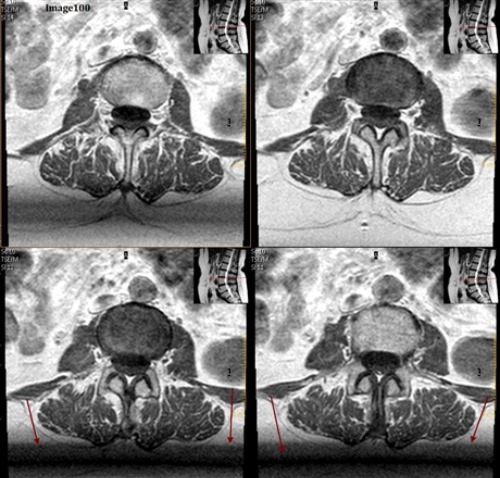
A. Gibbs truncation
B. Cross talk artifact
C. Dielectric effects
D. Wraparound (aliasing)
E. Partial volume averaging
B. Cross talk artifact

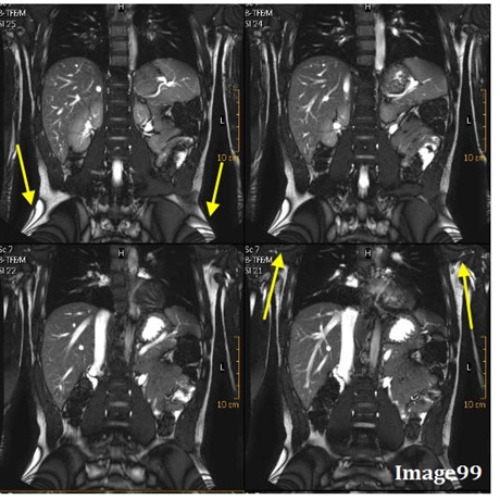
The artifact in Image 101 is caused by:
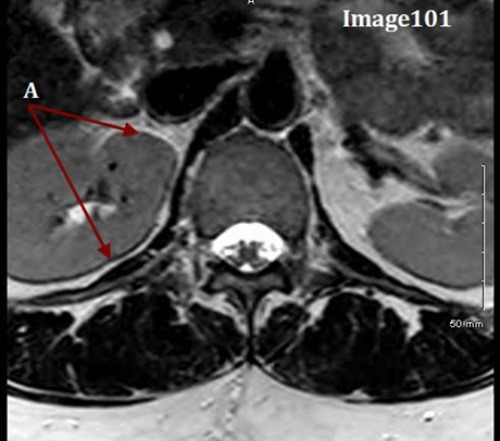
A. Local eddy currents due to the increased conductivity of body tissue
B. When a small matrix is used, it incompletely digitizes the echo by the end of the acquisition
C. Differing frequencies of fat and water
D. The imperfect shape of RF slice profiles, which leads to an unintended excitation of an adjacent slice or tissue
C. Differing frequencies of fat and water

A technologist notices that in a multi-slice T2 axial brain sequence, the slices in the middle of the stack appear to have lower SNR than the slices at the ends. This “cross talk” artifact can be minimized by:
A. Increase the interslice gap
B. Decrease the interslice gap
C. Oversample
D. Enable flow compensation
A. Increase the interslice gap

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses _______ separate magnetic fields to perform the task of routine image acquisition.
A. Two
B. Three
C. Four
D. Five
B. Three

Which of the following influences can lead to artifacts?
A. Magnetic field inhomogeneity
B. Machine hardware
C. The patient
D. All of the above
E. A & B only
D. All of the above

To reduce the appearance of a Gibbs truncation artifact, the:
A. Number of phase encodings must be increased
B. Number of phase encodings must be decreased
C. NEX must be increased
D. NEX must be decreased
A. Number of phase encodings must be increased

Image 86 is an example of which kind of artifact?
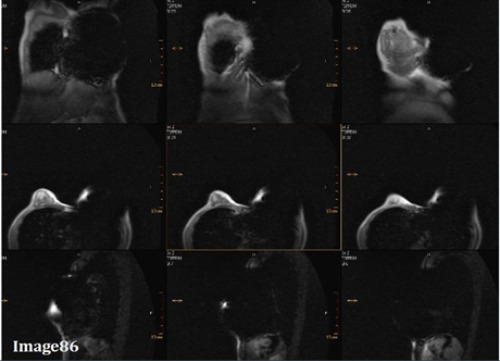
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. Dielectric effects
D. RF zipper
E. Magnetic susceptibility
E. Magnetic susceptibility

When trying to reduce artifacts from a metal implant, certain techniques that use a gradient echo acquisition should be avoided. Which of the following should be avoided in metal artifact reduction sequences?
A. Anti aliasing
B. Parallel imaging
C. Flow compensation
D. Partial echo
B. Parallel imaging
A FID crushing artifact can be eliminated with the use of:
A. Flow compensation technique
B. No phase wrap/anti-aliasing
C. Increased NEX
D. A and/or C
D. A and/or C
The arrows in Image 99 are pointing to a zebra-like artifact caused by interference patterns. What is this artifact called?
A. Gibbs truncation
B. Cross talk
C. Moire
D. Wraparound (aliasing)
C. Moire

On a sagittal T2 image of the cervical spine, you notice fine, parallel lines appearing within the spinal cord, mimicking a syrinx. You identify this as a Gibbs truncation artifact. What is the most effective way to remedy this?
A. Reduce the number of phase encodings
B. Increase the number of phase encodings
C. Increase the field of view
D. Decrease the TE
B. Increase the number of phase encodings

To reduce the severity of chemical shift artifacts seen at the interface of fat and muscle in an extremity MRI, the:
A. Receiver bandwidth should be increased
B. Number of echo train lengths should be increased
C. Receiver bandwidth should be decreased
D. Number of echo train lengths should be decreased
A. Receiver bandwidth should be increased

Letter A in Image 101 is pointing to the dark and bright bands along the border of the vertebral body. What type of MR artifact is this?
A. Partial volume averaging
B. Gibbs truncation
C. Cross talk
D. Wraparound (aliasing)
E. Chemical shift
E. Chemical shift

A technologist is trying to minimize susceptibility artifact from an implant. A colleague suggest shortening the TE. This helps because:
A. Susceptibility artifact increases
B. Susceptibility artifact decreases
C. Aliasing artifacts increase
D. Aliasing artifacts decrease
B. Susceptibility artifact decreases

Which of the following artifacts occurs because of chemical misregistration?
A. Wraparound
B. Gibbs truncation
C. Motion smearing
D. Chemical shift
D. Chemical shift

On a 3T abdominal scan of a large patient, you notice areas of shading and signal loss in the center of the image. These artifacts, caused by RD wavelength interactions with the body, are known as:
A. Aliasing artifacts
B. Truncation artifacts
C. Fine line artifacts
D. Dielectric effects
D. Dielectric effects

The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) set static magnetic field clinical use limits of ______ for the entire population and ________ for those over 1 month of age.
A. 1 Gauss; 5 Gauss
B. 5 Gauss; 10 Gauss
C. 3 Tesla; 7 Tesla
D. 4 Tesla; 8 Tesla
D. 4 Tesla; 8 Tesla

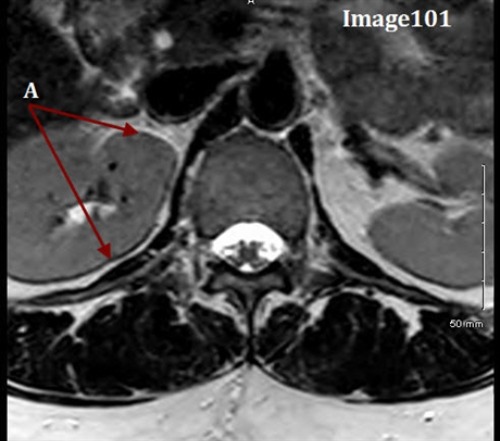
In this axial image of the Tib-Fib, the posterior anatomy appears to be “wrapped” around and superimposed on the anterior anatomy. What is this artifact?
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. RF zipper
D. Wraparound (aliasing)
E. Magnetic susceptibility
D. Wraparound (aliasing)

The cross talk artifact in Image 100 is caused by:
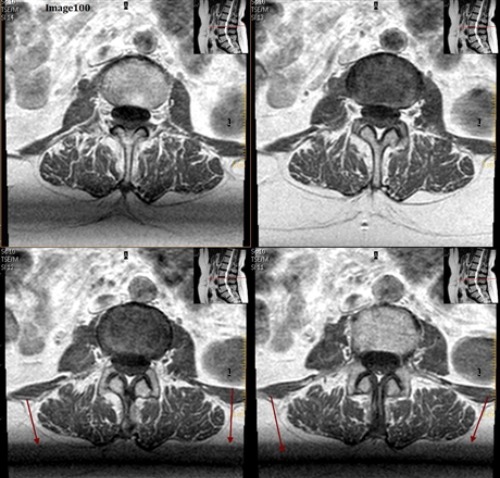
A. Local eddy currents due to the increased conductivity of body tissue
B. When a small matrix is used, it incompletely digitizes the echo by the end of the acquisition
C. Undersampled data at interfaces of differing tissue types
D. The imperfect shape of RF slice profiles, which leads to an unintended excitation of an adjacent slice or tissue
E. Tissue outside the FOV is undersampled
D. The imperfect shape of RF slice profiles, which leads to an unintended excitation of an adjacent slice or tissue

This image of the abdomen shows multiple, repeated “ghosts” of the anatomy shifted in the phase-encoding direction. This artifact is caused by:
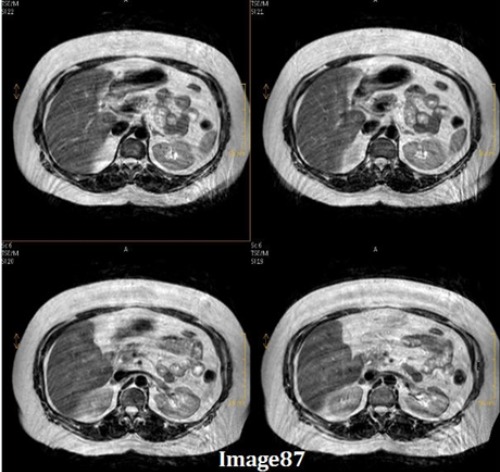
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. RF zipper
D. SENSE/parallel imaging artifact
E. Magnetic susceptibility
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction

To reduce chemical shift artifact when imaging the kidneys, which parameter should be adjusted and in what way?
A. Receiver bandwidth; decreased
B. Phase matrix; decreased
C. Receiver bandwidth; increased
D. Phase matrix; increased
C. Receiver bandwidth; increased

________ occurs when tissue outside the Field of View is undersampled, causing a misregistration of anatomical location, in the phase direction, but on the opposite side of the anatomical location, also known as wrap-around artifact.
A. Aliasing artifact
B. Chemical shift artifact
C. Zipper artifact
D. Gibbs truncation artifact
A. Aliasing artifact

In which of the following anatomical regions would you expect to see the least amount of chemical misregistration artifact?
A. Orbits
B. Kidneys
C. Thoracic spine
D. Cerebellum
D. Cerebellum

Which gradient is primarily responsible for performing the function of determining slice thickness, scan plane and orientation of a pulse sequence?
A. phase encoding gradient
B. frequency encoding gradient
C. Phased array gradient
D. Slice select gradient
D. Slice select gradient

The yellow arrows in Image 203 identify a bright, ribbon-like artifact near the edge of the FOV. This is known as an:
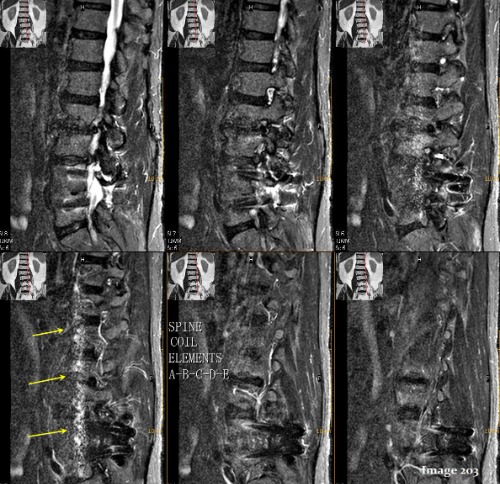
A. Magic angle
B. Dielectric
C. Aliasing
D. Annefact
D. Annefact

This image of the brain shows significant signal loss and distortion in the frontal region, likely due to the patient having dental work. This is an example of what type of artifact? (really?…)
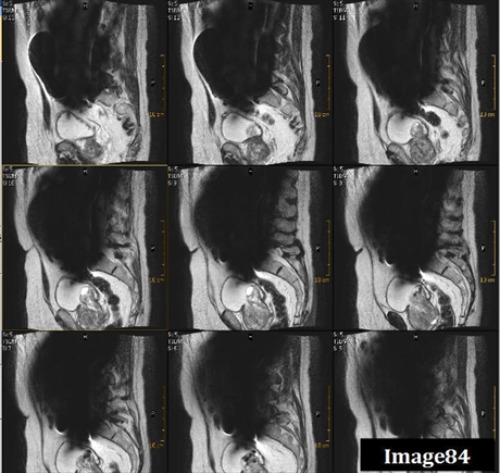
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. Dielectric effects
D. SENSE/parallel imaging artifact
E. Magnetic susceptibility
E. Magnetic susceptibility

Primarily stemming from active RF coil channels or elements outside the scanning field of view, _________ artifacts can be corrected by simply de-selecting the element(s) outside the scanning range.
A. Magic angle
B. Dielectric
C. Aliasing
D. Annefact
E. Parallel Imaging
D. Annefact

In a sagittal cervical spine MRI, prominent ghosting artifacts from CSF pulsation are obscuring the spinal cord. What could be done to compensate for these flow artifacts?
A. Swap phase encoding
B. Utilize an anterior presaturation band
C. Enable gradient moment nulling
D. Use fat suppression techniques
C. Enable gradient moment nulling
All of the following are potential risk factors for SAR thermal absorption during an MR pulse sequence EXCEPT:
A. Obesity
B. Hypotension
C. Elderly population
D. Diabetes
B. Hypotension

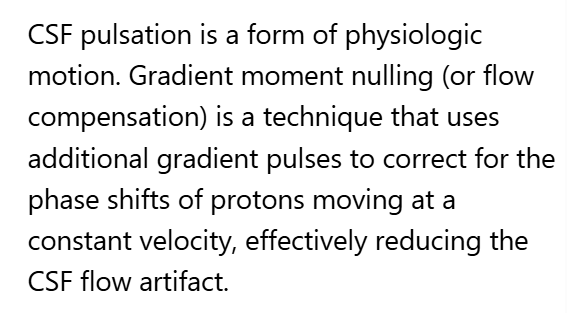
To correct for the fine line artifact shown in Image 173, which can be caused by unstable FID signals, the MRI Technologist would:
A. Increase NEX
B. Decrease NEX
C. Enable Flow Compensation
D. A or C
D. A or C (Increase NEX or Enable Flow Compensation)

Motion is seen as a smearing across the image in the:
A. Phase encoding direction
B. Frequency encoding direction
C. Slice select direction
D. Z axis direction
A. Phase encoding direction

One can correct for the cross talk artifact seen in Image 100 by:
A. Increasing interslice gap
B. Interleaved slice order
C. Acquiring stacks as complete packages
D. All of the above
D. All of the above

The arrows in Image 85 point to ringing lines parallel to the sharp boundary of the spinal cord. What kind of artifact is this?
A. Motion/ghosting in the phase direction
B. Gibbs truncation
C. Dielectric effects
D. RF zipper
B. Gibbs truncation

A STIR sequence of the ankle shows incomplete nulling of the subcutaneous fat. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this poor fat suppression?
A. Flip angle
B. Patient motion
C. Poor breath holder
D. Inhomogeneity
D. Inhomogeneity

What is the term used to measure the magnetic field strength in the periphery of the MRI scan room?
A. SAR
B. Vector
C. Tesla
D. Gauss
D. Gauss

The artifact identified by the orange arrows in Image 173 is a ________ artifact.
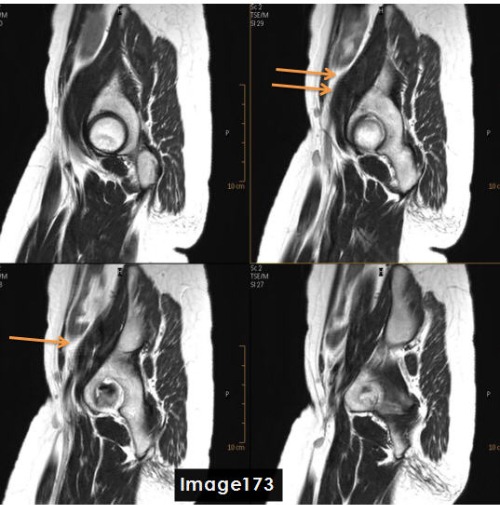
A. Chemical shift
B. FID crushing / fine line
C. Dielectric effects
D. Wraparound (aliasing)
B. FID crushing / fine line
